Abstract
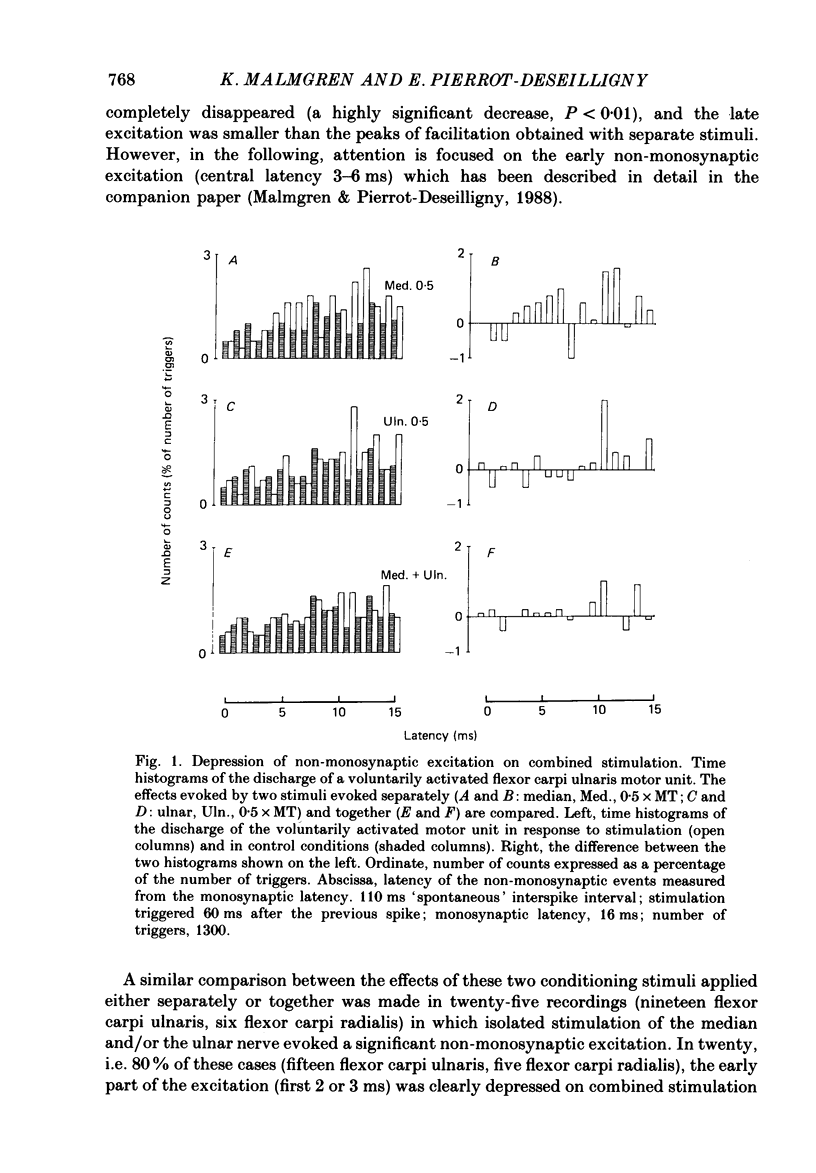
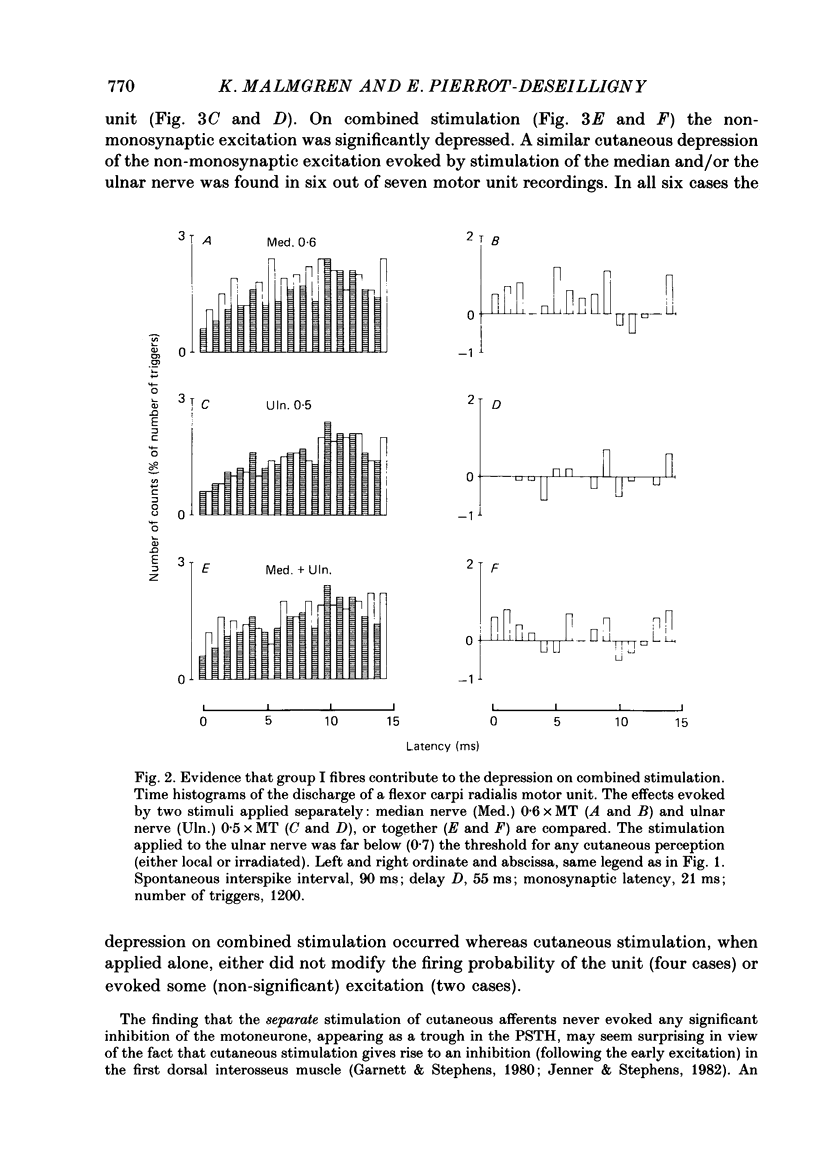
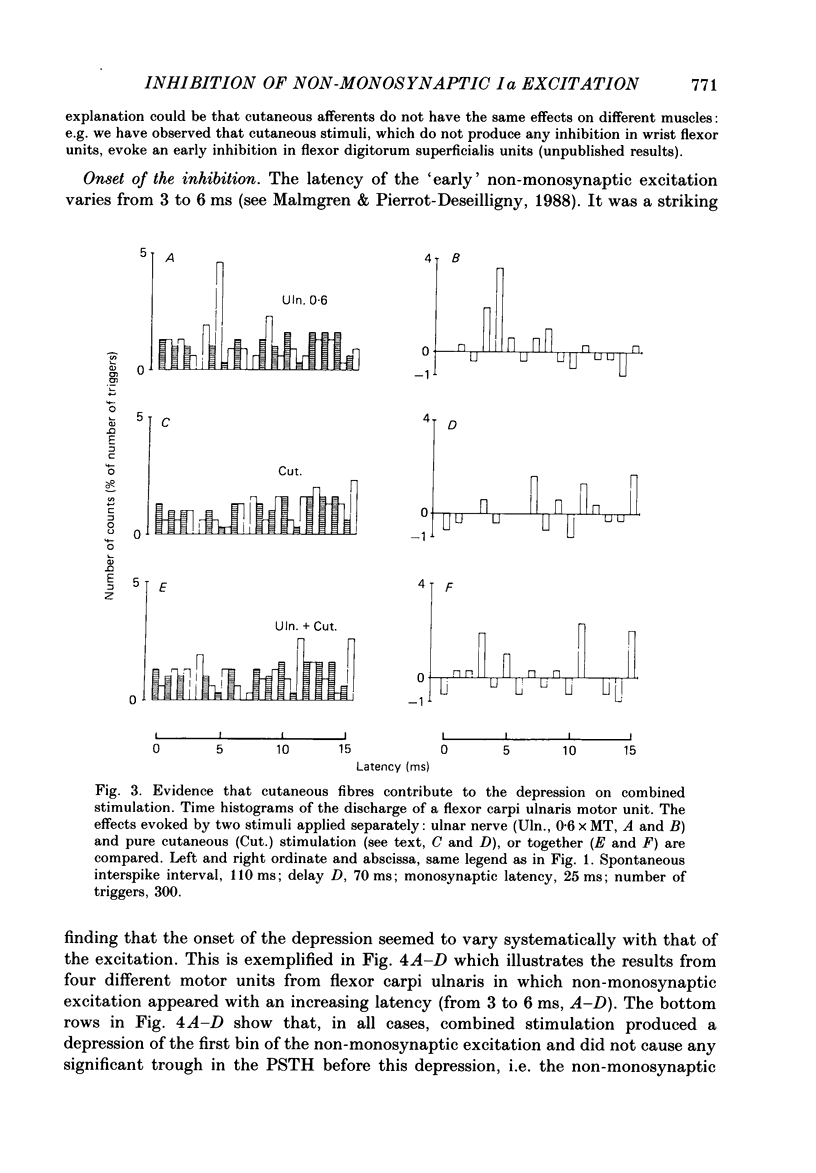
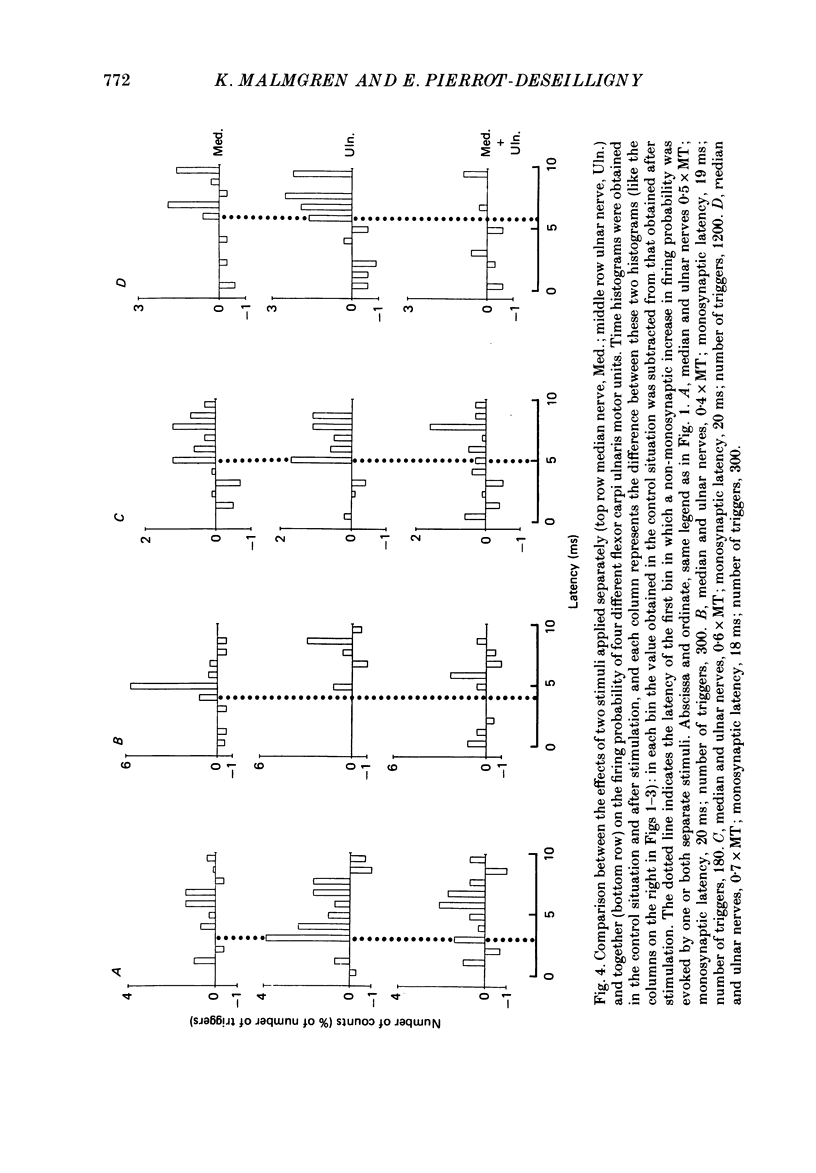
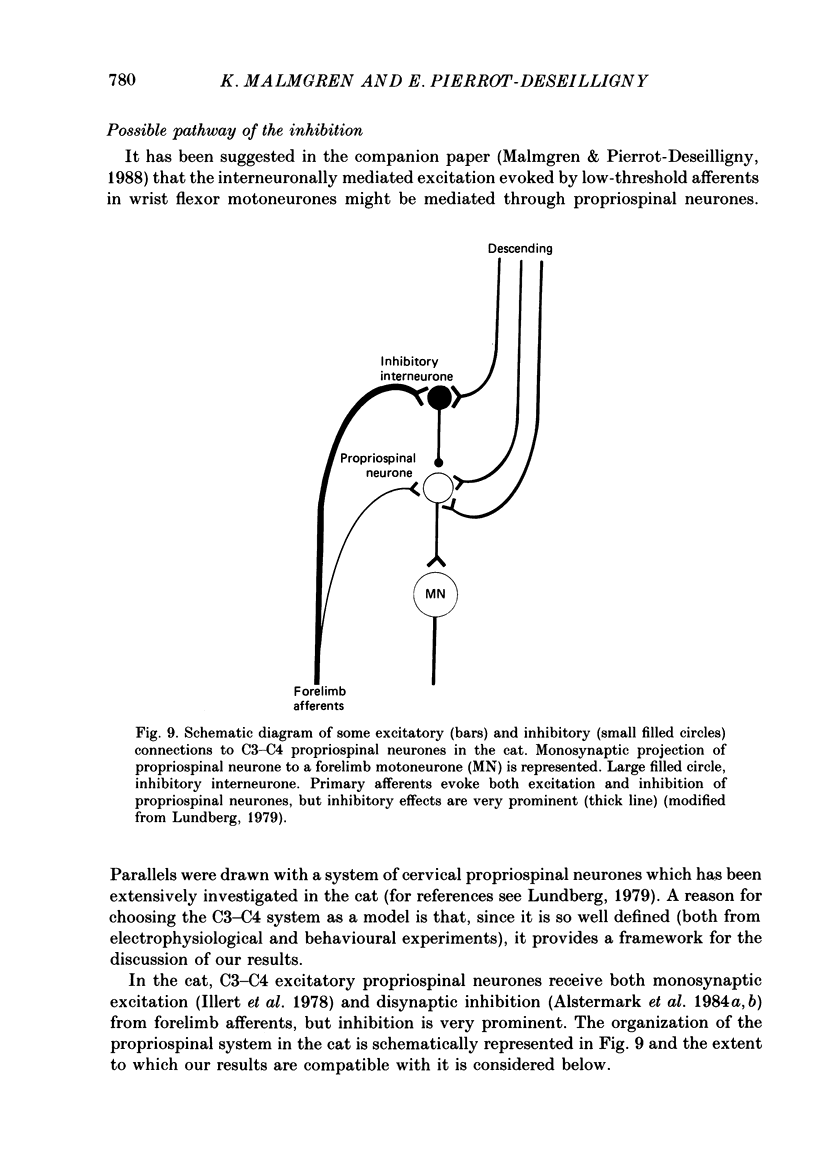
1. The possibility was investigated that the transmission of the interneuronally mediated Ia excitation to wrist flexor motoneurones described in the companion paper is inhibited by stimulation of afferent fibres. Two techniques were used: (i) the post-stimulus time histogram (PSTH) method for studying changes in firing probability of individual voluntarily activated wrist flexor motor units following various peripheral stimulations; and (ii) the indirect technique of spatial facilitation of the H reflex. 2. In those individual units where stimulation of the median and/or the ulnar nerve evoked a non-monosynaptic excitation, this excitation was reduced when the afferent input was increased. This reduction of the non-monosynaptic Ia excitation was found in 80% of the motor unit recordings, whether the afferent input was increased by increasing the stimulus intensity to one nerve or by using combined stimulation of two nerves. 3. Both group I muscle and low-threshold cutaneous afferents were shown to be able to reduce the non-monosynaptic Ia excitation. 4. The onset of the depression of the excitation was always found within the same 1 ms bin as that of the excitation. 5. Whatever the amount of afferent input (stimulus intensity increased up to motor threshold, spatial and temporal summation, summation of inhibitory effects from different origins), the depression could at the very most suppress the non-monosynaptic Ia excitation: i.e. a trough in the PSTH, reflecting an inhibition at the motoneuronal level, never appeared. In those units in which there was not non-monosynaptic excitation, peripheral stimulation did not evoke any inhibition appearing as a trough in the PSTH either. Hence, inhibition only appeared when there was a non-monosynaptic excitation, and then as a depression of it. 6. On the basis of these findings it is argued that the inhibition is not exerted directly onto motoneurones but acts at a pre-motoneuronal level on the interneurones mediating the non-monosynaptic Ia excitation to motoneurones. 7. Similarly, the homonymous non-monosynaptic Ia facilitation of the flexor carpi radialis H reflex was shown to be reduced by a preceding stimulation applied to the ulnar nerve. It is argued that this result is also compatible with an inhibition of transmission in interneuronal excitatory pathways to motoneurones. 8. It is suggested that the non-monosynaptic excitation of wrist flexor motoneurones in man and the inhibition of this excitation, both evoked by stimulation of low-threshold afferents, could be mediated through a system of cervical propriospinal neurones. Some aspects of the possible role of this system during movement are discussed.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
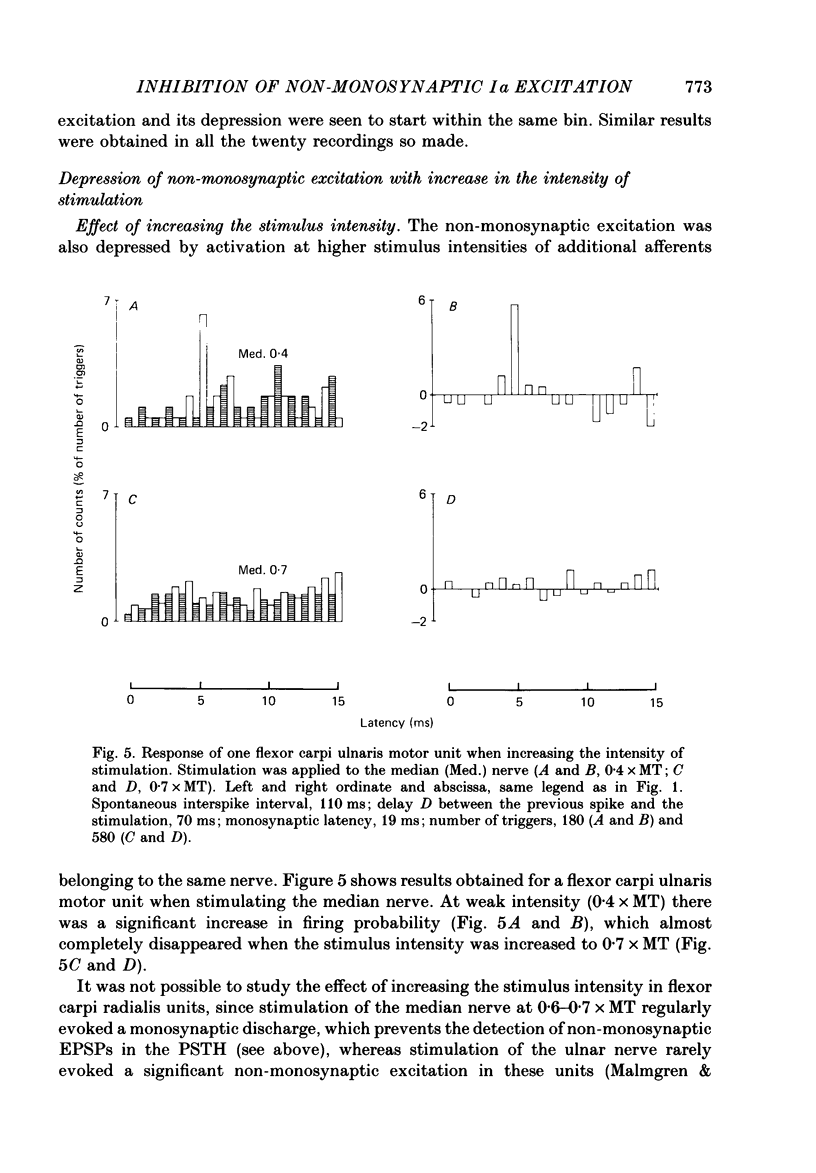
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
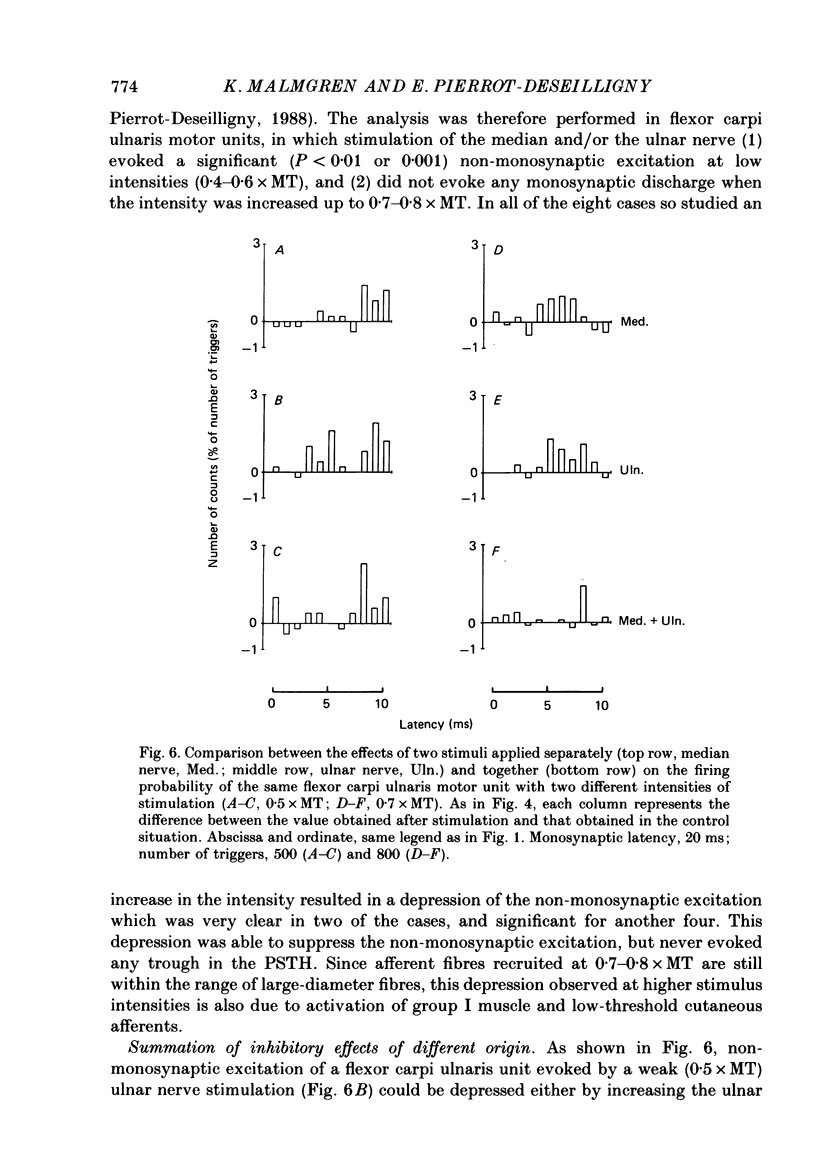
- Alstermark B., Górska T., Johannisson T., Lundberg A. Hypermetria in forelimb target-reaching after interruption of the inhibitory pathway from forelimb afferents to C3-C4 propriospinal neurones. Neurosci Res. 1986 Jul;3(5):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(86)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
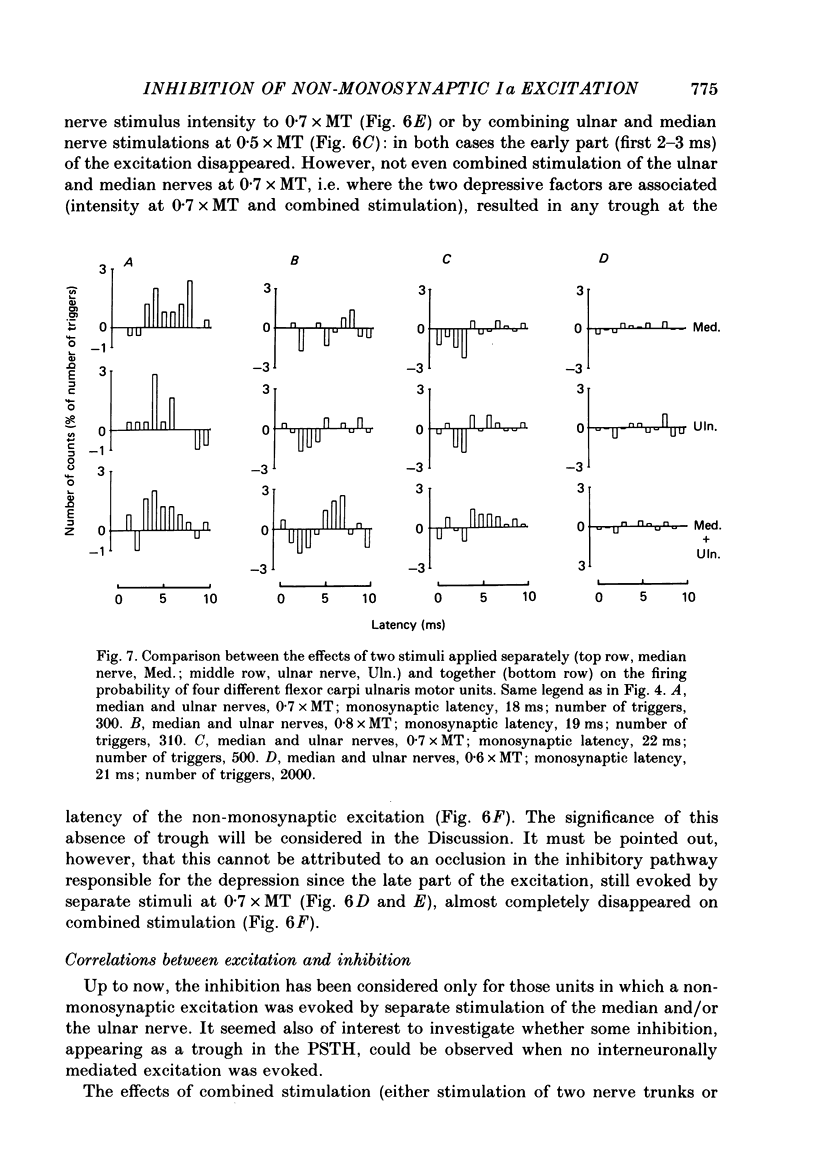
- Alstermark B., Lundberg A., Norrsell U., Sybirska E. Integration in descending motor pathways controlling the forelimb in the cat. 9. Differential behavioural defects after spinal cord lesions interrupting defined pathways from higher centres to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(3-4):299–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00237496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
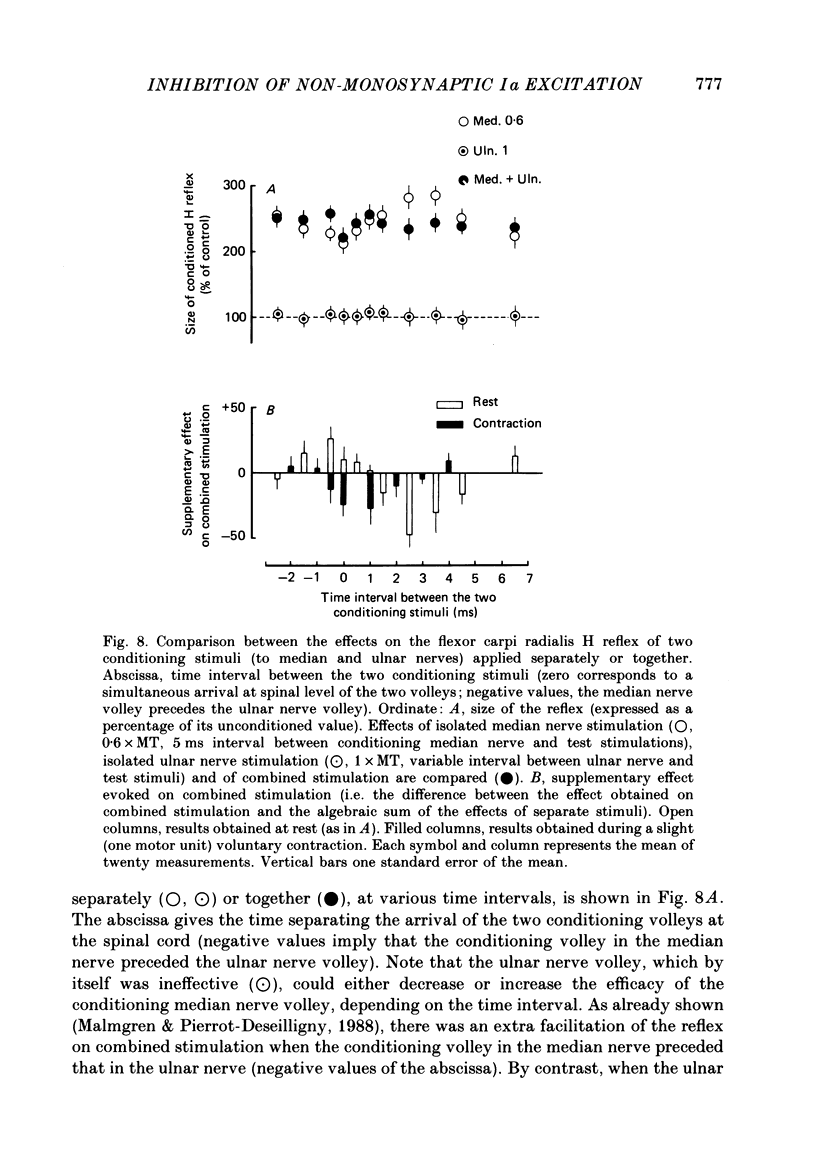
- Alstermark B., Lundberg A., Sasaki S. Integration in descending motor pathways controlling the forelimb in the cat. 11. Inhibitory pathways from higher motor centres and forelimb afferents to C3-C4 propriospinal neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1984;56(2):293–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00236285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alstermark B., Lundberg A., Sasaki S. Integration in descending motor pathways controlling the forelimb in the cat. 12. Interneurones which may mediate descending feed-forward inhibition and feed-back inhibition from the forelimb to C3-C4 propriospinal neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1984;56(2):308–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00236286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Mackenzie R. A., Skuse N. F., Lethlean A. K. Cutaneous afferent activity in median and radial nerve fascicles: a microelectrode study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Sep;38(9):855–864. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.9.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fetz E. E., Gustafsson B. Relation between shapes of post-synaptic potentials and changes in firing probability of cat motoneurones. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:387–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Evidence for interneuronally mediated Ia excitatory effects to human quadriceps motoneurones. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:143–169. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett R., Stephens J. A. The reflex responses of single motor units in human first dorsal interosseous muscle following cutaneous afferent stimulation. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:351–364. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illert M., Lundberg A., Padel Y., Tanaka R. Integration in descending motor pathways controlling the forelimb in the cat. 5. Properties of and monosynaptic excitatory convergence on C3--C4 propriospinal neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1978 Sep 15;33(1):101–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00238798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illert M., Lundberg A., Tanaka R. Integration in descending motor pathways controlling the forelimb in the cat. 3. Convergence on propriospinal neurones transmitting disynaptic excitation from the corticospinal tract and other descending tracts. Exp Brain Res. 1977 Sep 28;29(3-4):323–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00236174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenner J. R., Stephens J. A. Cutaneous reflex responses and their central nervous pathways studied in man. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:405–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren K., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Evidence for non-monosynaptic Ia excitation of human wrist flexor motoneurones, possibly via propriospinal neurones. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:747–764. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren K., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Evidence that low threshold afferents both evoke and depress polysynaptic excitation of wrist flexor motoneurones in man. Exp Brain Res. 1987;67(2):429–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00248563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


