Abstract
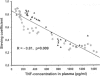
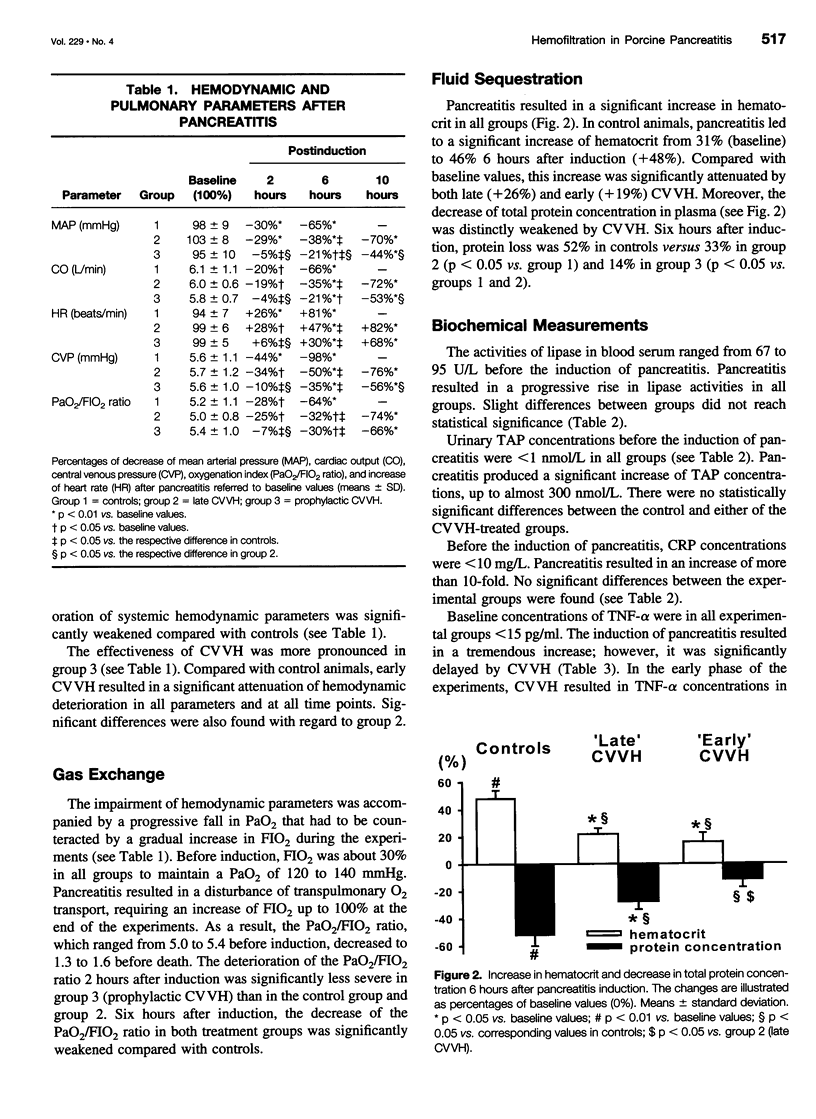
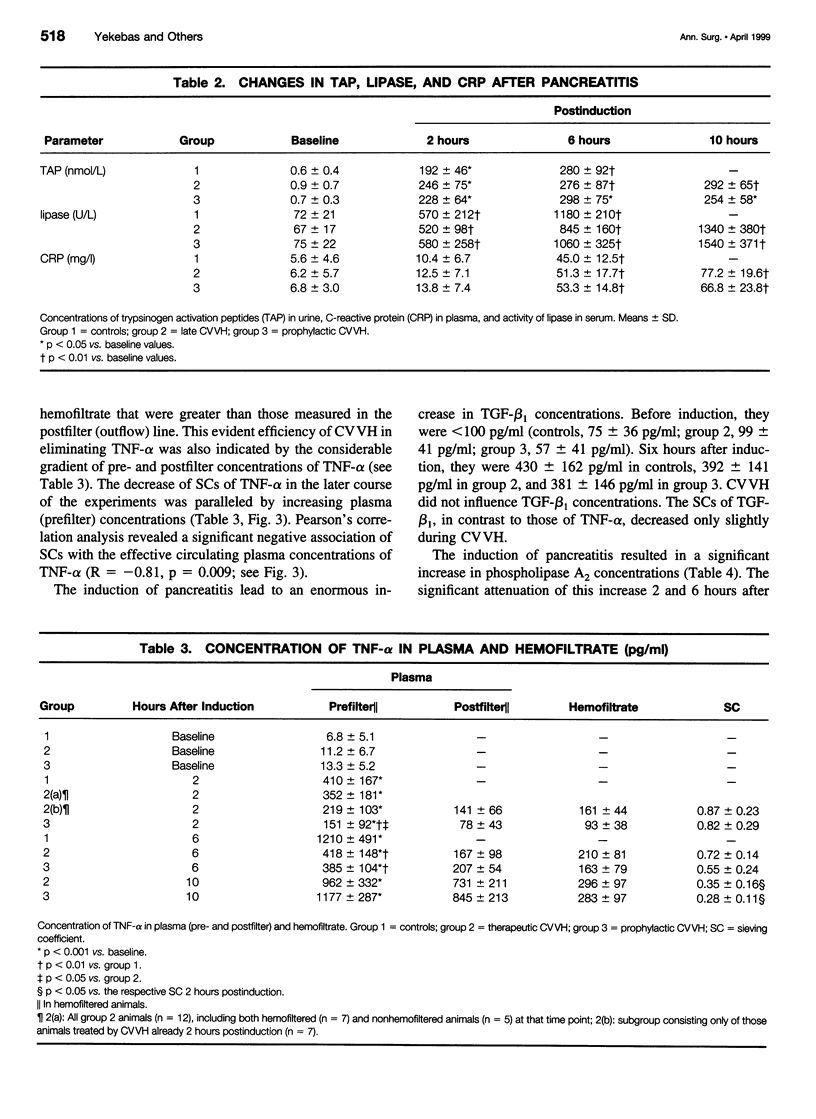
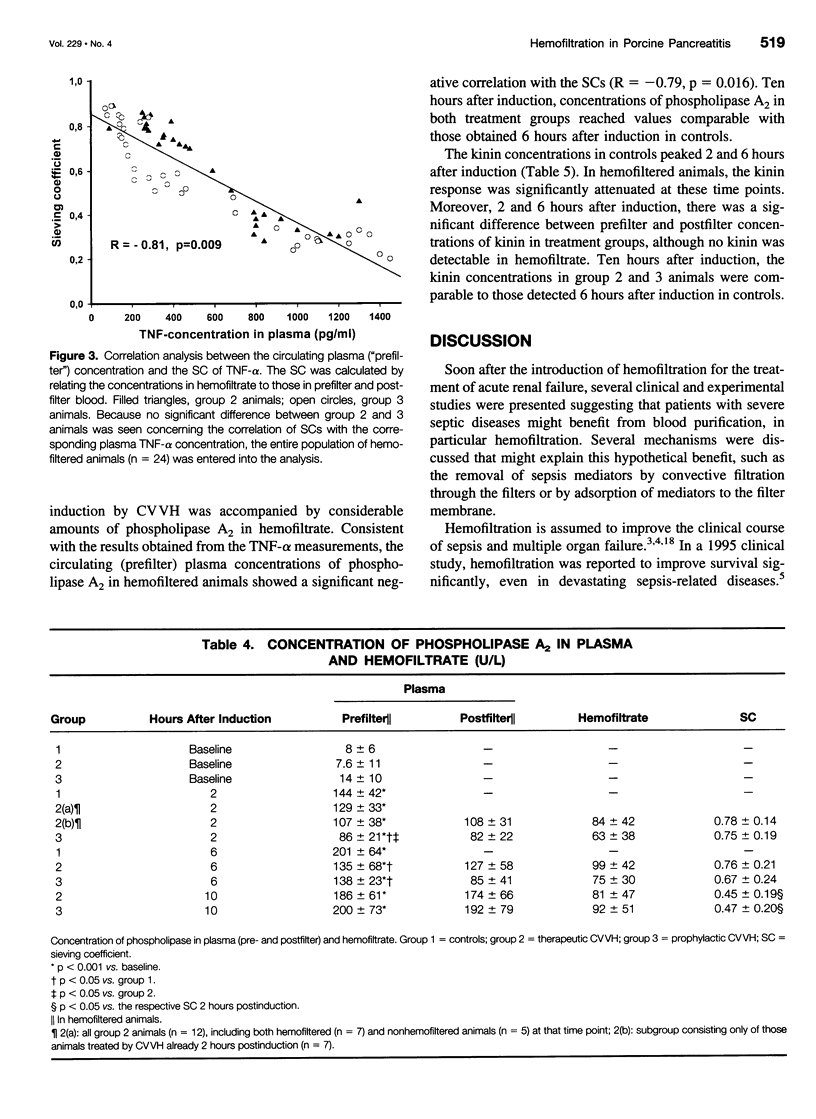
OBJECTIVE: To examine the impact of continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH) on the course of experimental pancreatitis in pigs. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: The activation of different mediator cascades is assumed to trigger multiple organ dysfunction or failure during necrotizing pancreatitis. CVVH has been suggested to be beneficial in those instances by eliminating several inflammatory mediators released in the circulation. METHODS: Pancreatitis was induced by a combined intraductal injection of sodium taurocholate and enterokinase. Control group animals received no treatment after induction. A second group underwent "therapeutic" CVVH after a 20% decline of mean arterial pressure. In the third group, "prophylactic" CVVH was started simultaneously with the induction of pancreatitis. The concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, transforming growth factor-beta1, kinin, and phospholipase A2 were measured at different time points in blood (pre- and postfilter) and in the hemofiltrate to calculate the respective sieving coefficients that reflect most accurately the plasma clearance of mediators by CVVH. RESULTS: Survival time was significantly prolonged both by therapeutic and prophylactic CVVH; it was more pronounced in the latter. CVVH did not influence the increase in transforming growth factor concentrations. However, 6 hours after induction, the increases of plasma concentrations of tumor necrosis factor, phospholipase, and kinin were significantly weakened by CVVH compared with controls. In the treatment groups, the plasma concentrations of tumor necrosis factor and phospholipase showed a significant negative correlation with the respective sieving coefficients, which decreased in the later course of the experiments. CONCLUSIONS: Experimental necrotizing pancreatitis was associated with a tremendous increase of plasma concentrations of tumor necrosis factor, phospholipase, and kinin. The effective removal of these mediators by CVVH resulted in significantly improved survival time. Animals that received prophylactic CVVH had a longer survival period than those in which CVVH was started after clinical impairment. The decreasing efficiency of CVVH in eliminating inflammatory mediators in the later course of the experiments suggested that the filter membranes were compromised by long-term application. These findings provide further evidence that CVVH offers therapeutic options even in the absence of conventional indications for blood-purifying treatments.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho H. J., Ahola R. A., Tolvanen A. M., Nevalainen T. J. Experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Changes in pulmonary phospholipids during sodium taurocholate-induced acute pancreatitis. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1983;182(1):79–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01852290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barzilay E., Kessler D., Berlot G., Gullo A., Geber D., Ben Zeev I. Use of extracorporeal supportive techniques as additional treatment for septic-induced multiple organ failure patients. Crit Care Med. 1989 Jul;17(7):634–637. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198907000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo R., Martin H., Parkin G., Love J., Kearley Y., Boyce N. Continuous arteriovenous haemodiafiltration in the critically ill: influence on major nutrient balances. Intensive Care Med. 1991;17(7):399–402. doi: 10.1007/BF01720677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo R., Tipping P., Boyce N. Continuous veno-venous hemofiltration with dialysis removes cytokines from the circulation of septic patients. Crit Care Med. 1993 Apr;21(4):522–526. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199304000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinzler L., Hausser J., Bödeker H., Zaune U., Martin E., Gebhardt C. Conservative treatment of severe necrotizing pancreatitis using early continuous venovenous hemofiltration. Contrib Nephrol. 1991;93:234–236. doi: 10.1159/000420226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. W., Jacobs S., Lee B. Predicting outcome among intensive care unit patients using computerised trend analysis of daily Apache II scores corrected for organ system failure. Intensive Care Med. 1988;14(5):558–566. doi: 10.1007/BF00263530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coraim F. J., Coraim H. P., Ebermann R., Stellwag F. M. Acute respiratory failure after cardiac surgery: clinical experience with the application of continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration. Crit Care Med. 1986 Aug;14(8):714–718. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198608000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Cruz L., Navarro S., Valderrama R., Sáenz A., Guarner L., Aparisi L., Espi A., Jaurietta E., Marruecos L., Gener J. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis: a multicenter study. Hepatogastroenterology. 1994 Apr;41(2):185–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt C., Bödeker H., Blinzler L., Kraus D., Hergdt G. Wandel in der Therapie der schweren akuten Pankreatitis. Chirurg. 1994 Jan;65(1):33–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez A., Wang R., Unruh H., Light R. B., Bose D., Chau T., Correa E., Mink S. hemofiltration reverses left ventricular dysfunction during sepsis in dogs. Anesthesiology. 1990 Oct;73(4):671–685. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199010000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotloib L., Barzilay E., Shustak A., Lev A. Sequential hemofiltration in nonoliguric high capillary permeability pulmonary edema of severe sepsis: preliminary report. Crit Care Med. 1984 Nov;12(11):997–1000. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198411000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotloib L., Barzilay E., Shustak A., Wais Z., Jaichenko J., Lev A. Hemofiltration in septic ARDS. The artificial kidney as an artificial endocrine lung. Resuscitation. 1986 Jan;13(2):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0300-9572(86)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotloib L., Shostak A., Lev A., Fudin R., Jaichenko J. Treatment of surgical and non-surgical septic multiorgan failure with bicarbonate hemodialysis and sequential hemofiltration. Intensive Care Med. 1995 Feb;21(2):104–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01726531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griesbacher T., Tiran B., Lembeck F. Pathological events in experimental acute pancreatitis prevented by the bradykinin antagonist, Hoe 140. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):405–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld A. B. Septic shock and multiple organ failure: treatment with haemofiltration? Intensive Care Med. 1990;16(8):489–490. doi: 10.1007/BF01709397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grootendorst A. F., van Bommel E. F., van der Hoven B., van Leengoed L. A., van Osta A. L. High volume hemofiltration improves right ventricular function in endotoxin-induced shock in the pig. Intensive Care Med. 1992;18(4):235–240. doi: 10.1007/BF01709839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudgeon A. M., Heath D. I., Hurley P., Jehanli A., Patel G., Wilson C., Shenkin A., Austen B. M., Imrie C. W., Hermon-Taylor J. Trypsinogen activation peptides assay in the early prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 1990 Jan 6;335(8680):4–8. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90135-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guice K. S., Oldham K. T., Wolfe R. R., Simon R. H. Lung injury in acute pancreatitis: primary inhibition of pulmonary phospholipid synthesis. Am J Surg. 1987 Jan;153(1):54–61. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(87)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann G. E., Neumann U. Modified photometric method for the determination of phospholipase A activities. Klin Wochenschr. 1989 Feb 1;67(3):106–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01711332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley P. R., Cook A., Jehanli A., Austen B. M., Hermon-Taylor J. Development of radioimmunoassays for free tetra-L-aspartyl-L-lysine trypsinogen activation peptides (TAP). J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jul 22;111(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karanjia N. D., Widdison A. L., Jehanli A., Hermon-Taylor J., Reber H. A. Assay of trypsinogen activation in the cat experimental model of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 1993 Mar;8(2):189–195. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199303000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus W. A., Draper E. A., Wagner D. P., Zimmerman J. E. Prognosis in acute organ-system failure. Ann Surg. 1985 Dec;202(6):685–693. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198512000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. A., Matson J. R., Pryor R. W., Hinshaw L. B. Continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration therapy for Staphylococcus aureus-induced septicemia in immature swine. Crit Care Med. 1993 Jun;21(6):914–924. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199306000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciver A. G., Metcalfe I. L., Possmayer F., Harding P. G., Passi R. B. Alteration of surfactant chemistry in experimental hemorrhagic pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 1977 Nov;23(5):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(77)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. P., Jenny M. E., Haessler H. Phospholipids, acute pancreatitis, and the lungs: effect of lecithinase infusion on pulmonary surface activity in dogs. Ann Surg. 1968 Mar;167(3):329–335. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196803000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtaugh M. P. Porcine cytokines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;43(1-3):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco C., Tetta C., Lupi A., Galloni E., Bettini M. C., Sereni L., Mariano F., DeMartino A., Montrucchio G., Camussi G. Removal of platelet-activating factor in experimental continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration. Crit Care Med. 1995 Jan;23(1):99–107. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199501000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staubach K. H., Rau H. G., Kooistra A., Schardey H. M., Hohlbach G., Schilberg F. W. Can hemofiltration increase survival time in acute endotoxemia--a porcine shock model. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;308:821–826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storck M., Hartl W. H., Zimmerer E., Inthorn D. Comparison of pump-driven and spontaneous continuous haemofiltration in postoperative acute renal failure. Lancet. 1991 Feb 23;337(8739):452–455. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93393-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL W. C., ZIEVE L. A rapid and sensitive turbidimetric method for serum lipase based upon differences between the lipases of normal and pancreatitis serum. Clin Chem. 1963 Apr;9:168–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]