Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the accuracy of technetium-99m-labeled polyethylene glycol-coated liposomes (99mTc-PEG liposomes) and technetium-99m-labeled nonspecific human immunoglobulin G (99mTc-HYNIC IgG) for the scintigraphic detection of experimental intraabdominal abscesses in comparison with that of a standard agent, gallium-67 citrate. BACKGROUND: Scintigraphic imaging techniques can be very useful for the rapid and accurate localization of intraabdominal abscesses. Two newly developed radiolabeled agents, 99mTc-PEG liposomes and 99mTc-HYNIC IgG, have shown to be excellent agents for imaging experimental focal infection, but have not yet been studied in the detection of abdominal abscesses. METHODS: Intraabdominal abscesses were induced in 42 rats using the cecal ligation and puncture technique. Seven days later, randomized groups of rats received 99mTc-PEG liposomes, 99mTc-HYNIC IgG, or 67Ga citrate intravenously. The rats were imaged up to 24 hours after the injection. The biodistribution of the radiolabel was determined by counting dissected tissues ex vivo. Macroscopic intraabdominal abnormalities and focal uptake on the images were independently scored on a semiquantitative scale. RESULTS: 99mTc-PEG liposomes provided the earliest scintigraphic visualization of the abscess (as soon as 2 hours after the injection vs. 4 hours for the other two agents). Liposomes, IgG, and gallium all showed similarly high absolute uptake in the abscess. Focal uptake of liposomes and gallium correlated best with the extent of the macroscopic abnormalities. CONCLUSIONS: 99mTc-PEG liposomes and 99mTc-HYNIC IgG performed at least as well as the standard agent, 67Ga citrate, in the detection of experimental intraabdominal abscesses, with obvious advantages such as lower radiation exposure and more favorable physical properties. Of the two technetium agents, the liposomes seemed to be superior, providing the earliest diagnostic image and the best correlation with the inflammatory abnormalities. In addition, the preferential localization of radiolabeled PEG liposomes holds promise for targeted delivery of liposome-encapsulated drugs.
Full text
PDF


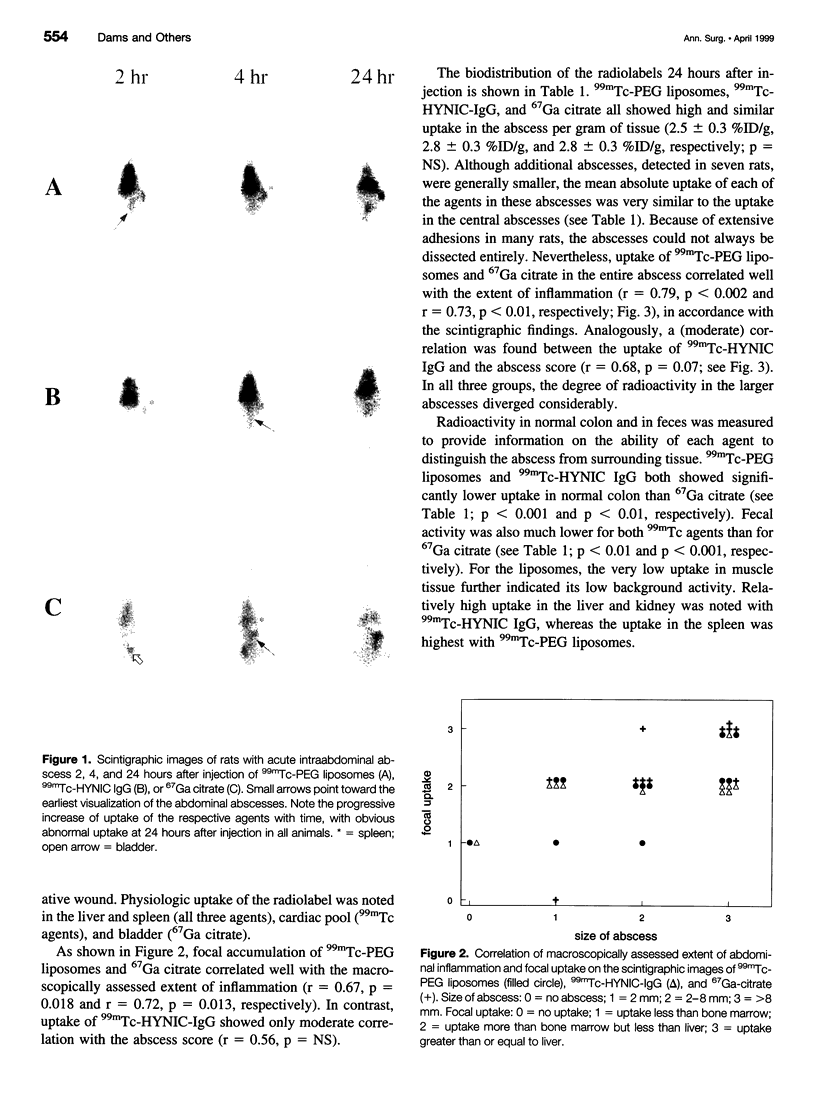
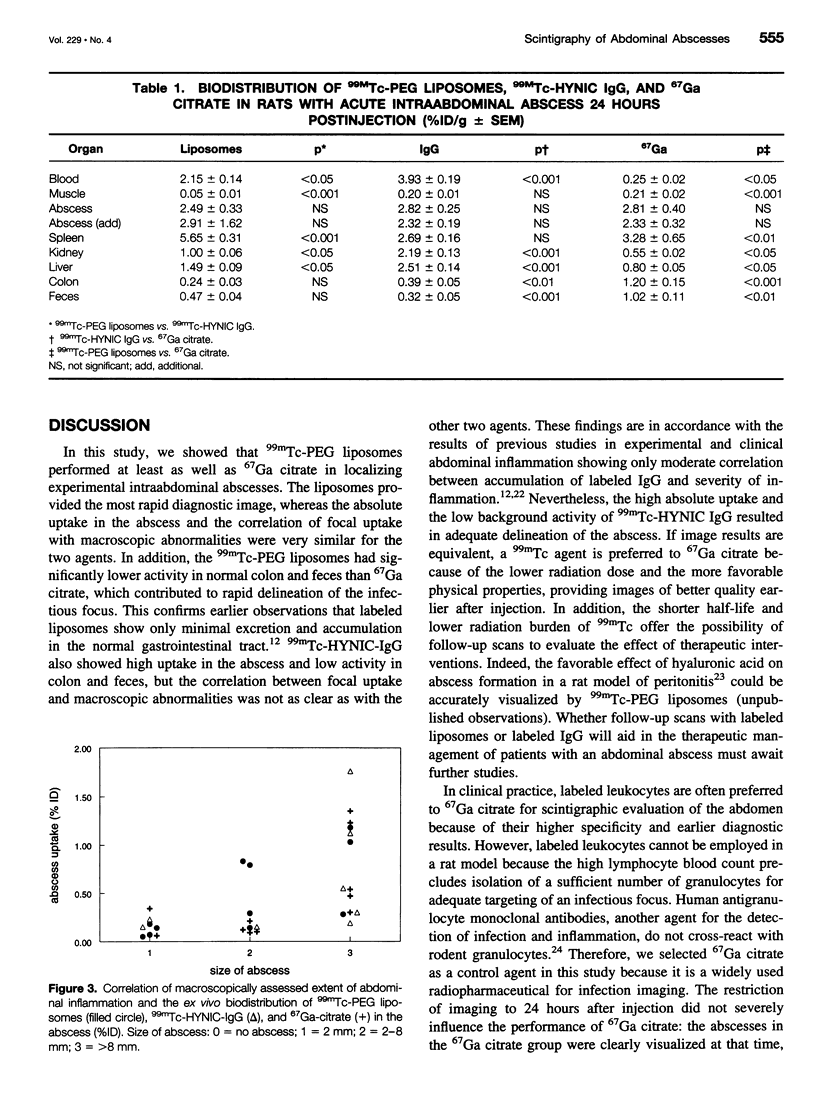


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams M. J., Juweid M., tenKate C. I., Schwartz D. A., Hauser M. M., Gaul F. E., Fuccello A. J., Rubin R. H., Strauss H. W., Fischman A. J. Technetium-99m-human polyclonal IgG radiolabeled via the hydrazino nicotinamide derivative for imaging focal sites of infection in rats. J Nucl Med. 1990 Dec;31(12):2022–2028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arndt J. W., van der Sluys Veer A., Blok D., Griffioen G., Verspaget H. W., Peña A. S., Lamers C. B., Pauwels E. K. A prospective comparison of 99mTc-labeled polyclonal human immunoglobulin and 111In granulocytes for localization of inflammatory bowel disease. Acta Radiol. 1992 Mar;33(2):140–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., Lokerse A. F., ten Kate M. T., Mouton J. W., Woodle M. C., Storm G. Liposomes with prolonged blood circulation and selective localization in Klebsiella pneumoniae-infected lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jul;168(1):164–171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohnen J., Boulanger M., Meakins J. L., McLean A. P. Prognosis in generalized peritonitis. Relation to cause and risk factors. Arch Surg. 1983 Mar;118(3):285–290. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1983.01390030017003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dams E. T., Oyen W. J., Boerman O. C., Claessens R. A., Wymenga A. B., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. Technetium-99m labeled to human immunoglobulin G through the nicotinyl hydrazine derivative: a clinical study. J Nucl Med. 1998 Jan;39(1):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dams E. T., Oyen W. J., Boerman O. C., Storm G., Laverman P., Koenders E. B., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. Technetium-99m-labeled liposomes to image experimental colitis in rabbits: comparison with technetium-99m-HMPAO-granulocytes and technetium-99m-HYNIC-IgG. J Nucl Med. 1998 Dec;39(12):2172–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datz F. L. Abdominal abscess detection: gallium, 111In-, and 99mTc-labeled leukocytes, and polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. Semin Nucl Med. 1996 Jan;26(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(96)80016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. E., Garrison R. N., Heitsch R. C., Calhoun K., Polk H. C., Jr Determinants of death in patients with intraabdominal abscess. Surgery. 1980 Oct;88(4):517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. E. Noninvasive imaging tests in the diagnosis and treatment of intra-abdominal abscesses in the postoperative patient. Surg Clin North Am. 1994 Jun;74(3):693–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardi P. D., Hoffer P. B., Rosenfield A. T. Correlative imaging in abdominal infection: an algorithmic approach using nuclear medicine, ultrasound, and computed tomography. Semin Nucl Med. 1988 Oct;18(4):320–334. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(88)80041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantto E. Investigation of suspected intra-abdominal sepsis: the contribution of nuclear medicine. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1994;203:11–14. doi: 10.3109/00365529409091389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverman P., Dams E. T., Oyen W. J., Storm G., Koenders E. B., Prevost R., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H., Boerman O. C. A novel method to label liposomes with 99mTc by the hydrazino nicotinyl derivative. J Nucl Med. 1999 Jan;40(1):192–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan G. J., Anderson I. D., Grant I. S., Fearon K. C. Outcome of patients with abdominal sepsis treated in an intensive care unit. Br J Surg. 1995 Apr;82(4):524–529. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800820429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. S., Wilson S. E. Intraabdominal abscesses: image-guided diagnosis and therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 1996 Jul;23(1):28–36. doi: 10.1093/clinids/23.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrell E. M., Tompkins R. G., Fischman A. J., Wilkinson R. A., Burke J. F., Rubin R. H., Strauss H. W., Yarmush M. L. Autoradiographic method for quantitation of radiolabeled proteins in tissues using indium-111. J Nucl Med. 1989 Sep;30(9):1538–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyen W. J., Boerman O. C., Storm G., van Bloois L., Koenders E. B., Claessens R. A., Perenboom R. M., Crommelin D. J., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. Detecting infection and inflammation with technetium-99m-labeled Stealth liposomes. J Nucl Med. 1996 Aug;37(8):1392–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyen W. J., Boerman O. C., van der Laken C. J., Claessens R. A., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. The uptake mechanisms of inflammation- and infection-localizing agents. Eur J Nucl Med. 1996 Apr;23(4):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF01247377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyen W. J., Claessens R. A., van Horn J. R., van der Meer J. W., Corstens F. H. Scintigraphic detection of bone and joint infections with indium-111-labeled nonspecific polyclonal human immunoglobulin G. J Nucl Med. 1990 Apr;31(4):403–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palestro C. J. The current role of gallium imaging in infection. Semin Nucl Med. 1994 Apr;24(2):128–141. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(05)80227-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels E. K., McCready V. R., Stoot J. H., van Deurzen D. F. The mechanism of accumulation of tumour-localising radiopharmaceuticals. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998 Mar;25(3):277–305. doi: 10.1007/s002590050229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. T., Rudolph A. S., Goins B., Timmons J. H., Klipper R., Blumhardt R. A simple method for producing a technetium-99m-labeled liposome which is stable in vivo. Int J Rad Appl Instrum B. 1992 Jul;19(5):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0883-2897(92)90149-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotstein O. D., Kao J. Prevention of intra-abdominal abscesses by fibrinolysis using recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):766–772. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schölmerich J., Schmidt E., Schümichen C., Billmann P., Schmidt H., Gerok W. Scintigraphic assessment of bowel involvement and disease activity in Crohn's disease using technetium 99m-hexamethyl propylene amine oxine as leukocyte label. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1287–1293. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabold J. E., Wilson D. G., Lieberman L. M., Boyd C. M. Unsuspected extra-abdominal sites of infection: scintigraphic detection with indium-111-labeled leukocytes. Radiology. 1984 Apr;151(1):213–217. doi: 10.1148/radiology.151.1.6701317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vipond M. N., Whawell S. A., Thompson J. N., Dudley H. A. Peritoneal fibrinolytic activity and intra-abdominal adhesions. Lancet. 1990 May 12;335(8698):1120–1122. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91125-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichterman K. A., Baue A. E., Chaudry I. H. Sepsis and septic shock--a review of laboratory models and a proposal. J Surg Res. 1980 Aug;29(2):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(80)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Goor H., de Graaf J. S., Kooi K., Sluiter W. J., Bom V. J., van der Meer J., Bleichrodt R. P. Effect of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator on intra-abdominal abscess formation in rats with generalized peritonitis. J Am Coll Surg. 1994 Oct;179(4):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



