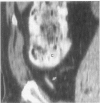
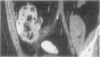
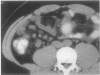
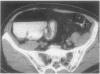
Abstract
OBJECTIVE To evaluate the impact of appendiceal computed tomography (CT) availability on negative appendectomy and appendiceal perforation rates. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Appendiceal CT is 98% accurate. However, its impact on negative appendectomy and appendiceal perforation rates has not been reported. METHODS: The authors reviewed the medical records of 493 consecutive patients who underwent appendectomy between 1992 and 1995, 209 consecutive patients who underwent appendectomy in 1997 (59% of whom had appendiceal CT), and 206 patients who underwent appendiceal CT in 1997 without subsequent appendectomy. RESULTS: Before appendiceal CT, 98/493 patients (20%) taken to surgery had a normal appendix. After CT availability, 15/209 patients (7%) taken to surgery had a normal appendix; 7 patients did not have CT, 5 patients had surgery despite a negative CT, and 3 patients had a false-positive CT. Negative appendectomy rates were lowered overall (20% to 7%), in men (11% to 5%), in women (35% to 11%), in boys (10% to 5%), and in girls (18% to 12%). Appendiceal perforation rates dropped from 22% to 14% after CT availability. CT excluded appendicitis in 206 patients in 1997 who avoided appendectomy and identified alternative diagnoses in 105 of these patients (51%). CONCLUSION: The availability of appendiceal CT coincided with a drop in the negative appendectomy rate from 20% to 7% in all patients, and to only 3% in patients with a positive CT. Perforation rates decreased from 22% to 14%. Appendiceal CT can be advocated in nearly all female and many male patients.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balthazar E. J., Birnbaum B. A., Yee J., Megibow A. J., Roshkow J., Gray C. Acute appendicitis: CT and US correlation in 100 patients. Radiology. 1994 Jan;190(1):31–35. doi: 10.1148/radiology.190.1.8259423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balthazar E. J., Megibow A. J., Siegel S. E., Birnbaum B. A. Appendicitis: prospective evaluation with high-resolution CT. Radiology. 1991 Jul;180(1):21–24. doi: 10.1148/radiology.180.1.2052696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder J. D., Gajraj H. Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of acute appendicitis. 1995 Aug 16-Sep 5Br J Hosp Med. 54(4):129–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch A. A., Shani N., Reiss R. Are some some appendectomies unnecessary? An analysis of 319 white appendices. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1983 Jan;28(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford R. D., Passinault W. J., Morse M. E. Diagnostic ultrasound for suspected appendicitis: does the added cost produce a better outcome? Am Surg. 1994 Nov;60(11):895–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Incesu L., Coskun A., Selcuk M. B., Akan H., Sozubir S., Bernay F. Acute appendicitis: MR imaging and sonographic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997 Mar;168(3):669–674. doi: 10.2214/ajr.168.3.9057512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jess P., Bjerregaard B., Brynitz S., Holst-Christensen J., Kalaja E., Lund-Kristensen J. Acute appendicitis. Prospective trial concerning diagnostic accuracy and complications. Am J Surg. 1981 Feb;141(2):232–234. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90164-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. J., Katz D. S., Ross B. A., Clautice-Engle T. L., Mindelzun R. E., Jeffrey R. B., Jr Unenhanced helical CT for suspected acute appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997 Feb;168(2):405–409. doi: 10.2214/ajr.168.2.9016216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis F. R., Holcroft J. W., Boey J., Dunphy E. Appendicitis. A critical review of diagnosis and treatment in 1,000 cases. Arch Surg. 1975 May;110(5):677–684. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360110223039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone A. J., Jr, Wolf C. R., Malmed A. S., Melliere B. F. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis: value of unenhanced CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993 Apr;160(4):763–766. doi: 10.2214/ajr.160.4.8456661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puylaert J. B. Imaging and intervention in patients with acute right lower quadrant disease. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1995 Mar;9(1):37–51. doi: 10.1016/0950-3528(95)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. M., Rhea J. T., Novelline R. A. CT diagnosis of mesenteric adenitis. Radiology. 1997 Jan;202(1):145–149. doi: 10.1148/radiology.202.1.8988204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. M., Rhea J. T., Novelline R. A., Dobbins J. M., Lawrason J. N., Sacknoff R., Stuk J. L. Helical CT with only colonic contrast material for diagnosing diverticulitis: prospective evaluation of 150 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998 Jun;170(6):1445–1449. doi: 10.2214/ajr.170.6.9609151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. M., Rhea J. T., Novelline R. A., McCabe C. J., Lawrason J. N., Berger D. L., Sacknoff R. Helical CT technique for the diagnosis of appendicitis: prospective evaluation of a focused appendix CT examination. Radiology. 1997 Jan;202(1):139–144. doi: 10.1148/radiology.202.1.8988203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. M., Rhea J. T., Novelline R. A., Mostafavi A. A., Lawrason J. N., McCabe C. J. Helical CT combined with contrast material administered only through the colon for imaging of suspected appendicitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997 Nov;169(5):1275–1280. doi: 10.2214/ajr.169.5.9353441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. M., Rhea J. T., Novelline R. A., Mostafavi A. A., McCabe C. J. Effect of computed tomography of the appendix on treatment of patients and use of hospital resources. N Engl J Med. 1998 Jan 15;338(3):141–146. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199801153380301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. M., Rhea J. T., Novelline R. A. Sensitivity and specificity of the individual CT signs of appendicitis: experience with 200 helical appendiceal CT examinations. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1997 Sep-Oct;21(5):686–692. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199709000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao P. M., Wittenberg J., McDowell R. K., Rhea J. T., Novelline R. A. Appendicitis: use of arrowhead sign for diagnosis at CT. Radiology. 1997 Feb;202(2):363–366. doi: 10.1148/radiology.202.2.9015058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux M., Langis P. Primary epiploic appendagitis: clinical, US, and CT findings in 14 cases. Radiology. 1994 May;191(2):523–526. doi: 10.1148/radiology.191.2.8153333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux M. Sonographic detection of the normal and abnormal appendix. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992 Apr;158(4):773–778. doi: 10.2214/ajr.158.4.1546592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. W., Vick C. W., Walsh J. W., McClure P. H. Computed tomography of benign ovarian masses. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985 Jul-Aug;9(4):784–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. C., Verga M., McCarthy S., Rosenfield A. T. Diagnosis of acute flank pain: value of unenhanced helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996 Jan;166(1):97–101. doi: 10.2214/ajr.166.1.8571915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velanovich V., Satava R. Balancing the normal appendectomy rate with the perforated appendicitis rate: implications for quality assurance. Am Surg. 1992 Apr;58(4):264–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade D. S., Marrow S. E., Balsara Z. N., Burkhard T. K., Goff W. B. Accuracy of ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis compared with the surgeon's clinical impression. Arch Surg. 1993 Sep;128(9):1039–1046. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1993.01420210103014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yacoe M. E., Jeffrey R. B., Jr Sonography of appendicitis and diverticulitis. Radiol Clin North Am. 1994 Sep;32(5):899–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Dombal F. T., Leaper D. J., Staniland J. R., McCann A. P., Horrocks J. C. Computer-aided diagnosis of acute abdominal pain. Br Med J. 1972 Apr 1;2(5804):9–13. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5804.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]