Abstract
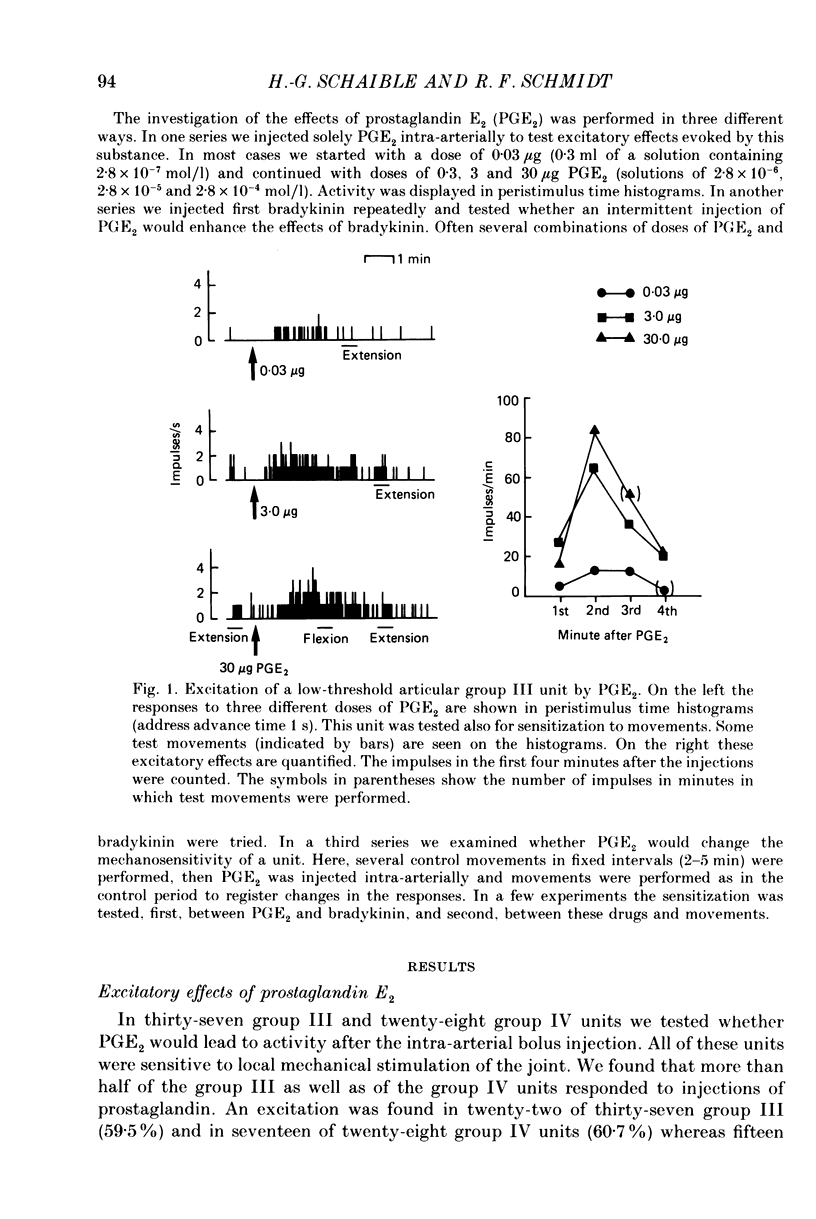
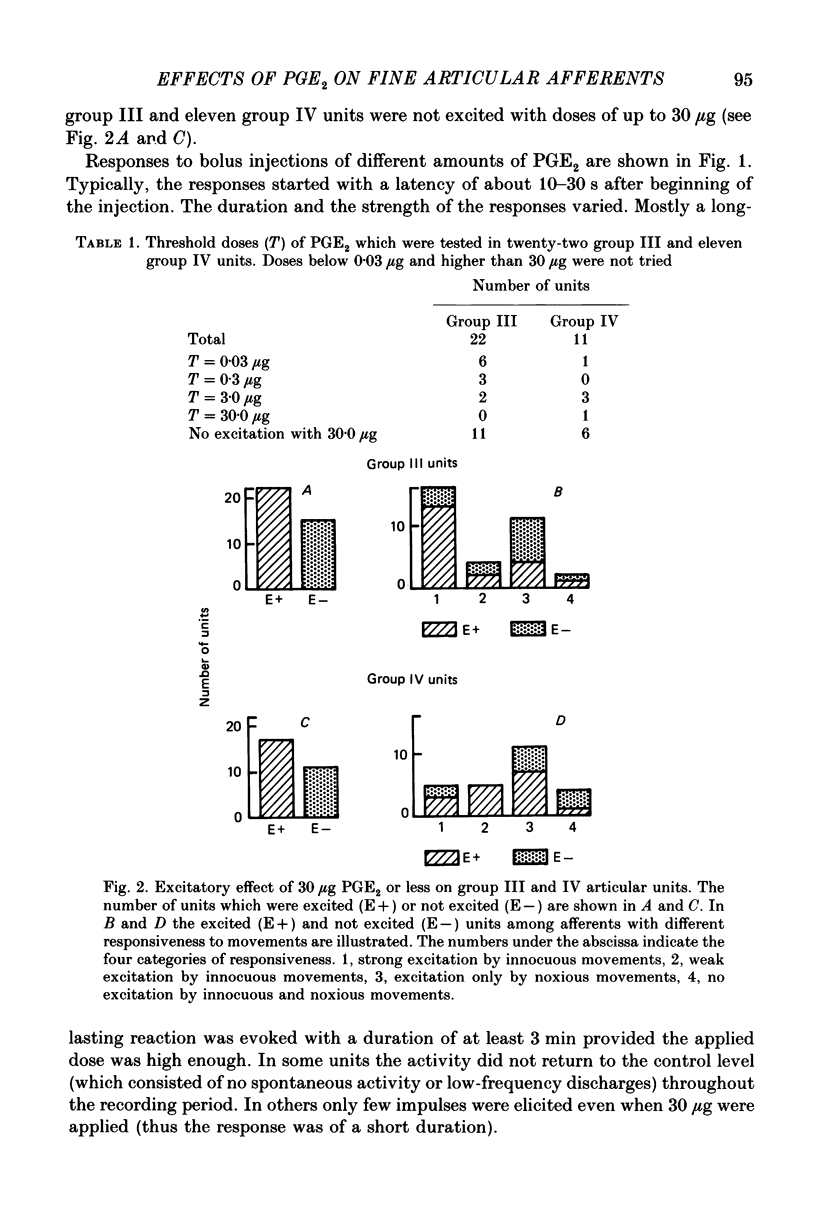
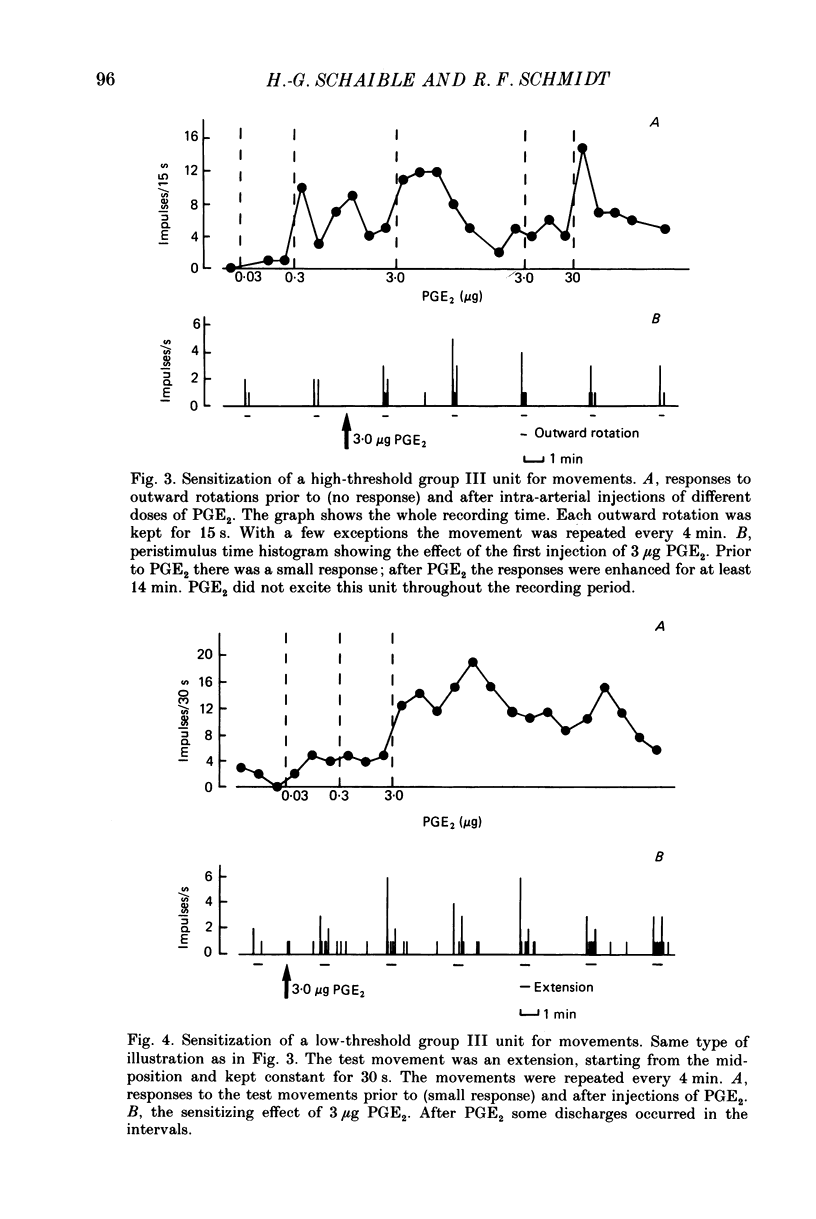
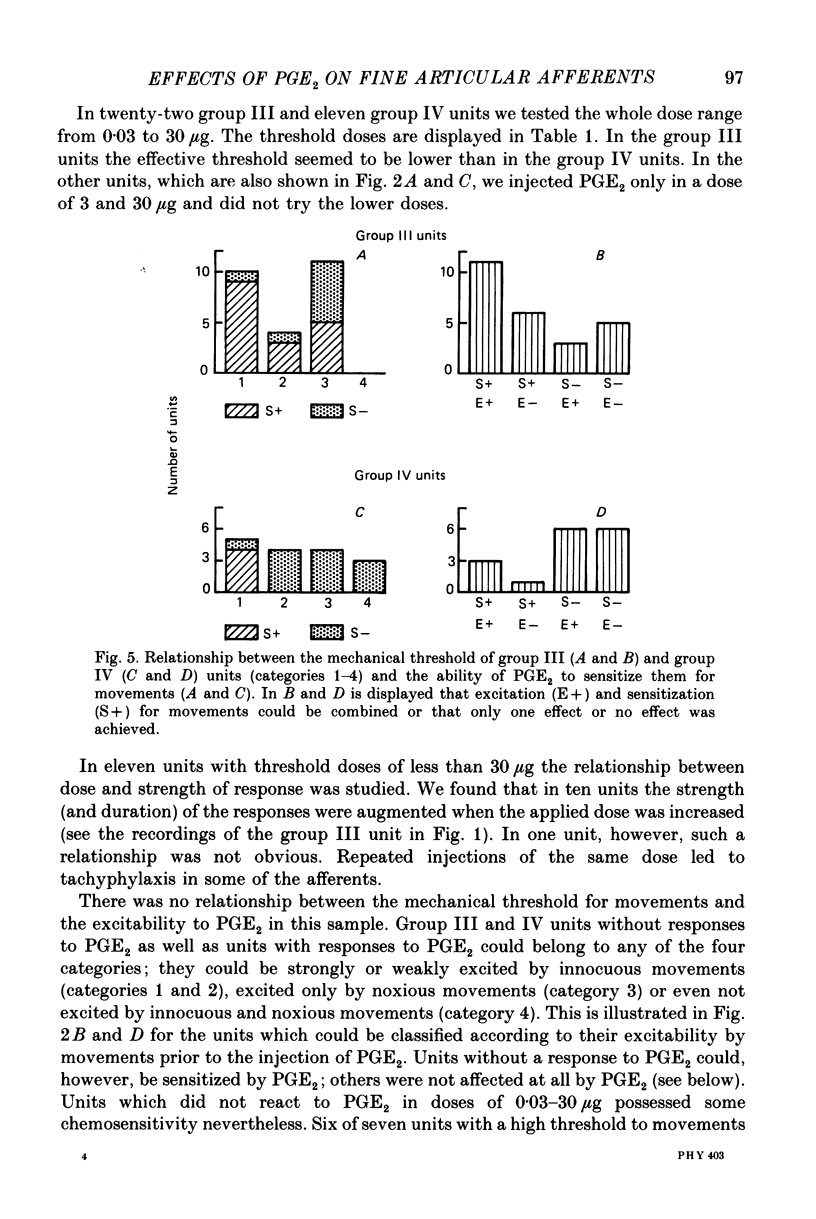
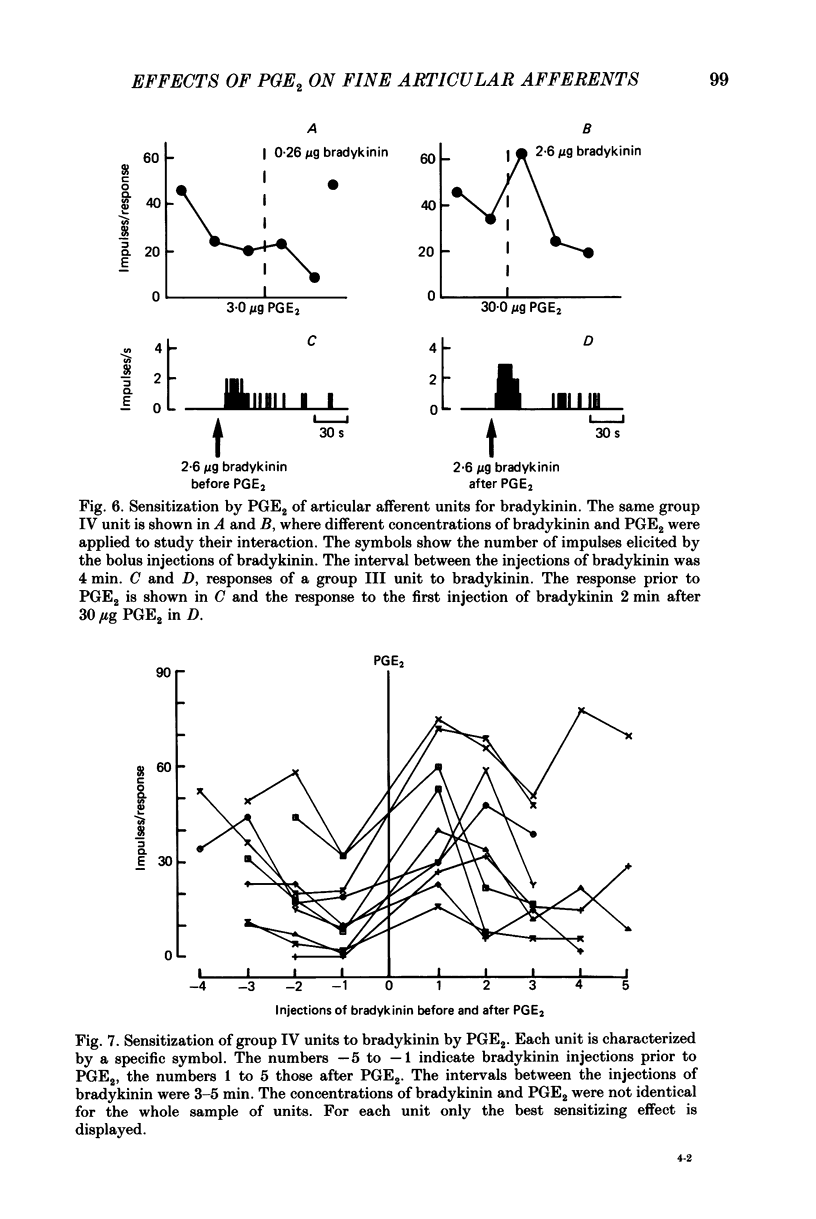
1. In cats anaesthetized with alpha-chloralose extracellular recordings were made from fine afferent units belonging to the medial articular nerve of the knee joint. The excitatory and sensitizing effects on articular afferents of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) applied intra-arterially close to the joint were examined. 2. Bolus injections of PGE2 doses of 0.03-30 micrograms excited about 60% of both the group III (conduction velocity 2.5-20 m/s) and the group IV units (conduction velocity less than 2.5 m/s). The duration and size of the responses were dose dependent consisting in most cases of low-frequency discharges which lasted up to several minutes. Excitation was found among afferents with low and high mechanosensitivity. 3. Among the group III units PGE2 sensitized 64% for their responses to movements and 50% for their responses to bradykinin (applied intra-arterially close to the joint). Sensitization did not depend on the mechanical threshold previous to chemical stimulation. Among the group IV units PGE2 sensitized only 25% for their responses to movements but 75% for their reactions to bradykinin. In group IV fibres a low mechanical threshold predisposed for sensitization to movements and a higher threshold for sensitization to bradykinin. 4. Some units were sensitized and excited, others were either sensitized or excited and some units were not affected by PGE2. We conclude that PGE2 induces in a large proportion of fine articular afferents of normal joints discharges which are similar to those induced by an experimental inflammation. Thus PGE2 may be an inflammatory mediator which has a major role in the generation of the afferent activity developing in the course of an arthritis.
Full text
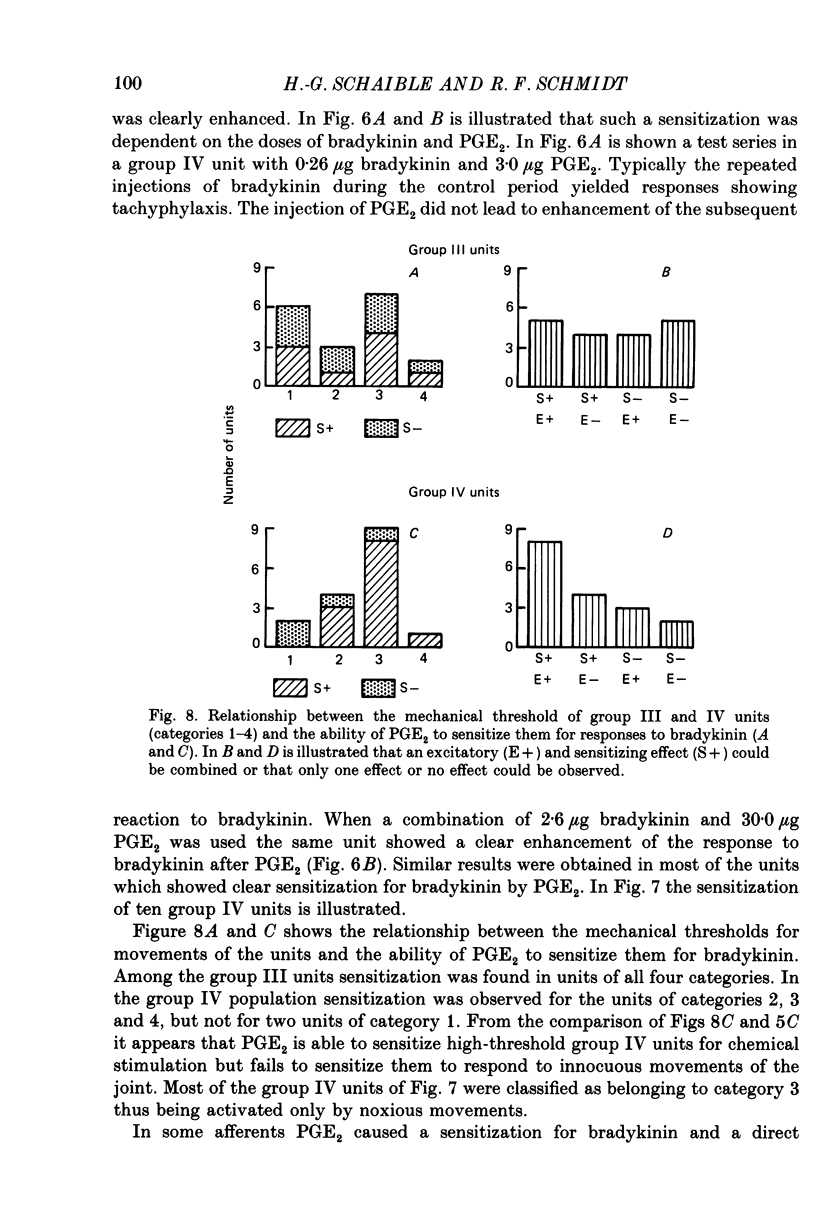
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackham A., Farmer J. B., Radziwonik H., Westwick J. The role of prostaglandins in rabbit monoarticular arthritis. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 May;51(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09629.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardieri S., Cattani P., Ciabattoni G., Di Munno O., Pasero G., Patrono C., Pinca E., Pugliese F. The synovial prostaglandin system in chronic inflammatory arthritis: differential effects of steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;73(4):893–901. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb08743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie M. J., Hensby C. N., Parke A., Gordon D. Is prostacyclin in the major pro-inflammatory prostanoid in joint fluid? Life Sci. 1980 Aug 18;27(7):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90310-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahl L. A., Iggo A. The effects of bradykinin and prostaglandin E1 on rat cutaneous afferent nerve activity. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;59(2):343–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Giroud J. P., Willoughby D. A. Studies on the mediators of the acute inflammatory response induced in rats in different sites by carrageenan and turpentine. J Pathol. 1971 May;104(1):15–29. doi: 10.1002/path.1711040103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick W. C., Grennan D. M., Zeitlin I. J. Studies on the relative effects of prostaglandins, bradykinin, 5-hydroxytryptamine and histamine on the synovial microcirculation in dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;56(3):313–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egg D., Günther R., Herold M., Kerschbaumer F. Prostaglandin E2 und F2 alpha Konzentrationen in der Synovia bei rheumatischen und traumatischen Kniegelenkerkrankungen. Z Rheumatol. 1980 May-Jun;39(5-6):170–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Nakamura M. I - Prostaglandin hyperalgesia, a cAMP/Ca2+ dependent process. Prostaglandins. 1979 Aug;18(2):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(79)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Nakamura M., de Abreu Castro M. S. The hyperalgesic effects of prostacyclin and prostaglandin E2. Prostaglandins. 1978 Jul;16(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and analgesia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):200–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio240200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppelmann B., Pfeffer A., Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Effects of acetylsalicylic acid and indomethacin on single groups III and IV sensory units from acutely inflamed joints. Pain. 1986 Sep;26(3):337–351. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(86)90062-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsapple M. P., Schnur M., Yim G. K. Pharmacological modulation of edema mediated by prostaglandin, serotonin and histamine. Agents Actions. 1980 Sep;10(4):368–373. doi: 10.1007/BF01971442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. G., Hay J. B., Movat H. Z. The modulation of enhanced vascular permeability by prostaglandins through alterations in blood flow (hyperemia). Agents Actions. 1976 Nov;6(6):705–711. doi: 10.1007/BF02026092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhlin L., Michaëlsson G. Cutaneous vascular reactions to prostaglandins in healthy subjects and in patients with urticaria and atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1969;49(3):251–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaka R., Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Activation of fine articular afferent units by bradykinin. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 18;327(1-2):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91501-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. J., Nelson D. J., Sugrue M. F. On the ability of prostaglandin E1, and arachidonic acid to modulate experimentally induced oedema in the rat paw. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;55(1):51–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mense S. Sensitization of group IV muscle receptors to bradykinin by 5-hydroxytryptamine and prostaglandin E2. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis as the mechanism of analgesia of aspirin-like drugs in the dog knee joint. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;31(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pateromichelakis S., Rood J. P. Prostaglandin E1-induced sensitization of A delta moderate pressure mechanoreceptors. Brain Res. 1982 Jan 28;232(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90612-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querfurth H. Transducer action of isolated frog muscle spindle evoked by pseudorandom noise stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jan;55(1):1–12. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Higgs G. A., Vane J. R., Bitensky L., Chayen J., Henderson B., Cashman B. Synthesis of arachidonate cyclo-oxygenase products by rheumatoid and nonrheumatoid synovial lining in nonproliferative organ culture. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Feb;42(1):36–39. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Activation of groups III and IV sensory units in medial articular nerve by local mechanical stimulation of knee joint. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Jan;49(1):35–44. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Effects of an experimental arthritis on the sensory properties of fine articular afferent units. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Nov;54(5):1109–1122. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.5.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible H. G., Schmidt R. F. Responses of fine medial articular nerve afferents to passive movements of knee joints. J Neurophysiol. 1983 May;49(5):1118–1126. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.5.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., West G. B. Letter: Prostaglandins as regulators of bradykinin responses. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;25(9):747–748. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb10059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trang L. E., Granström E., Lövgren O. Levels of prostaglandins F2 alpha and E2 and thromboxane B2 in joint fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1977;6(3):151–154. doi: 10.3109/03009747709095440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Peck M. J. Role of prostaglandin-mediated vasodilatation in inflammation. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):530–532. doi: 10.1038/270530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J. Prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin I2 and the vascular changes of inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;65(3):517–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb07860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


