Abstract
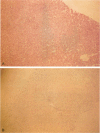
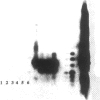
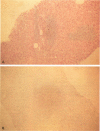
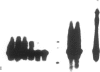
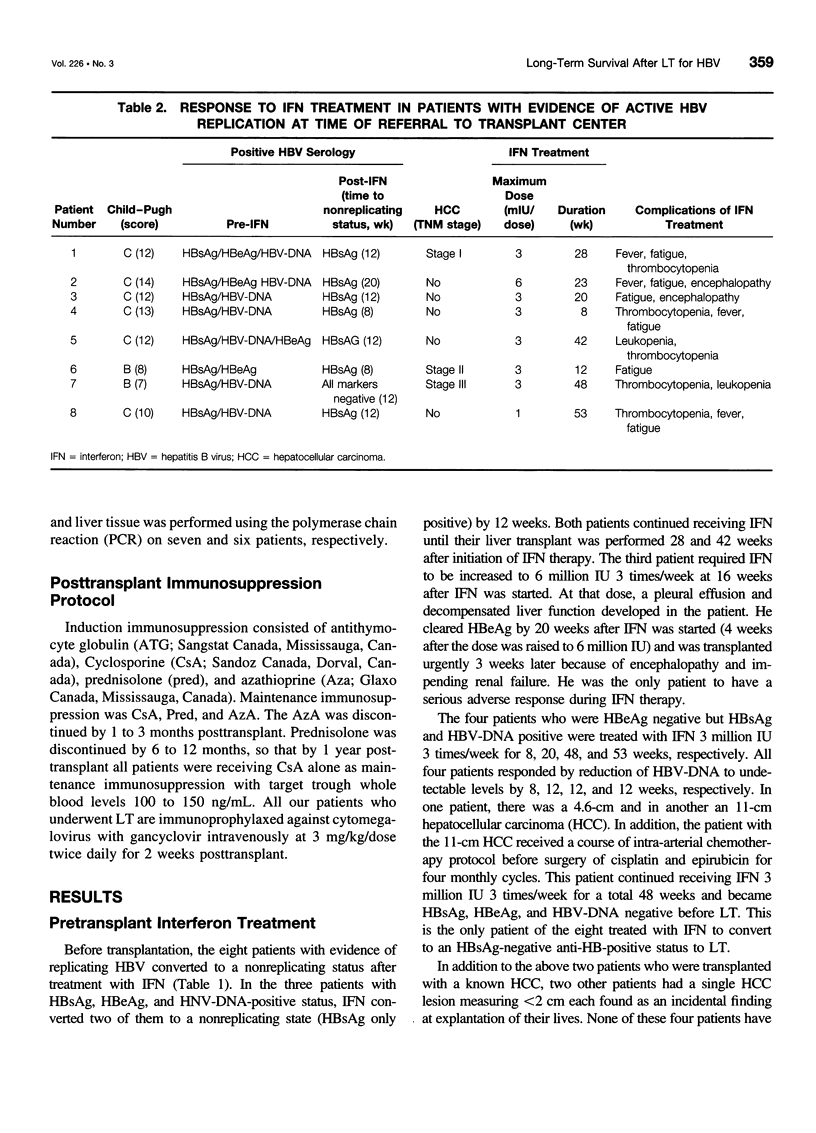
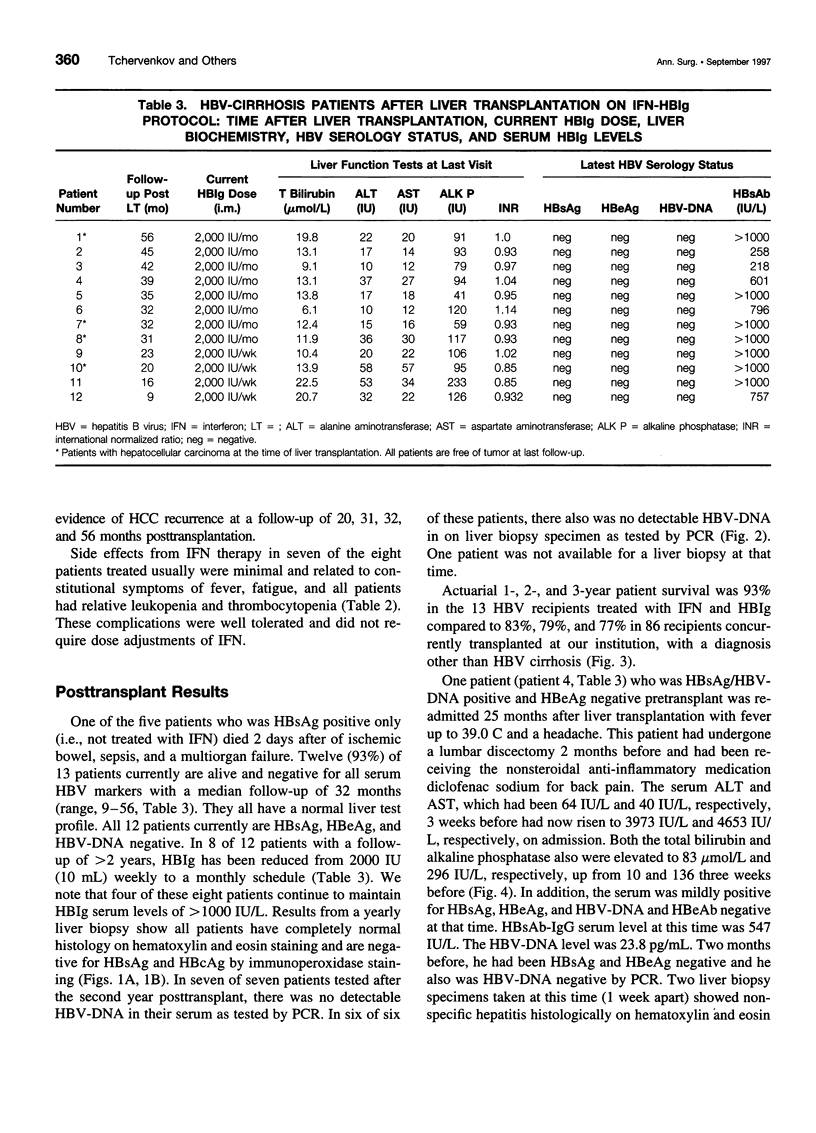
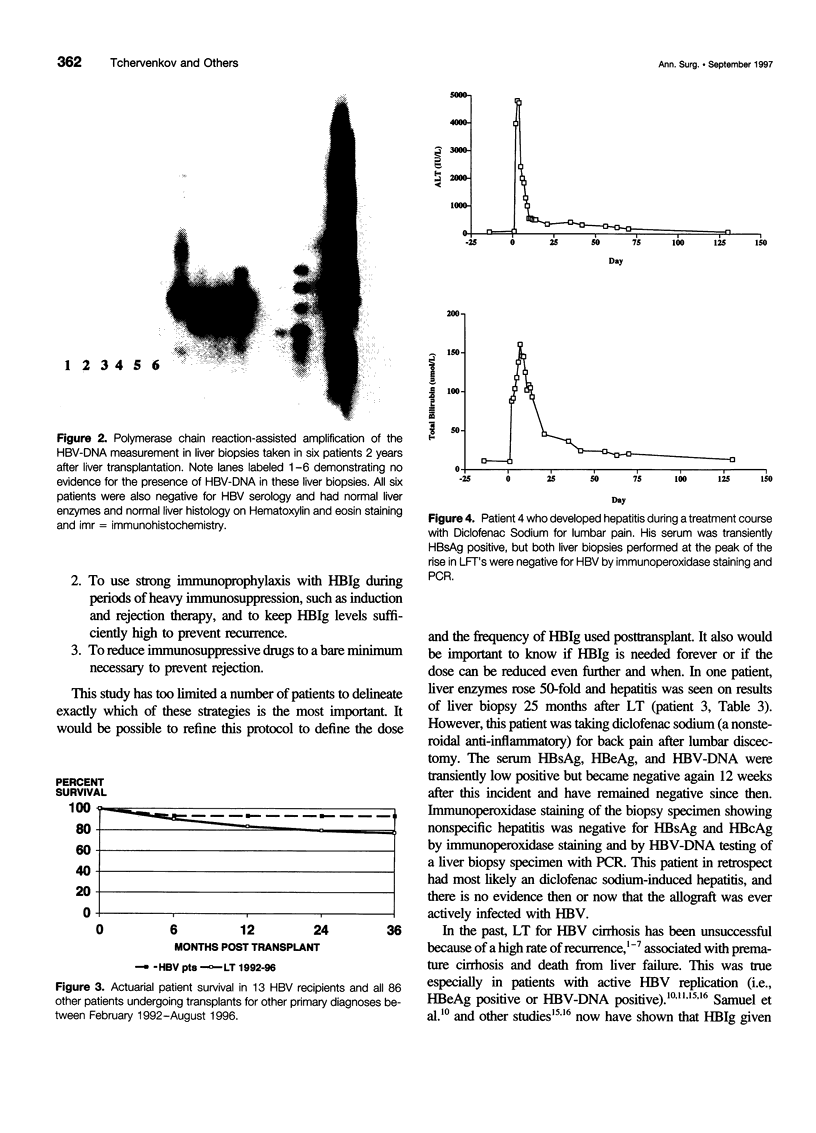
OBJECTIVE: The authors determined whether pretransplant reduction of hepatitis B virus (HBV) load using alpha-interferon-2b (IFN) and passive immunoprophylaxis using hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIg) posttransplantation can prevent HBV recurrence in patients undergoing liver transplantation (LT) for HBV cirrhosis. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Liver transplantation in patients with HBV cirrhosis is associated with a high rate of recurrence and reduced survival. In patients with evidence of replicating virus (HBV-DNA or hepatitis B e antigen [HBeAg]-positive serum or both), recurrence is nearly universal. Passive immunoprophylaxis with HBIg alone is not effective in preventing HBV recurrence posttransplant, especially in patients with evidence of active viral replication pretransplant. Higher doses of HBIg posttransplant has reduced recurrence rates to 30% to 50%. Lamivudine, a nucleoside analogue that has shown early promise, also is associated with significant HBV recurrence. The authors report a reliable method of preventing viral recurrence in patients even with evidence for active HBV replication pretransplant. METHODS: Pretransplant patients with evidence of replicating HBV were given IFN starting at 1 million IU 3 times per week subcutaneously. This dose was increased to 2 and then 3 million IU 3 times per week when patient's side effects permitted and was maintained until the patient underwent a LT. All patients were tested every 4 weeks for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), HBeAg, and HBV-DNA. When patients became negative for HBeAg and HBV-DNA, they were listed for LT. Patients that were only HBsAg positive were listed immediately and received a LT without prior IFN treatment. Post-LT, all patients began receiving HBIg 2000 IU (10 mL) daily from days 1 to 20 and then weekly for the first 2 years. After 2 years, all patients received 2000 IU (10 mL) monthly. Additional HBIg immunoprophylaxis was given during intense immunosuppression for rejection. Posttransplant serum was tested for HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV-DNA in all patients 1 week, 1 month, and every 3 months thereafter. Liver biopsies were done at least yearly and when liver enzymes were abnormal and were always tested for HBsAg and HBcAg by immunoperoxidase. RESULTS: Thirteen patients with decompensated HBV cirrhosis were transplanted. Pretransplant, eight patients had evidence of active viral replication at the initial assessment (HBeAg or HBV-DNA-positive serum or both). All eight were successfully treated with IFN (median duration, 24 weeks; range, 8-53) and converted to a negative status before transplantation. Side effects from IFN were minimal and well tolerated, except in one patient who required 6 million IU to convert to a nonreplicating status. The five patients that were only HBsAg positive were not treated with IFN pretransplant. After surgery, HBIg given as described achieved consistently serum levels greater than 1000 IU/L. Twelve of the 13 patients are alive with normal liver function and without serologic evidence of HBV recurrence at a median follow-up of 32 months (range, 9-56 months). None have evidence of HBV recurrence as measured by serum HBsAg/HBeAg/HBV-DNA at recent follow-up. The sera of the seven longest survivors has tested negative for HBV-DNA using the polymerase chain reaction method. In addition, a liver biopsy was obtained in six of these patients, the results of which also tested negative for HBV-DNA using polymerase chain reaction. Liver biopsy specimens have been negative for the presence of HBsAg and HBcAg by immunoperoxidase staining in all 12 patients. CONCLUSION: A reduction of viral load pretransplant with IFN and posttransplant HBIg prevents recurrence of hepatitis B and permits LT for HBV cirrhosis, even in patients with evidence of replicating virus. The IFN pretransplant was well tolerated, and the small frequent dosing of HBIg posttransplant did not cause side effects while achieving serum levels > 1000 IU/L.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bain V. G., Kneteman N. M., Ma M. M., Gutfreund K., Shapiro J. A., Fischer K., Tipples G., Lee H., Jewell L. D., Tyrrell D. L. Efficacy of lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B patients with active viral replication and decompensated cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1996 Nov 27;62(10):1456–1462. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199611270-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böker K. H., Dalley G., Bahr M. J., Maschek H., Tillmann H. L., Trautwein C., Oldhaver K., Bode U., Pichlmayr R., Manns M. P. Long-term outcome of hepatitis C virus infection after liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1997 Jan;25(1):203–210. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. E., Portmann B. C., O'Grady J. G., Aldis P. M., Chaggar K., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Hepatic histological findings after transplantation for chronic hepatitis B virus infection, including a unique pattern of fibrosing cholestatic hepatitis. Hepatology. 1991 Jan;13(1):150–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetris A. J., Jaffe R., Sheahan D. G., Burnham J., Spero J., Iwatsuki S., Van Theil D. H., Starzl T. E. Recurrent hepatitis B in liver allograft recipients. Differentiation between viral hepatitis B and rejection. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):161–172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin J., Smith H. M., O'Grady J. G., Portmann B., Tan K. C., Williams R. Impact of immunoprophylaxis and patient selection on outcome of transplantation for HBsAg-positive liver recipients. J Hepatol. 1994 Aug;21(2):204–210. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell L. D., Wright T. L., Roberts J., Ascher N., Lake J. Hepatitis C viral infection in liver transplant recipients. Hepatology. 1992 Oct;16(4):865–876. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grellier L., Mutimer D., Ahmed M., Brown D., Burroughs A. K., Rolles K., McMaster P., Beranek P., Kennedy F., Kibbler H. Lamivudine prophylaxis against reinfection in liver transplantation for hepatitis B cirrhosis. Lancet. 1996 Nov 2;348(9036):1212–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)04444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Peters M., Mullen K. D., Jones D. B., Rustgi V., Di Bisceglie A., Hallahan C., Park Y., Meschievitz C., Jones E. A. Randomized, controlled trial of recombinant human alpha-interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1318–1325. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90367-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König V., Hopf U., Neuhaus P., Bauditz J., Schmidt C. A., Blumhardt G., Bechstein W. O., Neuhaus R., Lobeck H. Long-term follow-up of hepatitis B virus-infected recipients after orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1994 Sep 15;58(5):553–559. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199409150-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauchart W., Müller R., Pichlmayr R. Immunoprophylaxis of hepatitis B virus reinfection in recipients of human liver allografts. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 3):2387–2389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauchart W., Müller R., Pichlmayr R. Long-term immunoprophylaxis of hepatitis B virus reinfection in recipients of human liver allografts. Transplant Proc. 1987 Oct;19(5):4051–4053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavine J. E., Lake J. R., Ascher N. L., Ferrell L. D., Ganem D., Wright T. L. Persistent hepatitis B virus following interferon alfa therapy and liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90611-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcellin P., Samuel D., Areias J., Loriot M. A., Arulnaden J. L., Gigou M., David M. F., Bismuth A., Reynes M., Bréchot C. Pretransplantation interferon treatment and recurrence of hepatitis B virus infection after liver transplantation for hepatitis B-related end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 1994 Jan;19(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGory R. W., Ishitani M. B., Oliveira W. M., Stevenson W. C., McCullough C. S., Dickson R. C., Caldwell S. H., Pruett T. L. Improved outcome of orthotopic liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B cirrhosis with aggressive passive immunization. Transplantation. 1996 May 15;61(9):1358–1364. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199605150-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Gubernatis G., Farle M., Niehoff G., Klein H., Wittekind C., Tusch G., Lautz H. U., Böker K., Stangel W. Liver transplantation in HBs antigen (HBsAg) carriers. Prevention of hepatitis B virus (HBV) recurrence by passive immunization. J Hepatol. 1991 Jul;13(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90869-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady J. G., Smith H. M., Davies S. E., Daniels H. M., Donaldson P. T., Tan K. C., Portmann B., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Hepatitis B virus reinfection after orthotopic liver transplantation. Serological and clinical implications. J Hepatol. 1992 Jan;14(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90138-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrillo R. P., Schiff E. R., Davis G. L., Bodenheimer H. C., Jr, Lindsay K., Payne J., Dienstag J. L., O'Brien C., Tamburro C., Jacobson I. M. A randomized, controlled trial of interferon alfa-2b alone and after prednisone withdrawal for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. The Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 2;323(5):295–301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008023230503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakela J., Wooten R. S., Batts K. P., Perkins J. D., Taswell H. F., Krom R. A. Failure of interferon to prevent recurrent hepatitis B infection in hepatic allograft. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989 Apr;64(4):429–432. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65733-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel D., Bismuth A., Mathieu D., Arulnaden J. L., Reynes M., Benhamou J. P., Brechot C., Bismuth H. Passive immunoprophylaxis after liver transplantation in HBsAg-positive patients. Lancet. 1991 Apr 6;337(8745):813–815. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel D., Muller R., Alexander G., Fassati L., Ducot B., Benhamou J. P., Bismuth H. Liver transplantation in European patients with the hepatitis B surface antigen. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 16;329(25):1842–1847. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312163292503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffman M. L., Contos M. J., Luketic V. A., Sanyal A. J., Purdum P. P., 3rd, Mills A. S., Fisher R. A., Posner M. P. Biochemical and histologic evaluation of recurrent hepatitis C following orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1994 Feb 27;57(4):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Van Thiel D. Liver transplantation (2). N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1092–1099. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todo S., Demetris A. J., Van Thiel D., Teperman L., Fung J. J., Starzl T. E. Orthotopic liver transplantation for patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver disease. Hepatology. 1991 Apr;13(4):619–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Thiel D. H., Wright H. I., Fagiuoli S. Liver transplantation for hepatitis B virus-associated cirrhosis: a progress report. Hepatology. 1994 Jul;20(1 Pt 2):20S–23S. doi: 10.1016/0270-9139(94)90268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright H. I., Gavaler J. S., Van Theil D. H. Preliminary experience with alpha-2b-interferon therapy of viral hepatitis in liver allograft recipients. Transplantation. 1992 Jan;53(1):121–124. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199201000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]