Abstract
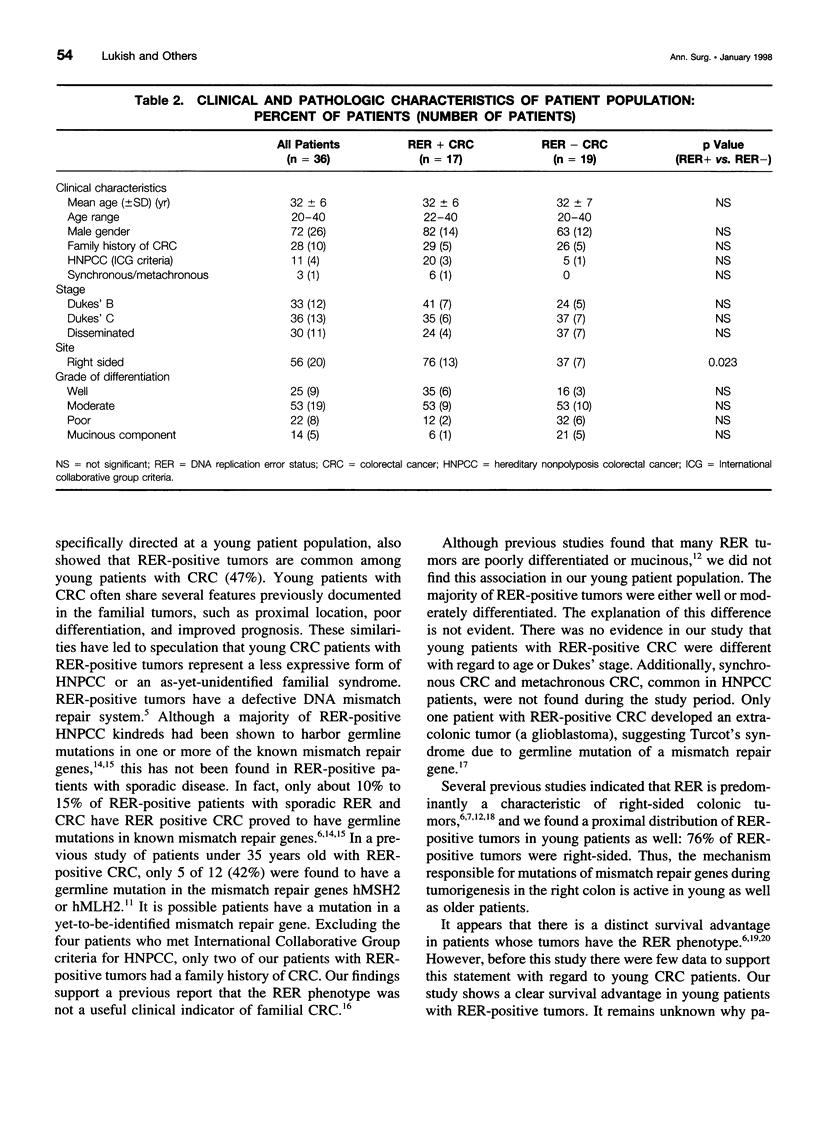
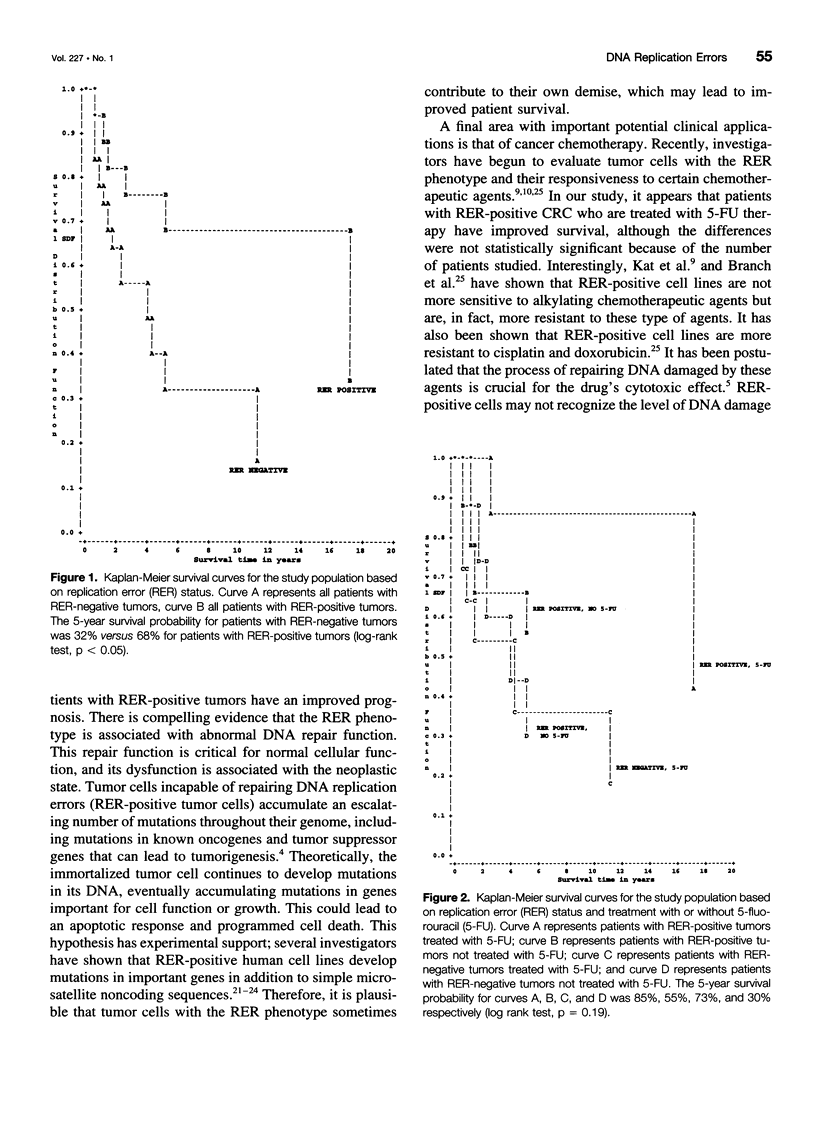
OBJECTIVE: To determine the DNA replication error (RER) status in young patients with colorectal cancer (CRC), and to compare the clinical and pathologic characteristics of RER-positive and RER-negative cases. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Recent studies suggest that patients with RER-positive CRC have an improved prognosis. Further data are required to confirm this observation in young CRC patients. METHODS: All patients 40 years of age and younger with CRC admitted to the National Naval Medical Center between 1970 and 1992 were considered for inclusion in the study. After review, 36 patients for whom the original archived pathology specimen could be retrieved served as the study population. The RER status was determined using a previously described polymerase chain reaction-based assay. The clinical and pathologic features and survival data were compared to RER status. RESULTS: RER-positive tumors were found in 17 cases (47%). There was no significant difference in Dukes' stage or histologic grade at the time of diagnosis between patients with RER-positive tumors compared to RER-negative tumors. Patients with RER-positive tumors were found to have an improved prognosis: the 5-year survival probability for patients with RER-positive tumors was 68%, as compared to 32% for patients with RER-negative tumors (p < 0.05). CONCLUSIONS: RER-positive tumors are common in young patients with CRC, and patients with RER-positive tumors have a significantly improved prognosis. Because of their young age, survival data and prognosis play an important role in the overall treatment plan of young patients with CRC. Therefore, knowledge of RER status could affect initial therapy, postoperative chemotherapy, and follow-up.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltonen L. A., Peltomäki P., Leach F. S., Sistonen P., Pylkkänen L., Mecklin J. P., Järvinen H., Powell S. M., Jen J., Hamilton S. R. Clues to the pathogenesis of familial colorectal cancer. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):812–816. doi: 10.1126/science.8484121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aaltonen L. A., Peltomäki P., Mecklin J. P., Järvinen H., Jass J. R., Green J. S., Lynch H. T., Watson P., Tallqvist G., Juhola M. Replication errors in benign and malignant tumors from hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1645–1648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthoney D. A., McIlwrath A. J., Gallagher W. M., Edlin A. R., Brown R. Microsatellite instability, apoptosis, and loss of p53 function in drug-resistant tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1996 Mar 15;56(6):1374–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aquilina G., Hess P., Branch P., MacGeoch C., Casciano I., Karran P., Bignami M. A mismatch recognition defect in colon carcinoma confers DNA microsatellite instability and a mutator phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):8905–8909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.8905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya N. P., Skandalis A., Ganesh A., Groden J., Meuth M. Mutator phenotypes in human colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6319–6323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch P., Aquilina G., Bignami M., Karran P. Defective mismatch binding and a mutator phenotype in cells tolerant to DNA damage. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):652–654. doi: 10.1038/362652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. C., Rustgi A. K. DNA mismatch repair and cancer. Gastroenterology. 1995 Nov;109(5):1685–1699. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90660-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshleman J. R., Lang E. Z., Bowerfind G. K., Parsons R., Vogelstein B., Willson J. K., Veigl M. L., Sedwick W. D., Markowitz S. D. Increased mutation rate at the hprt locus accompanies microsatellite instability in colon cancer. Oncogene. 1995 Jan 5;10(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. R., Liu B., Parsons R. E., Papadopoulos N., Jen J., Powell S. M., Krush A. J., Berk T., Cohen Z., Tetu B. The molecular basis of Turcot's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 30;332(13):839–847. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503303321302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionov Y., Peinado M. A., Malkhosyan S., Shibata D., Perucho M. Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):558–561. doi: 10.1038/363558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen J., Kim H., Piantadosi S., Liu Z. F., Levitt R. C., Sistonen P., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Hamilton S. R. Allelic loss of chromosome 18q and prognosis in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jul 28;331(4):213–221. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199407283310401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kat A., Thilly W. G., Fang W. H., Longley M. J., Li G. M., Modrich P. An alkylation-tolerant, mutator human cell line is deficient in strand-specific mismatch repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6424–6428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Jen J., Vogelstein B., Hamilton S. R. Clinical and pathological characteristics of sporadic colorectal carcinomas with DNA replication errors in microsatellite sequences. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jul;145(1):148–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. Y., Fletcher W. S., Sullivan E. S., Vetto J. T. Colorectal cancer in young patients: characteristics and outcome. Am Surg. 1994 Aug;60(8):607–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Farrington S. M., Petersen G. M., Hamilton S. R., Parsons R., Papadopoulos N., Fujiwara T., Jen J., Kinzler K. W., Wyllie A. H. Genetic instability occurs in the majority of young patients with colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 1995 Apr;1(4):348–352. doi: 10.1038/nm0495-348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Nicolaides N. C., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Parsons R. E., Jen J., Papadopolous N., Peltomäki P., de la Chapelle A., Hamilton S. R. Mismatch repair gene defects in sporadic colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability. Nat Genet. 1995 Jan;9(1):48–55. doi: 10.1038/ng0195-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lothe R. A., Peltomäki P., Meling G. I., Aaltonen L. A., Nyström-Lahti M., Pylkkänen L., Heimdal K., Andersen T. I., Møller P., Rognum T. O. Genomic instability in colorectal cancer: relationship to clinicopathological variables and family history. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 15;53(24):5849–5852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch H. T., Smyrk T. C., Watson P., Lanspa S. J., Lynch J. F., Lynch P. M., Cavalieri R. J., Boland C. R. Genetics, natural history, tumor spectrum, and pathology of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer: an updated review. Gastroenterology. 1993 May;104(5):1535–1549. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90368-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Wang J., Myeroff L., Parsons R., Sun L., Lutterbaugh J., Fan R. S., Zborowska E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Inactivation of the type II TGF-beta receptor in colon cancer cells with microsatellite instability. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1336–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.7761852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhyu M. S. Molecular mechanisms underlying hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Mar 6;88(5):240–251. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.5.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samowitz W. S., Slattery M. L., Kerber R. A. Microsatellite instability in human colonic cancer is not a useful clinical indicator of familial colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 1995 Dec;109(6):1765–1771. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90742-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibodeau S. N., Bren G., Schaid D. Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):816–819. doi: 10.1126/science.8484122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


