Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To study the safety and efficacy of laparoscopic splenectomy (LS) in patients with predominantly benign hematologic disorders. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: The technical feasibility of LS has been recently established. However, data regarding the efficacy of the procedure in a large cohort of patients are scarce. METHODS: One hundred three consecutive patients underwent LS between June 1992 and October 1997. Data were collected prospectively on all patients. RESULTS: Indications were idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), hereditary spherocytosis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, and others. Mean spleen size was 14 cm and mean weight was 263 g. Accessory spleens were found in 12 patients with ITP and in 5 patients without ITP. There were no deaths. Complications occurred in six patients, one requiring a second procedure for small bowel obstruction. Six patients received transfusions, and four procedures were converted to open splenectomy for bleeding. Mean surgical time was 161 minutes and was greater in the first 10 cases than the last 10. Mean postsurgical stay was 2.5 days. Thrombocytopenia resolved after surgery in 84% of patients with ITP, and hematocrit levels increased significantly in 70% of patients with chronic hemolytic anemias. A positive response was noted in 92% of patients with hereditary spherocytosis, without relapse for the duration of the observation. ITP relapsed in four patients during follow-up, three within 12 months. CONCLUSIONS: LS can be performed safely and effectively in a teaching institution. Rigorous technique will minimize capsular fractures, reducing the risk of splenosis. Accessory spleens can be successfully localized, thus improving response and limiting recurrence of ITP. LS should become the technique of choice for treatment of intractable benign hematologic disease.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
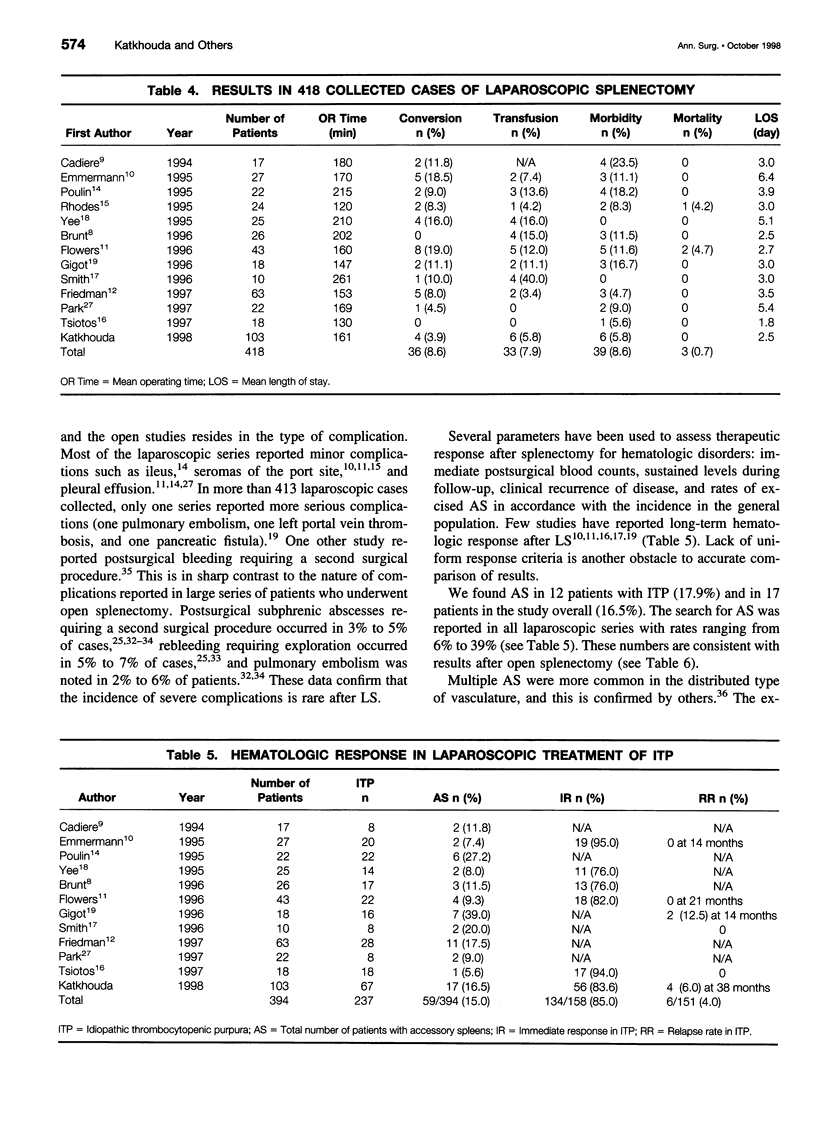
- Akwari O. E., Itani K. M., Coleman R. E., Rosse W. F. Splenectomy for primary and recurrent immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Current criteria for patient selection and results. Ann Surg. 1987 Oct;206(4):529–541. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198710000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARONOFSKY I. D., WALTON W., NOBLE J. F. Occult injury to the pancreas following splenectomy. Surgery. 1951 Jun;29(6):852–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunt L. M., Langer J. C., Quasebarth M. A., Whitman E. D. Comparative analysis of laparoscopic versus open splenectomy. Am J Surg. 1996 Nov;172(5):596–601. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(96)00241-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadiere G. B., Verroken R., Himpens J., Bruyns J., Efira M., De Wit S. Operative strategy in laparoscopic splenectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 1994 Dec;179(6):668–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis G. M., Movitz D. The Surgical Significance of the Accessory Spleen. Ann Surg. 1946 Feb;123(2):276–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAMESHEK W., RUBIO F., Jr, MAHONEY J. P., REEVES W. H., BURGIN L. A. Treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) with prednisone. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Apr 12;166(15):1805–1815. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.02990150001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaitre B., Maignien B. Splénectomie par voie coelioscopique. 1 observation (letter)] Presse Med. 1991 Dec 21;20(44):2263–2263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
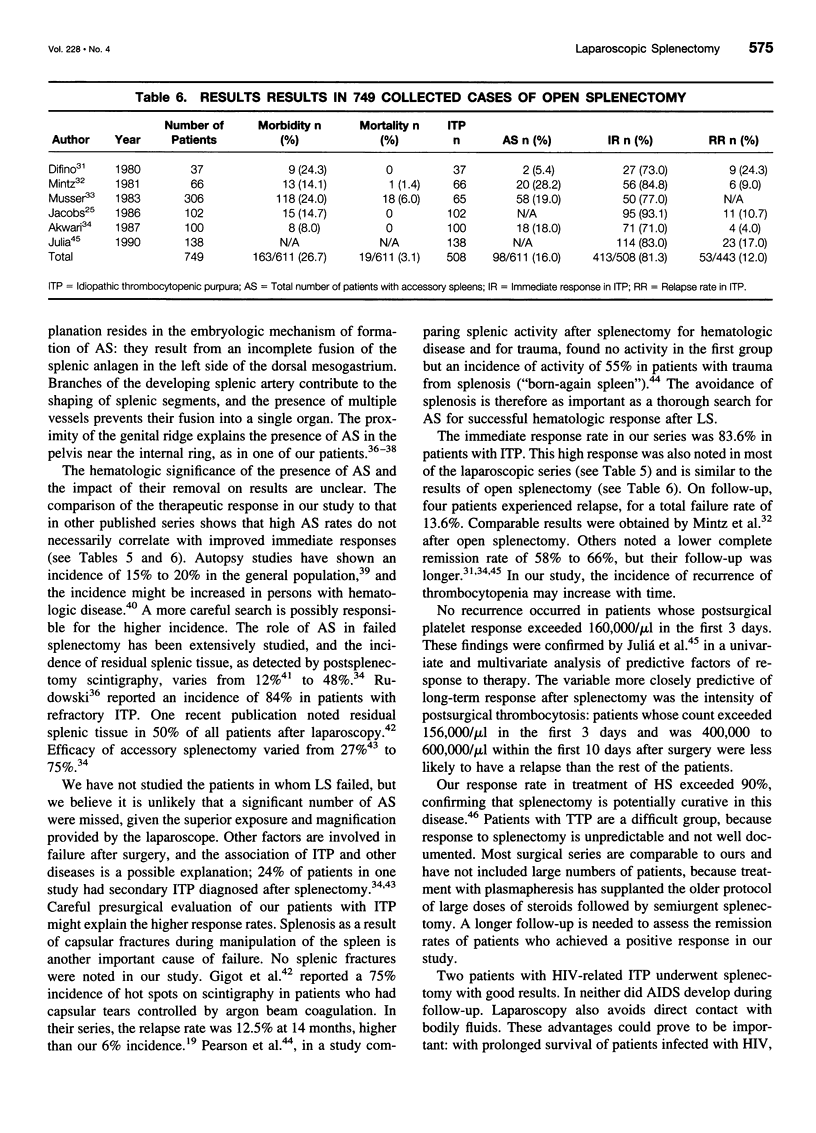
- DiFino S. M., Lachant N. A., Kirshner J. J., Gottlieb A. J. Adult idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Clinical findings and response to therapy. Am J Med. 1980 Sep;69(3):430–442. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmermann A., Zornig C., Peiper M., Weh H. J., Broelsch C. E. Laparoscopic splenectomy. Technique and results in a series of 27 cases. Surg Endosc. 1995 Aug;9(8):924–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eubanks S., Newman L., Lucas G. Reduction of HIV transmission during laparoscopic procedures. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1993 Feb;3(1):2–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facon T., Caulier M. T., Fenaux P., Plantier I., Marchandise X., Ribet M., Jouet J. P., Bauters F. Accessory spleen in recurrent chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol. 1992 Nov;41(3):184–189. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830410308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flowers J. L., Lefor A. T., Steers J., Heyman M., Graham S. M., Imbembo A. L. Laparoscopic splenectomy in patients with hematologic diseases. Ann Surg. 1996 Jul;224(1):19–28. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199607000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Hiatt J. R., Korman J. L., Facklis K., Cymerman J., Phillips E. H. Laparoscopic or open splenectomy for hematologic disease: which approach is superior? J Am Coll Surg. 1997 Jul;185(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagner M., Lacroix A., Prinz R. A., Bolté E., Albala D., Potvin C., Hamet P., Kuchel O., Quérin S., Pomp A. Early experience with laparoscopic approach for adrenalectomy. Surgery. 1993 Dec;114(6):1120–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Woolf S. H., Raskob G. E., Wasser J. S., Aledort L. M., Ballem P. J., Blanchette V. S., Bussel J. B., Cines D. B., Kelton J. G. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a practice guideline developed by explicit methods for the American Society of Hematology. Blood. 1996 Jul 1;88(1):3–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., el-Harake M. A., Raskob G. E. Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1994 Nov 3;331(18):1207–1211. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199411033311807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigot J. F., Jamar F., Ferrant A., van Beers B. E., Lengele B., Pauwels S., Pringot J., Kestens P. J., Gianello P., Detry R. Inadequate detection of accessory spleens and splenosis with laparoscopic splenectomy. A shortcoming of the laparoscopic approach in hematologic diseases. Surg Endosc. 1998 Feb;12(2):101–106. doi: 10.1007/s004649900607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigot J. F., de Ville de Goyet J., Van Beers B. E., Reding R., Etienne J., Jadoul P., Michaux J. L., Ferrant A., Cornu G., Otte J. B. Laparoscopic splenectomy in adults and children: experience with 31 patients. Surgery. 1996 Apr;119(4):384–389. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(96)80136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbard M. L. Is laparoscopic splenectomy appropriate for the management of hematologic and oncologic diseases? Surg Endosc. 1996 Apr;10(4):387–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00191620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRINGTON W. J., MINNICH V., HOLLINGSWORTH J. W., MOORE C. V. Demonstration of a thrombocytopenic factor in the blood of patients with thrombocytopenic purpura. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jul;38(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinder R. A., Filipi C. J., Wetscher G., Neary P., DeMeester T. R., Perdikis G. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg. 1994 Oct;220(4):472–483. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199410000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P., Wood L., Dent D. M. Results of treatment in immune thrombocytopenia. Q J Med. 1986 Feb;58(226):153–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliá A., Araguás C., Rosselló J., Bueno J., Domenech P., Olona M., Guardia R., Petit J., Flores A. Lack of useful clinical predictors of response to splenectomy in patients with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1990 Oct;76(2):250–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katkhouda N., Waldrep D. J., Feinstein D., Soliman H., Stain S. C., Ortega A. E., Mouiel J. Unresolved issues in laparoscopic splenectomy. Am J Surg. 1996 Nov;172(5):585–590. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(96)00243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinger P. J., Smith S. L., Abendstein B. J., Hinder R. A. Hand-assisted laparoscopic splenectomy for isolated splenic metastasis from an ovarian carcinoma: a case report with review of the literature. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1998 Feb;8(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R. Therapy for adults with refractory chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Feb 15;126(4):307–314. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-126-4-199702150-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz S. J., Petersen S. R., Cheson B., Cordell L. J., Richards R. C. Splenectomy for immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Arch Surg. 1981 May;116(5):645–650. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380170121022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser G., Lazar G., Hocking W., Busuttil R. W. Splenectomy for hematologic disease. The UCLA experience with 306 patients. Ann Surg. 1984 Jul;200(1):40–45. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198407000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen W. R., Beaudoin D. E. Increased incidence of accessory spleens in hematologic disease. Arch Surg. 1969 Jun;98(6):762–763. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340120110019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park A., Gagner M., Pomp A. The lateral approach to laparoscopic splenectomy. Am J Surg. 1997 Feb;173(2):126–130. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)89602-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H. A., Johnston D., Smith K. A., Touloukian R. J. The born-again spleen. Return of splenic function after splenectomy for trauma. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 22;298(25):1389–1392. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806222982504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulin E. C., Thibault C., Mamazza J. Laparoscopic splenectomy. Surg Endosc. 1995 Feb;9(2):172–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00191961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulin E. C., Thibault C. The anatomical basis for laparoscopic splenectomy. Can J Surg. 1993 Oct;36(5):484–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes M., Rudd M., O'Rourke N., Nathanson L., Fielding G. Laparoscopic splenectomy and lymph node biopsy for hematologic disorders. Ann Surg. 1995 Jul;222(1):43–46. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199507000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudowski W. J. Accessory spleens: clinical significance with particular reference to the recurrence of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. World J Surg. 1985 Jun;9(3):422–430. doi: 10.1007/BF01655277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. I. Role of splenectomy in hematologic disorders. World J Surg. 1996 Nov-Dec;20(9):1156–1159. doi: 10.1007/s002689900176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Meyer T. A., Goretsky M. J., Hyams D., Luchette F. A., Fegelman E. J., Nussbaum M. S. Laparoscopic splenectomy by the lateral approach: a safe and effective alternative to open splenectomy for hematologic diseases. Surgery. 1996 Nov;120(5):789–794. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6060(96)80085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias M., Targarona E. M., Balagué C. Laparoscopic splenectomy: an evolving technique. A comparison between anterior and lateral approaches. Surg Endosc. 1996 Apr;10(4):389–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00191621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiotos G., Schlinkert R. T. Laparoscopic splenectomy for immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Arch Surg. 1997 Jun;132(6):642–646. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1997.01430300084017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheyden C. N., Beart R. W., Jr, Clifton M. D., Phyliky R. L. Accessory splenectomy in management of recurrent idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Mayo Clin Proc. 1978 Jul;53(7):442–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadham B. M., Adams P. B., Johnson M. A. Incidence and location of accessory spleens. N Engl J Med. 1981 Apr 30;304(18):1111–1111. doi: 10.1056/nejm198104303041822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee L. F., Carvajal S. H., de Lorimier A. A., Mulvihill S. J. Laparoscopic splenectomy. The initial experience at University of California, San Francisco. Arch Surg. 1995 Aug;130(8):874–879. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1995.01430080076012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


