Abstract
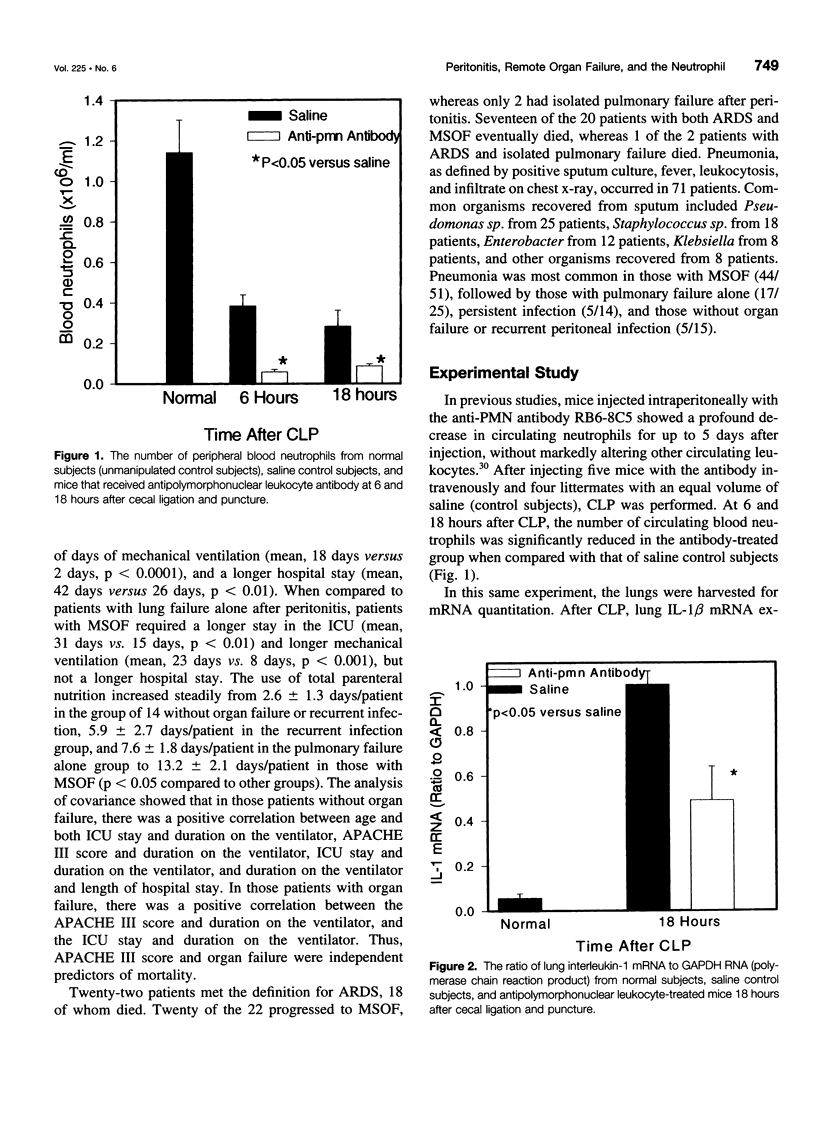
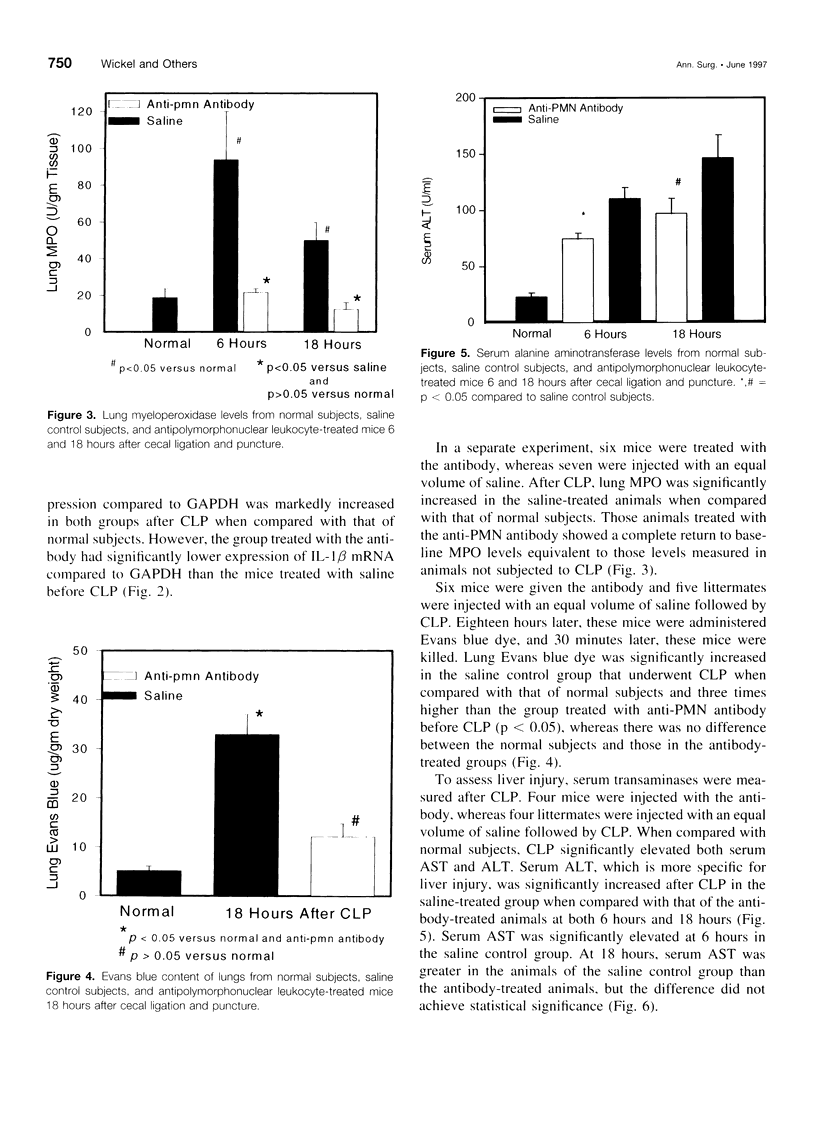
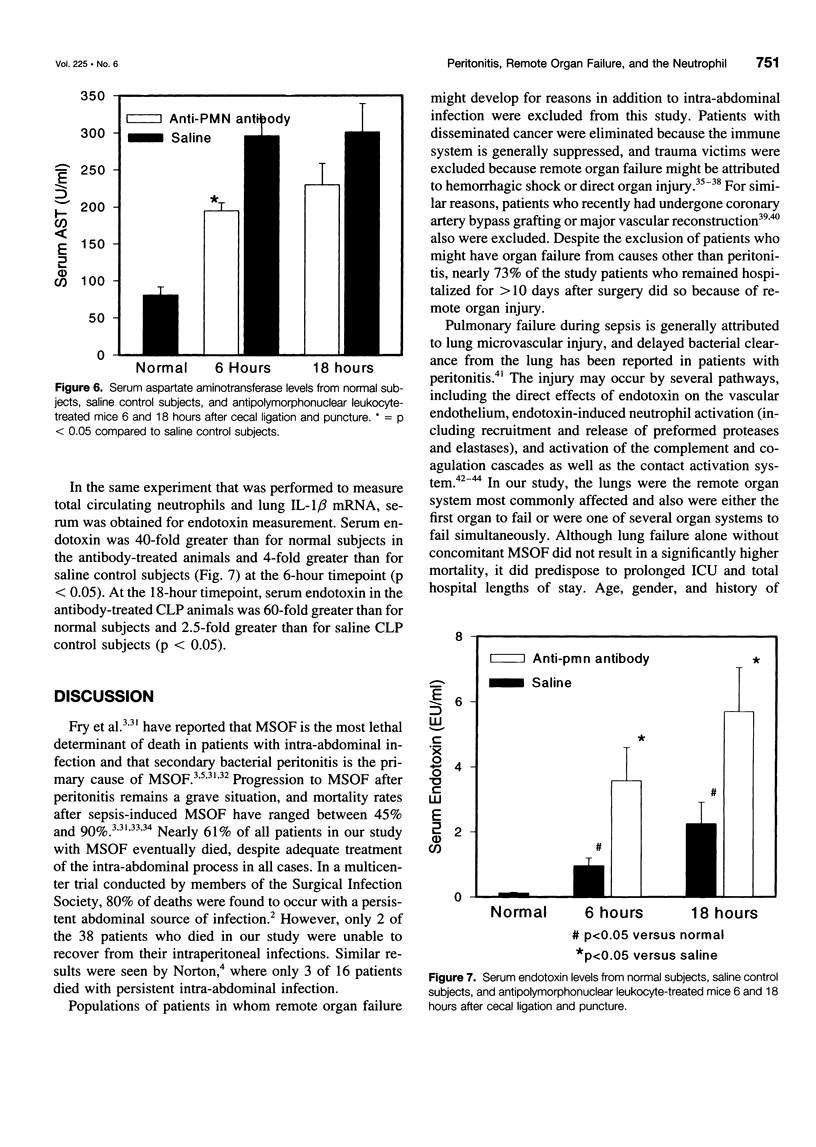
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of the study is to determine whether organ failure develops in patients despite control of peritoneal infection and whether the process is, in part, neutrophil (polymorphonuclear leukocyte [PMN]) mediated. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Peritonitis generally responds to prompt surgical intervention and systemic antibiotics; however, some patients continue a septic course and progress to organ failure and death. METHODS: One hundred five consecutive patients with peritonitis between 1988 and 1996 who required operation and a postoperative hospital stay greater than 10 days were studied. Mice were injected with a monoclonal anti-PMN antibody 24 hours before cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) to deplete PMNs. RESULTS: Thirty-eight patients died, and all but 1 had identified organ failure. Seventy-seven patients had either pulmonary failure alone (25 patients) or as a component of multisystem organ failure (52 patients). All but one of these patients showed resolution of their intraperitoneal infection as evident by clinical course, abdominal computed tomographic scan, second-look laparotomy, or autopsy. Recurrent intra-abdominal infection developed in 15 patients, but only 1 had organ failure, and 2 died. At 18 hours after CLP, lung injury, PMN content, interleukin-1 mRNA expression, and liver injury were significantly reduced by anti-PMN treatment, whereas serum endotoxin levels actually increased. CONCLUSIONS: Disease acuity and organ failure, and not recurrent peritoneal infection, are the major causes of adverse outcome in patients with peritonitis. The authors' experimental data indicate that such organ injury is, in part, PMN mediated but not endotoxin mediated. Attraction of PMNs toward the site of primary infection, and thereby away from remote organs, is a logical future therapeutic approach in such patients who are critically ill with peritonitis.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert R. K. Mechanisms of the adult respiratory distress syndrome: selectins. Thorax. 1995 Sep;50 (Suppl 1):S49–S52. doi: 10.1136/thx.50.suppl_1.s49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan G., Bhattacherjee P., Brook C. D., Read N. G., Parke A. J. Myeloperoxidase activity as a quantitative marker of polymorphonuclear leukocyte accumulation into an experimental myocardial infarct--the effect of ibuprofen on infarct size and polymorphonuclear leukocyte accumulation. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Nov-Dec;7(6):1154–1160. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198511000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. O., Brown J. M., Harken A. H. Mechanisms of neutrophil-mediated tissue injury. J Surg Res. 1991 Aug;51(2):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. W., Deitch E. A., Li M., Berg R. D., Specian R. D. Hemorrhagic shock induces bacterial translocation from the gut. J Trauma. 1988 Jul;28(7):896–906. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198807000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baue A. E. Multiple, progressive, or sequential systems failure. A syndrome of the 1970s. Arch Surg. 1975 Jul;110(7):779–781. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360130011001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer E. P., Redaelli C., von Segesser L. K., Turina M. I. Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms: predictors for early complications and death. Surgery. 1993 Jul;114(1):31–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal A. L., Cerra F. B. Multiple organ failure syndrome in the 1990s. Systemic inflammatory response and organ dysfunction. JAMA. 1994 Jan 19;271(3):226–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom R. J., Simon L. M., Benitz W. E. Endotoxin and pulmonary cell injury. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Aug;167(2):92–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Balk R. A., Cerra F. B., Dellinger R. P., Fein A. M., Knaus W. A., Schein R. M., Sibbald W. J. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992 Jun;101(6):1644–1655. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.6.1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Balk R., Slotman G., Maunder R., Silverman H., Hyers T. M., Kerstein M. D. Adult respiratory distress syndrome. Sequence and importance of development of multiple organ failure. The Prostaglandin E1 Study Group. Chest. 1992 Feb;101(2):320–326. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.2.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botha A. J., Moore F. A., Moore E. E., Sauaia A., Banerjee A., Peterson V. M. Early neutrophil sequestration after injury: a pathogenic mechanism for multiple organ failure. J Trauma. 1995 Sep;39(3):411–417. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199509000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlos T. M., Harlan J. M. Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood. 1994 Oct 1;84(7):2068–2101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. W. Endotoxin-induced pulmonary leukostasis in the rat: role of platelet-activating factor and tumor necrosis factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1994 Jan;123(1):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheadle W. G., Mercer-Jones M., Heinzelmann M., Polk H. C., Jr Sepsis and septic complications in the surgical patient: who is at risk? Shock. 1996;6 (Suppl 1):S6–S9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Kaplan J. C., Maire P., Gautron S., Kahn A. Transcription of the dystrophin gene in human muscle and non-muscle tissue. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):858–860. doi: 10.1038/333858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Katz M., Katz R., Hauptman E., Schachner A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1995 Mar;109(3):574–581. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(95)70291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouser E. D., Dorinsky P. M. Gastrointestinal tract dysfunction in critical illness: pathophysiology and interaction with acute lung injury in adult respiratory distress syndrome/multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. New Horiz. 1994 Nov;2(4):476–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F., Maroushek N., Wagner R. D., Steinberg H. Administration of anti-granulocyte mAb RB6-8C5 impairs the resistance of mice to Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 15;152(4):1836–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellinger E. P., Wertz M. J., Meakins J. L., Solomkin J. S., Allo M. D., Howard R. J., Simmons R. L. Surgical infection stratification system for intra-abdominal infection. Multicenter trial. Arch Surg. 1985 Jan;120(1):21–29. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390250015003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiseman B., Beart R., Norton L. Multiple organ failure. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1977 Mar;144(3):323–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertel W., Friedl H. P., Trentz O. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) following multiple trauma: rationale and concept of therapeutic approach. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1994 Aug;4(4):243–248. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1066112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faist E., Baue A. E., Dittmer H., Heberer G. Multiple organ failure in polytrauma patients. J Trauma. 1983 Sep;23(9):775–787. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198309000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. E., Garrison R. N., Heitsch R. C., Calhoun K., Polk H. C., Jr Determinants of death in patients with intraabdominal abscess. Surgery. 1980 Oct;88(4):517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. E., Pearlstein L., Fulton R. L., Polk H. C., Jr Multiple system organ failure. The role of uncontrolled infection. Arch Surg. 1980 Feb;115(2):136–140. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380020006003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goris R. J., te Boekhorst T. P., Nuytinck J. K., Gimbrère J. S. Multiple-organ failure. Generalized autodestructive inflammation? Arch Surg. 1985 Oct;120(10):1109–1115. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1985.01390340007001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiminas D. J., McMasters K. M., Peyton J. C., Cheadle W. G. Tissue tumor necrosis factor mRNA expression following cecal ligation and puncture or intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin. J Surg Res. 1994 Jun;56(6):549–555. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1994.1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiminas D. J., McMasters K. M., Peyton J. C., Cook M. D., Cheadle W. G. Passive immunization against tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 fails to reduce lung neutrophil sequestration in chronic sepsis. Shock. 1994 Nov;2(5):376–380. doi: 10.1097/00024382-199411000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heflin A. C., Jr, Brigham K. L. Prevention by granulocyte depletion of increased vascular permeability of sheep lung following endotoxemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1253–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI110371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka A., Stephens K. E., Tazelaar H. D., Hall E. W., O'Hanley P., Raffin T. A. Pulmonary edema after Escherichia coli peritonitis correlates with thiobarbituric-acid-reactive materials in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):783–789. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. A., Miller C. F., Kubos K. L., Rogers M. C. Evaluation of sepsis in a critically ill surgical population. Crit Care Med. 1987 Oct;15(10):897–904. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198710000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus W. A., Wagner D. P., Draper E. A., Zimmerman J. E., Bergner M., Bastos P. G., Sirio C. A., Murphy D. J., Lotring T., Damiano A. The APACHE III prognostic system. Risk prediction of hospital mortality for critically ill hospitalized adults. Chest. 1991 Dec;100(6):1619–1636. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.6.1619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike K., Moore E. E., Moore F. A., Franciose R. J., Fontes B., Kim F. J. CD11b blockade prevents lung injury despite neutrophil priming after gut ischemia/reperfusion. J Trauma. 1995 Jul;39(1):23–28. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199507000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landow L., Andersen L. W. Splanchnic ischaemia and its role in multiple organ failure. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1994 Oct;38(7):626–639. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1994.tb03969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan G. J., Anderson I. D., Grant I. S., Fearon K. C. Outcome of patients with abdominal sepsis treated in an intensive care unit. Br J Surg. 1995 Apr;82(4):524–529. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800820429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. E., Moore F. A., Franciose R. J., Kim F. J., Biffl W. L., Banerjee A. The postischemic gut serves as a priming bed for circulating neutrophils that provoke multiple organ failure. J Trauma. 1994 Dec;37(6):881–887. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199412000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. A., Moore E. E. Evolving concepts in the pathogenesis of postinjury multiple organ failure. Surg Clin North Am. 1995 Apr;75(2):257–277. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)46587-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. A., Moore E. E., Poggetti R., McAnena O. J., Peterson V. M., Abernathy C. M., Parsons P. E. Gut bacterial translocation via the portal vein: a clinical perspective with major torso trauma. J Trauma. 1991 May;31(5):629–638. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199105000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. A., Moore E. E., Read R. A. Postinjury multiple organ failure: role of extrathoracic injury and sepsis in adult respiratory distress syndrome. New Horiz. 1993 Nov;1(4):538–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton L. W. Does drainage of intraabdominal pus reverse multiple organ failure? Am J Surg. 1985 Mar;149(3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky M. R., Vincent J. L., Deviere J., Alegre M., Kahn R. J., Dupont E. Serum cytokine levels in human septic shock. Relation to multiple-system organ failure and mortality. Chest. 1993 Feb;103(2):565–575. doi: 10.1378/chest.103.2.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr Generalized peritonitis: a continuing challenge. Surgery. 1979 Nov;86(5):777–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr, Shields C. L. Remote organ failure: a valid sign of occult intra-abdominal infection. Surgery. 1977 Mar;81(3):310–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangel-Frausto M. S., Pittet D., Costigan M., Hwang T., Davis C. S., Wenzel R. P. The natural history of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). A prospective study. JAMA. 1995 Jan 11;273(2):117–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. D., DeCamp M. M., Garrison R. N., Fry D. E. Pulmonary infection complicating intra-abdominal sepsis: clinical and experimental observations. Ann Surg. 1982 Jun;195(6):732–738. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198206000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spec-Marn A., Tos L., Kremzar B., Milic-Emili J., Ranieri V. M. Oxygen delivery-consumption relationship in adult respiratory distress syndrome patients: the effects of sepsis. J Crit Care. 1993 Mar;8(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0883-9441(93)90032-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen M., Loewenthal J. Generalized infective peritonitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1978 Aug;147(2):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens K. E., Ishizaka A., Wu Z. H., Larrick J. W., Raffin T. A. Granulocyte depletion prevents tumor necrosis factor-mediated acute lung injury in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Nov;138(5):1300–1307. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.5.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland J. E., Davis W. B., Holter J. F., Mohammed J. R., Dorinsky P. M., Gadek J. E. Lung neutrophils in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clinical and pathophysiologic significance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):218–225. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada O., Moldow C. F., Sacks T., Craddock P. R., Boogaerts M. A., Jacob H. S. Deleterious effects of endotoxin on cultured endothelial cells: an in vitro model of vascular injury. Inflammation. 1981 Jun;5(2):115–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00914201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


