Abstract
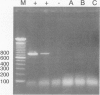
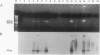
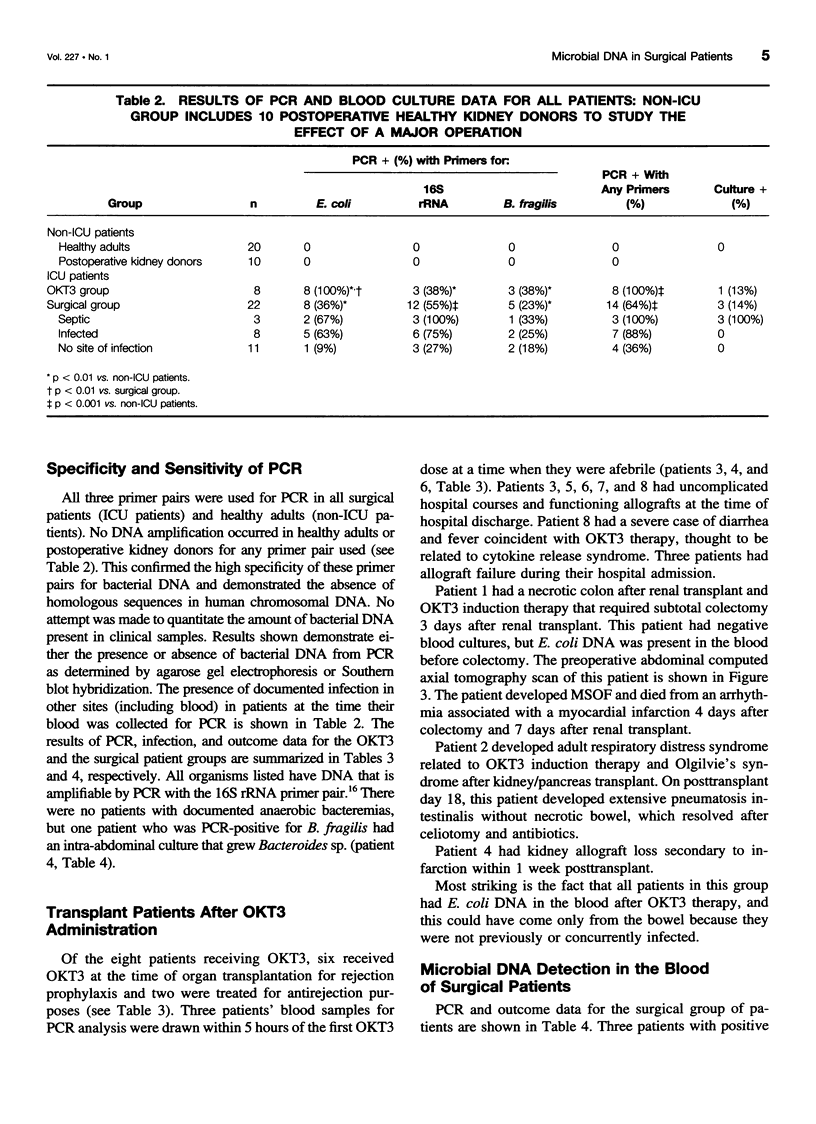
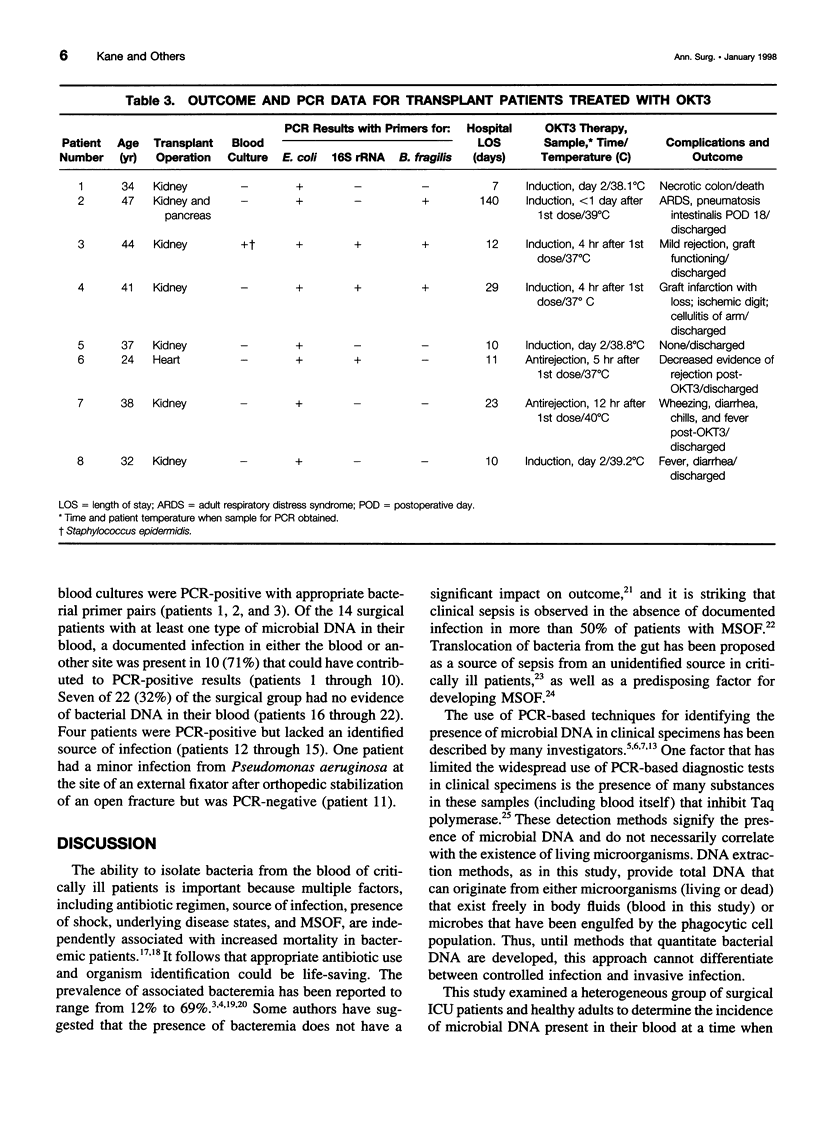
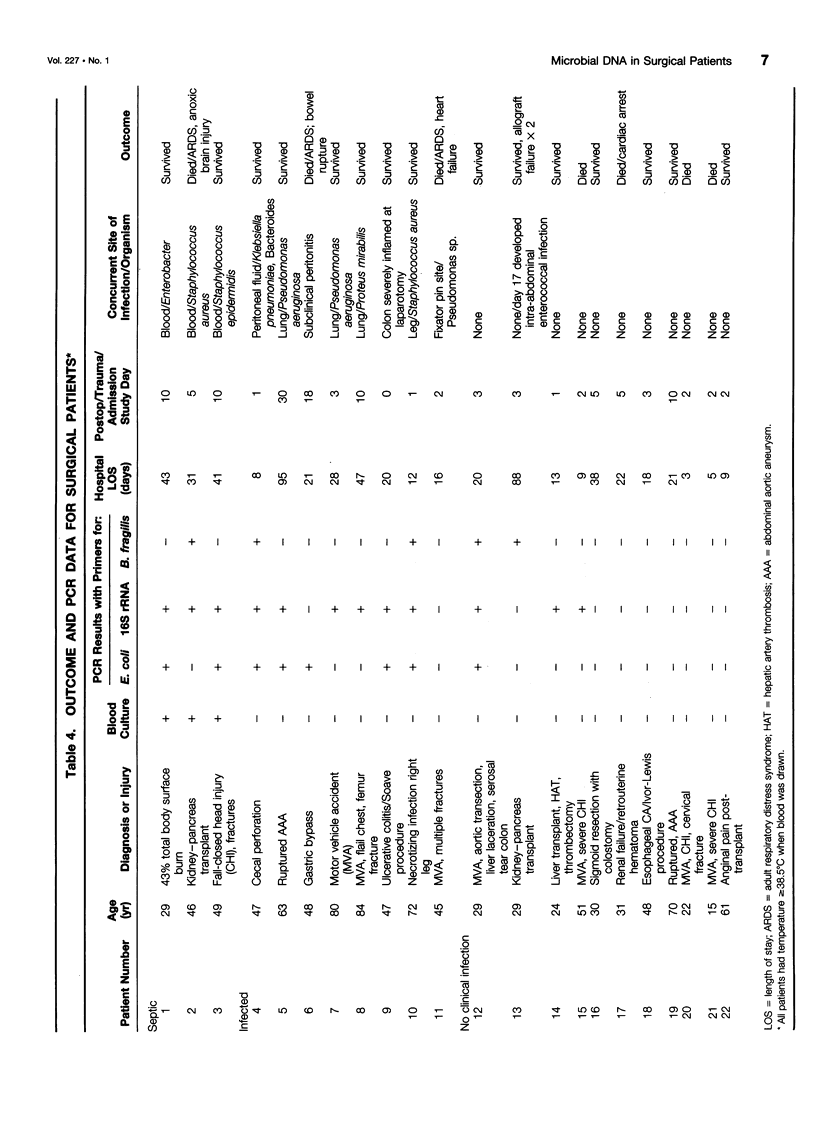
OBJECTIVE: The purpose was to determine the sensitivity of detecting microbial DNA in the blood of surgical patients as a measure for diagnosing systemic infection and/or translocation from the gut. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Microbial infections and translocation of intestinal bacteria are thought to contribute to multiple system organ failure, but bacterial cultures are often negative in patients with this complication. METHODS: DNA was extracted from the blood of 40 surgical patients and 20 healthy controls. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques were used to amplify genes from Escherichia coli, Bacteroides fragilis, and a region of 16S ribosomal RNA found in many gram-positive and -negative bacteria. RESULTS: Bacterial DNA genes were not detected in healthy volunteers but were found in all patients with positive blood cultures. All eight transplant patients receiving OKT3 therapy had microbial DNA in their blood, possibly indicating translocation from the gut. Sixty-four percent of critically ill patients had microbial DNA detected in their blood, but only 3 (14%) had positive blood cultures. CONCLUSIONS: The PCR method is more sensitive than blood cultures for detecting bacterial components in the blood of critically ill surgical patients and may detect microbial translocation from the intestine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barriere S. L., Lowry S. F. An overview of mortality risk prediction in sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1995 Feb;23(2):376–393. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199502000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernet C., Garret M., de Barbeyrac B., Bebear C., Bonnet J. Detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by using the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Nov;27(11):2492–2496. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.11.2492-2496.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border J. R., Hassett J., LaDuca J., Seibel R., Steinberg S., Mills B., Losi P., Border D. The gut origin septic states in blunt multiple trauma (ISS = 40) in the ICU. Ann Surg. 1987 Oct;206(4):427–448. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198710000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breese E. J., Michie C. A., Nicholls S. W., Murch S. H., Williams C. B., Domizio P., Walker-Smith J. A., MacDonald T. T. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-producing cells in the intestinal mucosa of children with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jun;106(6):1455–1466. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson-Noël A., Gicquel B., Lecossier D., Lévy-Frébault V., Nassif X., Hance A. J. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis by amplification of mycobacterial DNA in clinical samples. Lancet. 1989 Nov 4;2(8671):1069–1071. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerra F. B. Hypermetabolism, organ failure, and metabolic support. Surgery. 1987 Jan;101(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner R. L., Elin R. J., Hosseini J. M., Wesley R. A., Reilly J. M., Parillo J. E. Endotoxemia in human septic shock. Chest. 1991 Jan;99(1):169–175. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredricks D. N., Relman D. A. Sequence-based identification of microbial pathogens: a reconsideration of Koch's postulates. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996 Jan;9(1):18–33. doi: 10.1128/cmr.9.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. E., Pearlstein L., Fulton R. L., Polk H. C., Jr Multiple system organ failure. The role of uncontrolled infection. Arch Surg. 1980 Feb;115(2):136–140. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380020006003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennari R., Alexander J. W., Pyles T., Hartmann S., Ogle C. K. Effects of antimurine interleukin-6 on bacterial translocation during gut-derived sepsis. Arch Surg. 1994 Nov;129(11):1191–1197. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420350089012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilf M., Yu V. L., Sharp J., Zuravleff J. J., Korvick J. A., Muder R. R. Antibiotic therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia: outcome correlations in a prospective study of 200 patients. Am J Med. 1989 Nov;87(5):540–546. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(89)80611-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeyarajah D. R., Thistlethwaite J. R., Jr General aspects of cytokine-release syndrome: timing and incidence of symptoms. Transplant Proc. 1993 Apr;25(2 Suppl 1):16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane T. D., Johnson S. R., Alexander J. W., Babcock G. F., Ogle C. K. Detection of intestinal bacterial translocation using PCR. J Surg Res. 1996 Jun;63(1):59–63. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1996.0223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbreras C., Fernandez I., Velosa J., Munn S., Sterioff S., Paya C. V. Infectious complications following pancreatic transplantation: incidence, microbiological and clinical characteristics, and outcome. Clin Infect Dis. 1995 Mar;20(3):514–520. doi: 10.1093/clinids/20.3.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe K. M., Khan G., Zhang Y. H., Mason E. O., McCabe E. R. Amplification of bacterial DNA using highly conserved sequences: automated analysis and potential for molecular triage of sepsis. Pediatrics. 1995 Feb;95(2):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle C. K., Mao J. X., Wu J. Z., Ogle J. D., Alexander J. W. The 1994 Lindberg Award. The production of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and prostaglandin E2 by isolated enterocytes and gut macrophages: effect of lipopolysaccharide and thermal injury. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1994 Nov-Dec;15(6):470–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panaccio M., Lew A. PCR based diagnosis in the presence of 8% (v/v) blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1151–1151. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Myers B. Fluorometric determination of DNA in aquatic microorganisms by use of hoechst 33258. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1393–1399. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1393-1399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relman D. A., Schmidt T. M., MacDermott R. P., Falkow S. Identification of the uncultured bacillus of Whipple's disease. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 30;327(5):293–301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207303270501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush B. F., Jr, Sori A. J., Murphy T. F., Smith S., Flanagan J. J., Jr, Machiedo G. W. Endotoxemia and bacteremia during hemorrhagic shock. The link between trauma and sepsis? Ann Surg. 1988 May;207(5):549–554. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198805000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbald W. J., Vincent J. L. Round table conference on clinical trials for the treatment of sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1995 Feb;23(2):394–399. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199502000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprung C. L. Definitions of sepsis--have we reached a consensus? Crit Care Med. 1991 Jul;19(7):849–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran D. D., Cuesta M. A., van Leeuwen P. A., Nauta J. J., Wesdorp R. I. Risk factors for multiple organ system failure and death in critically injured patients. Surgery. 1993 Jul;114(1):21–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran D. D., Groeneveld A. B., van der Meulen J., Nauta J. J., Strack van Schijndel R. J., Thijs L. G. Age, chronic disease, sepsis, organ system failure, and mortality in a medical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 1990 May;18(5):474–479. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199005000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzun O., Akalin H. E., Hayran M., Unal S. Factors influencing prognosis in bacteremia due to gram-negative organisms: evaluation of 448 episodes in a Turkish university hospital. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Nov;15(5):866–873. doi: 10.1093/clind/15.5.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waymack J. P., Penn I., First M. R., Alexander J. W. Portal vein gas and sepsis after administration of OKT3. Lancet. 1987 Apr 25;1(8539):984–984. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita Y., Kohno S., Koga H., Tomono K., Kaku M. Detection of Bacteroides fragilis in clinical specimens by PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Mar;32(3):679–683. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.3.679-683.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]