Abstract
1. In fetal lambs in late gestation, systemic infusion of L-5-hydroxytryptophan (L-5-HTP) during normoxia greatly increases the incidence of fetal breathing movements (FBM) and high-voltage electrocortical activity (HV ECoG). It also induces FBM during HV ECoG and increases blood pressure. To investigate its mechanism of action, L-5-HTP was administered in conjunction with the 5-hydroxy-tryptamine (5-HT) antagonists ketanserin or cyproheptadine. L-5-HTP was also infused with or without the antagonists during hypoxia, to test whether it would overcome the inhibition of FBM by hypoxia. 2. When L-5-HTP was given in normoxia, cyproheptadine blocked and ketanserin reduced the increase in blood pressure, both drugs blocked the stimulation of FBM, but neither drug prevented the induction of prolonged episodes of HV ECoG. 3. In hypoxia, L-5-HTP similarly stimulated FBM. This effect was also blocked by cyproheptadine and was delayed by ketanserin. 4. The antagonism of the effects of L-5-HTP on blood pressure and the incidence of FBM in normoxia and hypoxia is consistent with the action of L-5-HTP via 5-HT receptors. At present there is no clear explanation of the mechanism by which L-5-HTP induces HV ECoG.
Full text
PDF

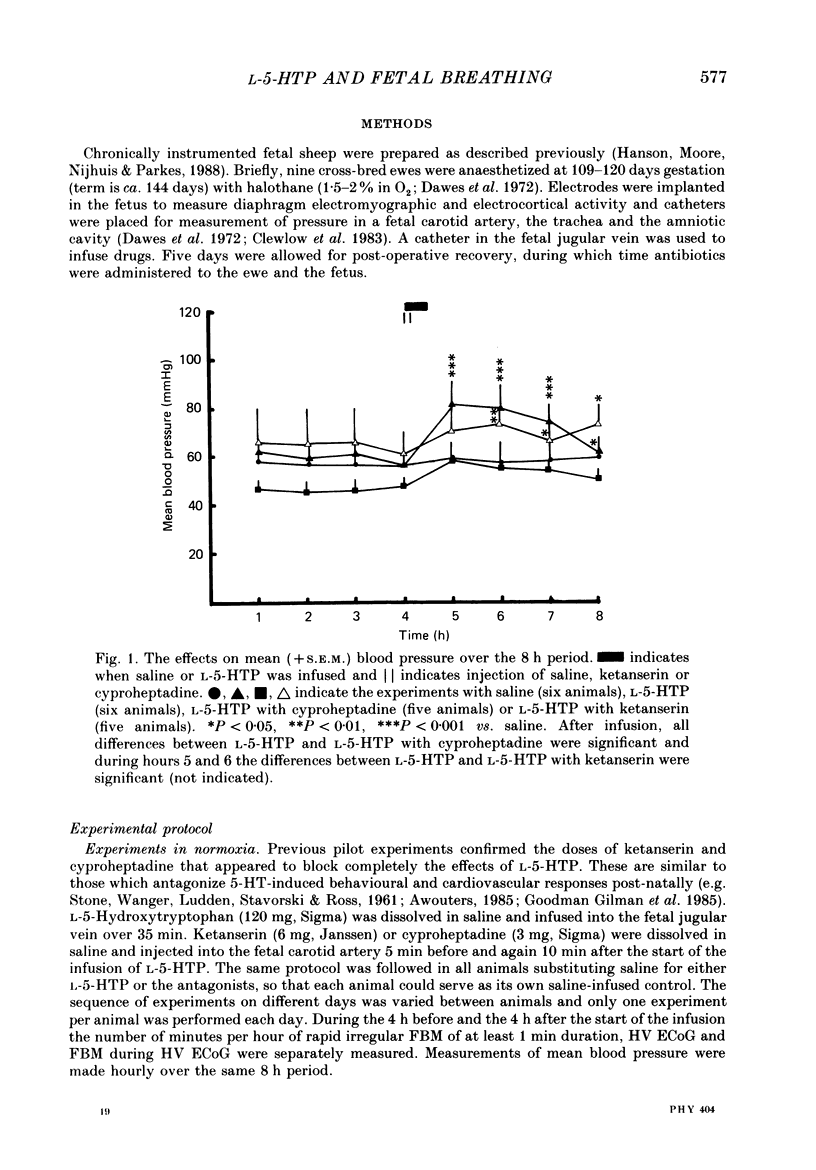
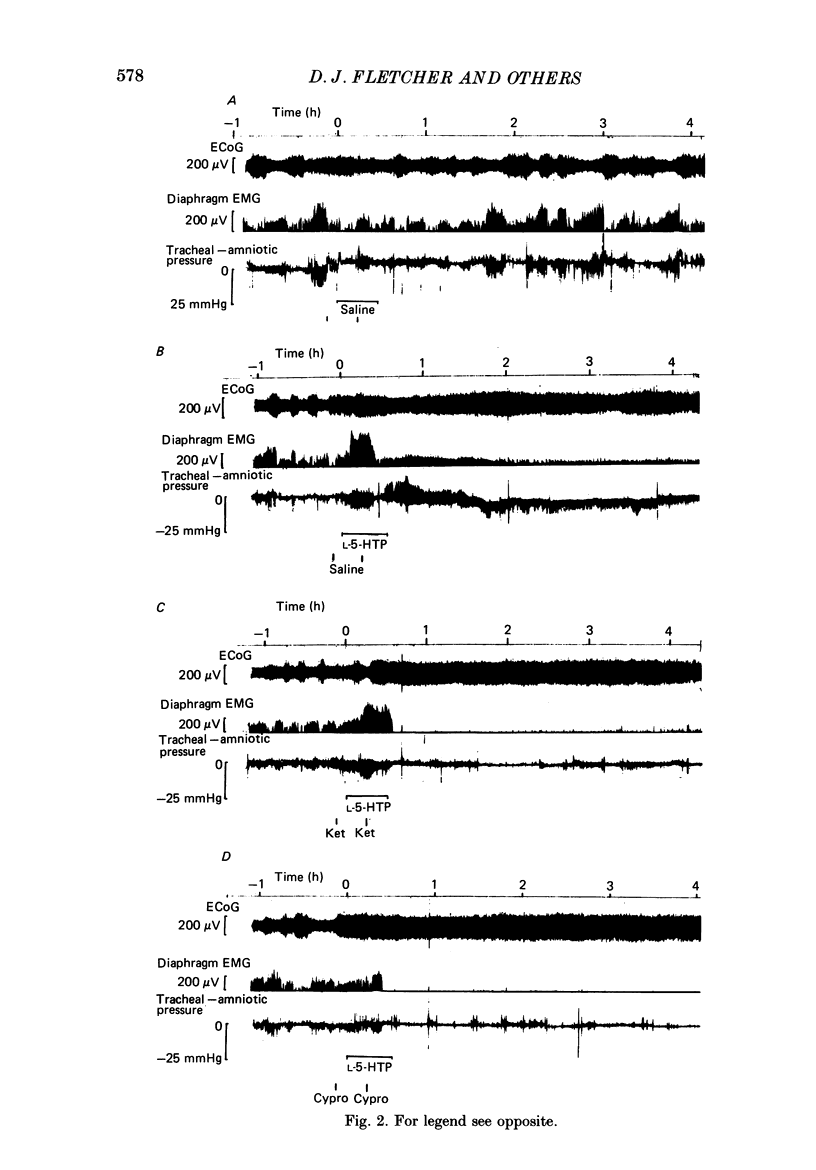
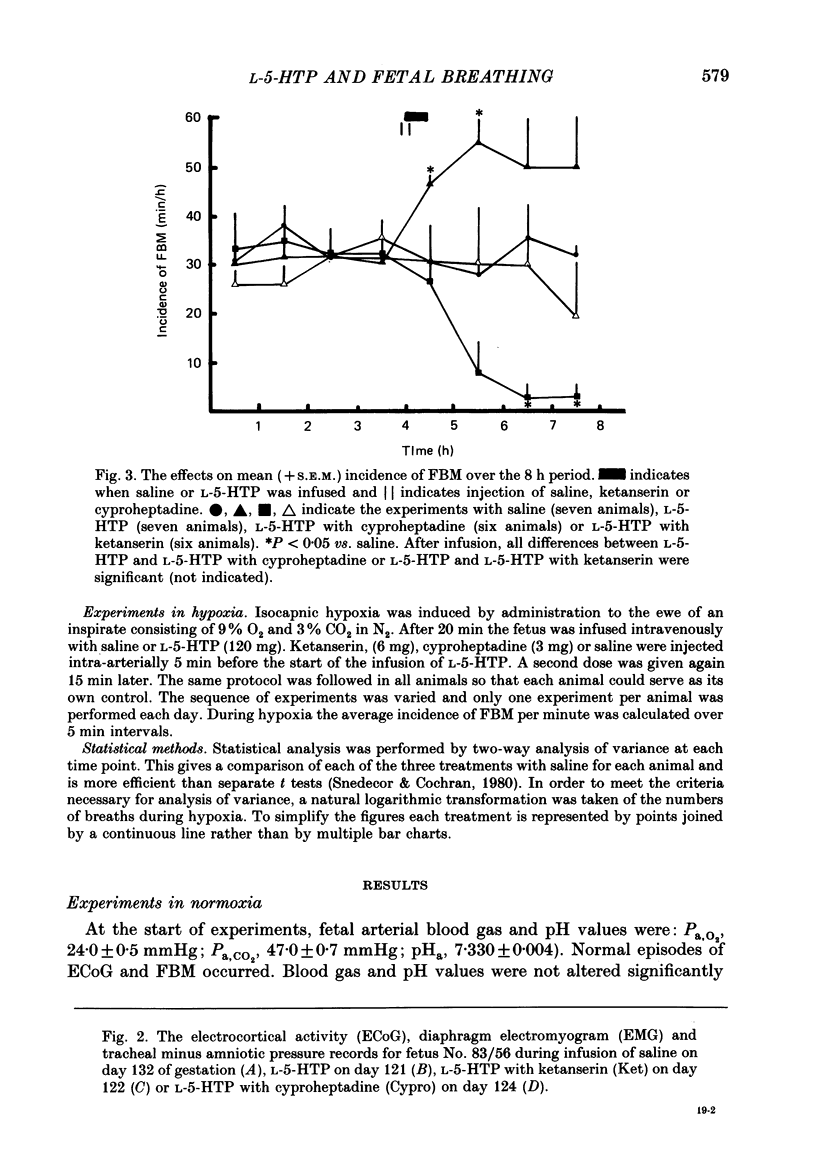
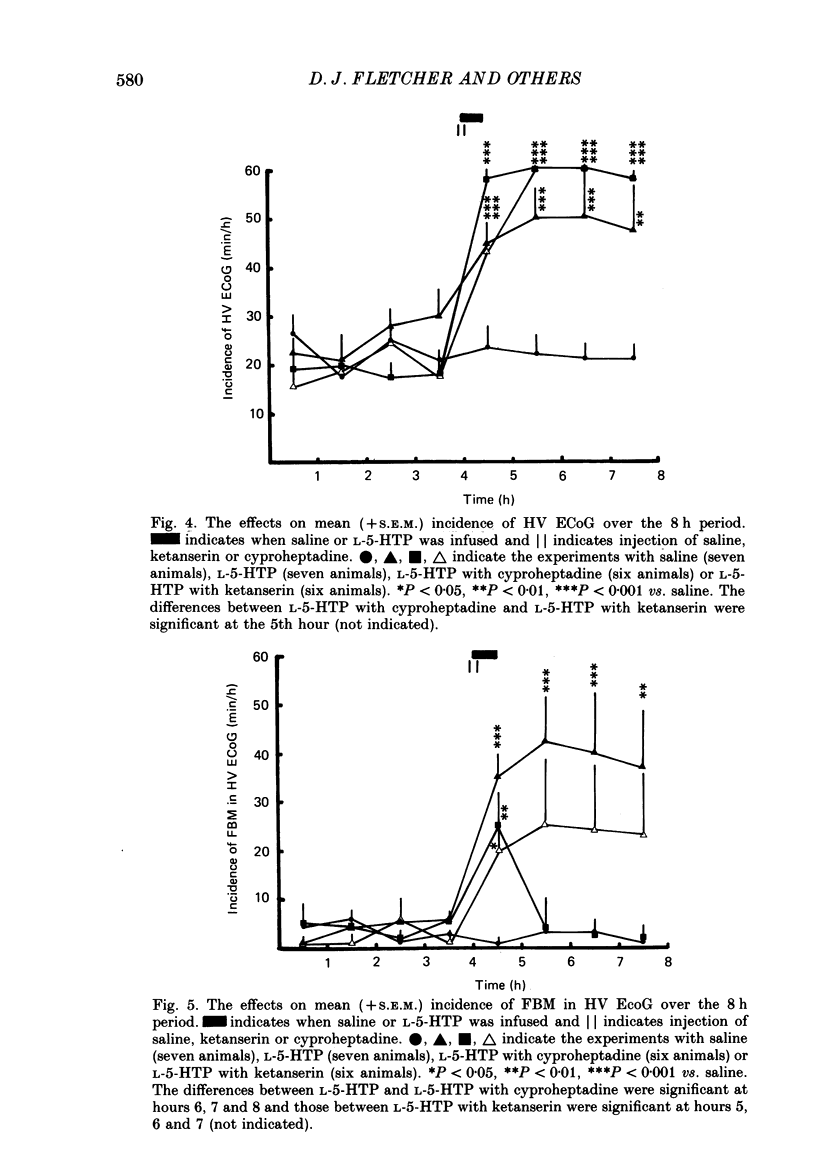
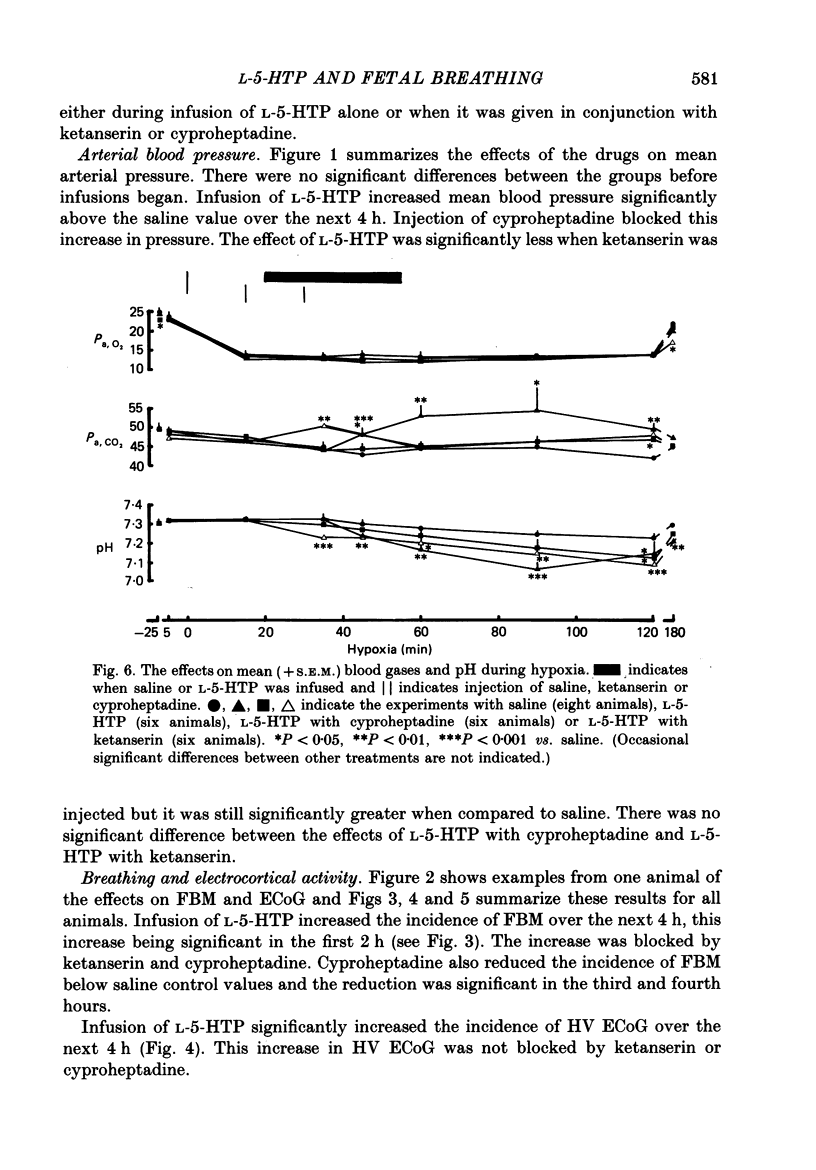
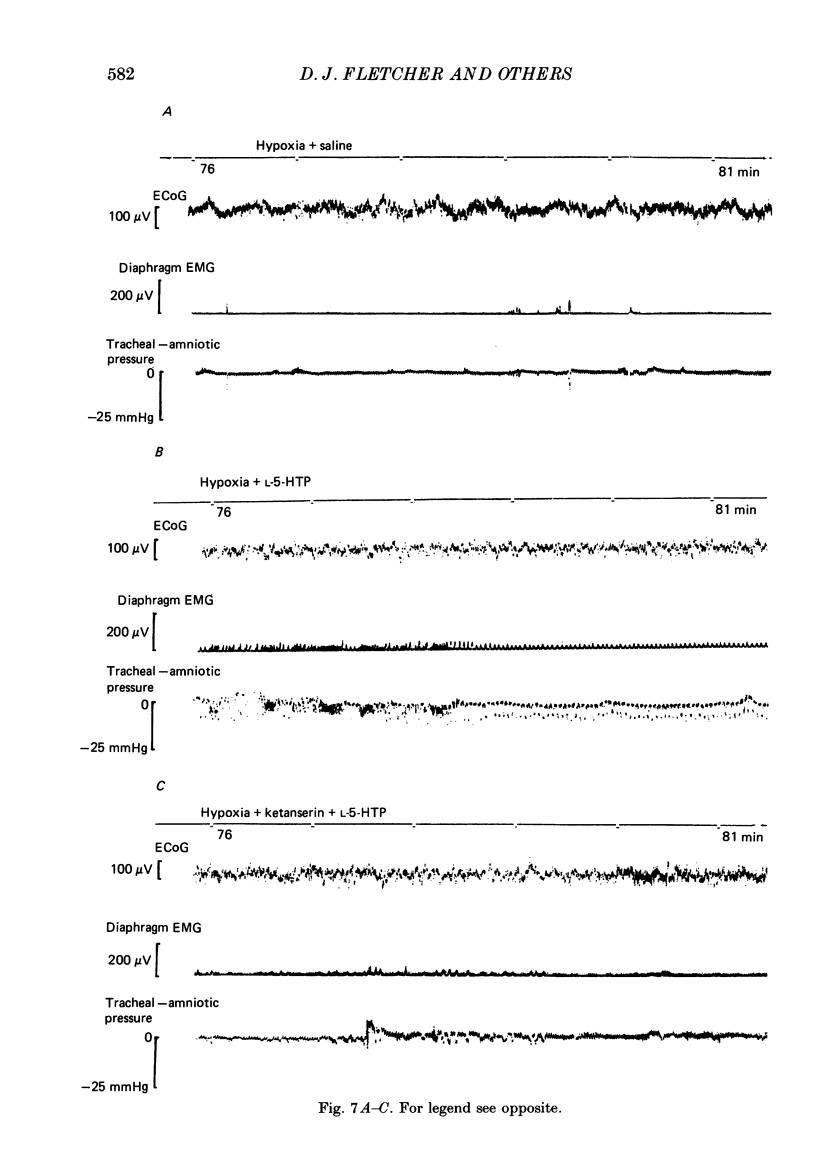
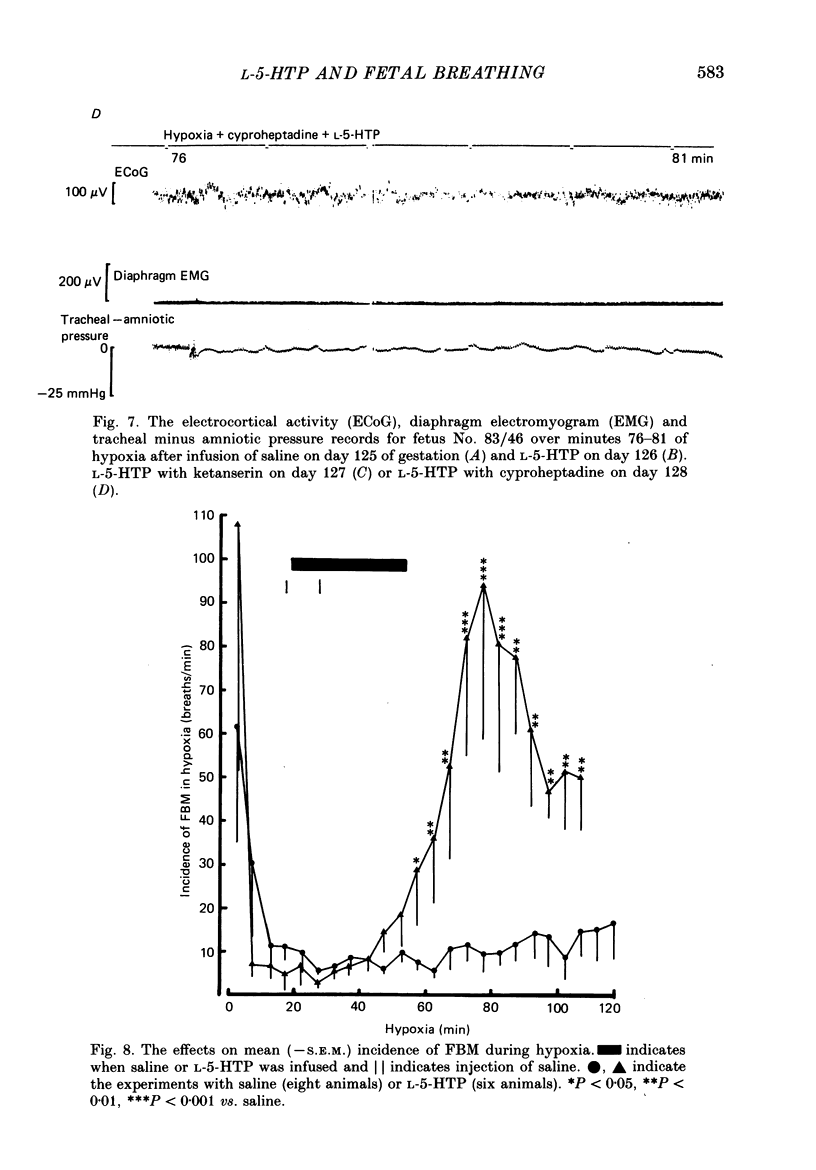
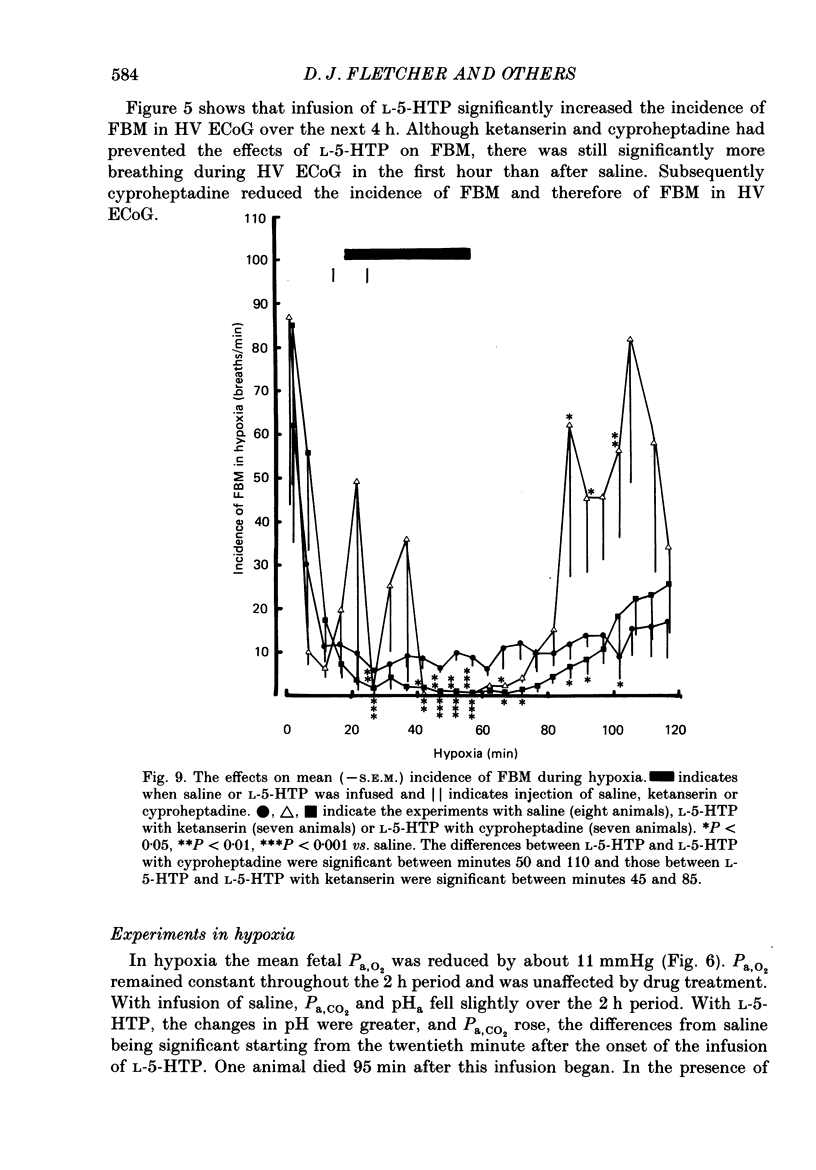





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD J., INSCOE J. K. THE UPTAKE AND BINDING OF CIRCULATING SEROTONIN AND THE EFFECT OF DRUGS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Aug;141:161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson S. L., Patrick J. E., Challis J. R. Effects of naloxone on the breathing, electrocortical, heart rate, glucose and cortisol responses to hypoxia in the sheep fetus. J Dev Physiol. 1984 Dec;6(6):495–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford O. S., Dawes G. S., Denny R., Ward R. A. Effects of the alpha 2-adrenergic agonist clonidine and its antagonist idazoxan on the fetal lamb. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:29–37. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford O. S., Dawes G. S., Hanson M. A., Ward R. A. The effects of doxapram on breathing, heart rate and blood pressure in fetal lambs. Respir Physiol. 1986 Dec;66(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(86)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford O. S., Dawes G. S., Ward R. A. Effects of apomorphine and haloperidol in fetal lambs. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:37–47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennet L., Gluckman P. D., Johnston B. M. The central effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone on the breathing movements and electrocortical activity of the fetal sheep. Pediatr Res. 1988 Jan;23(1):72–75. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198801000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy K., Dawes G. S., Fisher R., Pinter S., Robinson J. S. Foetal respiratory movements, electrocortical and cardiovascular responses to hypoxaemia and hypercapnia in sheep. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):599–618. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Engel G., Feniuk W., Fozard J. R., Humphrey P. P., Middlemiss D. N., Mylecharane E. J., Richardson B. P., Saxena P. R. Proposals for the classification and nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Jun;25(6):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. Pharmacology. 5-HT3 receptors in the brain? Nature. 1987 Dec 24;330(6150):696–696. doi: 10.1038/330696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewlow F., Dawes G. S., Johnston B. M., Walker D. W. Changes in breathing, electrocortical and muscle activity in unanaesthetized fetal lambs with age. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:463–476. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Fox H. E., Leduc B. M., Liggins G. C., Richards R. T. Respiratory movements and rapid eye movement sleep in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):119–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Gardner W. N., Johnston B. M., Walker D. W. Breathing in fetal lambs: the effect of brain stem section. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:535–553. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes G. S., Gardner W. N., Johnston B. M., Walker D. W. Effects of hypercapnia on tracheal pressure, diaphragm and intercostal electromyograms in unanaesthetized fetal lambs. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:461–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman P. D., Johnston B. M. Lesions in the upper lateral pons abolish the hypoxic depression of breathing in unanaesthetized fetal lambs in utero. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:373–383. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen A. H., Ioffe S., Chernick V. Stimulation of fetal breathing activity by beta-adrenergic mechanisms. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Jun;60(6):1938–1945. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.6.1938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston B. M., Gluckman P. D. GABA-mediated inhibition of breathing in the late gestation sheep fetus. J Dev Physiol. 1983 Dec;5(6):353–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvet M. The role of monoamines and acetylcholine-containing neurons in the regulation of the sleep-waking cycle. Ergeb Physiol. 1972;64:166–307. doi: 10.1007/3-540-05462-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koella W. P. The organization and regulation of sleep. A review of the experimental evidence and a novel integrated model of the organizing and regulating apparatus. Experientia. 1984 Apr 15;40(4):309–338. doi: 10.1007/BF01952538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koos B. J. Central stimulation of breathing movements in fetal lambs by prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors. J Physiol. 1985 May;362:455–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koos B. J., Sameshima H., Power G. G. Fetal breathing, sleep state, and cardiovascular responses to graded hypoxia in sheep. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Mar;62(3):1033–1039. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.3.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J. E., Awouters F., Kennis L., Laduron P. M., Vandenberk J., Janssen P. A. Receptor binding profile of R 41 468, a novel antagonist at 5-HT2 receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 2;28(9):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90747-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molteni R. A., Melmed M. H., Sheldon R. E., Jones M. D., Meschia G. Induction of fetal breathing by metabolic acidemia and its effect on blood flow to the respiratory muscles. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Mar 1;136(5):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)91012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quilligan E. J., Clewlow F., Johnston B. M., Walker D. W. Effect of 5-hydroxytryptophan on electrocortical activity and breathing movements of fetal sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Oct 1;141(3):271–275. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32632-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallanon M., Buda C., Janin M., Jouvet M. 5-HT antagonists suppress sleep and delay its restoration after 5-HTP in p-chlorophenylalanine-pretreated cats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Aug 13;82(1-2):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90549-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


