Abstract
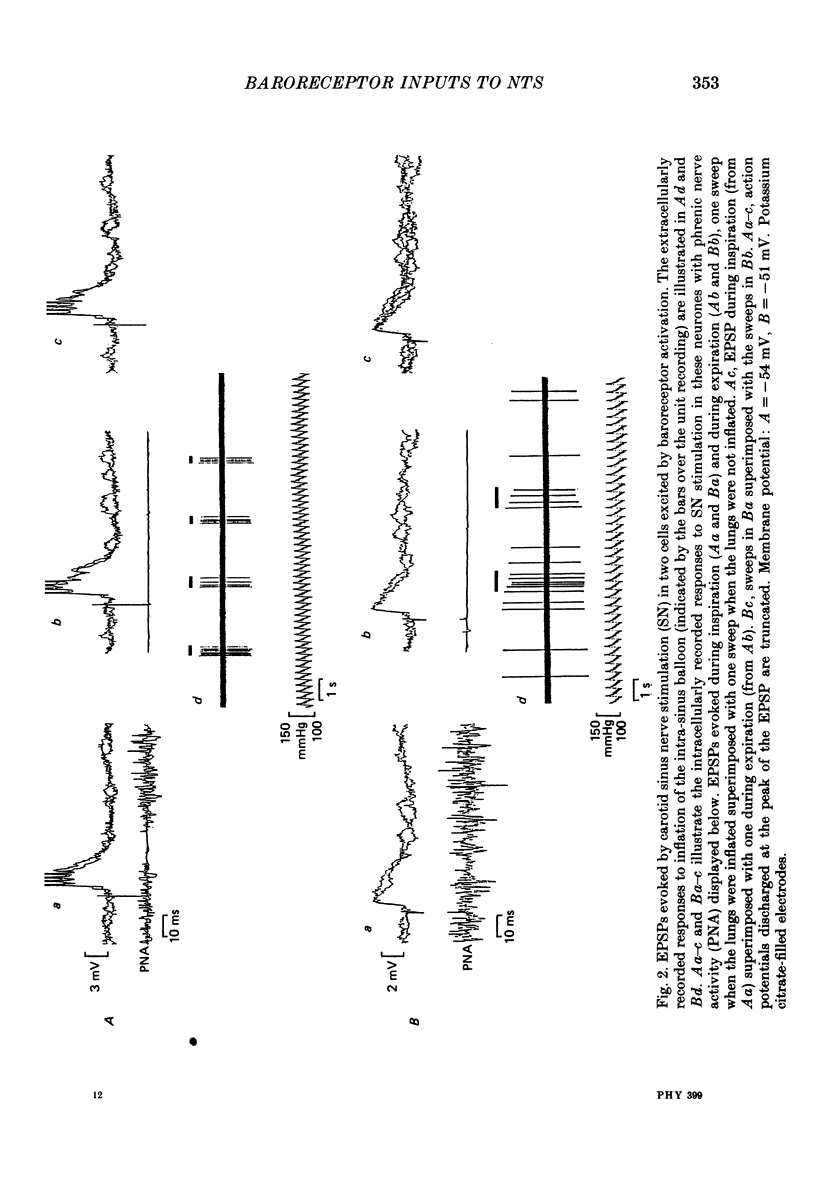
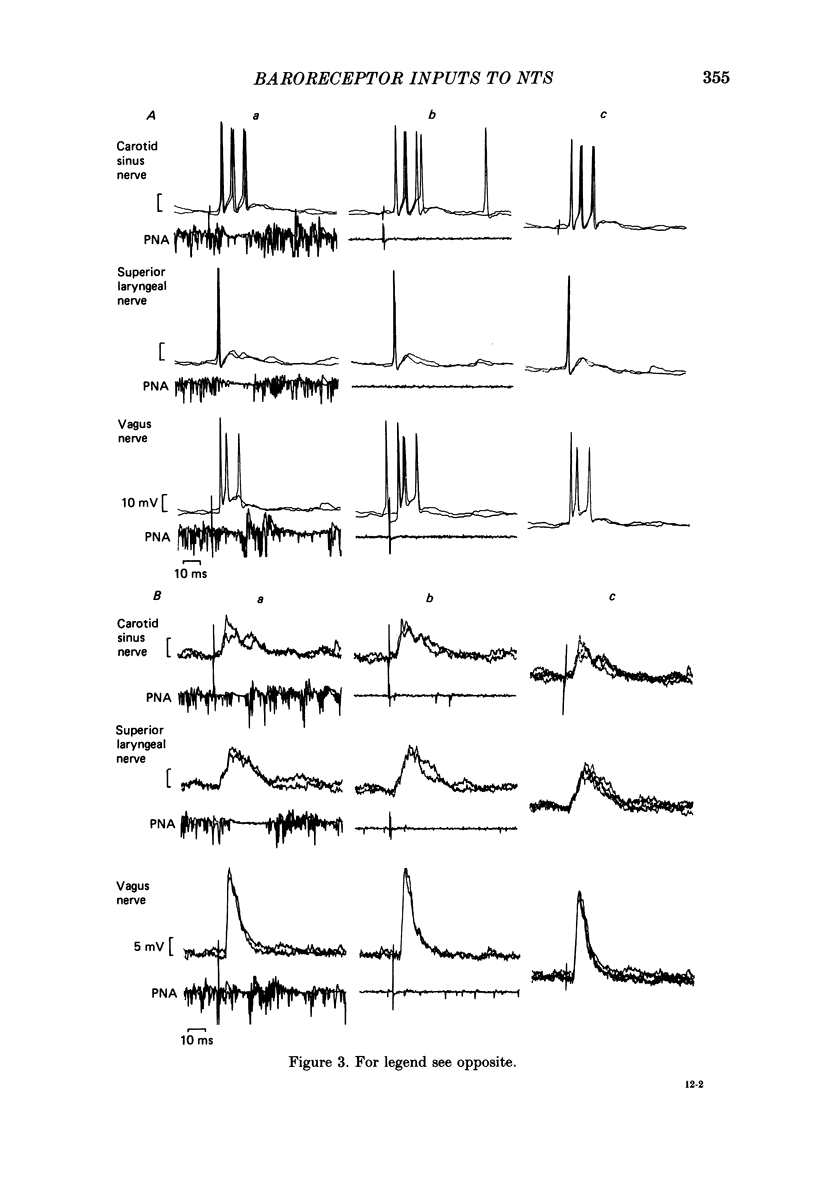
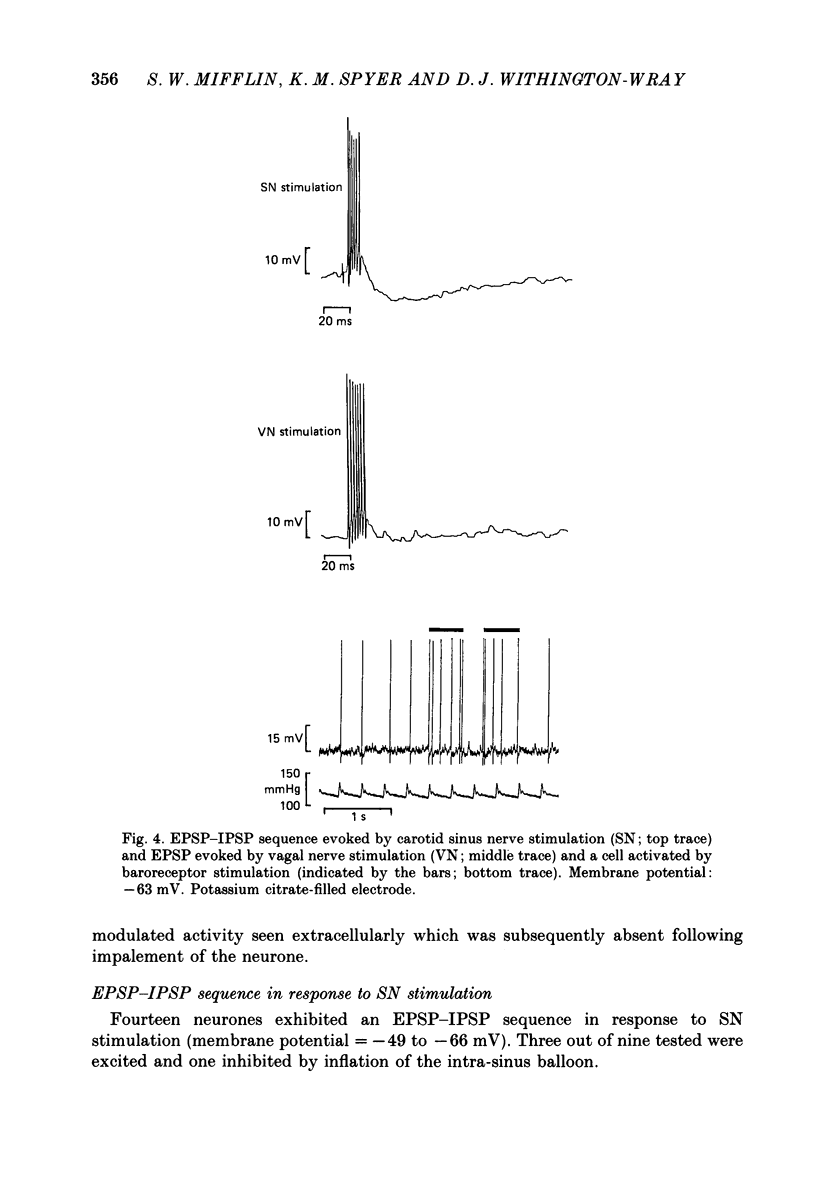
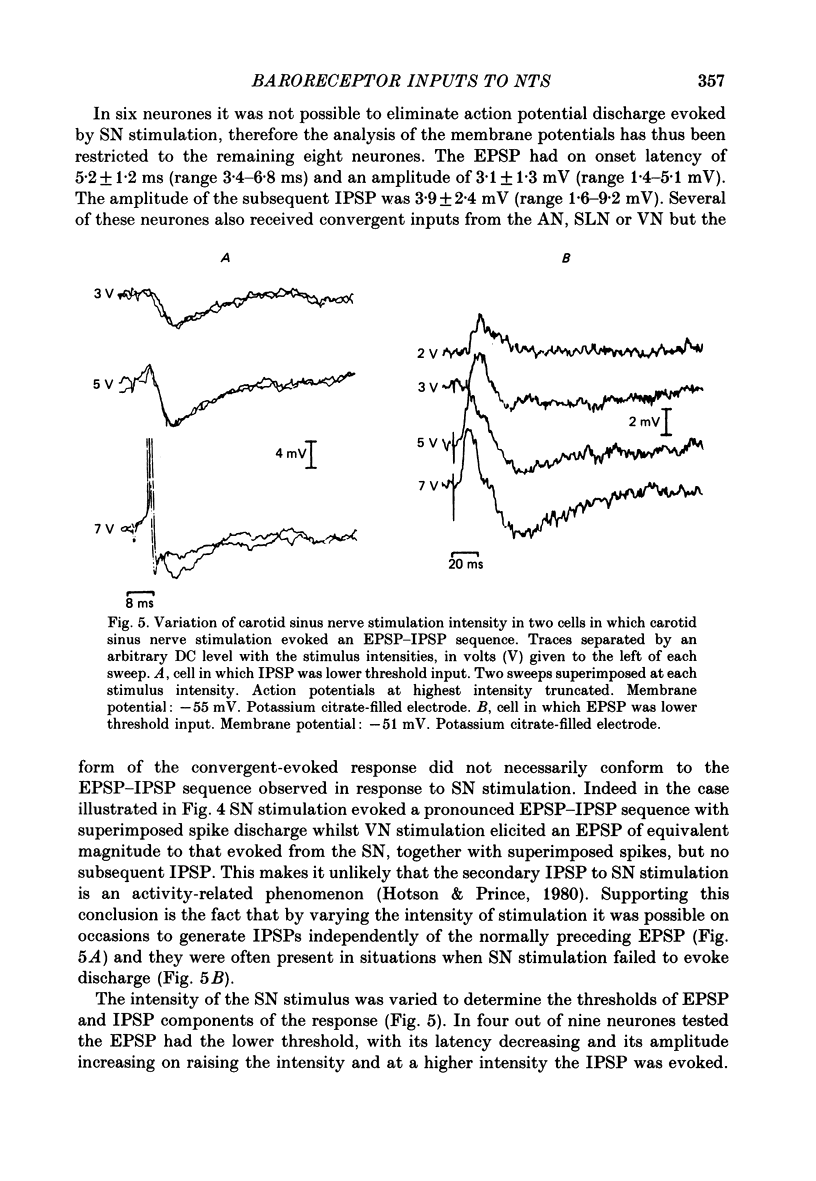
1. The postsynaptic action of carotid sinus nerve (SN), aortic nerve (AN), superior laryngeal nerve (SLN) and vagal nerve (VN) stimulation has been studied on neurones in the nucleus of the tractus solitarius (NTS) in vivo. 2. Three distinct patterns of postsynaptic responses were evoked by SN stimulation, an EPSP, an EPSP-IPSP sequence and an IPSP, observed separately in individual neurones. This diversity of response was represented in cells proven to receive baroreceptor input by inflation of a balloon-tipped catheter within the ipsilateral carotid sinus. 3. Virtually none of the neurones identified as baroreceptive exhibited pulse-related discharge. 4. A variety of influences to AN, SLN and VN stimulation were observed in neurones receiving baroreceptor afferent information. This wide convergence of input implies that this region of the brain stem is important in the integration of cardiovascular reflexes. 5. The hypothesis was tested that respiratory 'gating' of the baroreceptor reflex is produced by synaptic actions within the NTS. There was an absence of any modification of PSPs by lung inflation and by variations in the timing of the stimulation of the afferent nerves within the respiratory cycle. These observations indicate that respiratory modifications of the baroreceptor reflex must occur at later stages in the reflex pathway.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barillot J. C. Deplarisation présynaptique des fibres sensitives vagales et laryngées. Etde unitaire. J Physiol (Paris) 1970 May-Jun;62(3):273–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Sampson S. R. An analysis of the inhibition of phrenic motoneurones which occurs on stimulation of some cranial nerve afferents. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(2):375–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champagnat J., Denavit-Saubié M., Grant K., Shen K. F. Organization of synaptic transmission in the mammalian solitary complex, studied in vitro. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:551–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czachurski J., Lackner K. J., Ockert D., Seller H. Localization of neurones with baroreceptor input in the medial solitary nucleus by means of intracellular application of horseradish peroxidase in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Feb 12;28(2):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly M. D., Ward J., Wood L. M. Modification by lung inflation of the vascular responses from the carotid body chemoreceptors and other receptors in dogs. J Physiol. 1986 Sep;378:13–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. S., Goldner S., McCloskey D. I. Respiratory modulation of barareceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes affecting heart rate and cardiac vagal efferent nerve activity. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(2):523–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue S., Felder R. B., Gilbey M. P., Jordan D., Spyer K. M. Post-synaptic activity evoked in the nucleus tractus solitarius by carotid sinus and aortic nerve afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:261–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue S., Felder R. B., Jordan D., Spyer K. M. The central projections of carotid baroreceptors and chemoreceptors in the cat: a neurophysiological study. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:397–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue S., Garcia M., Jordan D., Spyer K. M. Identification and brain-stem projections of aortic baroreceptor afferent neurones in nodose ganglia of cats and rabbits. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:337–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue S., Garcia M., Jordan D., Spyer K. M. The brain-stem projections of pulmonary stretch afferent neurones in cats and rabbits. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:353–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Jordan D., Richter D. W., Spyer K. M. Synaptic mechanisms involved in the inspiratory modulation of vagal cardio-inhibitory neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:65–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. R. Central connections of aortic depressor and carotid sinus nerves. Exp Neurol. 1974 Dec;45(3):590–605. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(74)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A. A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;43(2):409–419. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D., Mifflin S. W., Spyer K. M. Hypothalamic inhibition of neurones in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the cat is GABA mediated. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:389–404. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D., Spyer K. M. Brainstem integration of cardiovascular and pulmonary afferent activity. Prog Brain Res. 1986;67:295–314. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62769-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D., Spyer K. M. Studies on the excitability of sinus nerve afferent terminals. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):123–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhorst P., Stroh-Werz M., Dittmar K., Camerer H. Facultative coupling of reticular neuronal activity with peripheral cardiovascular and central cortical rhythms. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 11;87(2-3):407–418. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90437-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., McAllen R. M., Spyer K. M. The sinus nerve and baroreceptor input to the medulla of the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;251(1):61–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mifflin S. W., Spyer K. M., Withington-Wray D. J. Baroreceptor inputs to the nucleus tractus solitarius in the cat: modulation by the hypothalamus. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:369–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R. Frequency dependence of synaptic transmission in nucleus of the solitary tract in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1986 May;55(5):1076–1090. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.5.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M. Postsynaptic potentials recorded from nucleus of the solitary tract and its subjacent reticular formation elicited by stimulation of the carotid sinus nerve. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 19;100(2):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. K. Inspiratory inhibition of vagal responses to baroreceptor and chemoreceptor stimuli in the dog. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:177–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Smith T. G., Nelson P. G., Frank K. Dendritic location of synapses and possible mechanisms for the monosynaptic EPSP in motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1169–1193. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W., Jordan D., Ballantyne D., Meesmann M., Spyer K. M. Presynaptic depolarization in myelinated vagal afferent fibres terminating in the nucleus of the tractus solitarius in the cat. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Jan;406(1):12–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00582946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seller H., Illert M. The localization of the first synapse in the carotid sinus baroreceptor reflex pathway and its alteration of the afferent input. Pflugers Arch. 1969;306(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00586608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spyer K. M. Central nervous integration of cardiovascular control. J Exp Biol. 1982 Oct;100:109–128. doi: 10.1242/jeb.100.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spyer K. M. Neural organisation and control of the baroreceptor reflex. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:24–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypert G. W., Munson J. B., Fleshman J. W. Effect of presynaptic inhibition on axonal potentials, terminal potentials, focal synaptic potentials, and EPSPs in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Oct;44(4):792–803. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.44.4.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


