Abstract
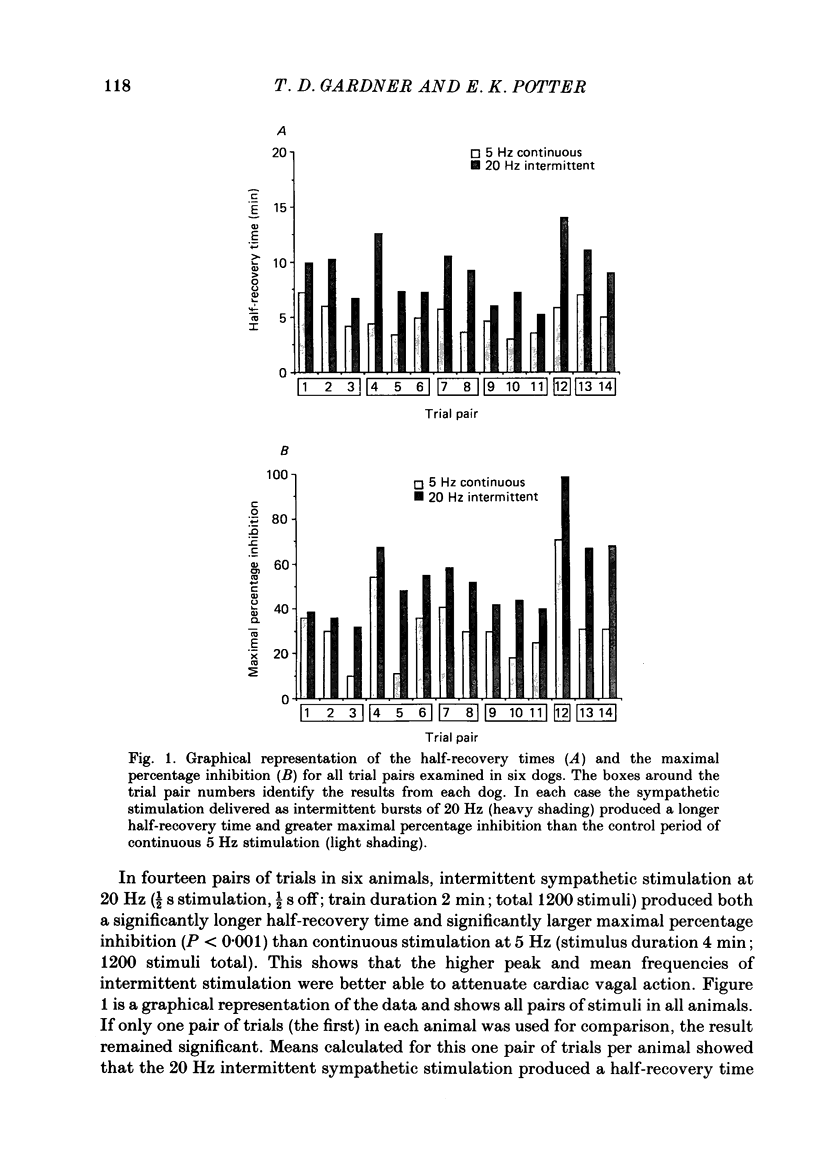
1. It is known that stimulation of the sympathetic cardioaccelerator nerve is followed by prolonged inhibition of cardiac vagal action. This prolonged inhibitory action of the sympathetic nerve is not blocked by alpha- or beta-adrenoceptor blockade, and is not duplicated by administration of noradrenaline. It has been proposed that it is due to the release of neuropeptide Y (NPY) from the sympathetic nerve terminals (Potter, 1984, 1985). 2. The present experiments examined whether prolonged inhibition of cardiac vagal action could be preferentially produced by sympathetic stimulation of different temporal distribution. The experiments were performed on anaesthetized, vagotomized dogs, with pharmacological beta-adrenoceptor blockade. 3. In six animals intermittent supramaximal sympathetic stimulation at 20 Hz (1/2 s stimulation, 1/2 s off; train duration 2 min; total 1200 stimuli) produced significantly greater inhibition (P less than 0.01) of cardiac vagal action than did continuous stimulation at 5 Hz (stimulus duration 4 min; 1200 stimuli). 4. In another series the same total period of stimulation (2.5 min; 1200 stimuli) was used and it was found that intermittent sympathetic stimulation of 16 Hz (1/2 s stimulation, 1/2 s off) produced significantly greater cardiac vagal inhibition (P less than 0.02) than continuous stimulation at 8 Hz. In this case the mean frequency of stimulation was constant but the higher peak stimulation frequency attenuated cardiac vagal action more effectively.
Full text
PDF


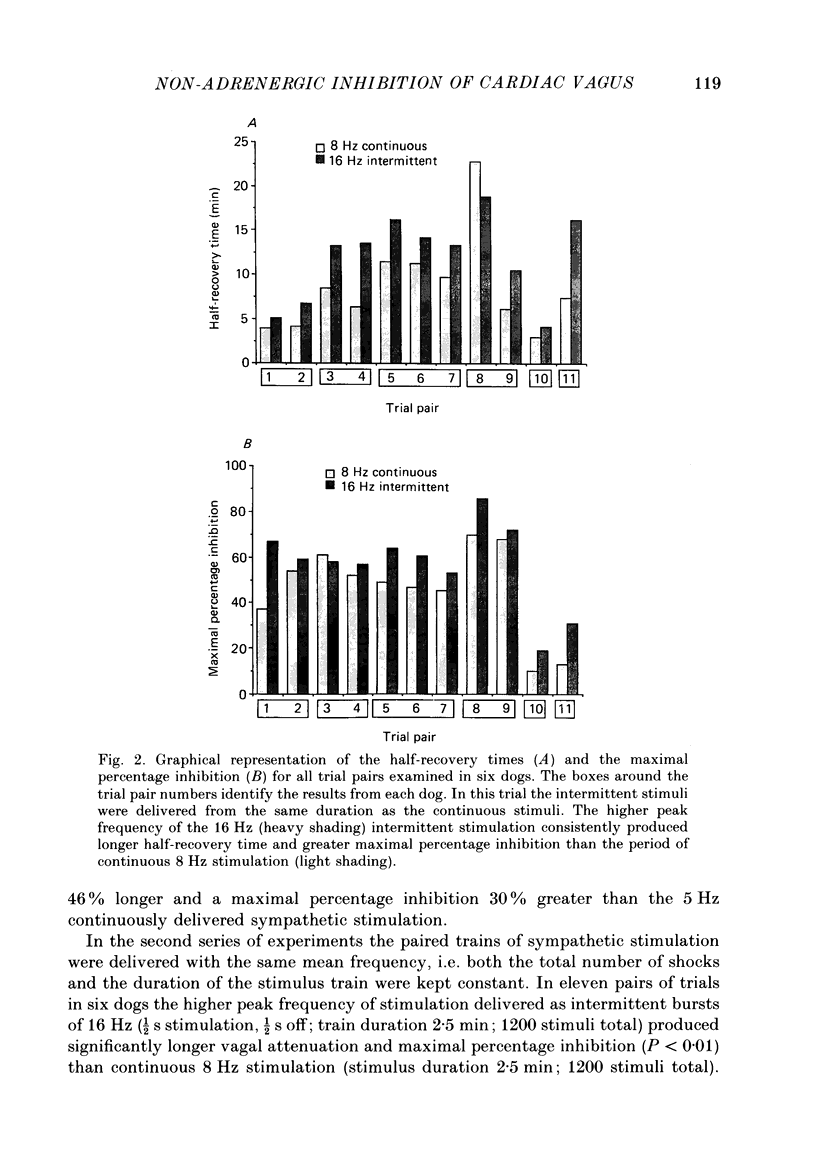



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Bircham P. M., Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Release of neuropeptide Y in response to splanchnic nerve stimulation in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:401–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Gjörstrup P., Björkman J. A., Ek L., Abrahamsson T., Bloom S. R. Studies on cardiac distribution and function of neuropeptide Y. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Mar;126(3):405–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Polak J. M., Rodrigo J., Darcy K., Bloom S. R. Localisation of neuropeptide Y in nerves of the rat cardiovascular system and the effect of 6-hydroxydopamine. Cardiovasc Res. 1985 Sep;19(9):570–577. doi: 10.1093/cvr/19.9.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius W., Hagbarth K. E., Hongell A., Wallin B. G. General characteristics of sympathetic activity in human muscle nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Jan;84(1):65–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Lundberg J. M., Theodorsson-Norheim E. Subcellular storage and axonal transport of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in relation to catecholamines in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Sep;125(1):145–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Terenius L., Brodin E., Efendic S., Dockray G., Fahrenkrug J., Goldstein M., Hökfelt T. Neuropeptide Y, enkephalin and noradrenaline coexist in sympathetic neurons innervating the bovine spleen. Biochemical and immunohistochemical evidence. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;243(3):495–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00218056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M. Evidence for differential localization of noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y in neuronal storage vesicles isolated from rat vas deferens. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):450–458. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00450.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., Polak J. M., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY)--a major cardiac neuropeptide. Lancet. 1983 May 7;1(8332):1008–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92642-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu J., Polak J. M., Allen J. M., Huang W. M., Sheppard M. N., Tatemoto K., Bloom S. R. High concentrations of a novel peptide, neuropeptide Y, in the innervation of mouse and rat heart. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 May;32(5):467–472. doi: 10.1177/32.5.6546942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Vallbo A. B. Pulse and respiratory grouping of sympathetic impulses in human muscle-nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Sep-Oct;74(1):96–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilborn M. J., Potter E. K., McCloskey D. I. Neuromodulation of the cardiac vagus: comparison of neuropeptide Y and related peptides. Regul Pept. 1985 Oct;12(2):155–161. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollai M., Koizumi K. Cardiovascular reflexes and interrelationships between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1981 Jul;4(2):135–148. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(81)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollai M., Koizumi K. Reciprocal and non-reciprocal action of the vagal and sympathetic nerves innervating the heart. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1979 Oct;1(1):33–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(79)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Fried G., Pernow J., Theodorsson-Norheim E. Co-release of neuropeptide Y and catecholamines upon adrenal activation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Feb;126(2):231–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07810.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Rudehill A., Sollevi A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Hamberger B. Frequency- and reserpine-dependent chemical coding of sympathetic transmission: differential release of noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y from pig spleen. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jan 2;63(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M. High levels of neuropeptide Y in peripheral noradrenergic neurons in various mammals including man. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 2;42(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIZERES N. J. The origin and course of the cardioaccelerator fibers in the dog. Anat Rec. 1958 Nov;132(3):261–279. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091320304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P., Celler B. G., Potter E. K., McCloskey D. I. Vagal stimulation and cardiac slowing. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 Sep;11(2):226–231. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. K. Prolonged non-adrenergic inhibition of cardiac vagal action following sympathetic stimulation: neuromodulation by neuropeptide Y? Neurosci Lett. 1985 Mar 15;54(2-3):117–121. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(85)80065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudehill A., Sollevi A., Franco-Cereceda A., Lundberg J. M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) and the pig heart: release and coronary vasoconstrictor effects. Peptides. 1986 Sep-Oct;7(5):821–826. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Quidt M. E., Richardson P. J., Emson P. C. Subcellular distribution of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in guinea pig neocortex. Brain Res. 1985 Jun 3;335(2):354–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90493-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]