Abstract
OBJECTIVE: There were two aims of this study. The first was to evaluate the application of helical computed tomography of the thorax (HCTT) for the diagnosis of blunt aortic injury (BAI). The second was to evaluate the efficacy of beta-blockers with or without nitroprusside in preventing aortic rupture. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Aortography has been the standard for diagnosing BAI for the past 4 decades. Conventional chest CT has not proven to be of significant value. Helical CT scanning is faster and has higher resolution than conventional CT. Retrospective studies have suggested the efficacy of antihypertensives in preventing aortic rupture. METHODS: A prospective study comparing HCTT to aortography in the diagnosis of BAI was performed. A protocol of beta-blockers with or without nitroprusside was also examined for efficacy in preventing rupture before aortic repair and in allowing delayed repair in patients with significant associated injuries. RESULTS: Over a period of 4 years, 494 patients were studied. BAI was diagnosed in 71 patients. Sensitivity was 100% for HCTT versus 92% for aortography. Specificity was 83% for HCTT versus 99% for aortography. Accuracy was 86% for HCTT versus 97% for aortography. Positive predictive value was 50% for HCTT versus 97% for aortography. Negative predictive value was 100% for HCTT versus 97% for aortography. No patient had spontaneous rupture in this study. CONCLUSIONS: HCTT is sensitive for diagnosing intimal injuries and pseudoaneurysms. Patients without direct HCTT evidence of BAI require no further evaluation. Aortography can be reserved for indeterminate HCTT scans. Early diagnosis with HCTT and presumptive treatment with the antihypertensive regimen eliminated in-hospital aortic rupture.
Full text
PDF

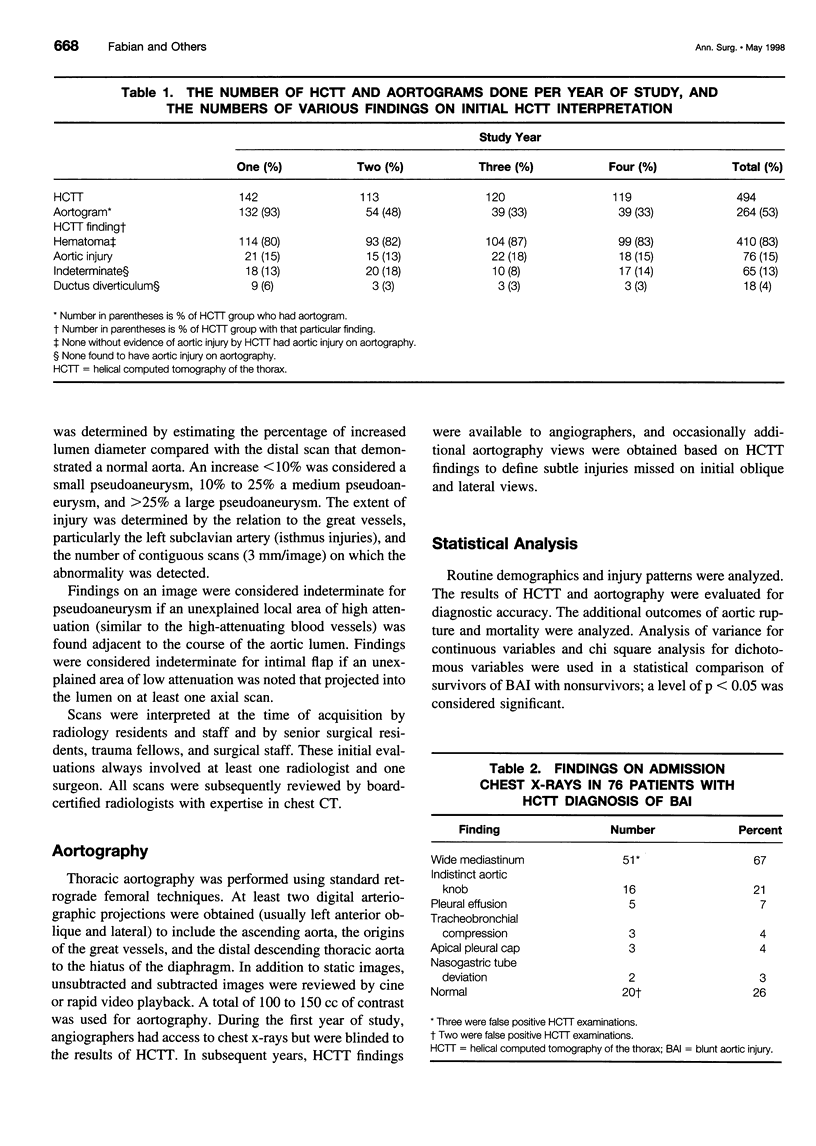
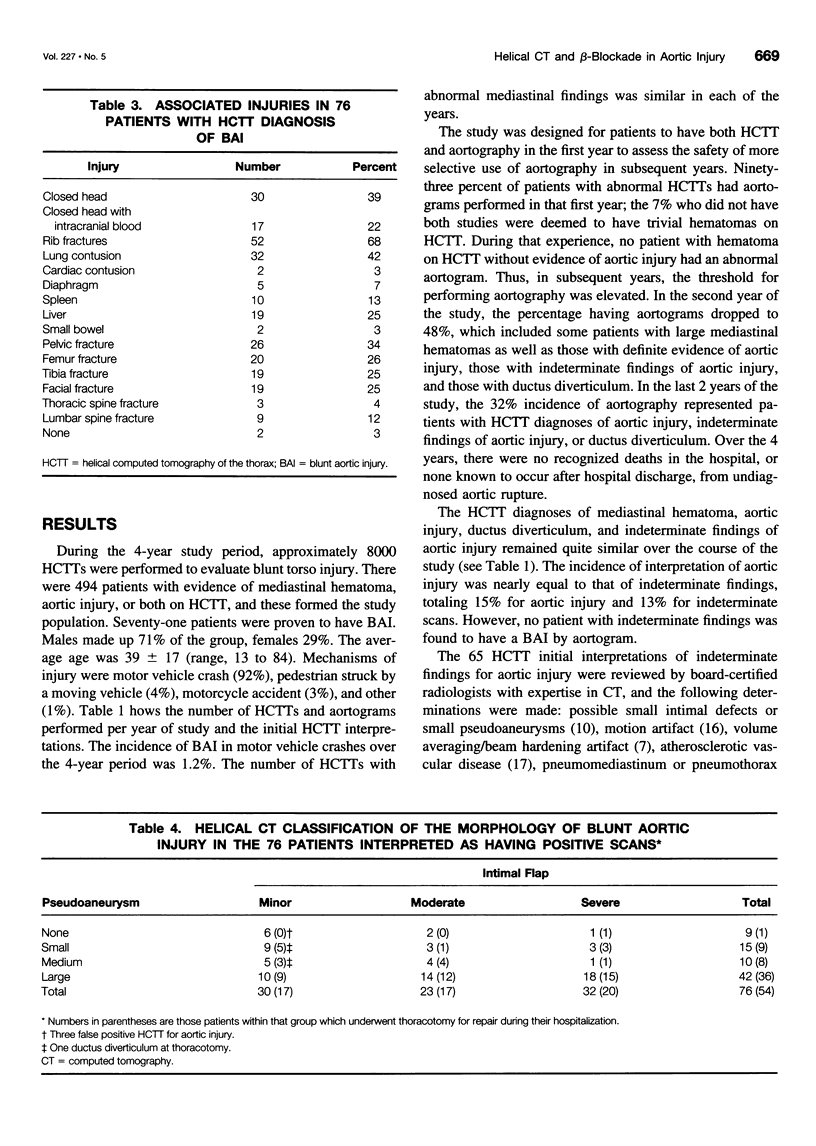
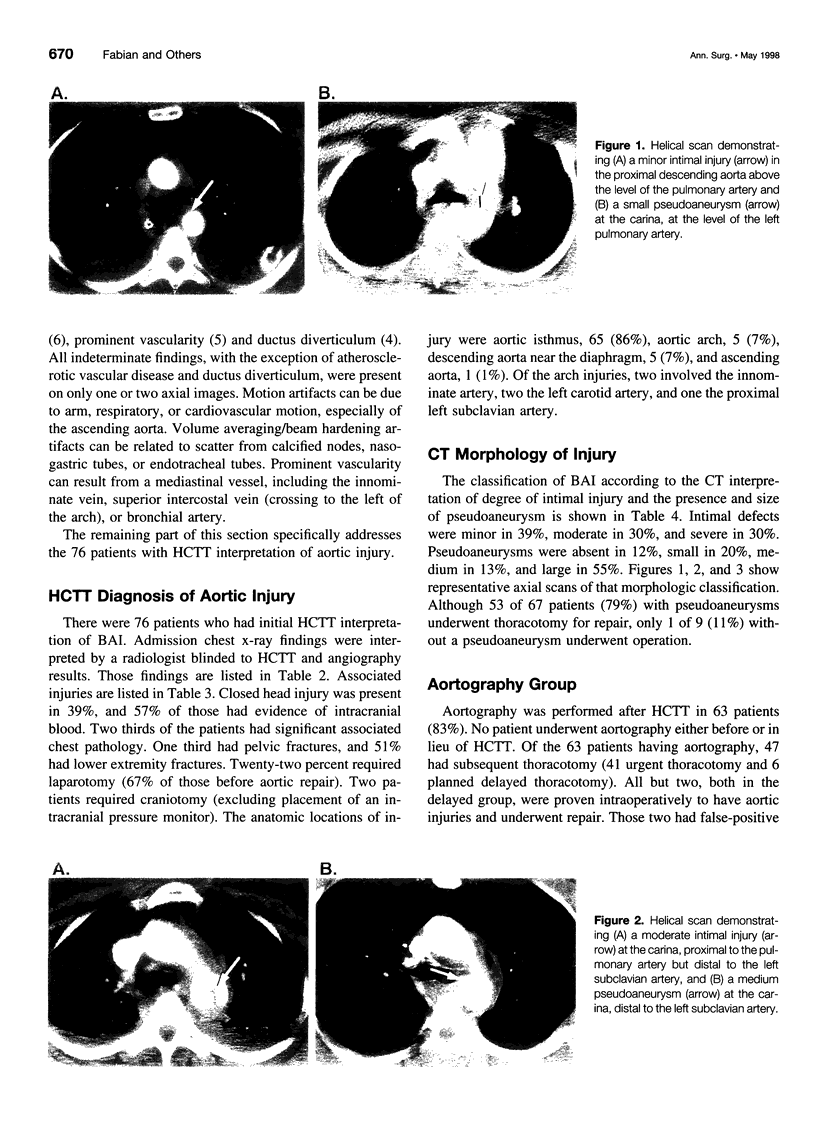



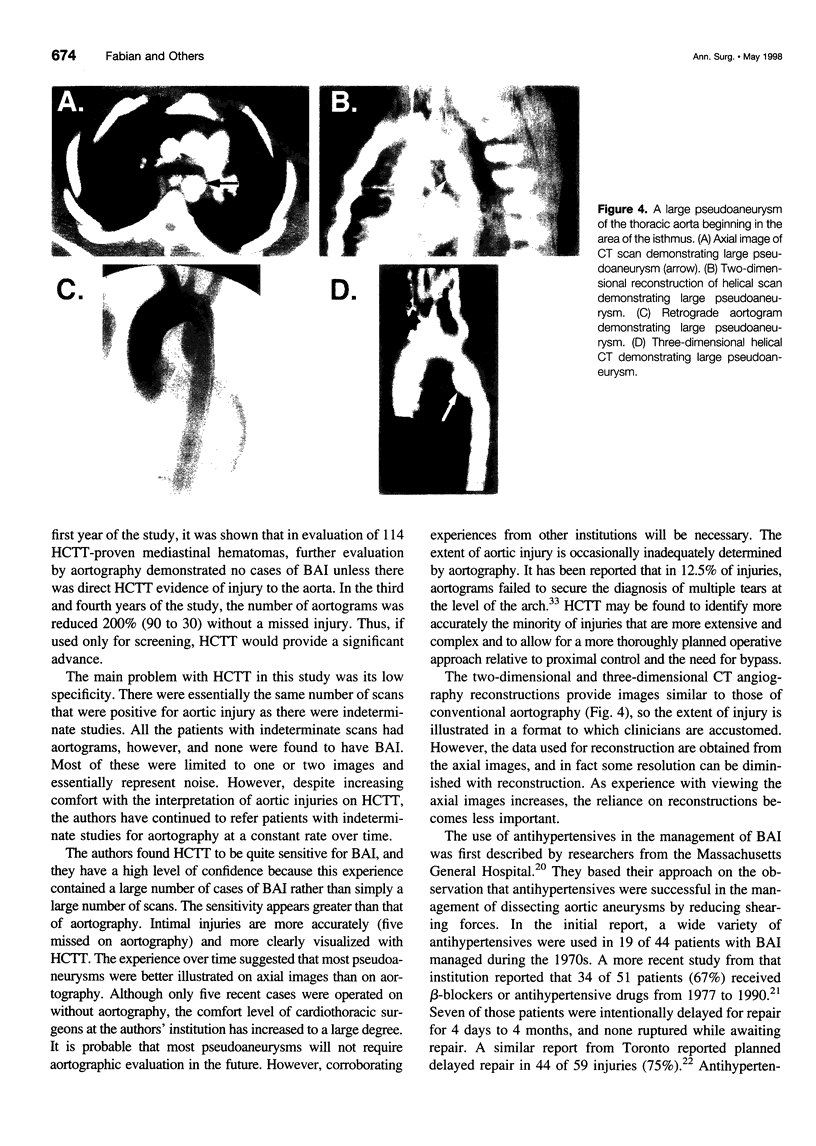


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agee C. K., Metzler M. H., Churchill R. J., Mitchell F. L. Computed tomographic evaluation to exclude traumatic aortic disruption. J Trauma. 1992 Dec;33(6):876–881. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199212000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akins C. W., Buckley M. J., Daggett W., McIlduff J. B., Austen W. G. Acute traumatic disruption of the thoracic aorta: a ten-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1981 Apr;31(4):305–309. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)60955-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A. P., Olson L. K., Shackford S. R. Computed tomography in the diagnosis of traumatic rupture of the thoracic aorta. Clin Radiol. 1989 Mar;40(2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(89)80071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DelRossi A. J., Cernaianu A. C., Madden L. D., Cilley J. H., Jr, Spence R. K., Alexander J. B., Ross S. E., Camishion R. C. Traumatic disruptions of the thoracic aorta: treatment and outcome. Surgery. 1990 Nov;108(5):864–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durham R. M., Zuckerman D., Wolverson M., Heiberg E., Luchtefeld W. B., Herr D. J., Shapiro M. J., Mazuski J. E., Salimi Z., Sundaram M. Computed tomography as a screening exam in patients with suspected blunt aortic injury. Ann Surg. 1994 Nov;220(5):699–704. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199411000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian T. C., Richardson J. D., Croce M. A., Smith J. S., Jr, Rodman G., Jr, Kearney P. A., Flynn W., Ney A. L., Cone J. B., Luchette F. A. Prospective study of blunt aortic injury: Multicenter Trial of the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma. J Trauma. 1997 Mar;42(3):374–383. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199703000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenner M. N., Fisher K. S., Sergel N. L., Porter D. B., Metzmaker C. O. Evaluation of possible traumatic thoracic aortic injury using aortography and CT. Am Surg. 1990 Aug;56(8):497–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. G., Chasen M. H., Lamki N. Diagnosis of injuries of the aorta and brachiocephalic arteries caused by blunt chest trauma: CT vs aortography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994 May;162(5):1047–1052. doi: 10.2214/ajr.162.5.8165979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. G., Oria R. A., Mattox K. L., Whigham C. J., Pickard L. R. Conservative management of aortic lacerations due to blunt trauma. J Trauma. 1990 Dec;30(12):1562–1566. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199012000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. G., Sanchez-Torres M., Whigham C. J., Thomas J. W. "Lumps" and "bumps" that mimic acute aortic and brachiocephalic vessel injury. Radiographics. 1997 Jul-Aug;17(4):825–834. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.17.4.9225385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavant M. L., Flick P., Menke P., Gold R. E. CT aortography of thoracic aortic rupture. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996 Apr;166(4):955–961. doi: 10.2214/ajr.166.4.8610581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavant M. L., Menke P. G., Fabian T., Flick P. A., Graney M. J., Gold R. E. Blunt traumatic aortic rupture: detection with helical CT of the chest. Radiology. 1995 Oct;197(1):125–133. doi: 10.1148/radiology.197.1.7568809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgenberg A. D., Logan D. L., Akins C. W., Buckley M. J., Daggett W. M., Vlahakes G. J., Torchiana D. F. Blunt injuries of the thoracic aorta. Ann Thorac Surg. 1992 Feb;53(2):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(92)91324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Nakajima Y., Kaji T. The role of CT in traumatic rupture of the thoracic aorta and its proximal branches. Semin Roentgenol. 1989 Jan;24(1):38–46. doi: 10.1016/0037-198x(89)90052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madayag M. A., Kirshenbaum K. J., Nadimpalli S. R., Fantus R. J., Cavallino R. P., Crystal G. J. Thoracic aortic trauma: role of dynamic CT. Radiology. 1991 Jun;179(3):853–855. doi: 10.1148/radiology.179.3.2028005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggisano R., Nathens A., Alexandrova N. A., Cina C., Boulanger B., McKenzie R., Harrison A. W. Traumatic rupture of the thoracic aorta: should one always operate immediately? Ann Vasc Surg. 1995 Jan;9(1):44–52. doi: 10.1007/BF02015316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean T. R., Olinger G. N., Thorsen M. K. Computed tomography in the evaluation of the aorta in patients sustaining blunt chest trauma. J Trauma. 1991 Feb;31(2):254–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. B., Richardson J. D., Thomas H. A., Cryer H. M., Willing S. J. Role of CT in diagnosis of major arterial injury after blunt thoracic trauma. Surgery. 1989 Oct;106(4):596–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirvis S. E., Kostrubiak I., Whitley N. O., Goldstein L. D., Rodriguez A. Role of CT in excluding major arterial injury after blunt thoracic trauma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987 Sep;149(3):601–605. doi: 10.2214/ajr.149.3.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirvis S. E., Shanmuganathan K., Miller B. H., White C. S., Turney S. Z. Traumatic aortic injury: diagnosis with contrast-enhanced thoracic CT--five-year experience at a major trauma center. Radiology. 1996 Aug;200(2):413–422. doi: 10.1148/radiology.200.2.8685335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan P. W., Goodman L. R., Aprahamian C., Foley W. D., Lipchik E. O. Evaluation of traumatic aortic injury: does dynamic contrast-enhanced CT play a role? Radiology. 1992 Mar;182(3):661–666. doi: 10.1148/radiology.182.3.1535878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. S., Glickman M. G., Greenwood L. H., Denny D. F., Jr, Strauss E. B., Stavens B. R., Yoselevitz M. Traumatic aortic rupture: false-positive aortographic diagnosis due to atypical ductus diverticulum. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988 Apr;150(4):793–796. doi: 10.2214/ajr.150.4.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARMLEY L. F., MATTINGLY T. W., MANION W. C., JAHNKE E. J., Jr Nonpenetrating traumatic injury of the aorta. Circulation. 1958 Jun;17(6):1086–1101. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.17.6.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. W., Fabian T. C., Walker W. Traumatic rupture of the aortic isthmus: an emergency? World J Surg. 1995 Jan-Feb;19(1):119–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00316994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raptopoulos V., Sheiman R. G., Phillips D. A., Davidoff A., Silva W. E. Traumatic aortic tear: screening with chest CT. Radiology. 1992 Mar;182(3):667–673. doi: 10.1148/radiology.182.3.1535879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P., Mirvis S. E., Scorpio R., Dunham C. M. Value of CT in determining the need for angiography when findings of mediastinal hemorrhage on chest radiographs are equivocal. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991 Feb;156(2):273–279. doi: 10.2214/ajr.156.2.1898798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Cassidy J. M., Souther S., Morris E. J., Sapin P. M., Johnson S. B., Kearney P. A. Transesophageal echocardiography in the diagnosis of traumatic rupture of the aorta. N Engl J Med. 1995 Feb 9;332(6):356–362. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199502093320603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm J. T., Hankins D. G., Young G. Thoracic aortography following blunt chest trauma. Am J Emerg Med. 1990 Mar;8(2):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0735-6757(90)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomiak M. M., Rosenblum J. D., Messersmith R. N., Zarins C. K. Use of CT for diagnosis of traumatic rupture of the thoracic aorta. Ann Vasc Surg. 1993 Mar;7(2):130–139. doi: 10.1007/BF02001006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. L., Akins C. W., Conn A. K., Hilgenberg A. D., McCabe C. J. Acute traumatic disruption of the thoracic aorta: emergency department management. Ann Emerg Med. 1992 Apr;21(4):391–396. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(05)82657-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D., Voystock J. F., Sariego J., Kerstein M. D. Role of computed tomography scan in evaluating the widened mediastinum. Am Surg. 1994 Jun;60(6):421–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]