Abstract
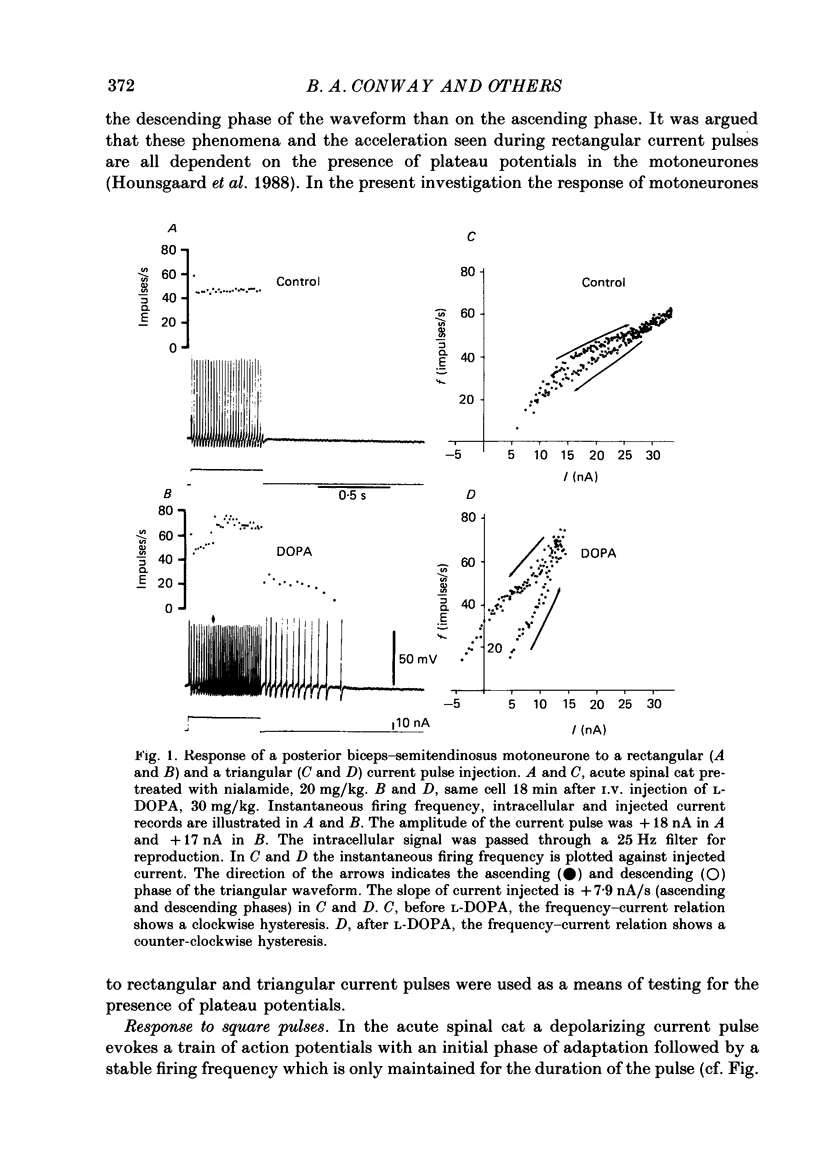
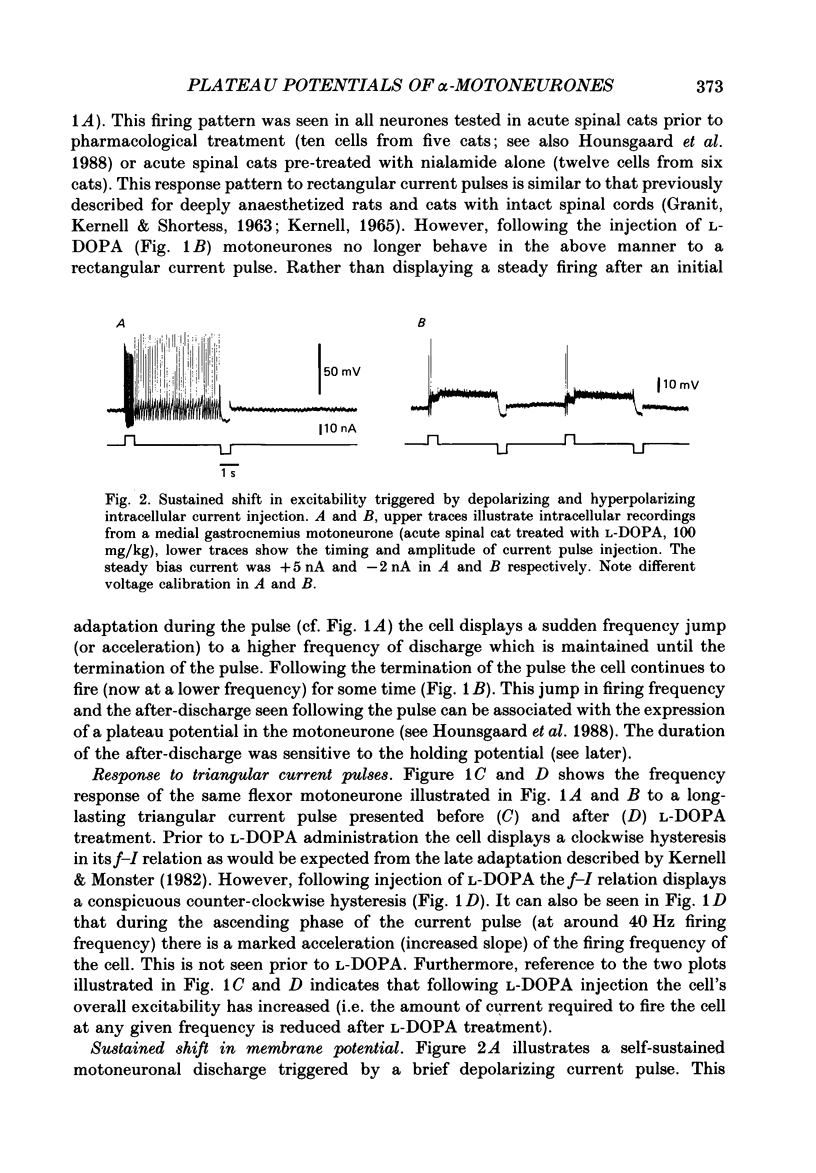
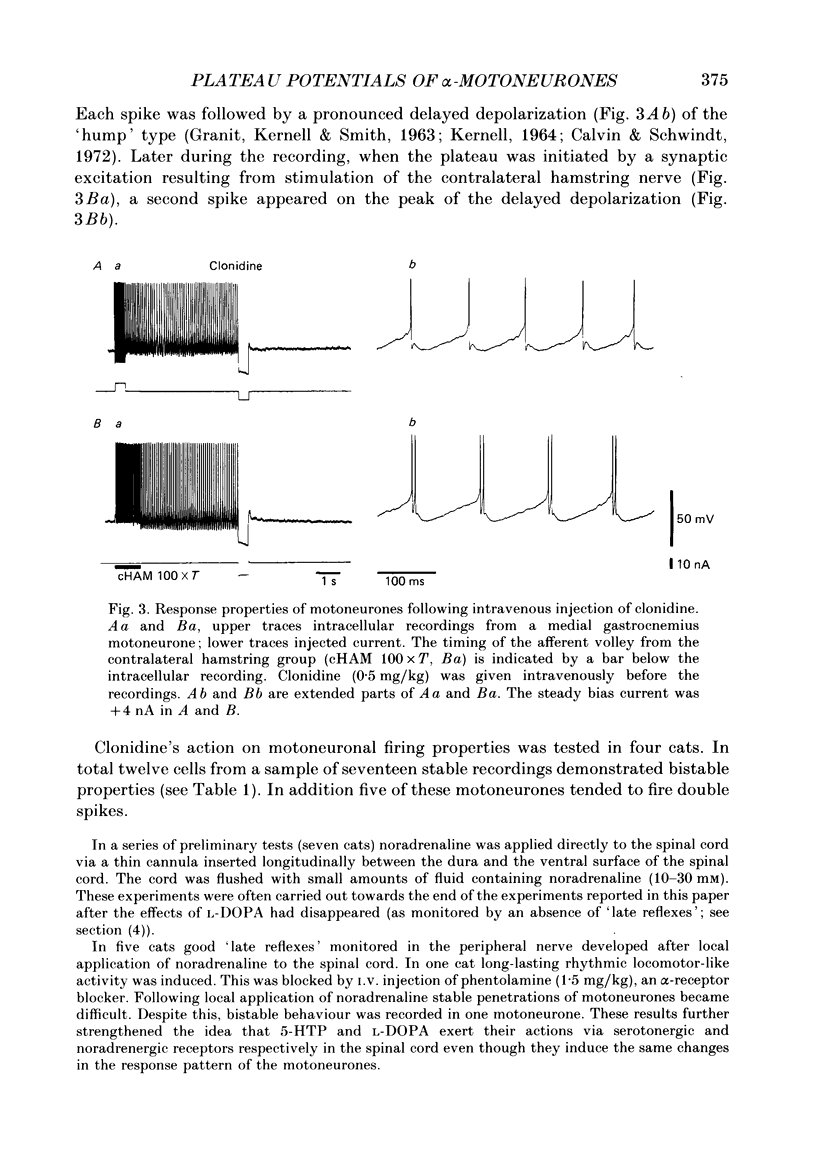
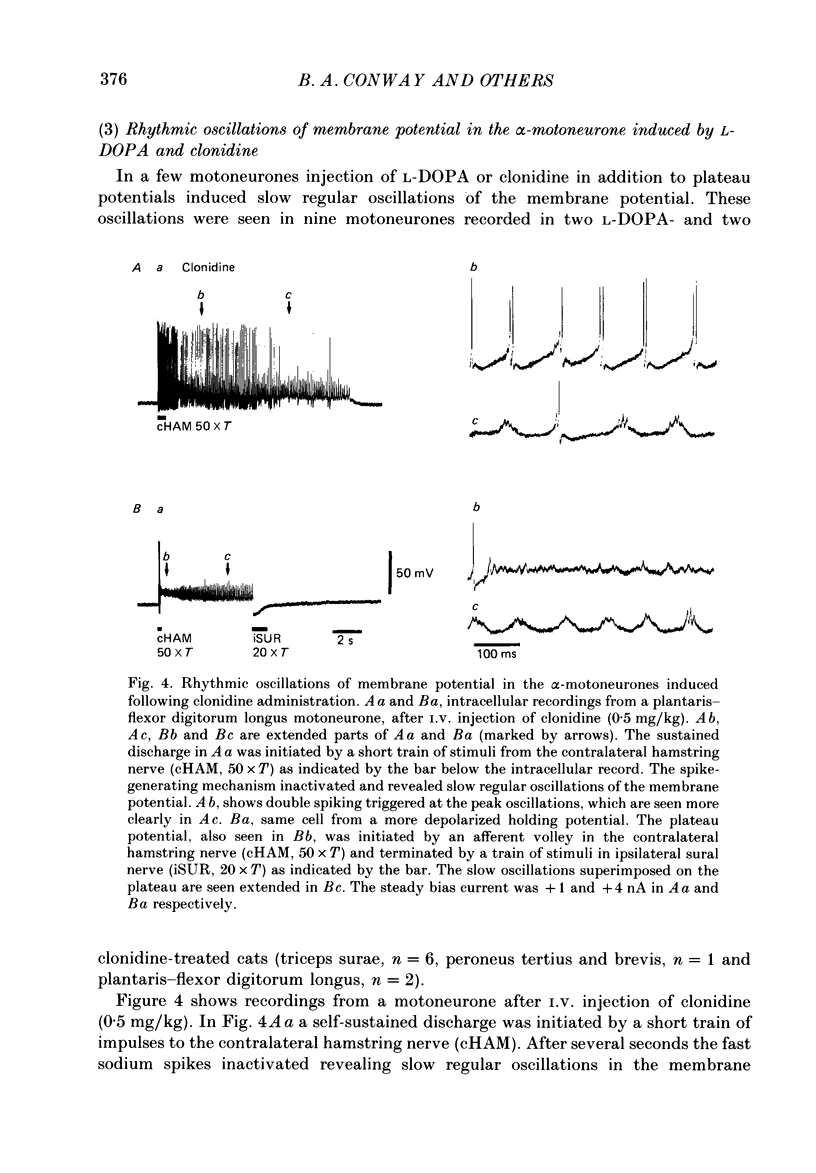
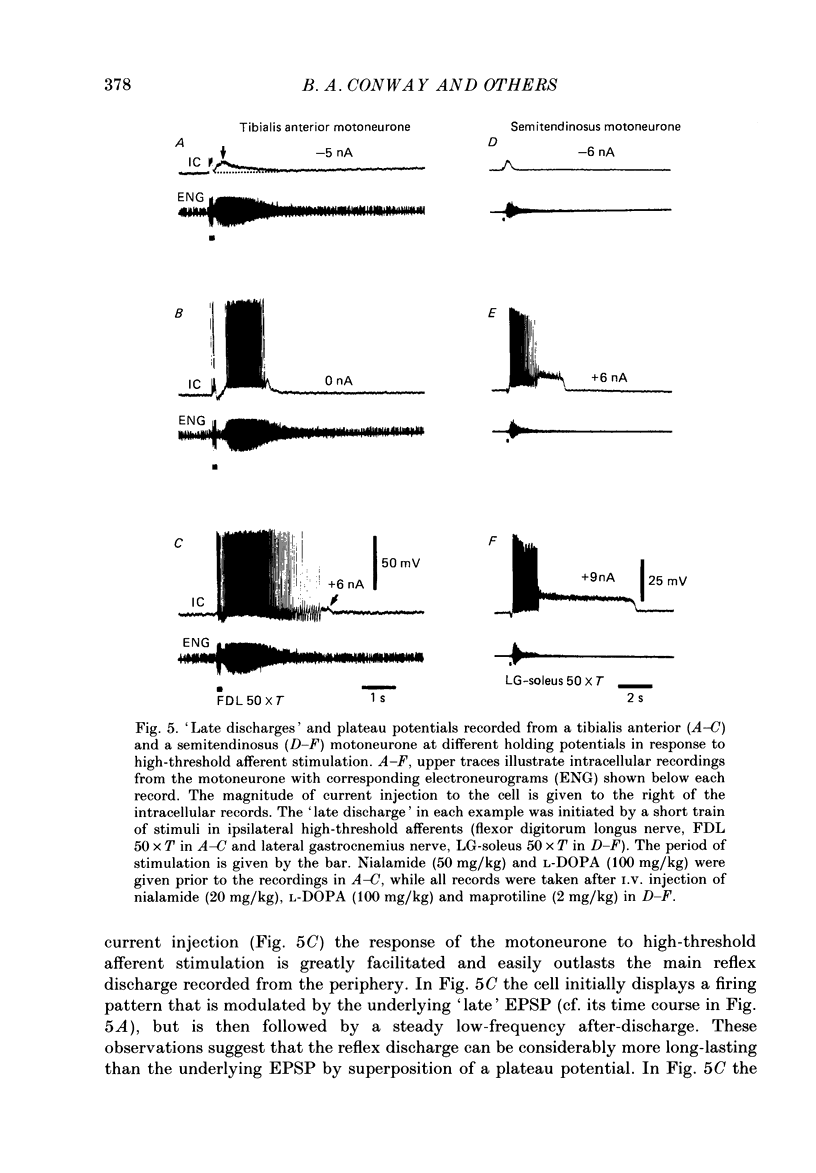
1. Intracellular recordings were made from lumbar alpha-motoneurones in unanaesthetized decerebrate acute spinal cats. The response of motoneurones to direct current pulse injection or synaptic excitation was investigated following intravenous injection of L-beta-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA, 20-120 mg/kg) alone, nialamide (10-50 mg/kg) and L-DOPA or clonidine (0.5-1 mg/kg). 2. The response properties of motoneurones were tested with rectangular and triangular current waveforms. Before L-DOPA treatment motoneuronal firing during a rectangular current pulse is characterized by an initial high firing frequency which rapidly decreases to a lower steady-state firing which is maintained only for the duration of the pulse. Following administration of L-DOPA an acceleration in firing frequency is apparent following the initial adaptation seen with rectangular current pulses. A transient after-depolarization or an after-discharge often followed the termination of the pulse. The frequency-current relation in response to a triangular current injection changed from a clockwise to a counter-clockwise hysteresis after L-DOPA treatment (i.e. after L-DOPA the firing frequency was higher for any given current during the descending phase than during the ascending phase of the triangular waveform). 3. Firing acceleration during and self-sustained firing after rectangular current pulses and counter-clockwise hysteresis of firing frequency with triangular current pulses are causally related to the presence of plateau potentials, which can be directly visualized after inactivation of the spikes. Plateau potentials in motoneurones could be generated by short-lasting intracellular depolarizing current pulses or brief excitatory synaptic inputs and terminated by short-lasting hyperpolarizing current pulses or brief inhibitory synaptic inputs. Plateau potentials were demonstrated in flexor and extensor motoneurones. 4. All bistable properties described in the preceding paragraphs following L-DOPA administration could also be seen after administration of the alpha-receptor agonist clonidine. 5. Slow rhythmic oscillations of the membrane potential (7.5-10 Hz) were seen superimposed on plateau potentials in a few cells after administration of L-DOPA and clonidine. The oscillations had an amplitude in the range 10-20 mV and represent the expression of an intrinsic property of the motoneurone. 6. It is demonstrated that plateau potentials in the motoneurones contribute to the late long-lasting reflexes observed in L-DOPA-treated spinal cats. 7. It is concluded that L-DOPA (and clonidine) change the response properties of the motoneurones in an analogous way to 5-hydroxy-DL-tryptophan (5-HTP).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDEN N. E., JUKES M. G., LUNDBERG A. SPINAL REFLEXES AND MONOAMINE LIBERATION. Nature. 1964 Jun 20;202:1222–1223. doi: 10.1038/2021222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson G., Sjölund B. The ventral spino-olivocerebellar system in the cat. IV. Spinal transmission after administration of clonidine and L-dopa. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Oct 13;33(2):227–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00238062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt B., Hökfelt T., Rydin C., Svensson T. Evidence for a central noradrenaline receptor stimulation by clonidine. Life Sci. 1970 May 1;9(9):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Grabowska M., Strömbom U. Different alpha-adrenoreceptors in the central nervous system mediating biochemical and functional effects of clonidine and receptor blocking agents. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976;292(1):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00506488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Jukes M. G., Lundberg A. The effect of DOPA on the spinal cord. 2. A pharmacological analysis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jul-Aug;67(3):387–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andén N. E., Jukes M. G., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. The effect of DOPA on the spinal cord. 1. Influence on transmission from primary afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jul-Aug;67(3):373–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aston-Jones G., Ennis M., Pieribone V. A., Nickell W. T., Shipley M. T. The brain nucleus locus coeruleus: restricted afferent control of a broad efferent network. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):734–737. doi: 10.1126/science.3775363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin J. H., Nygren L. G., Fuxe K. A system for measuring the noradrenaline receptor contribution to the flexor reflex. Med Biol. 1976 Dec;54(5):352–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin W. H., Schwindt P. C. Steps in production of motoneuron spikes during rhythmic firing. J Neurophysiol. 1972 May;35(3):297–310. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commissiong J. W., Sedgwick E. M. Depletion of 5-HT by L-DOPA in spinal cord and brainstem of rat. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 2;25(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C., Hultborn H., Kiehn O., Mazieres L., Wigström H. Maintained changes in motoneuronal excitability by short-lasting synaptic inputs in the decerebrate cat. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:321–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson P. S., Nagy F. Control of a central pattern generator by an identified modulatory interneurone in crustacea. II. Induction and modification of plateau properties in pyloric neurones. J Exp Biol. 1983 Jul;105:59–82. doi: 10.1242/jeb.105.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg I., Marshall K. C. Mechanism of noradrenaline hyperpolarization in spinal cord motoneurones of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Sep;83(1):142–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg I., Ryall R. W. The inhibitory action of noradrenaline and other monoamines on spinal neurones. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(2):298–322. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamm R. E., Harris-Warrick R. M. Aminergic modulation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion. I. Effects on motor pattern and activity of neurons within the pyloric circuit. J Neurophysiol. 1986 May;55(5):847–865. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.5.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forssberg H., Grillner S. The locomotion of the acute spinal cat injected with clonidine i.v. Brain Res. 1973 Feb 14;50(1):184–186. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90606-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KERNELL D., SHORTESS G. K. QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF REPETITIVE FIRING OF MAMMALIAN MOTONEURONES, CAUSED BY INJECTED CURRENTS. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:911–931. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KERNELL D., SMITH R. S. DELAYED DEPOLARIZATION AND THE REPETITIVE RESPONSE TO INTRACELLULAR STIMULATION OF MAMMALIAN MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:890–910. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Hultborn H., Jespersen B., Kiehn O. Bistability of alpha-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat and in the acute spinal cat after intravenous 5-hydroxytryptophan. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:345–367. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hounsgaard J., Kiehn O. Ca++ dependent bistability induced by serotonin in spinal motoneurons. Exp Brain Res. 1985;57(2):422–425. doi: 10.1007/BF00236551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman A. M., Kuypers H. G., Verburgh C. A. Quantitative differences in collateralization of the descending spinal pathways from red nucleus and other brain stem cell groups in rat as demonstrated with the multiple fluorescent retrograde tracer technique. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 30;209(2):271–286. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Jukes M. G., Lund S., Lundberg A. The effect of DOPA on the spinal cord. 5. Reciprocal organization of pathways transmitting excitatory action to alpha motoneurones of flexors and extensors. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Jul-Aug;70(3):369–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., Jukes M. G., Lund S., Lundberg A. The effect of DOPA on the spinal cord. 6. Half-centre organization of interneurones transmitting effects from the flexor reflex afferents. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Jul-Aug;70(3):389–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERNELL D. THE DELAYED DEPOLARIZATION IN CAT AND RAT MOTONEURONES. Prog Brain Res. 1964;12:42–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60616-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Monster A. W. Time course and properties of late adaptation in spinal motoneurones of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1982;46(2):191–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00237176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Saito K., Ohga A. Effects of catecholamines on spinal motoneurones and spinal reflex discharges in the isolated spinal cord of the newborn rat. Brain Res. 1985 Mar;351(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(85)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima M., Takeuchi Y., Kawata M., Sano Y. Motoneurons innervating the cremaster muscle of the rat are characteristically densely innervated by serotoninergic fibers as revealed by combined immunohistochemistry and retrograde fluorescence DAPI-labelling. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1983;168(1):41–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00305397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall R. B., Aghajanian G. K. Serotonergic facilitation of facial motoneuron excitation. Brain Res. 1979 Jun 15;169(1):11–27. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. Y., Chase T. N., Colburn R. W., Kopin I. J. L-Dopa-induced release of cerebral monoamines. Science. 1970 Oct 2;170(3953):76–77. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3953.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygren L. G., Fuxe K., Jonsson G., Olson L. Functional regeneration of 5-hydroxytryptamine nerve terminals in the rat spinal cord following 5, 6-dihydroxytryptamine induced degeneration. Brain Res. 1974 Oct 4;78(3):377–394. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90922-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygren L. G., Olson L. On spinal noradrenaline receptor supersensitivity: correlation between nerve terminal densities and flexor reflexes various times after intracisternal 6-hydroxydopamine. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 12;116(3):455–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90493-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. F., Hartline D. K. Slow active potentials and bursting motor patterns in pyloric network of the lobster, Panulirus interruptus. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Oct;48(4):914–937. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.4.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson T. H., Bunney B. S., Aghajanian G. K. Inhibition of both noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons in brain by the alpha-adrenergic agonist clonidine. Brain Res. 1975 Jul 11;92(2):291–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanderMaelen C. P., Aghajanian G. K. Intracellular studies showing modulation of facial motoneurone excitability by serotonin. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):346–347. doi: 10.1038/287346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandermaelen C. P., Aghajanian G. K. Serotonin-induced depolarization of rat facial motoneurons in vivo: comparison with amino acid transmitters. Brain Res. 1982 May 6;239(1):139–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90838-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. R., Neuman R. S. Facilitation of spinal motoneurone excitability by 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 21;188(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90561-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. R., Neuman R. S. Pharmacological antagonism of facilitatory but not inhibitory effects of serotonin and norepinephrine on excitability of spinal motoneurons. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Apr;22(4):489–494. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Polosa C., Nishi S. Noradrenaline induces rhythmic bursting in sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 8;420(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



