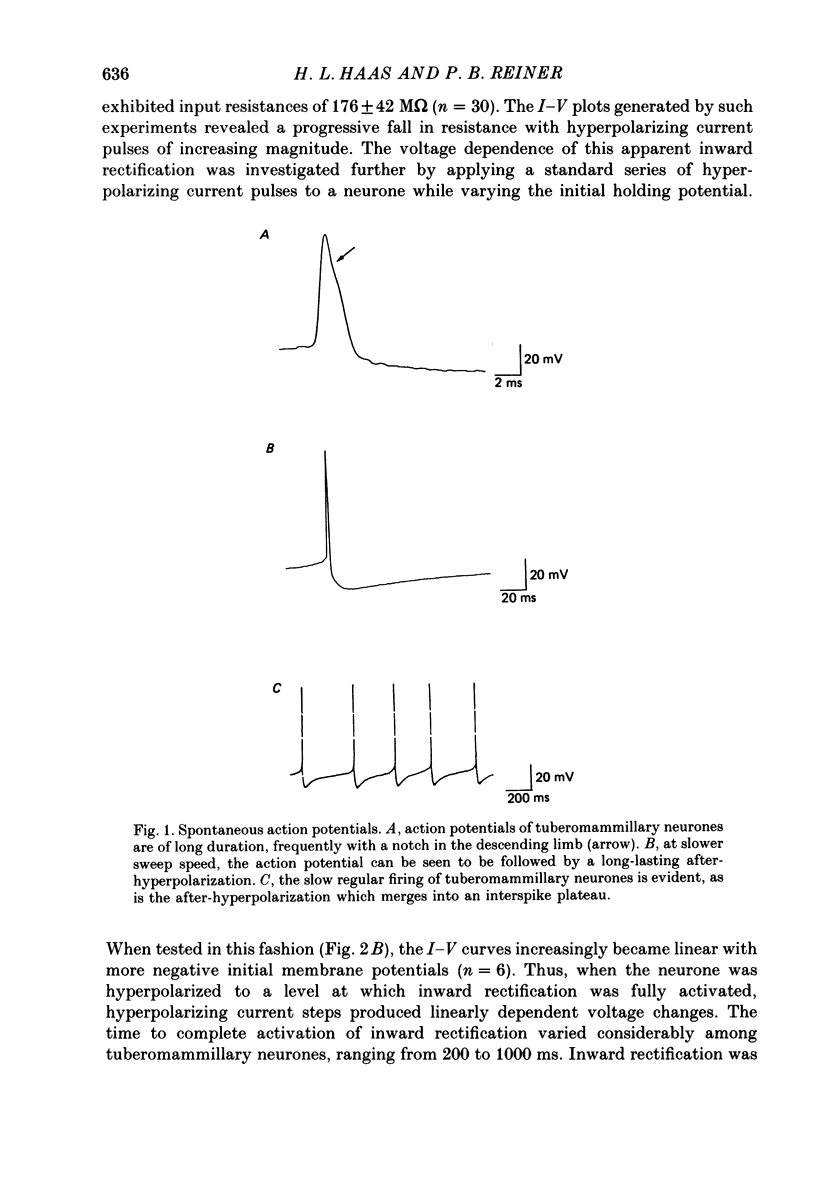
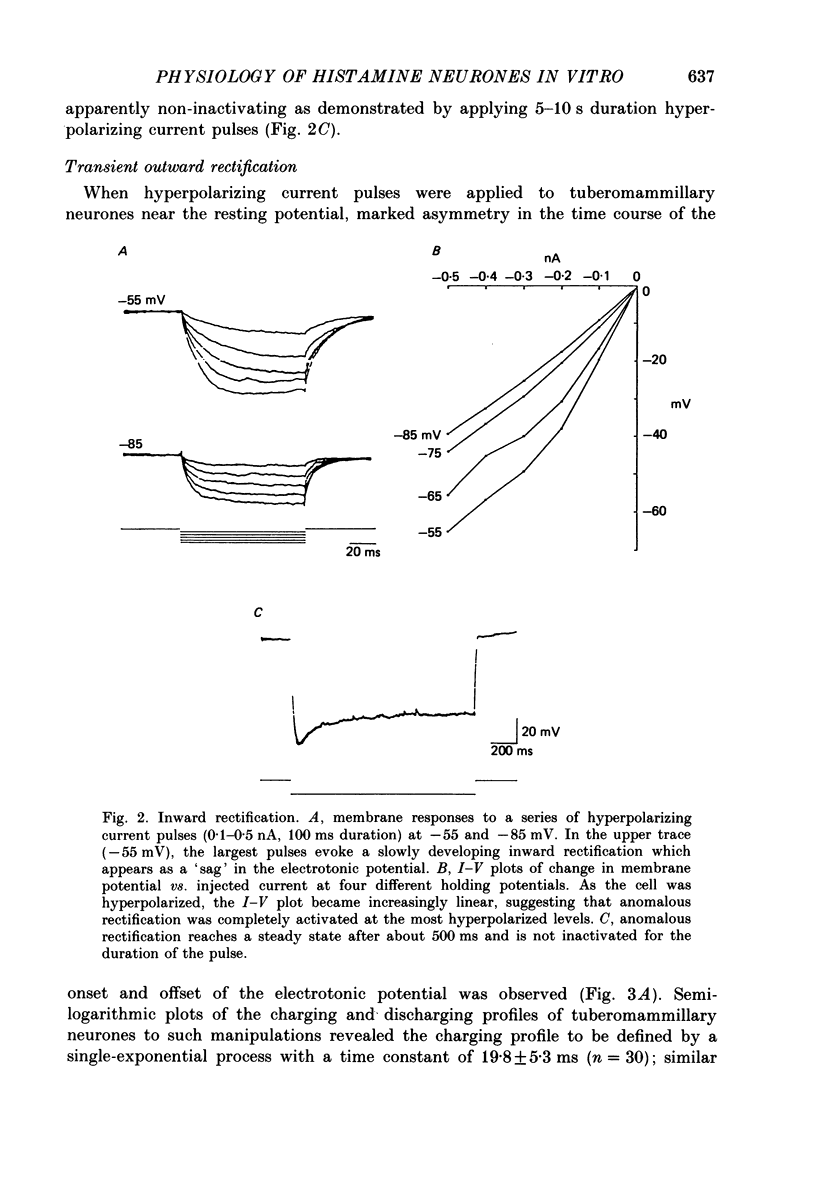
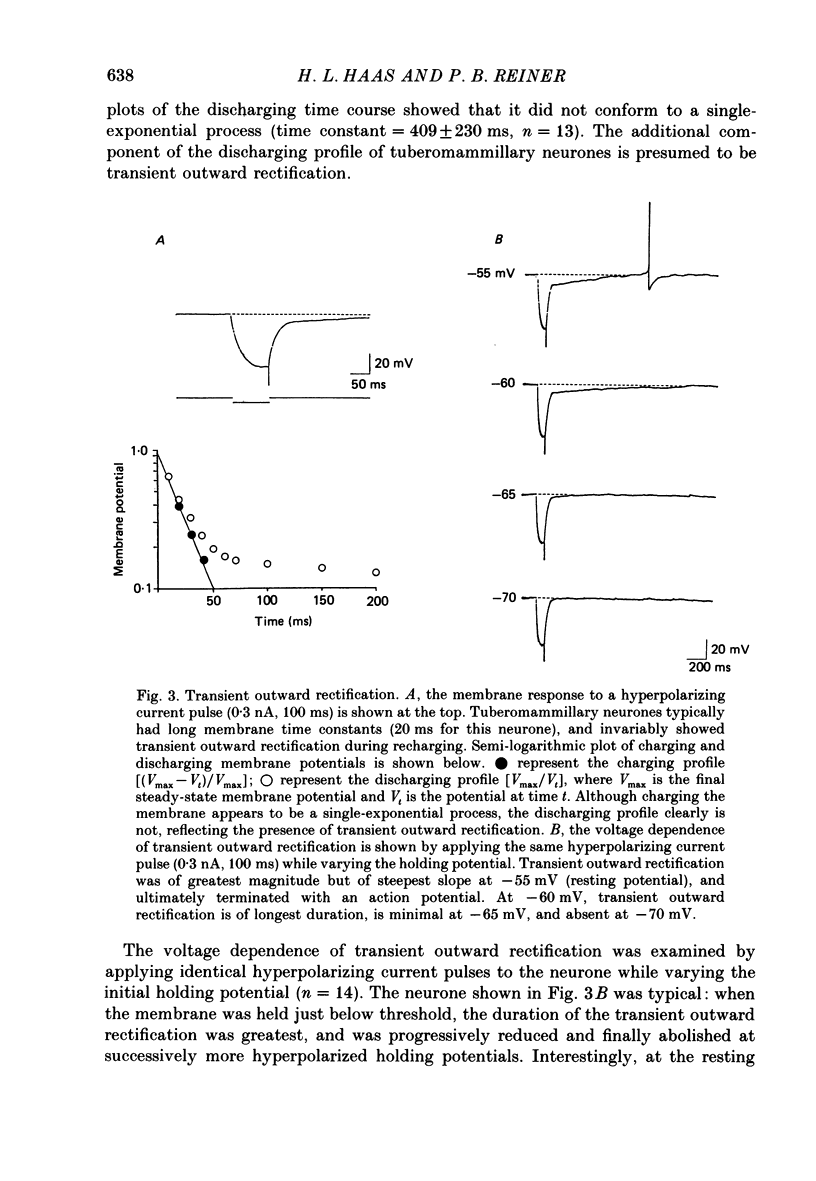
Abstract
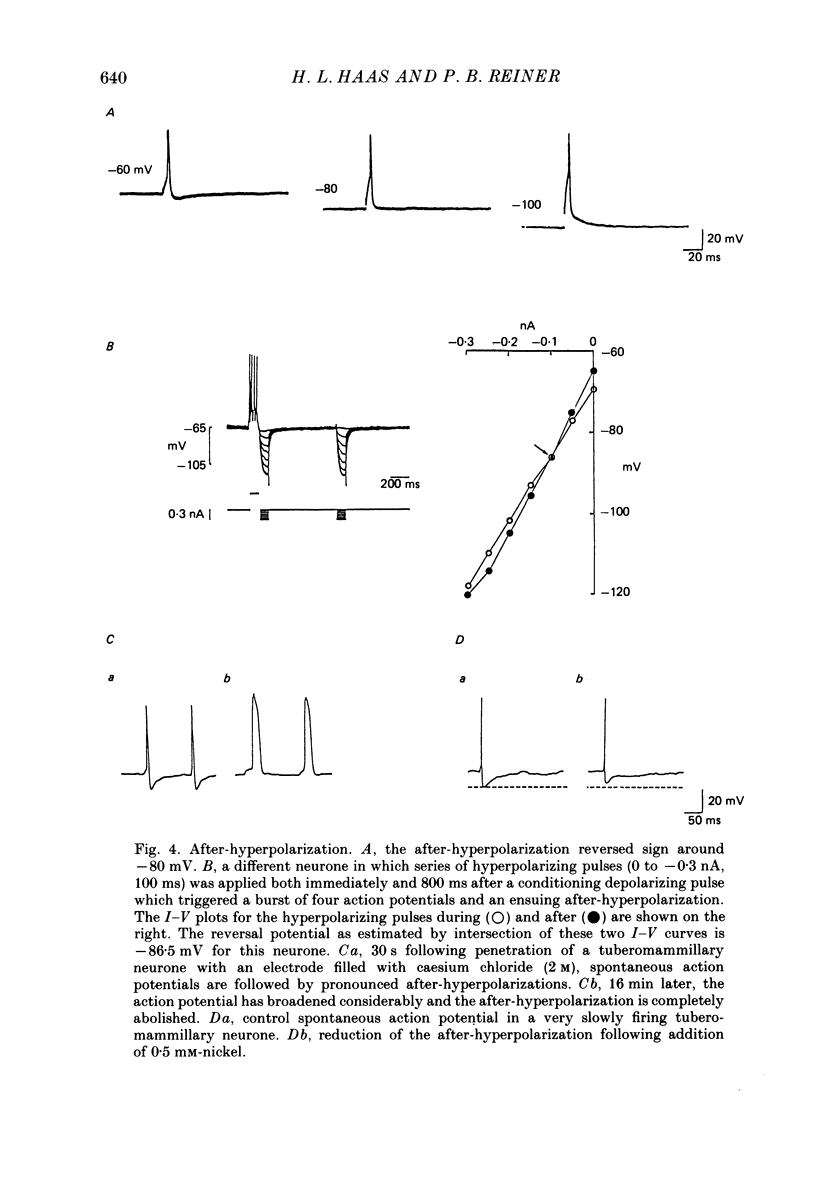
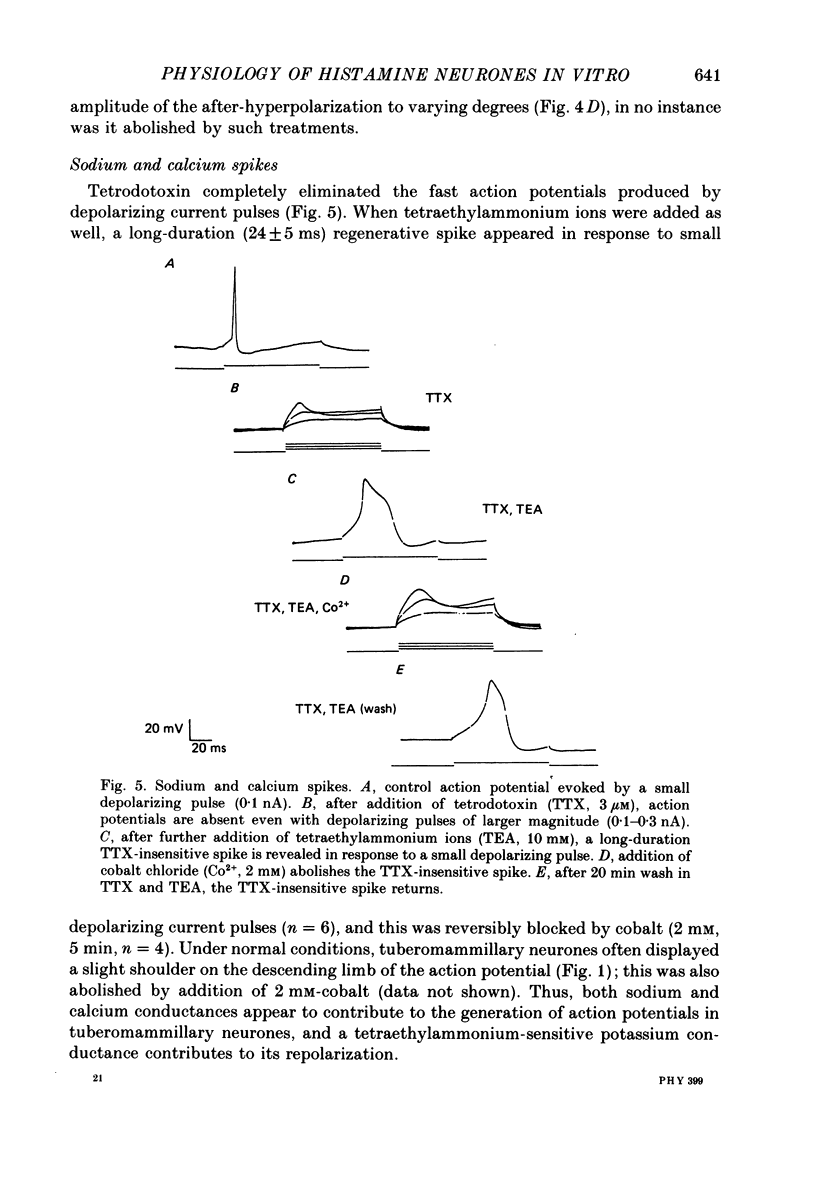
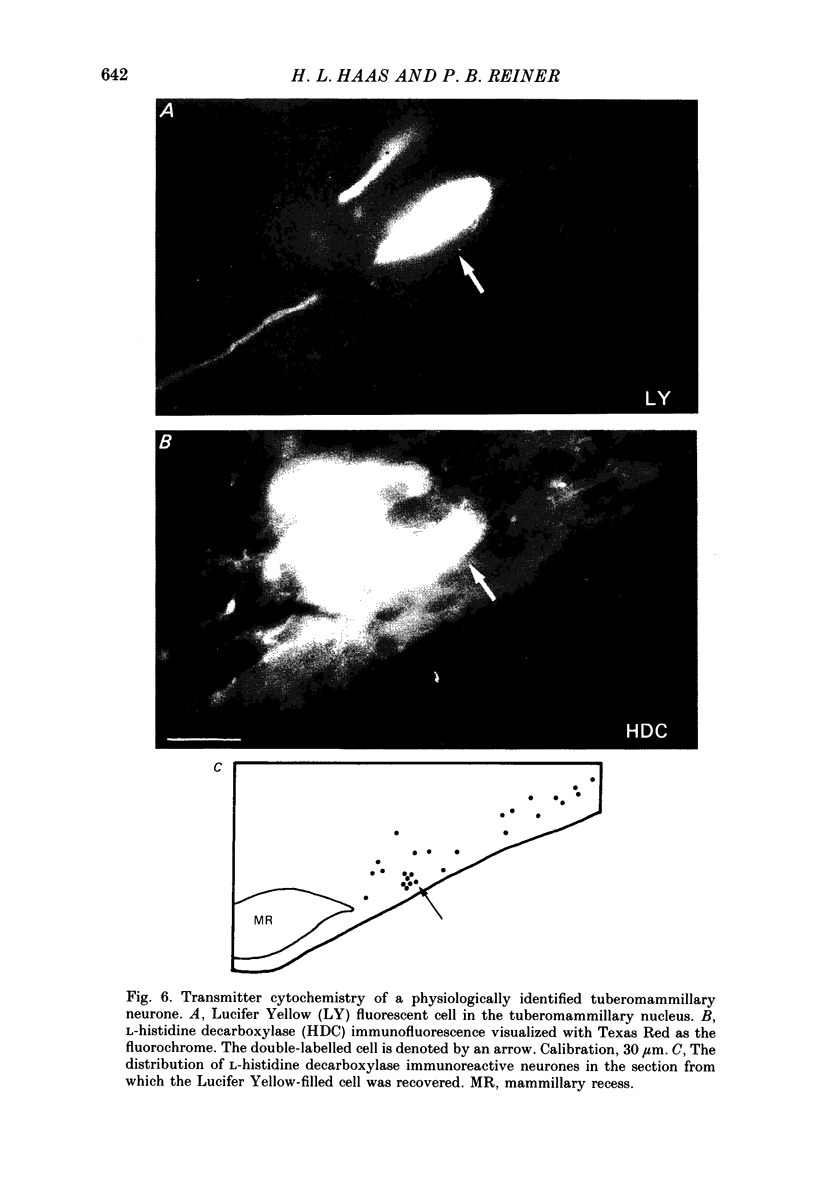
1. Intracellular recordings were obtained from neurones of the tuberomammillary nucleus in an in vitro explant of the rat hypothalamus. 2. Tuberomammillary neurones were spontaneously active (2.1 +/- 0.6 Hz) at the resting potential which was around -50 mV. Action potential amplitude was 75 +/- 8 mV (n = 9); mean mid-amplitude duration was 1.8 +/- 0.4 ms (n = 9). 3. The mean input resistance of tuberomammillary neurones was 176 +/- 42 M omega (n = 30), and the mean membrane time constant was 19.8 +/- 5.3 ms (n = 30). These neurones exhibited inward rectification with hyperpolarization from the resting potential, and transient outward rectification at the offset of hyperpolarizing electrotonic pulses. 4. Action potentials were followed by an after-hyperpolarization of 300-600 ms duration and 12-18 mV amplitude. This after-hyperpolarization had a reversal potential around -80 mV, was abolished by intracellular loading with caesium, and was reduced but not abolished by bath application of either cadmium, cobalt or nickel. 5. Tetrodotoxin abolished spontaneous action potentials. Further addition of tetraethylammonium ions revealed a regenerative spike which was reversibly blocked by the addition of cobalt. 6. That tuberomammillary neurones exhibiting these properties were indeed histaminergic was confirmed in five cases by intracellular ionophoresis of Lucifer Yellow and subsequent double labelling by immunofluorescent localization of the histamine synthetic enzyme L-histidine decarboxylase.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Galvan M. Voltage-dependent currents of vertebrate neurons and their role in membrane excitability. Adv Neurol. 1986;44:137–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade R., Aghajanian G. K. Locus coeruleus activity in vitro: intrinsic regulation by a calcium-dependent potassium conductance but not alpha 2-adrenoceptors. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):161–170. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00161.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Prediction of repetitive firing behaviour from voltage clamp data on an isolated neurone soma. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):31–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Forda S., Brooks P. A., Wilson K. C., Wise J. C., Kelly J. S. Passive membrane properties of neurones in the dorsal raphe and periaqueductal grey recorded in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Oct 10;40(3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Tillotson D. L. Calcium-mediated inactivation of the calcium conductance in caesium-loaded giant neurones of Aplysia californica. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:265–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Galvan M., Grafe P., Wigström H. A transient outward current in a mammalian central neurone blocked by 4-aminopyridine. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):252–254. doi: 10.1038/299252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Greene R. W. Effects of histamine on hippocampal pyramidal cells of the rat in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1986;62(1):123–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00237408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Konnerth A. Histamine and noradrenaline decrease calcium-activated potassium conductance in hippocampal pyramidal cells. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):432–434. doi: 10.1038/302432a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Schaerer B., Vosmansky M. A simple perfusion chamber for the study of nervous tissue slices in vitro. J Neurosci Methods. 1979 Dec;1(4):323–325. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(79)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotson J. R., Prince D. A. A calcium-activated hyperpolarization follows repetitive firing in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;43(2):409–419. doi: 10.1152/jn.1980.43.2.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. EGTA and motoneuronal after-potentials. J Physiol. 1978 Feb;275:199–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panula P., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Histamine-containing neurons in the rat hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2572–2576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H., Pachot I., Schwartz J. C. Monoclonal antibody against L-histidine decarboxylase for localization of histaminergic cells. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Feb 28;54(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(85)80117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puil E., Werman R. Internal cesium ions block various K conductances in spinal motoneurons. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Dec;59(12):1280–1284. doi: 10.1139/y81-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner P. B., McGeer E. G. Electrophysiological properties of cortically projecting histamine neurons of the rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 2;73(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner P. B., Semba K., Watanabe T., Wada H. En bloc immunohistochemistry reveals extensive distribution of histidine decarboxylase-immunoreactive neurons on the ventral surface of the rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jun 15;77(2):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90575-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. A potent transient outward current regulates excitability of dorsal raphe neurons. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 16;359(1-2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solc C. K., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Single-channel and genetic analyses reveal two distinct A-type potassium channels in Drosophila. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1094–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.2437657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines W. A., Daddona P. E., Nagy J. I. The organization and hypothalamic projections of the tuberomammillary nucleus in the rat: an immunohistochemical study of adenosine deaminase-positive neurons and fibers. Neuroscience. 1987 Nov;23(2):571–596. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandermaelen C. P., Aghajanian G. K. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of serotonergic dorsal raphe neurons recorded extracellularly and intracellularly in rat brain slices. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 19;289(1-2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanni-Mercier G., Sakai K., Jouvet M. Neurones spécifiques de l'éveil dans l'hypothalamus postérieur du chat. C R Acad Sci III. 1984;298(7):195–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Taguchi Y., Shiosaka S., Tanaka J., Kubota H., Terano Y., Tohyama M., Wada H. Distribution of the histaminergic neuron system in the central nervous system of rats; a fluorescent immunohistochemical analysis with histidine decarboxylase as a marker. Brain Res. 1984 Mar 12;295(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90811-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., North R. A., Shefner S. A., Nishi S., Egan T. M. Membrane properties of rat locus coeruleus neurones. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):137–156. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90265-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]