Abstract
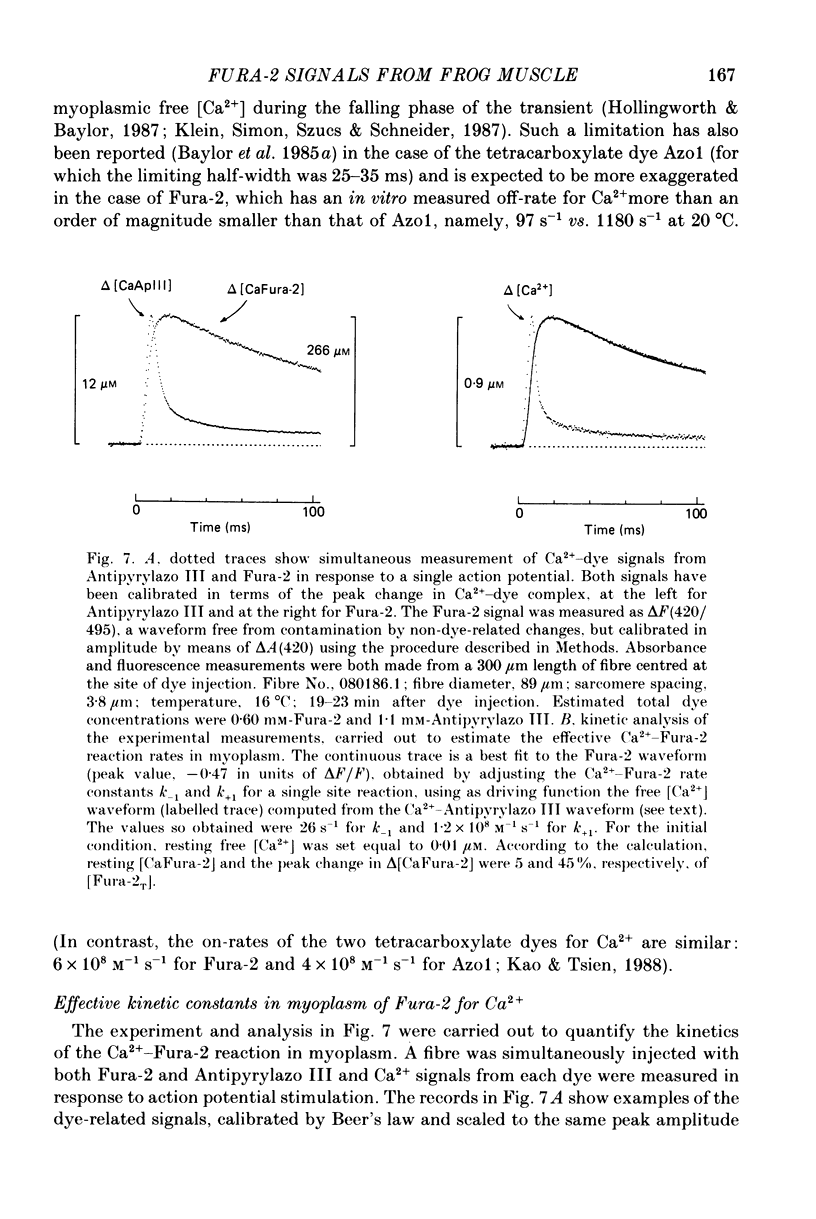
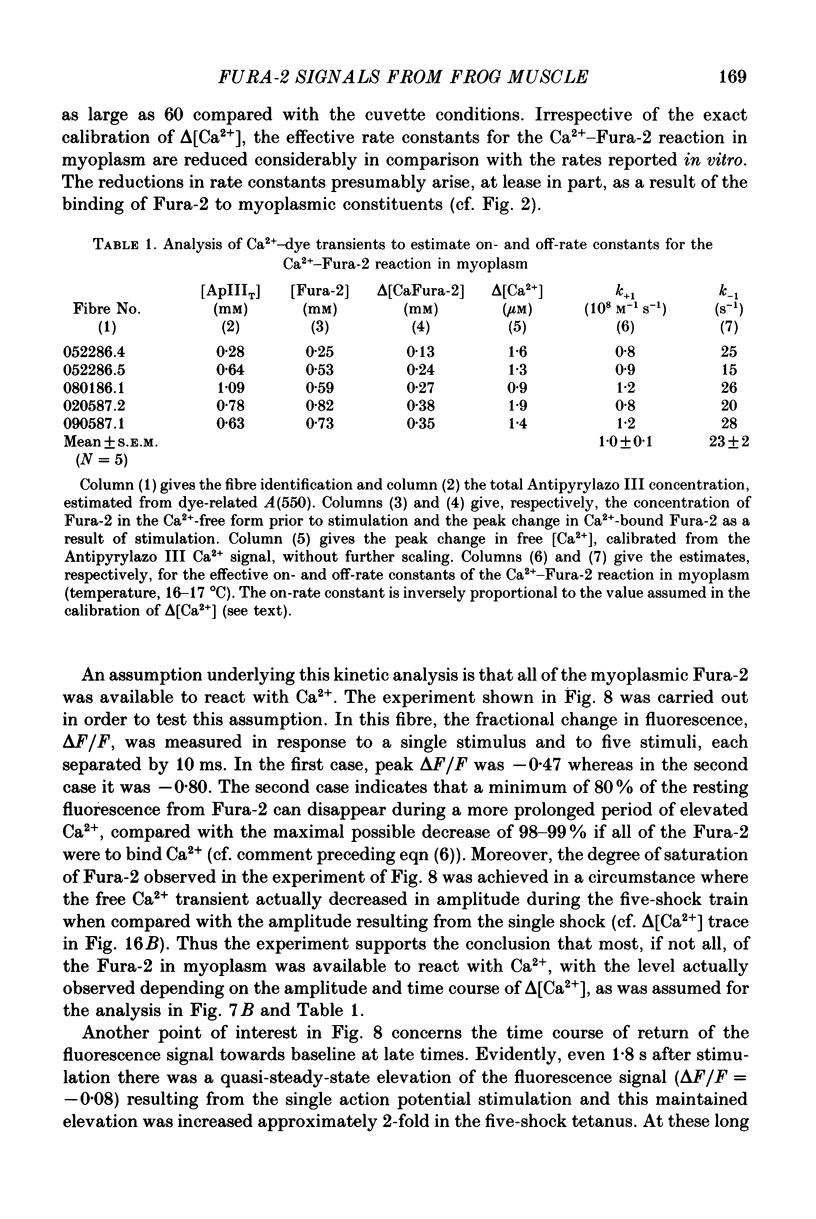
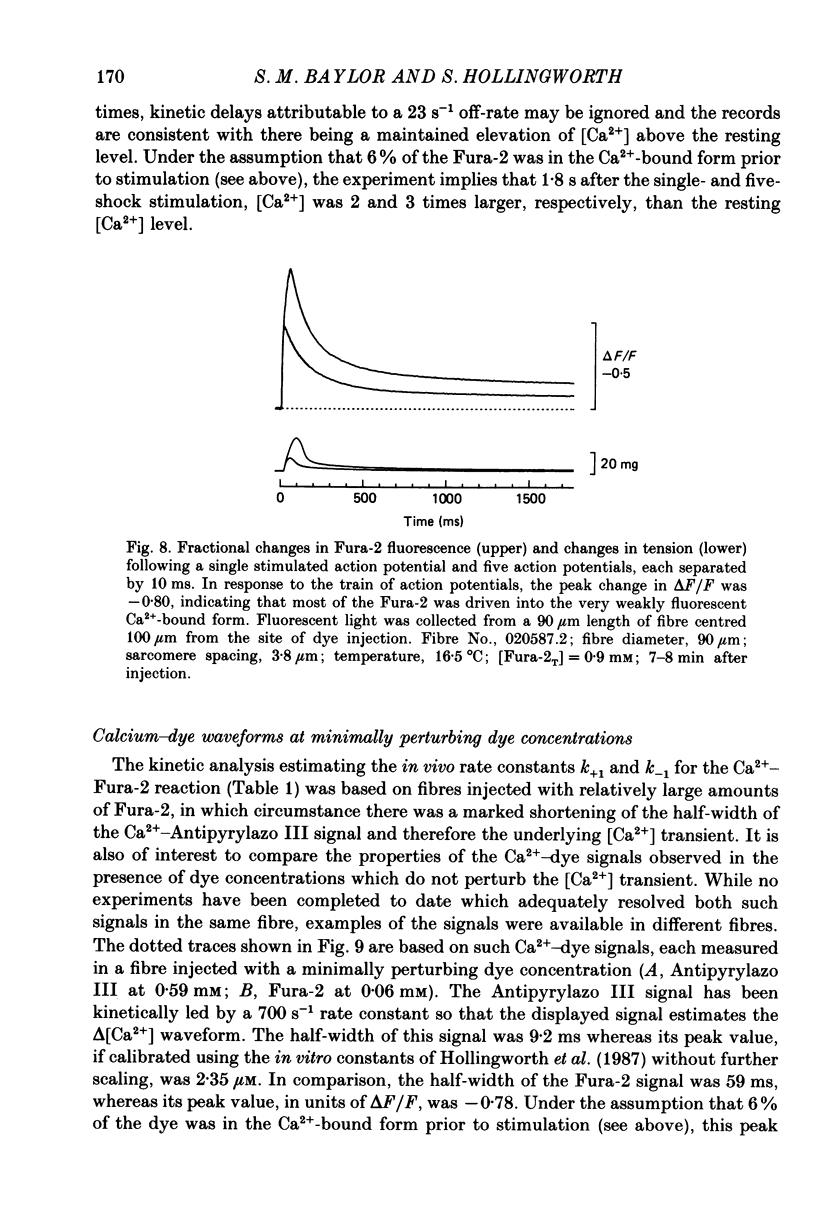
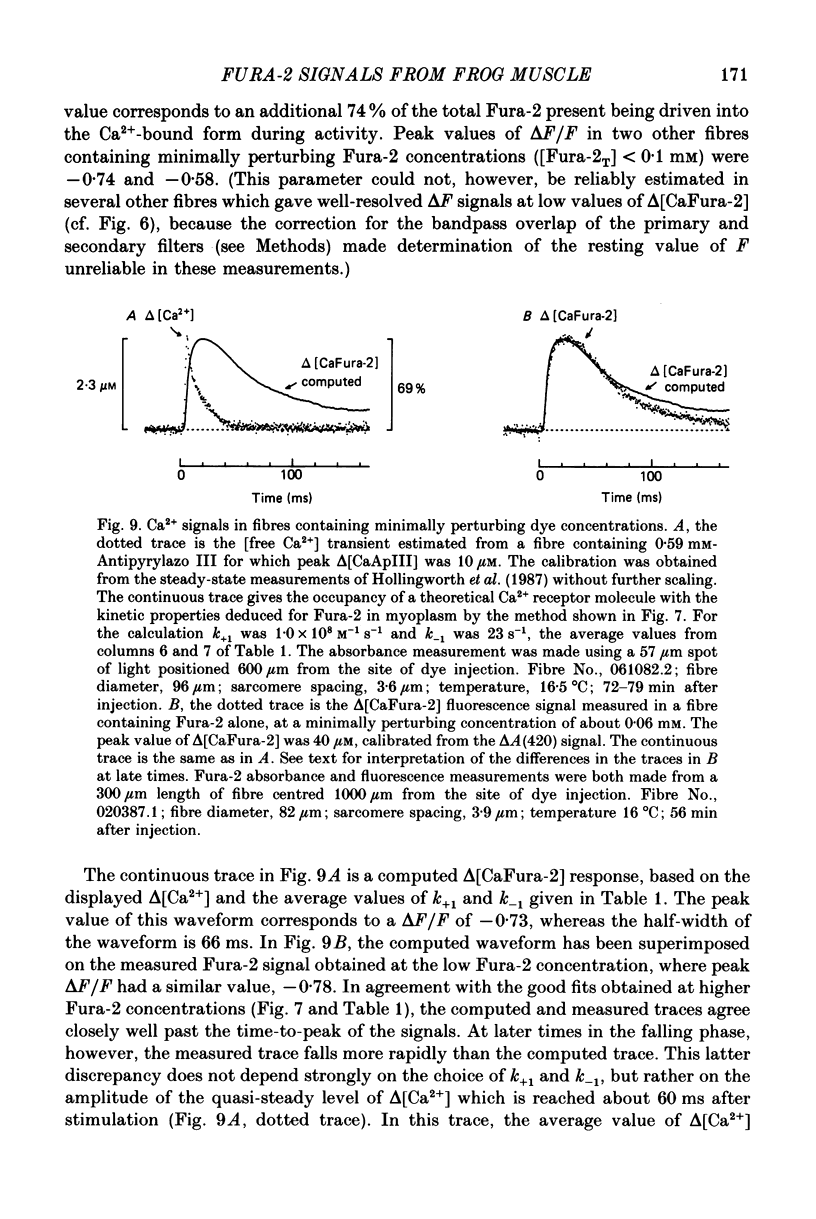
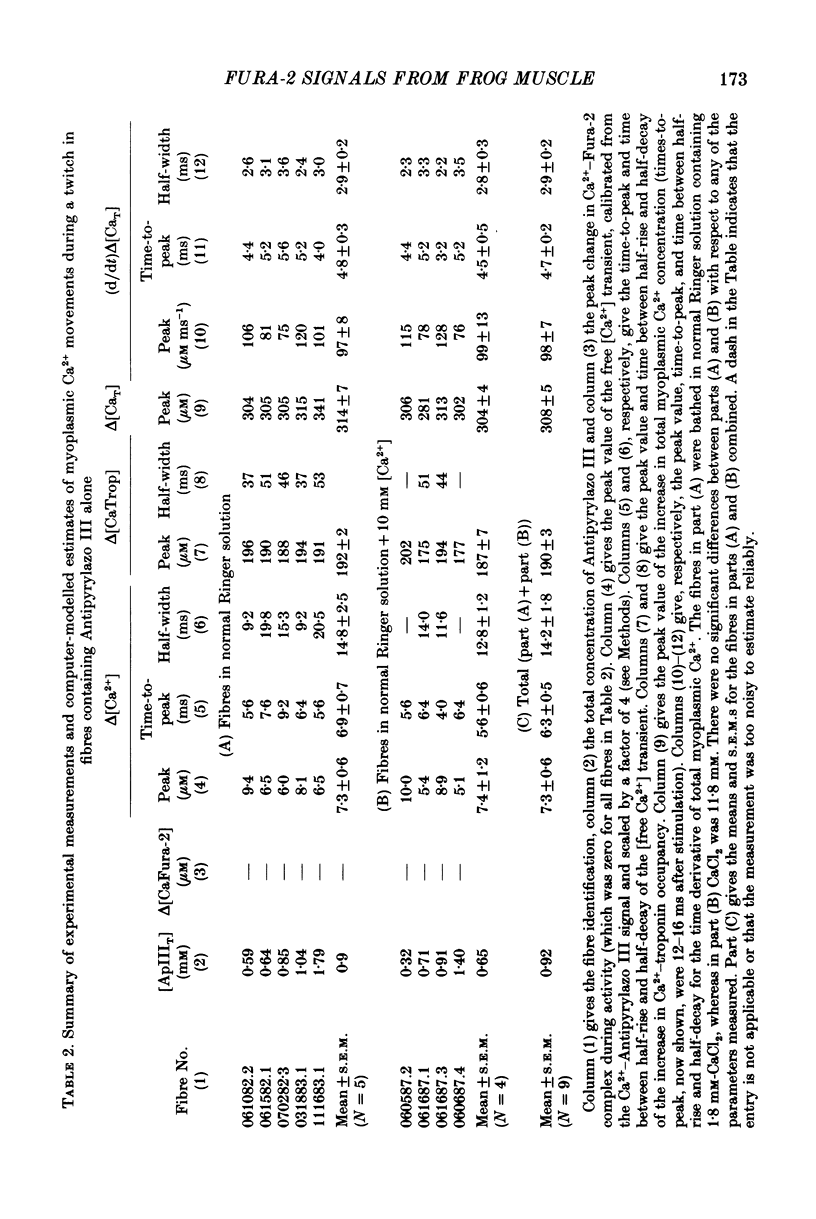
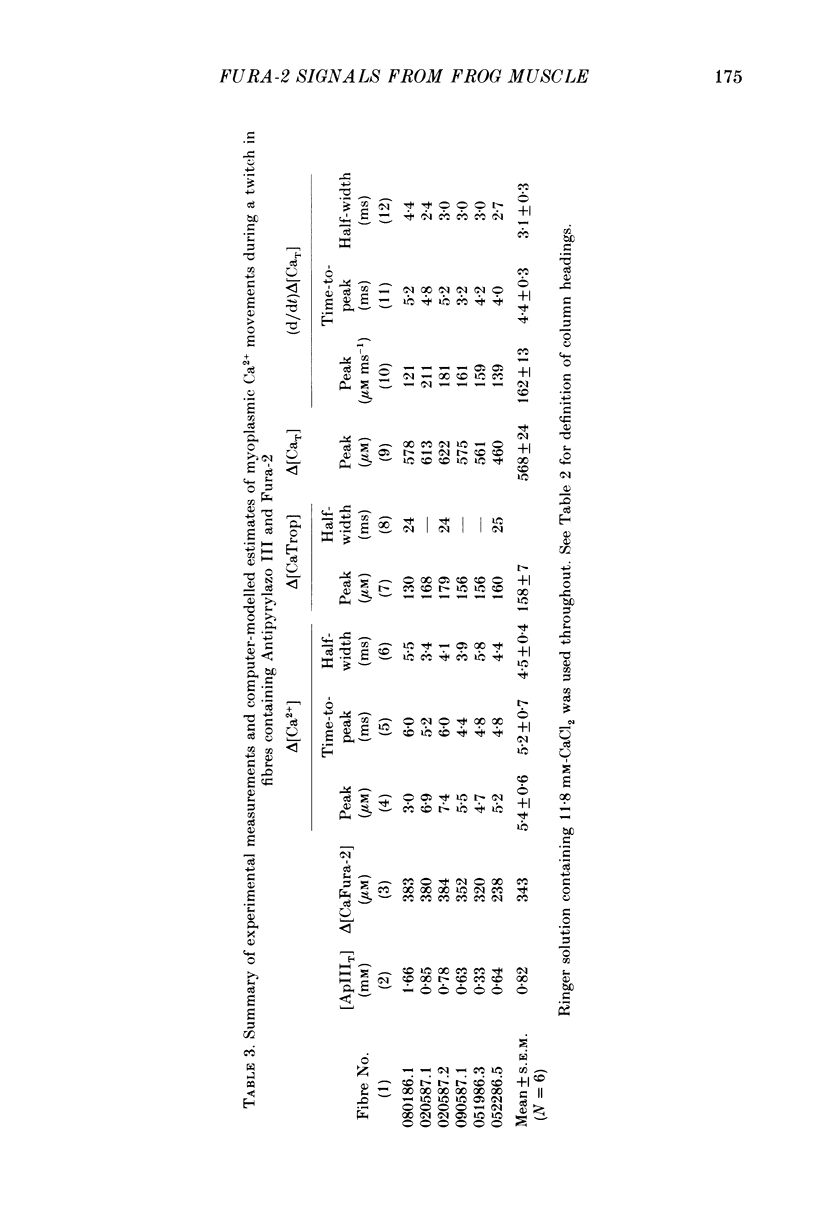
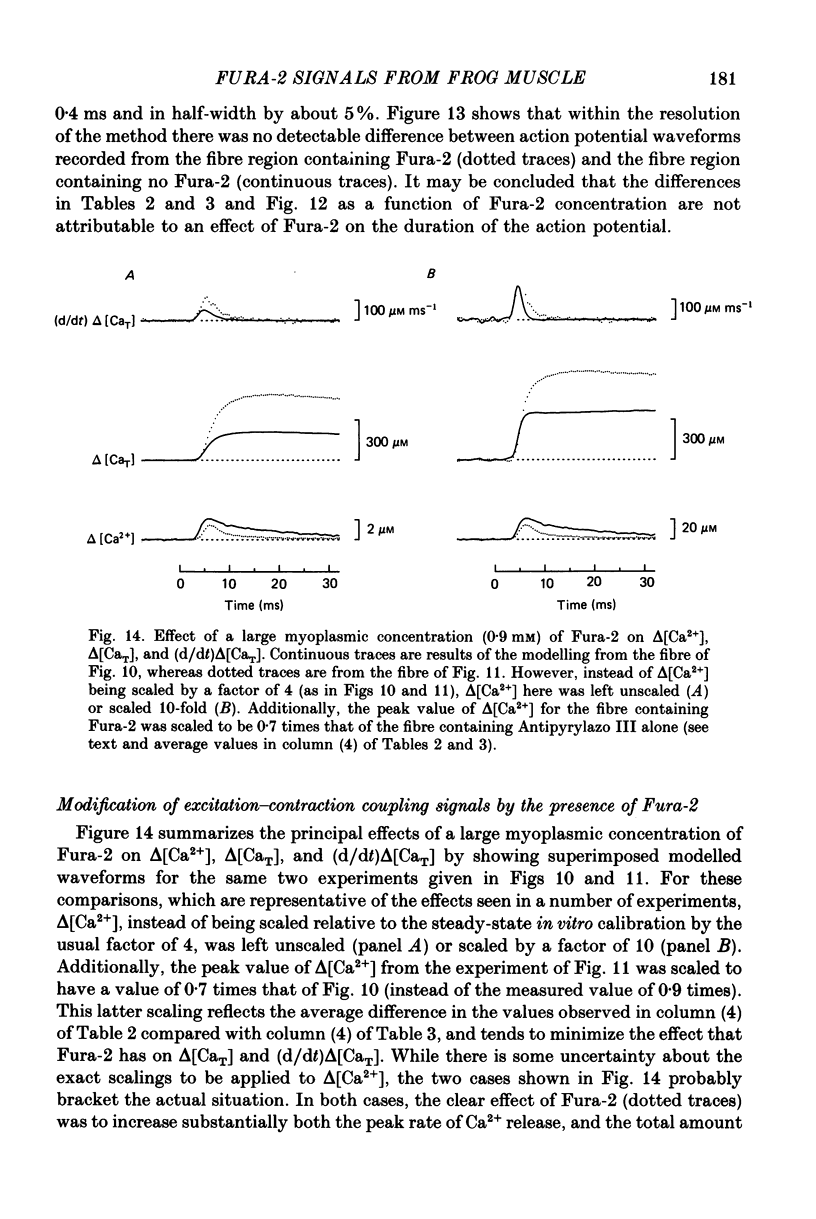
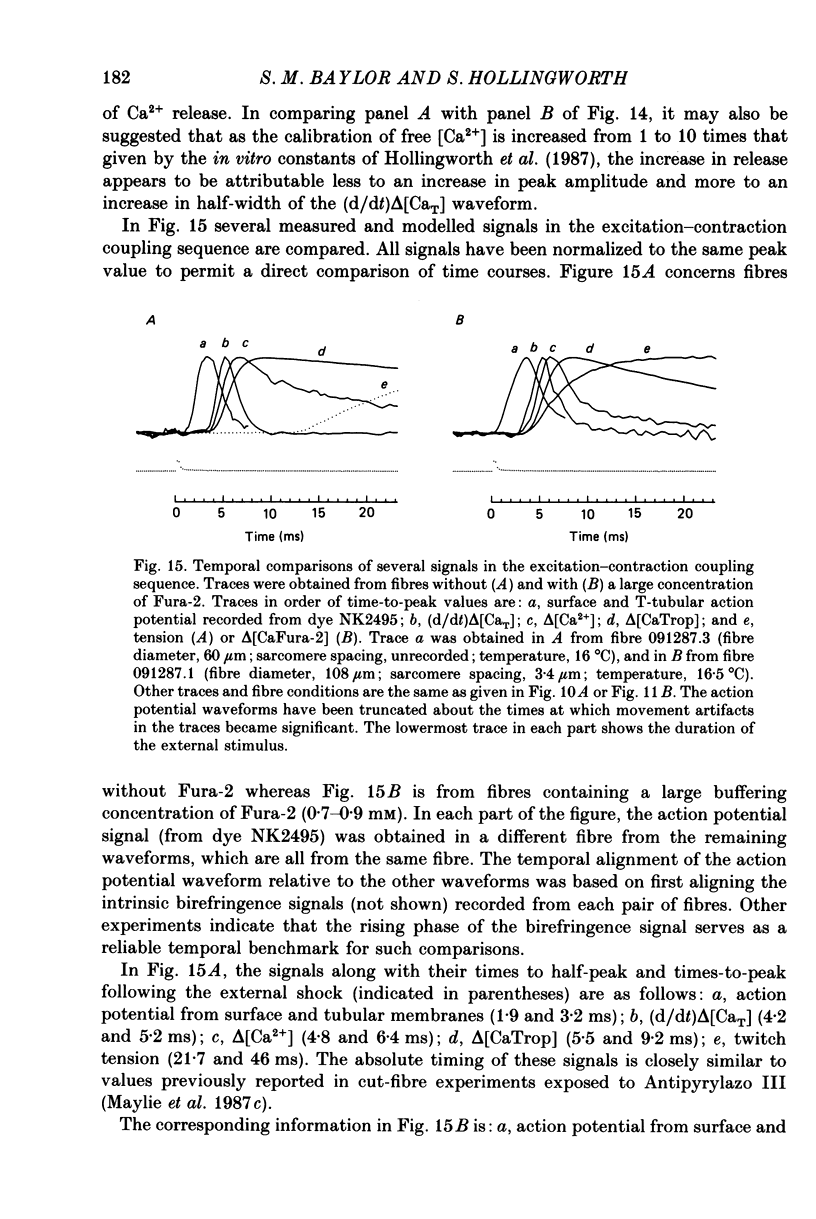
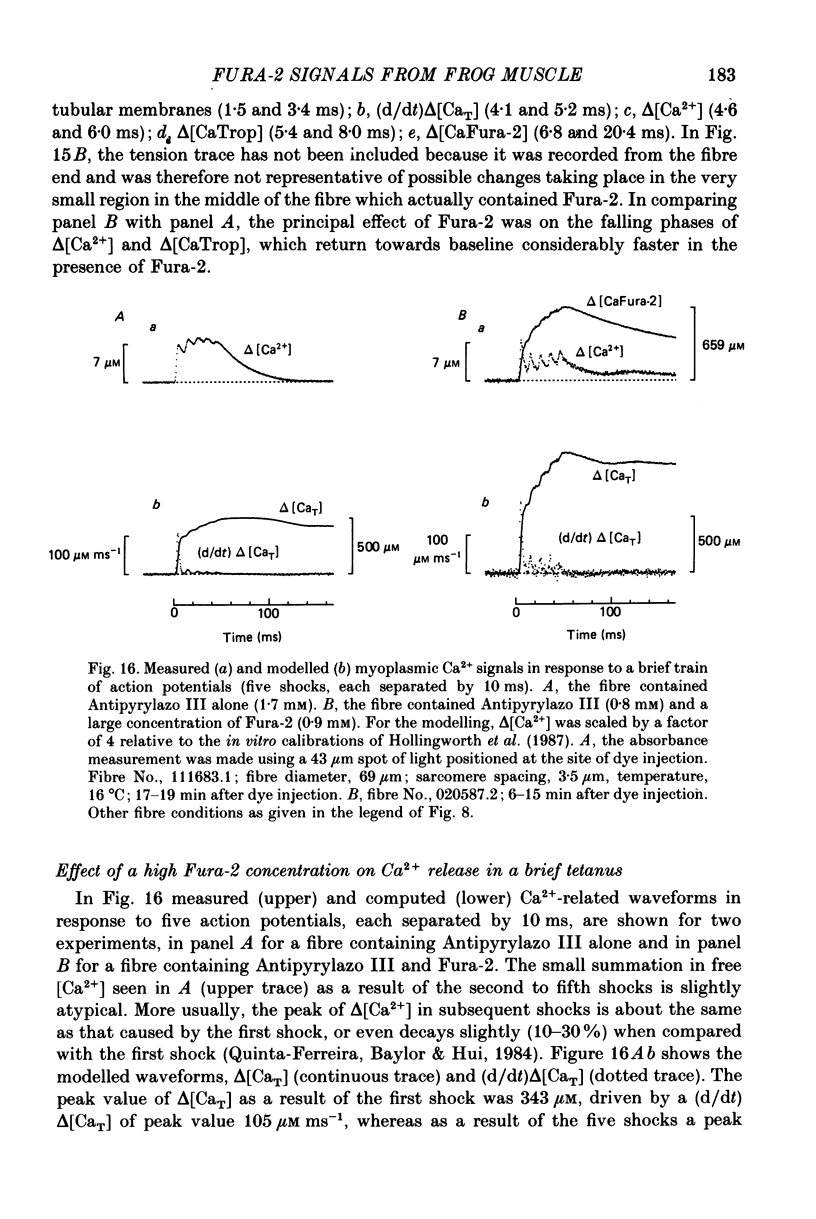
1. Intact single twitch fibres from frog muscle were mounted at long sarcomere spacing (3.5-4.2 microns) on an optical bench apparatus for the measurement of absorbance and fluorescence signals following the myoplasmic injection of either or both of the Ca2+ indicator dyes Fura-2 and Antipyrylazo III. Dye-related signals were measured at 16-17 degrees C in fibres at rest and stimulated electrically to give a single action potential or brief train of action potentials. 2. The apparent diffusion constant of Fura-2 in myoplasm, Dapp, was estimated from Fura-2 fluorescence measured as a function of time and distance from the site of dye injection. On average (N = 7), Dapp was 0.36 x 10(-6) cm2 s-1, a value nearly 3-fold smaller than expected if all the Fura-2 was freely dissolved in the myoplasmic solution. The small value of Dapp is explained if approximately 60-65% of the Fura-2 molecules were bound to relatively immobile sites in myoplasm. 3. In resting fibres the fraction of Fura-2 in the Ca2+-bound form was estimated to be small, on average (N = 11) 0.06 of total dye. However, because of the large fraction of Fura-2 not freely dissolved in myoplasm, and the indirect method employed for estimating Ca2+-bound dye, calibration of the resting level of myoplasmic free Ca2+ ([Ca2+]) from the fraction of Ca2+-bound dye was not considered reliable. 4. In response to a single action potential, large changes in Fura-2 fluorescence (delta F) and absorbance (delta A) were detected, which had identical time courses. As expected, the directions of these transients corresponded to an increase in Ca2+-dye complex. For wavelengths, lambda, between 380 and 460 nm, peak delta A(lambda) was closely similar to the Ca2+-dye difference spectrum for Fura-2 determined in in vitro calibrations. Beer's law was used to calibrate the concentration of Ca2+-dye complex formed during activity (delta[CaFura-2]) from the delta A(lambda) signal. Peak delta[CaFura-2] was found to vary between 0.01 and 0.4 mM, depending on the total concentration of injected Fura-2 ([Fura-2T]), which ranged as high as 0.9 mM. 5. In fibres in which peak delta[CaFura-2] was less than 0.06 mM, delta[CaFura-2] had a limiting minimal half-width of 50-60 ms. However, as peak delta[CaFura-2] increased (up to 0.3-0.4 mM), delta[CaFura-2] half-width became markedly prolonged (up to 150-200 ms), indicative of a strong buffering action of large concentrations of Fura-2 on the underlying [Ca2+] transient (delta[Ca2+]).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





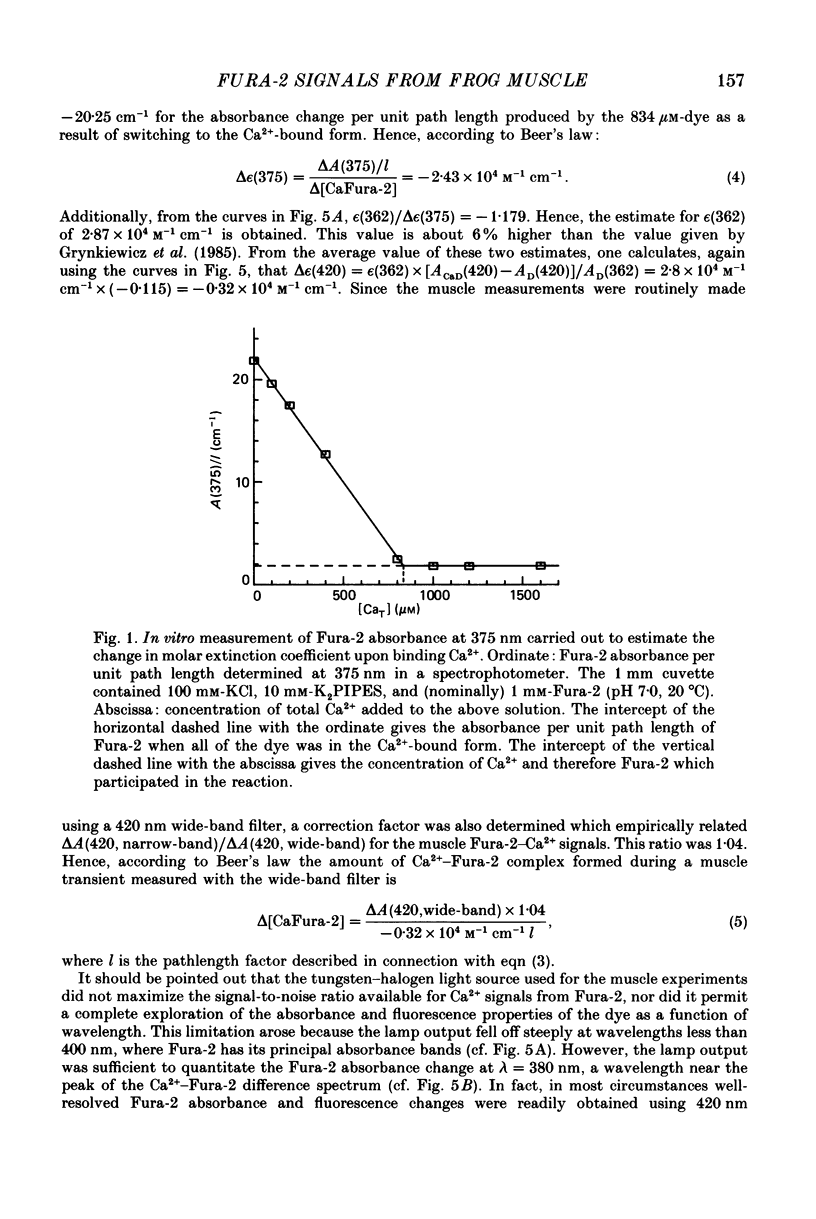


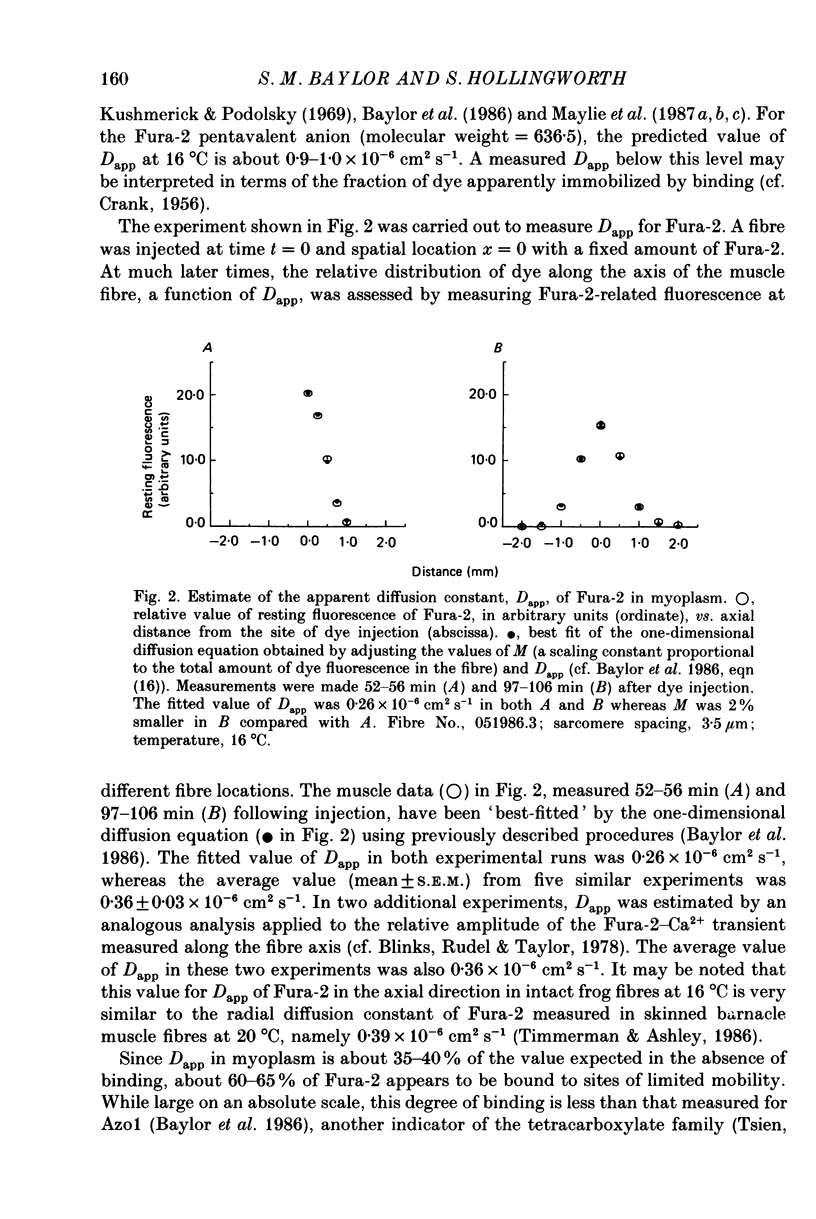


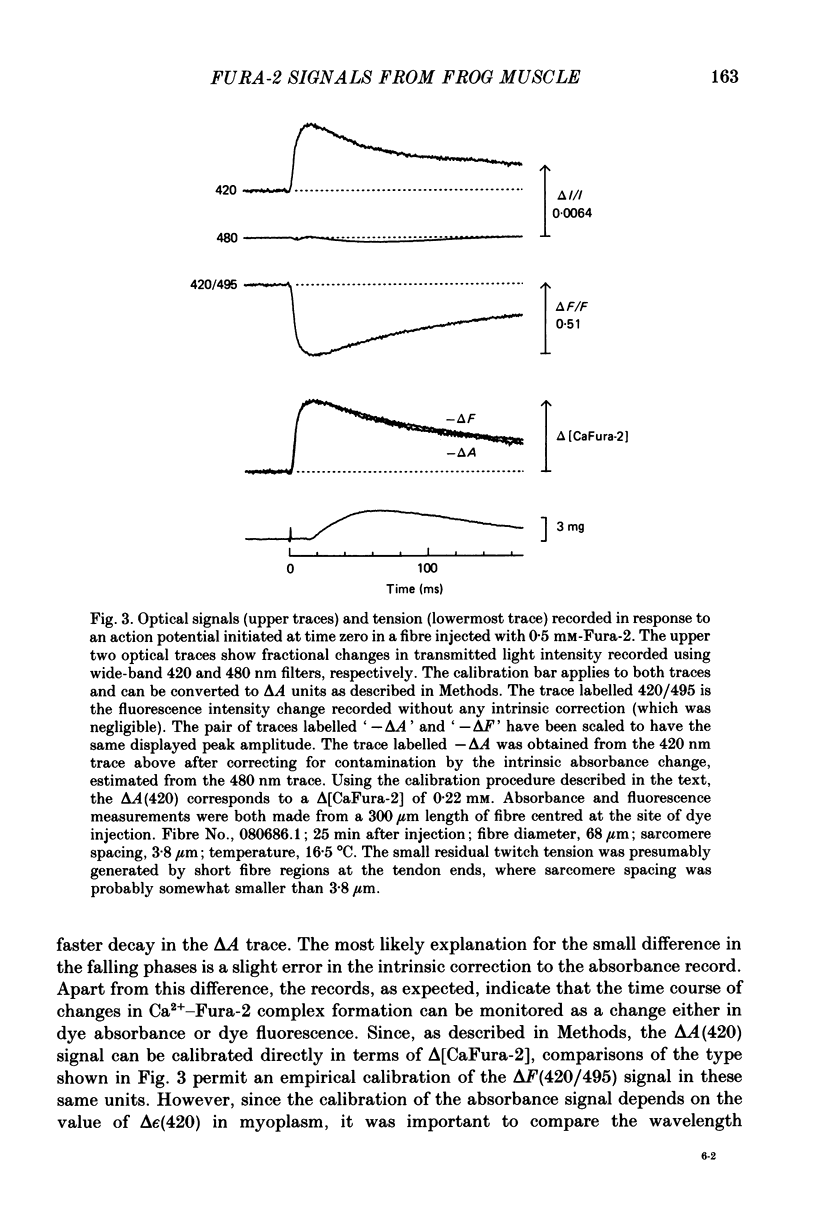
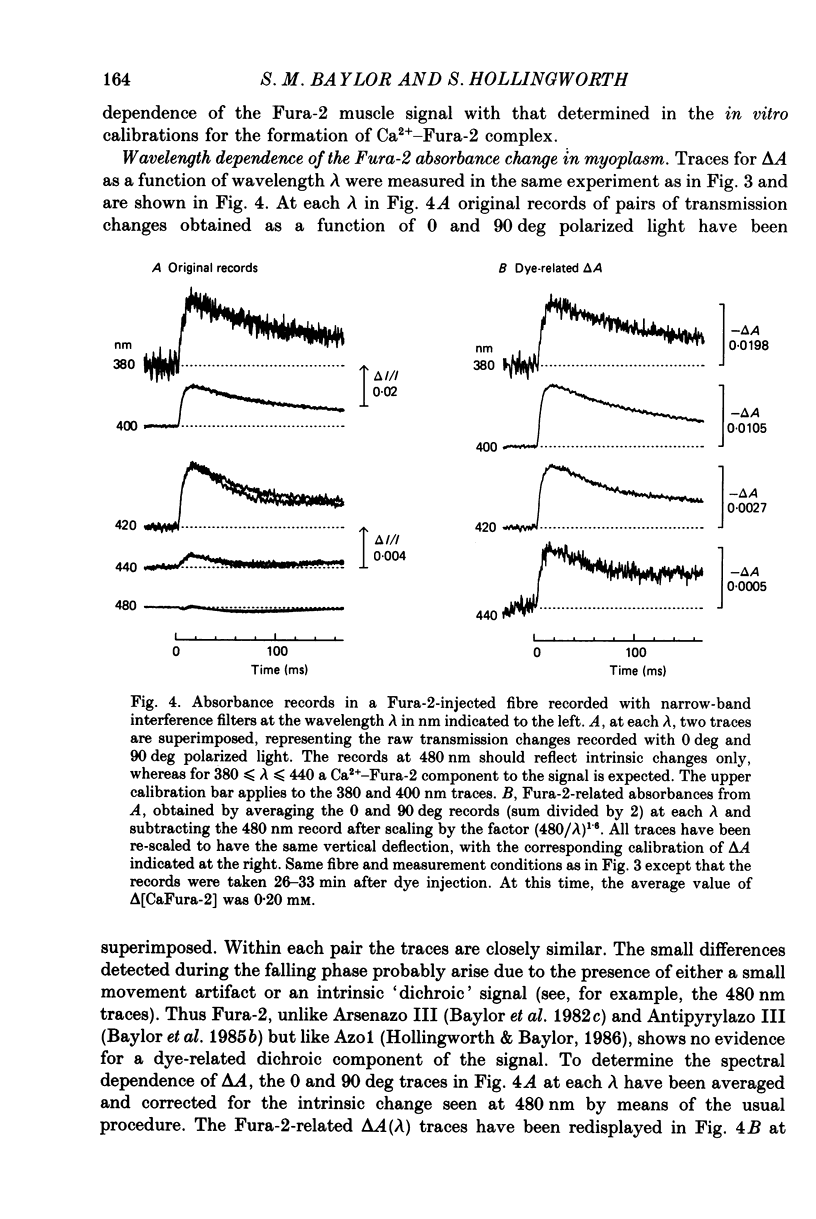
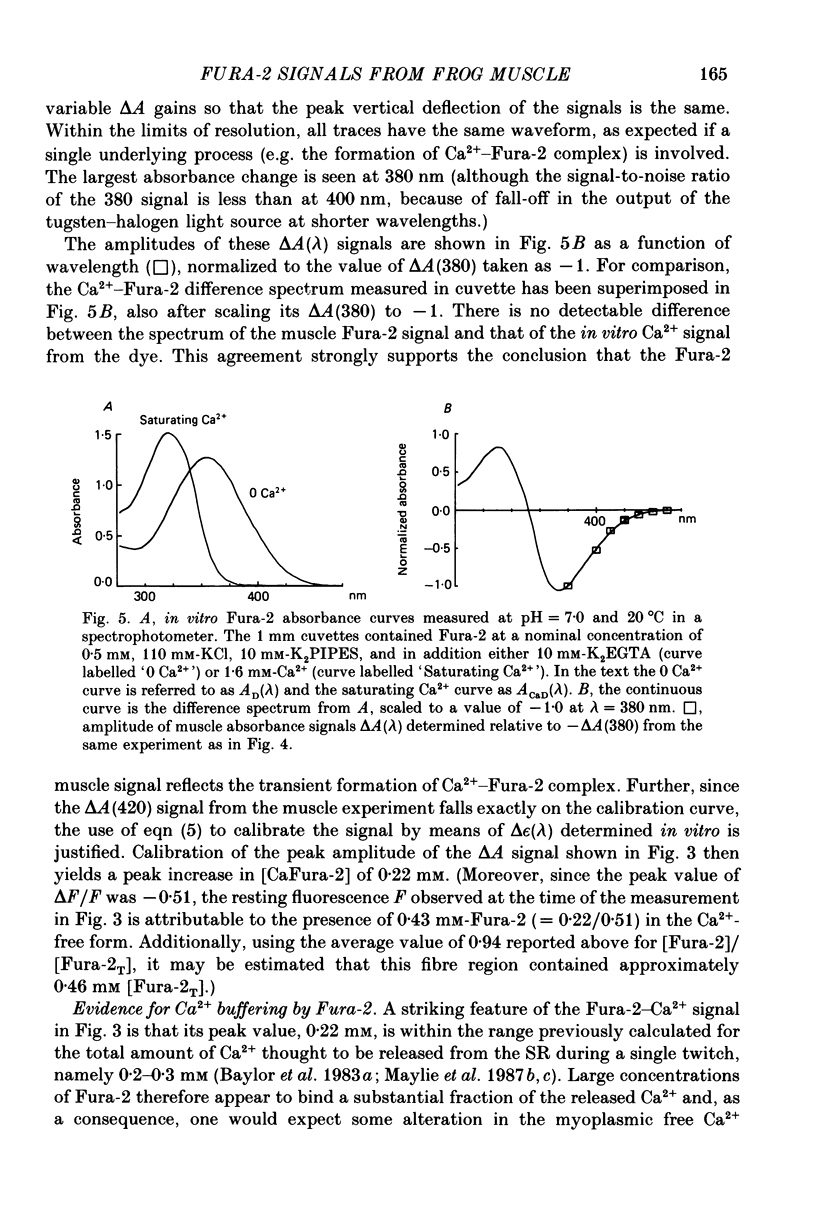













Selected References
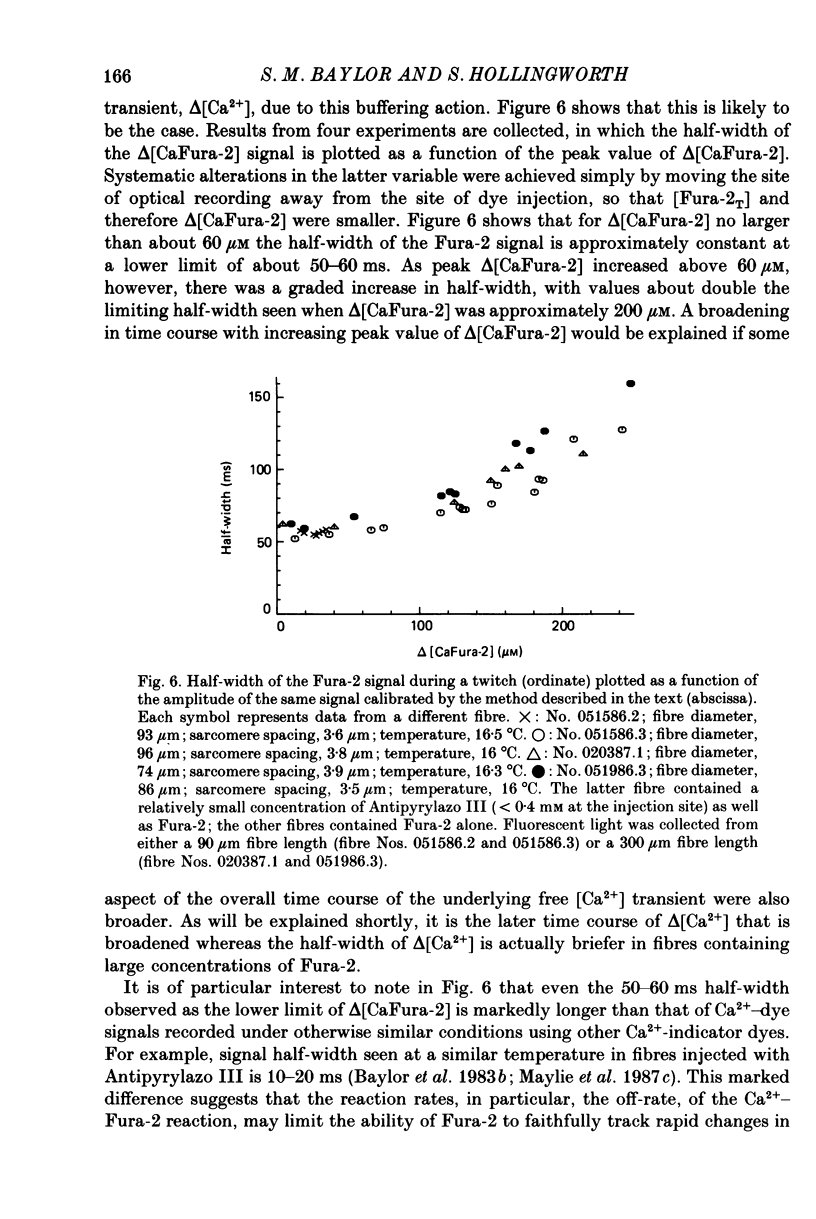
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. M., Horowicz P. Twitches in the presence of ethylene glycol bis( -aminoethyl ether)-N,N'-tetracetic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Arsenazo III signals in singly dissected frog twitch fibres [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:23P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Calcium release and sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane potential in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:209–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Dichroic components of Arsenazo III and dichlorophosphonazo III signals in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:179–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Optical measurements of intracellular pH and magnesium in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:105–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres estimated from Arsenazo III calcium transients. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:625–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Chandler W. K., Marshall M. W. Use of metallochromic dyes to measure changes in myoplasmic calcium during activity in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:139–177. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Hollingworth S., Hui C. S., Quinta-Ferreira M. E. Properties of the metallochromic dyes Arsenazo III, Antipyrylazo III and Azo1 in frog skeletal muscle fibres at rest. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:89–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Oetliker H. Birefringence experiments on isolated skeletal muscle fibres suggest a possible signal from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1975 Jan 10;253(5487):97–101. doi: 10.1038/253097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylor S. M., Quinta-Ferreira M. E., Hui C. S. Comparison of isotropic calcium signals from intact frog muscle fibers injected with Arsenazo III or Antipyrylazo III. Biophys J. 1983 Oct;44(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84282-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler T. J., Schibeci A., Martonosi A. The binding of arsenazo III to cell components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Ríos E., Stéfani E. Effects of extracellular calcium on calcium movements of excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:441–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Allen D. G. Model of calcium movements during activation in the sarcomere of frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin N. A., Woledge R. C. Energy changes and muscular contraction. Physiol Rev. 1978 Jul;58(3):690–761. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.3.690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mello W. C. Membrane sealing in frog skeletal-muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):982–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Tanaka M., Ogawa Y. Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):34–36. doi: 10.1038/228034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford L. E., Podolsky R. J. Regenerative calcium release within muscle cells. Science. 1970 Jan 2;167(3914):58–59. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3914.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Lindley B. D. Influence of temperature upon contractile activation and isometric force production in mechanically skinned muscle fibers of the frog. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Aug;80(2):279–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin-rey C., Gerday C. Parvalbumins from frog skeletal muscle (Rana temporaria L.). Isolation and characterization. Structural modifications associated with calcium binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 27;492(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiny J. A., Vergara J. Dichroic behavior of the absorbance signals from dyes NK2367 and WW375 in skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):805–837. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Aldrich R. W., Baylor S. M. In vitro calibration of the equilibrium reactions of the metallochromic indicator dye antipyrylazo III with calcium. Biophys J. 1987 Mar;51(3):383–393. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83360-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibers injected with Azo1, a tetracarboxylate Ca2+ indicator. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1986;40:261–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. P., Timmerman M. P., Bagshaw C. R., Ashley C. C. The kinetics of calcium binding to fura-2 and indo-1. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80752-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs L., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Measurement and modification of free calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres by a metallochromic indicator dye. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:161–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Ríos E., Schneider M. F. Calcium transients and intramembrane charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):391–396. doi: 10.1038/279391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács L., Schümperli R. A., Szücs G. Comparison of birefringence signals and calcium transients in voltage-clamped cut skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:579–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Podolsky R. J. Ionic mobility in muscle cells. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1297–1298. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Irving M., Sizto N. L., Boyarsky G., Chandler W. K. Calcium signals recorded from cut frog twitch fibers containing tetramethylmurexide. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):145–176. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Irving M., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Calcium signals recorded from cut frog twitch fibers containing antipyrylazo III. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):83–143. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maylie J., Irving M., Sizto N. L., Chandler W. K. Comparison of arsenazo III optical signals in intact and cut frog twitch fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jan;89(1):41–81. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melzer W., Rios E., Schneider M. F. Time course of calcium release and removal in skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1984 Mar;45(3):637–641. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84203-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Nakajima S., Parker I., Takahashi T. Effects of membrane polarization on sarcoplasmic calcium release in skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Sep 17;213(1190):1–13. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Schalow G. Measurement of calcium transients in frog muscle by the use of arsenazo III. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Aug 22;198(1131):201–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients evoked by action potentials in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:655–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients in frog skeletal muscle fibres following conditioning stimuli. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:223–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I., Zhu P. H. Calcium transients studied under voltage-clamp control in frog twitch muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:649–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Gilai A. Action potentials of isolated single muscle fibers recorded by potential-sensitive dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Dec;76(6):729–750. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.6.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Gilai A. Radial propagation of muscle action potential along the tubular system examined by potential-sensitive dyes. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Dec;76(6):751–762. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.6.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oetliker H. An appraisal of the evidence for a sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane potential and its relation to calcium release in skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1982 Sep;3(3):247–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00713037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P., Vergara J. Arsenazo III and antipyrylazo III calcium transients in single skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Apr;79(4):679–707. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.4.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade P., Vergara J. Stoichiometries of arsenazo III-Ca complexes. Biophys J. 1983 Sep;43(3):355–369. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84359-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poledna J., Morad M. Effect of caffeine on the birefringence signal in single skeletal muscle fibers and mammalian heart. Possible mechanism of action. Pflugers Arch. 1983 May;397(3):184–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00584355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowski R. F., Best P. M., James-Kracke M. R. Voltage dependence of membrane charge movement and calcium release in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Aug;6(4):403–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00712580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. N., Salzberg B. M., Cohen L. B., Grinvald A., Davila H. V., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H. Changes in absorption, fluorescence, dichroism, and Birefringence in stained giant axons: : optical measurement of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1977 May 6;33(1-2):141–183. doi: 10.1007/BF01869514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Gonzalez-Serratos H. G., Shuman H., McClellan G., Somlyo A. P. Calcium release and ionic changes in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of tetanized muscle: an electron-probe study. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):577–594. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson D. G., Williams D. A. Calcium-activated force responses in fast- and slow-twitch skinned muscle fibres of the rat at different temperatures. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:281–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Kurtz G., Parker I. Birefringence signals and calcium transients in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):746–748. doi: 10.1038/270746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman M. P., Ashley C. C. Fura-2 diffusion and its use as an indicator of transient free calcium changes in single striated muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 1;209(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. Intracellular measurements of ion activities. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1983;12:91–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.12.060183.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J., Delay M. A transmission delay and the effect of temperature at the triadic junction of skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Oct 22;229(1254):97–110. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


