Abstract
1. By the use of whole-cell and excised-patch tight-seal recording techniques, we studied ionic conductances in voltage-clamped solitary hair cells isolated from the bull-frog's sacculus. As a basis for assessing their contributions to hair cell electrical resonance, we developed kinetic models describing voltage-dependent Ca2+ and Ca2+-dependent K+ conductances. 2. A transient K+ current (IA) was activated by steps to potentials positive to -50 mV from holding potentials more negative than -70 mV. In the steady state, the current was fully inactivated at the normal resting potential. Possibly due to the dissipation of a Donnan potential between the pipette's interior and the cell, the voltage dependence of IA inactivation slowly shifted in the negative direction during whole-cell recording. 3. The voltage-gated Ca2+ current (ICa) was isolated by blocking IA with 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and Ca2+-activated K+ current with tetraethylammonium (TEA). The ICa was activated at potentials more positive than -60 to -50 mV and was maximal at about -10 mV. Its magnitude was highly variable among cells, with an average value of -240 pA at -30 mV. Its activation could be fitted well by a third-order (m3) gating scheme. 4. A Ca2+-activated K+ current (IK(Ca)) was isolated as the component of membrane current blocked by TEA. This current was activated at potentials more positive than -60 to -50 mV and had an average value of 1.5 nA at -30 mV. The Ca2+-activated K+ conductance (gK(Ca)) showed a high apparent voltage dependence, increasing e-fold every 3 mV at potentials between -50 and -40 mV. 5. The Ca2+-activated K+ current displayed rapid activation and deactivation kinetics. The current reached half-maximal activation in 2-4 ms at voltages between -50 and -30 mV, and the tail current decayed exponentially with a time constant of 1.0 ms at -70 mV. The activation rate and magnitude of IK(Ca) were reduced by lowering the extracellular Ca2+ concentration. 6. The open probability of Ca2+-activated K+ channels was estimated by ensemble-fluctuation analysis of whole-cell currents evoked by voltage steps to -30 mV. The average open probability was estimated to be 0.8 at this potential. 7. K+-selective channels with a high conductance (140-200 pS) were examined in excised, inside-out membrane patches. The activity of these channels depended on intracellular Ca2+ and membrane potential. These properties suggest that the channels underlie the whole-cell Ca2+-activated K+ current.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
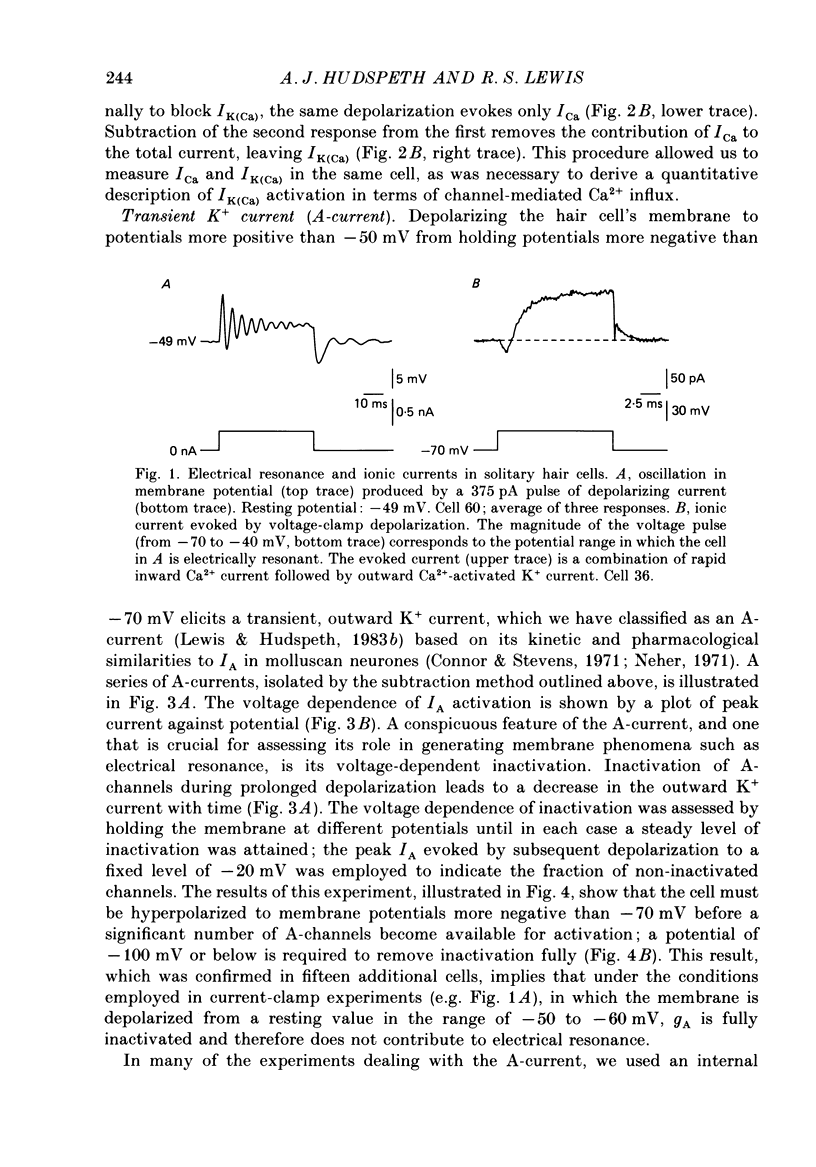
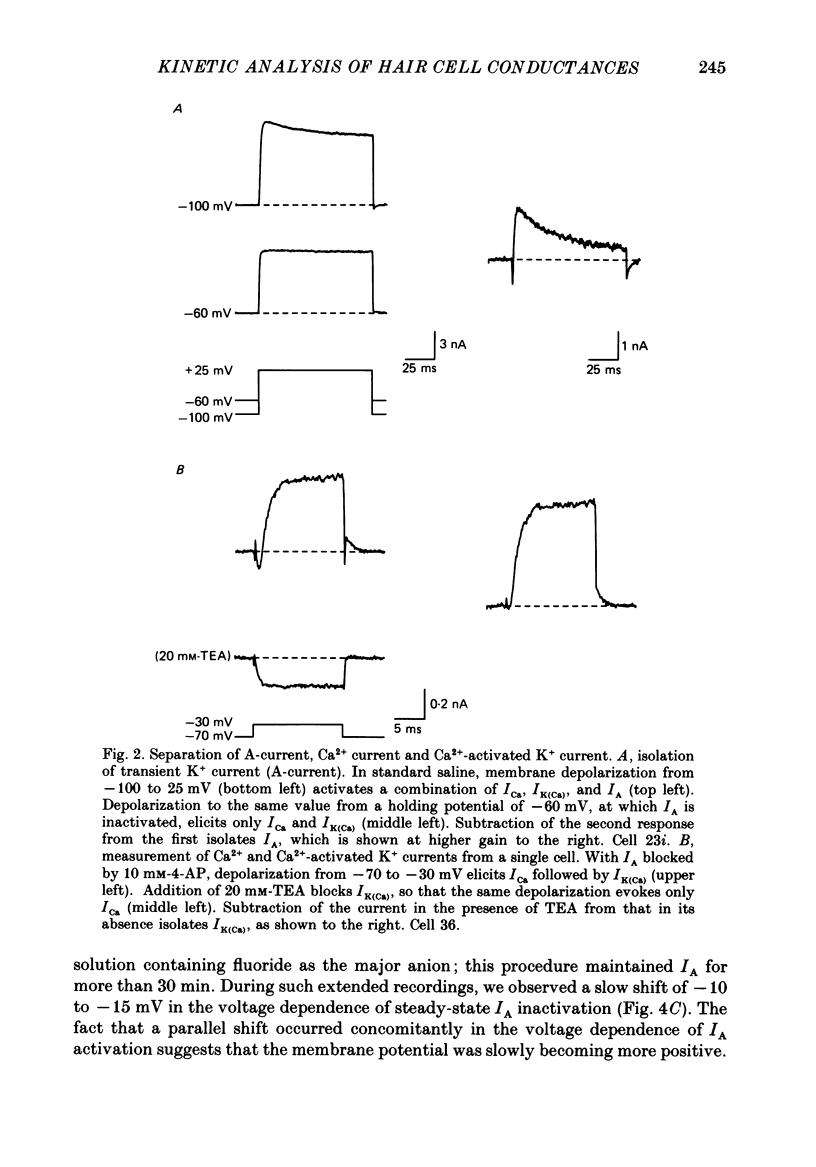
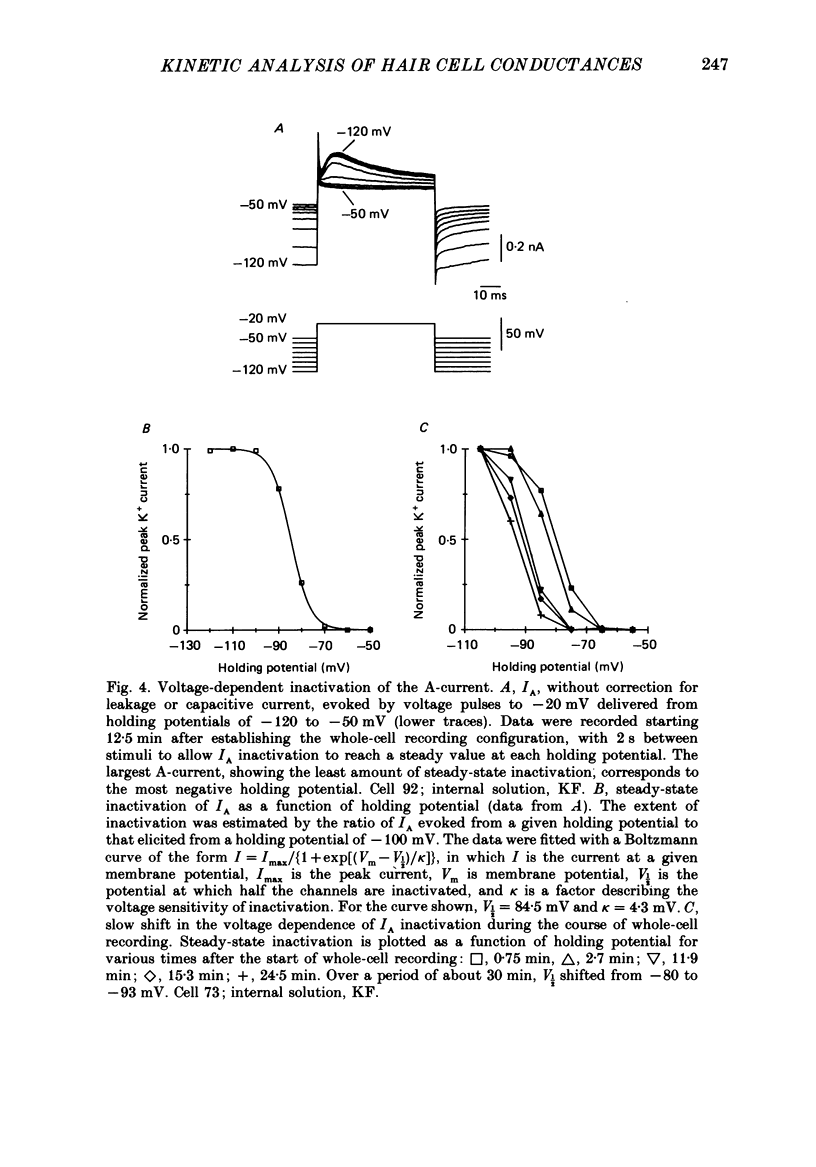
Full text
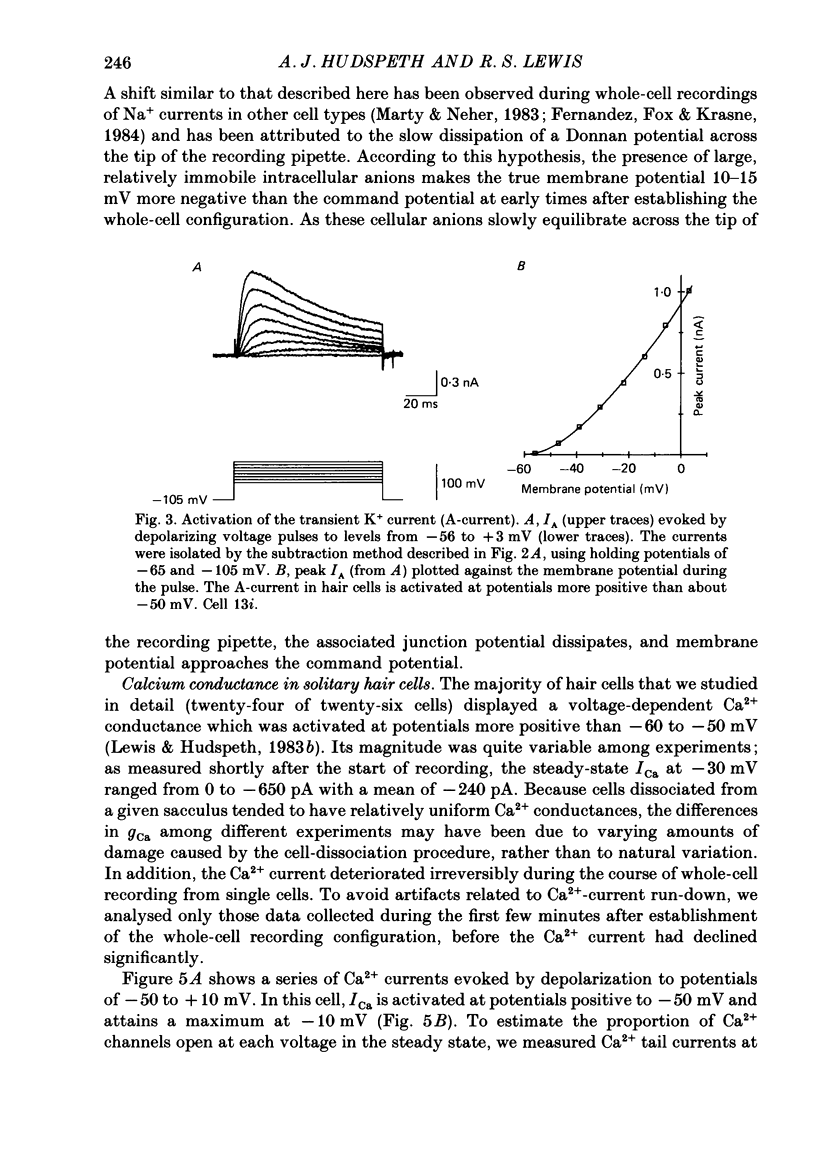
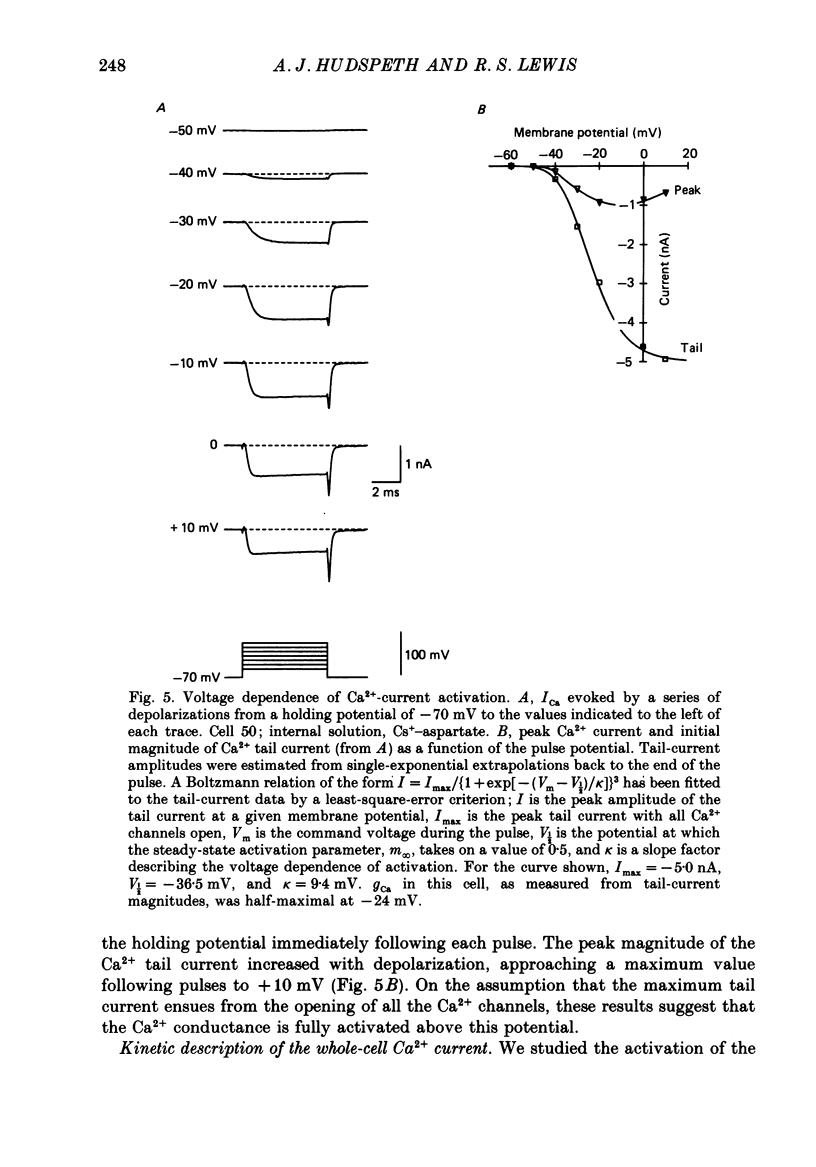
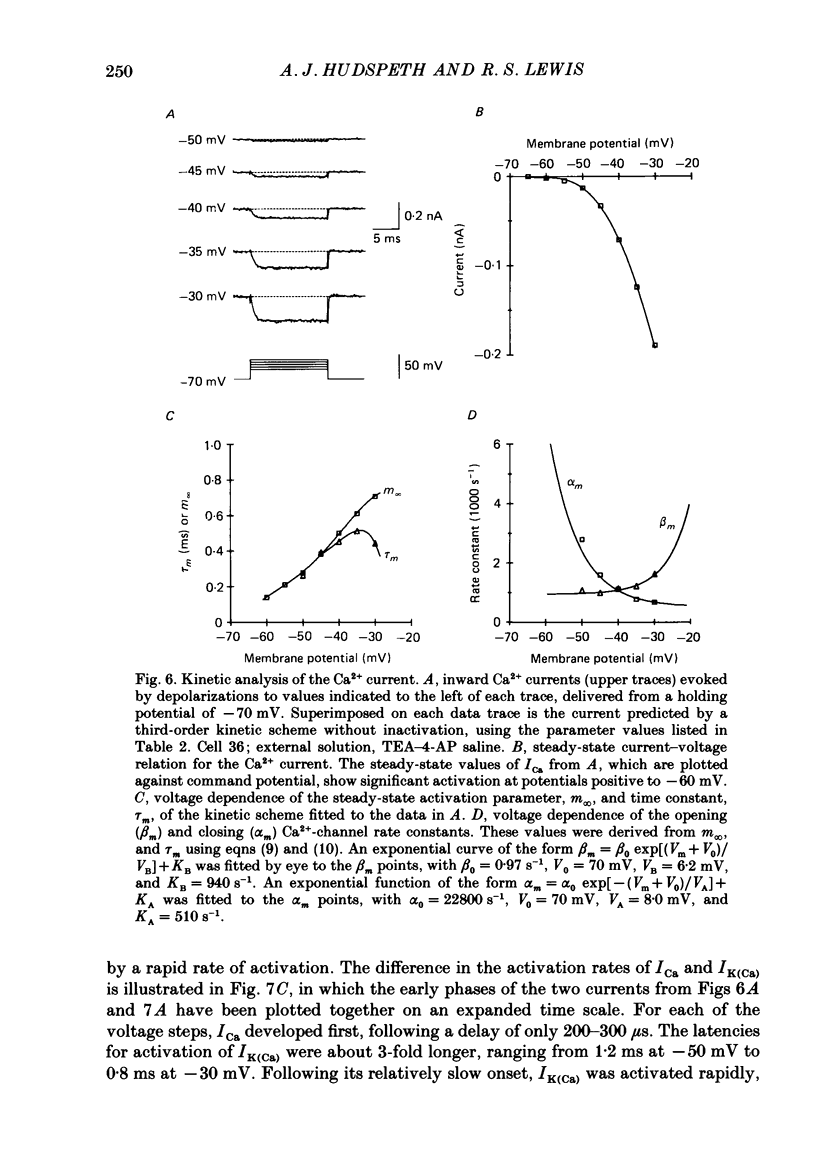
PDF






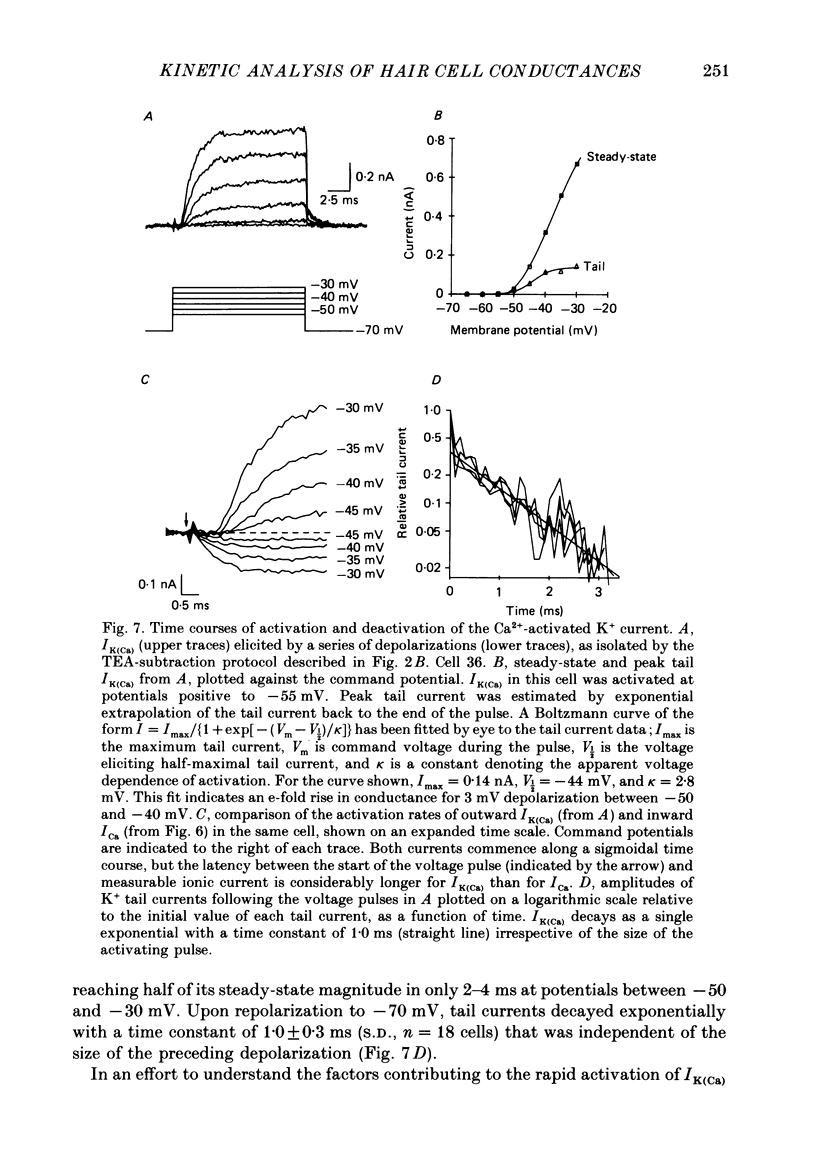
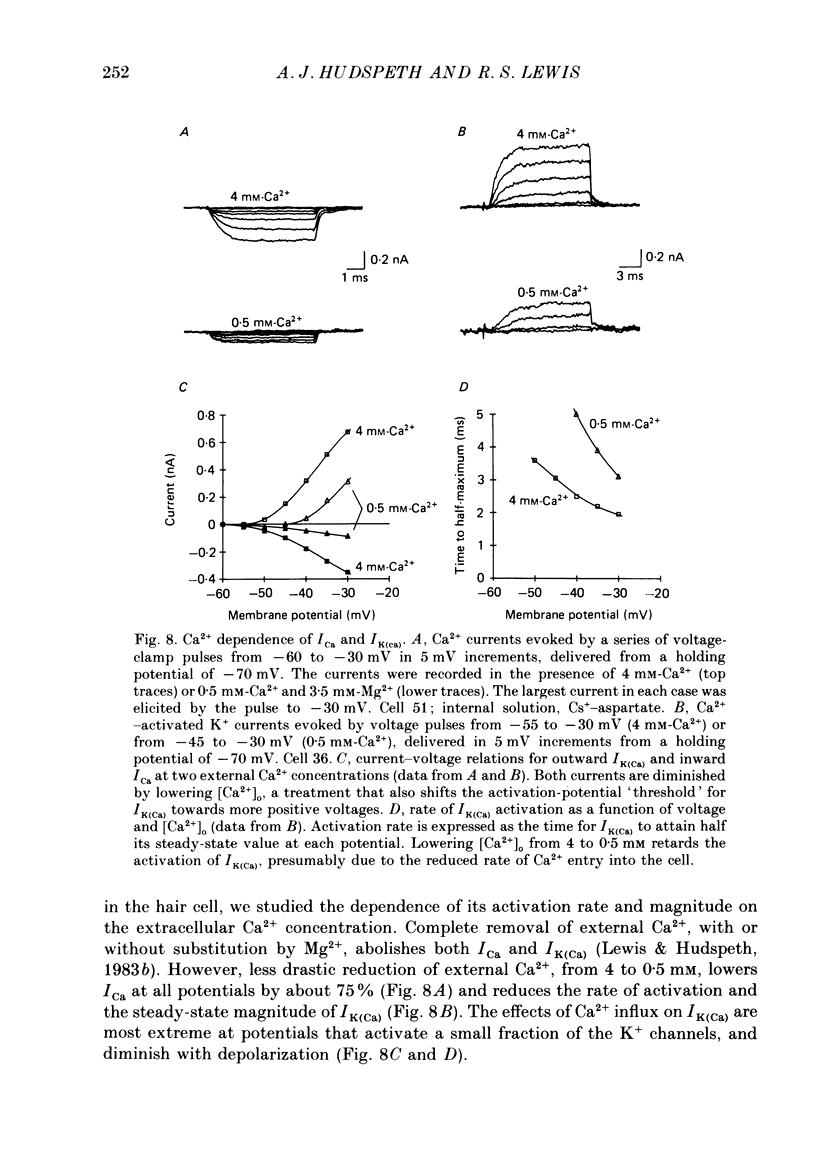

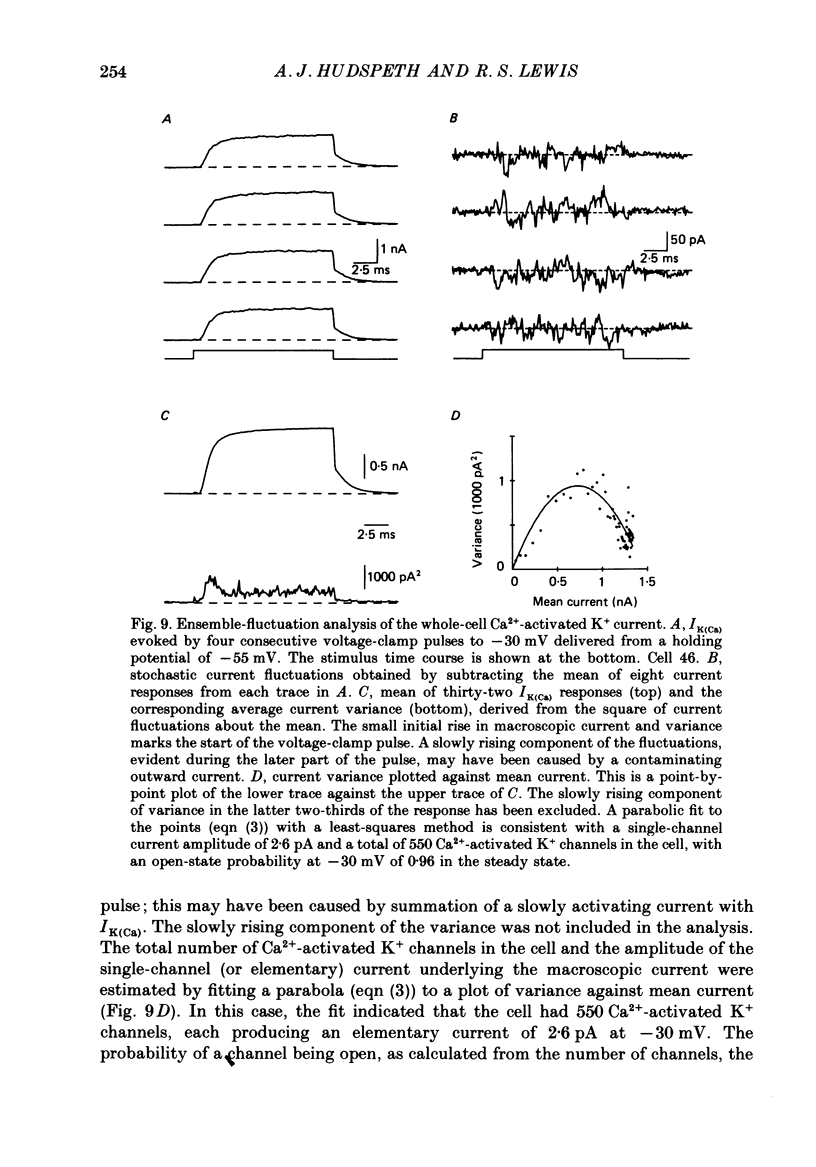

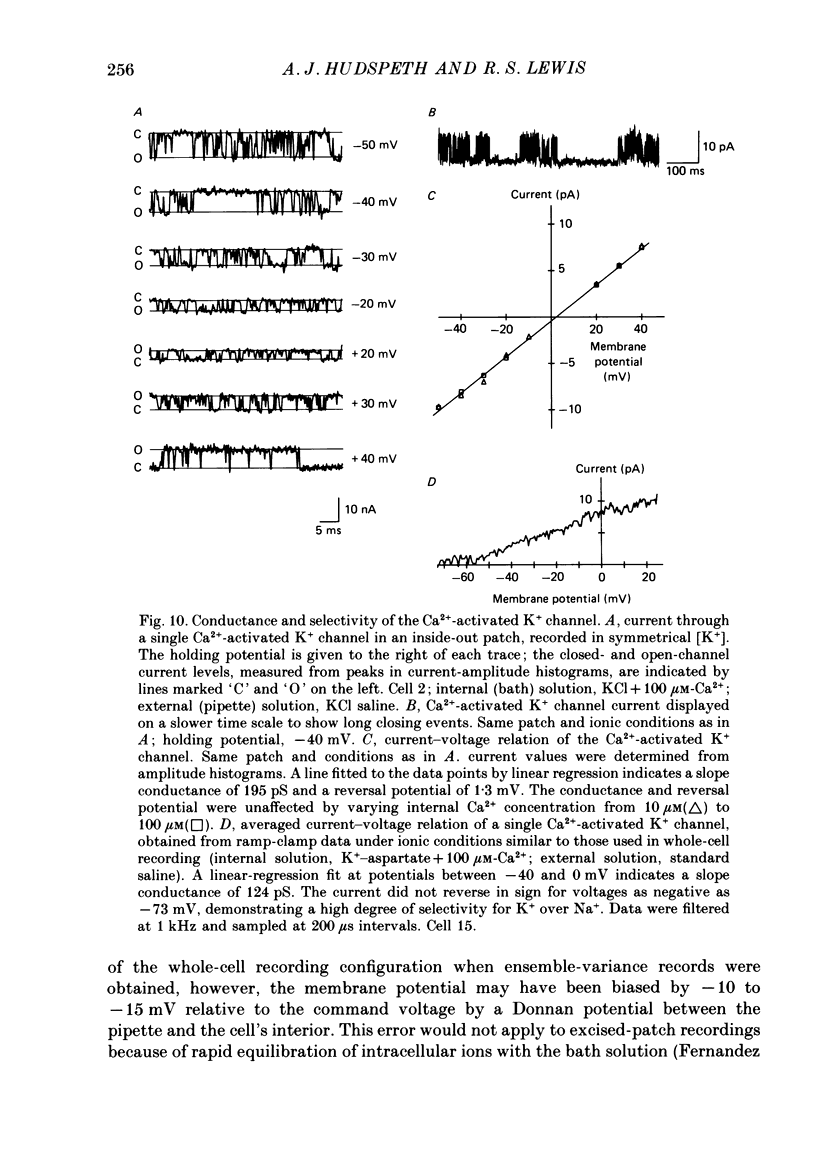
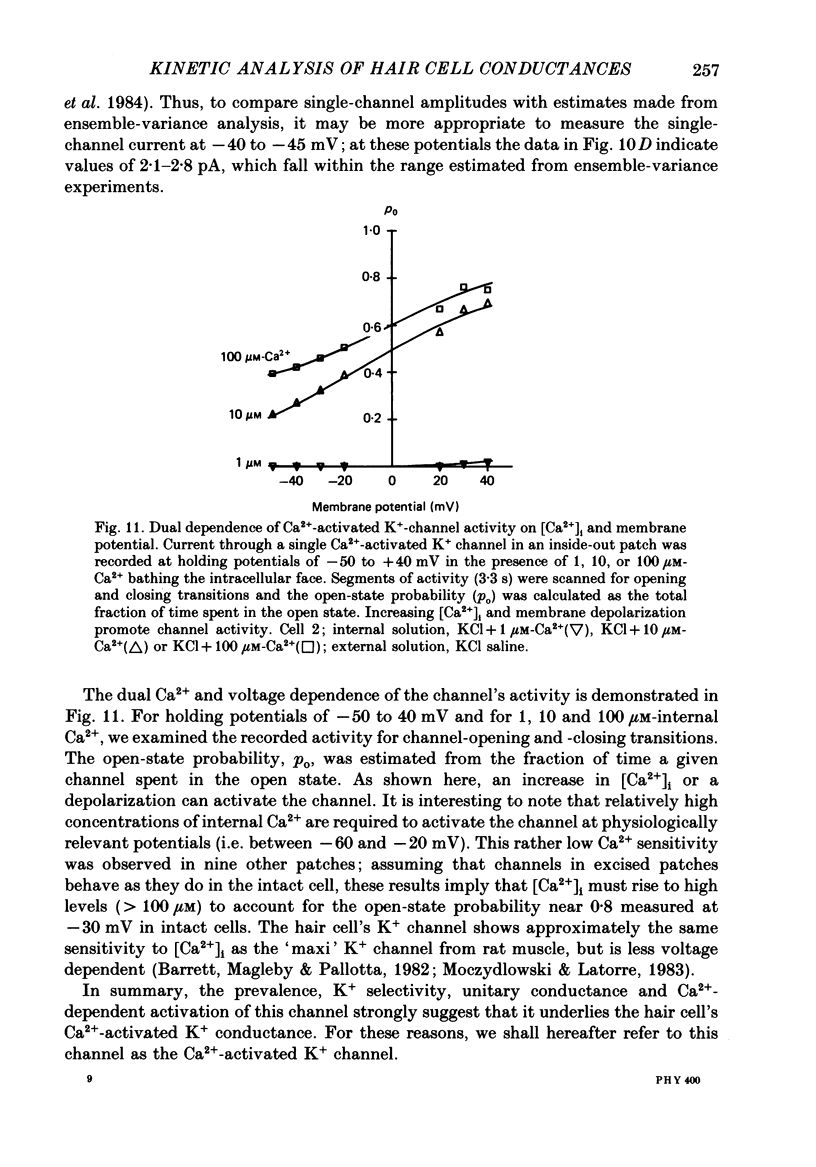


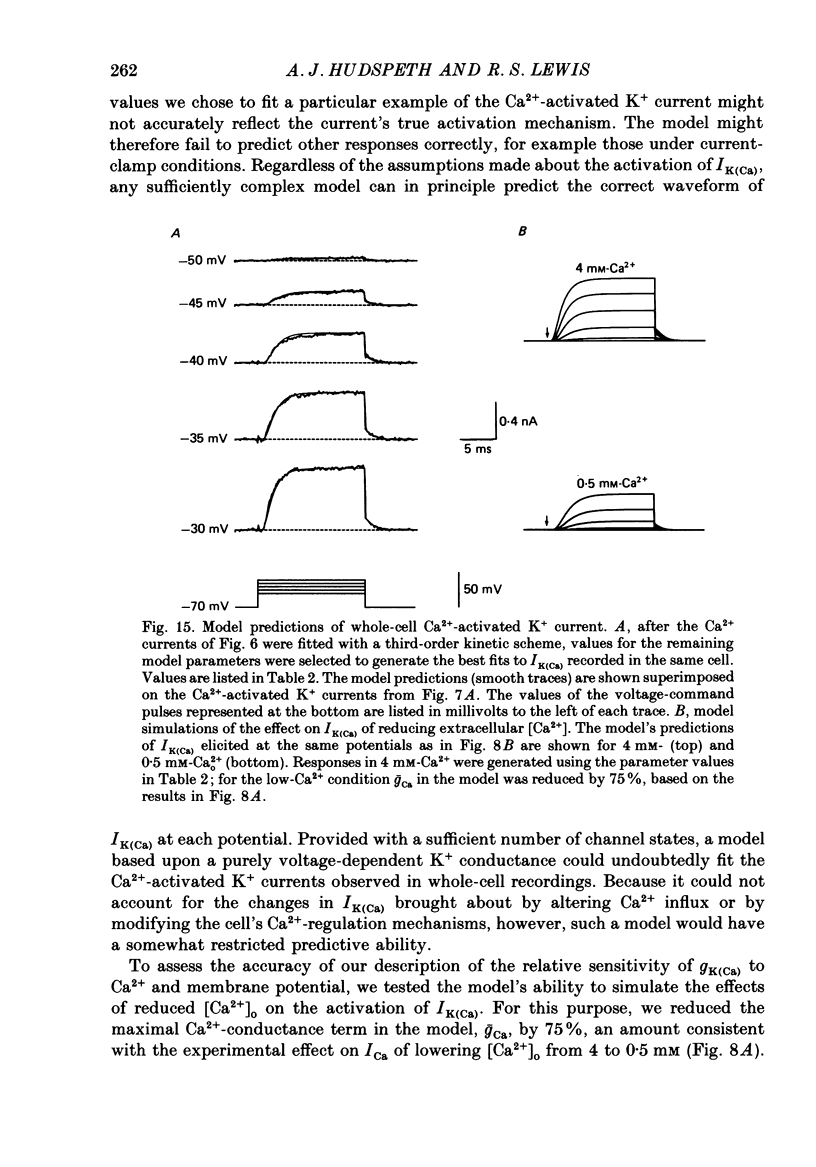












Selected References
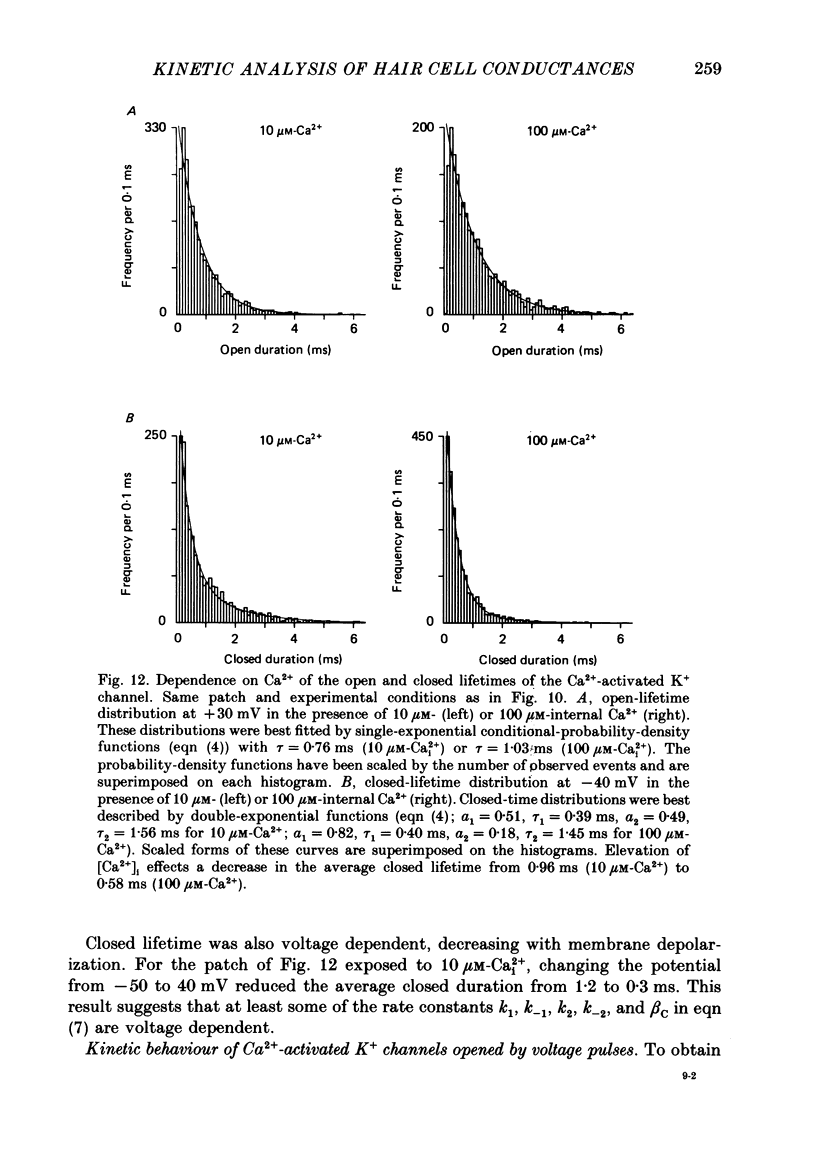
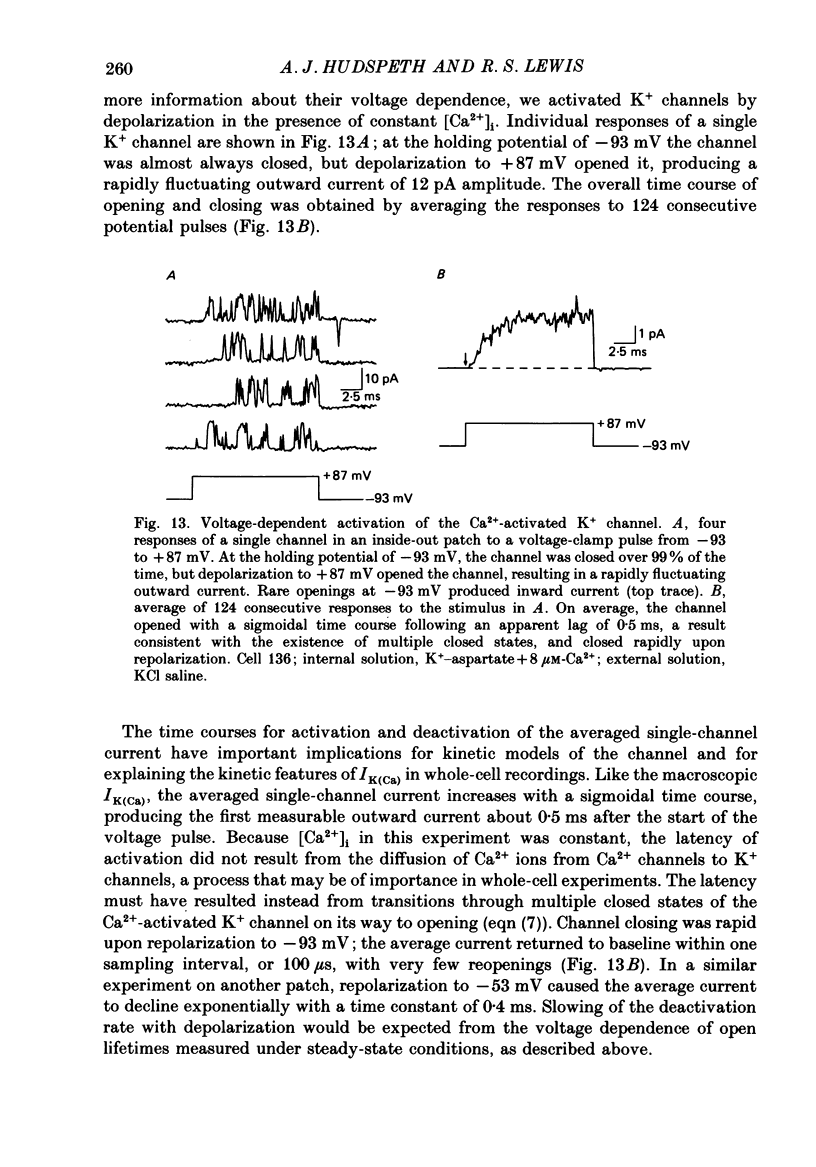
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Measurement of calcium influx under voltage clamp in molluscan neurones using the metallochromic dye arsenazo III. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:61–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Art J. J., Fettiplace R., Fuchs P. A. Synaptic hyperpolarization and inhibition of turtle cochlear hair cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:525–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Art J. J., Fettiplace R. Variation of membrane properties in hair cells isolated from the turtle cochlea. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:207–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore J. F. Frequency tuning in a frog vestibular organ. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):536–538. doi: 10.1038/304536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashmore J. F., Meech R. W. Ionic basis of membrane potential in outer hair cells of guinea pig cochlea. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):368–371. doi: 10.1038/322368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barish M. E., Thompson S. H. Calcium buffering and slow recovery kinetics of calcium-dependent outward current in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:201–219. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M. A simple method for the accurate determination of free [Ca] in Ca-EGTA solutions. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):C404–C408. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.5.C404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A., Adams P. R. Ca-activated potassium current in vertebrate sympathetic neurons. Cell Calcium. 1983 Dec;4(5-6):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Hagiwara S. Calcium currents in internally perfused nerve cell bodies of Limnea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:503–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Yazejian B. Intracellular factors for the maintenance of calcium currents in perfused neurones from the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:631–650. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Slow repetitive activity from fast conductance changes in neurons. Fed Proc. 1978 Jun;37(8):2139–2145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. P., Dubinsky J. M., Schwartz E. A. The calcium current in inner segments of rods from the salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum) retina. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:557–575. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. P., Hudspeth A. J. Ionic basis of the receptor potential in a vertebrate hair cell. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):675–677. doi: 10.1038/281675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. C., Fettiplace R. An electrical tuning mechanism in turtle cochlear hair cells. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:377–412. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. C., Fettiplace R. The frequency selectivity of auditory nerve fibres and hair cells in the cochlea of the turtle. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:79–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky J. M., Oxford G. S. Ionic currents in two strains of rat anterior pituitary tumor cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):309–339. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Fox A. P., Krasne S. Membrane patches and whole-cell membranes: a comparison of electrical properties in rat clonal pituitary (GH3) cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Matsuura S. Adaptive rundown of excitatory post-synaptic potentials at synapses between hair cells and eight nerve fibres in the goldfish. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:193–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Levy S., Nasi E., Tillotson D. Intracellular calcium measured with calcium-sensitive micro-electrodes and Arsenazo III in voltage-clamped Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:127–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Potassium conductance and internal calcium accumulation in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:287–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of calcium channels in rat clonal pituitary cells with patch electrode voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:231–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J., Lewis R. S. A model for electrical resonance and frequency tuning in saccular hair cells of the bull-frog, Rana catesbeiana. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:275–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J. Mechanoelectrical transduction by hair cells in the acousticolateralis sensory system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:187–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J. The cellular basis of hearing: the biophysics of hair cells. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):745–752. doi: 10.1126/science.2414845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J. The ionic channels of a vertebrate hair cell. Hear Res. 1986;22:21–27. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(86)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. S., Hudspeth A. J. Voltage- and ion-dependent conductances in solitary vertebrate hair cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):538–541. doi: 10.1038/304538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Calcium dependence of open and shut interval distributions from calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:585–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Neher E. Potassium channels in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:117–141. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Evidence for two voltage-dependent Ca2+ binding reactions. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):511–542. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. The calcium current and the activation of a slow potassium conductance in voltage-clamped mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:307–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Two fast transient current components during voltage clamp on snail neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jul;58(1):36–53. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H. Studies of ionic currents in the isolated vestibular hair cell of the chick. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:561–581. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Hepler J. R., Oglesby S. A., Harden T. K. A comparison of calcium-activated potassium channel currents in cell-attached and excised patches. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):985–997. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell W. F. The effects of furosemide on the endocochlear potential and auditory-nerve fiber tuning curves in cats. Hear Res. 1984 Jun;14(3):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0378-5955(84)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., MacDermott A. B., Weight F. F. Detection of intracellular Ca2+ transients in sympathetic neurones using arsenazo III. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):350–352. doi: 10.1038/304350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Aequorin response facilitation and intracellular calcium accumulation in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:167–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. A binding-site model for calcium channel inactivation that depends on calcium entry. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 22;217(1206):101–110. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan W. E., Konishi M. Segregation of stimulus phase and intensity coding in the cochlear nucleus of the barn owl. J Neurosci. 1984 Jul;4(7):1787–1799. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-07-01787.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


