Abstract
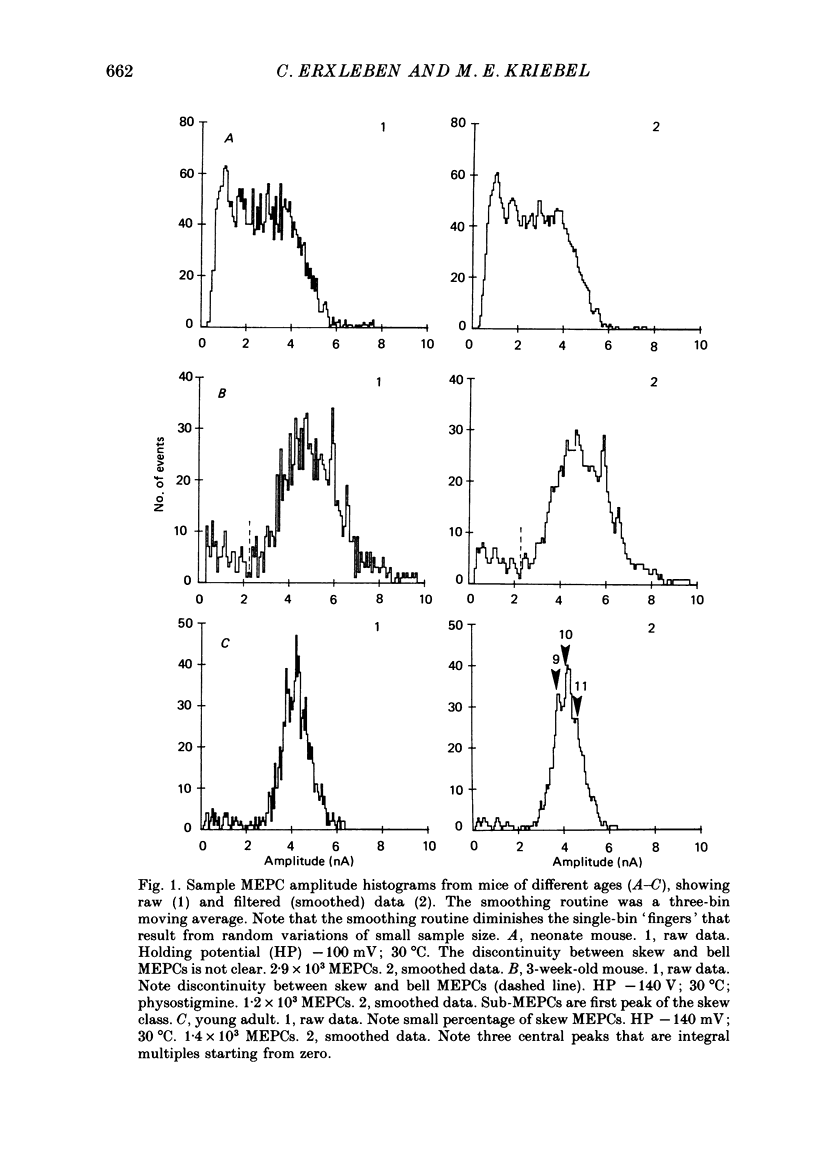
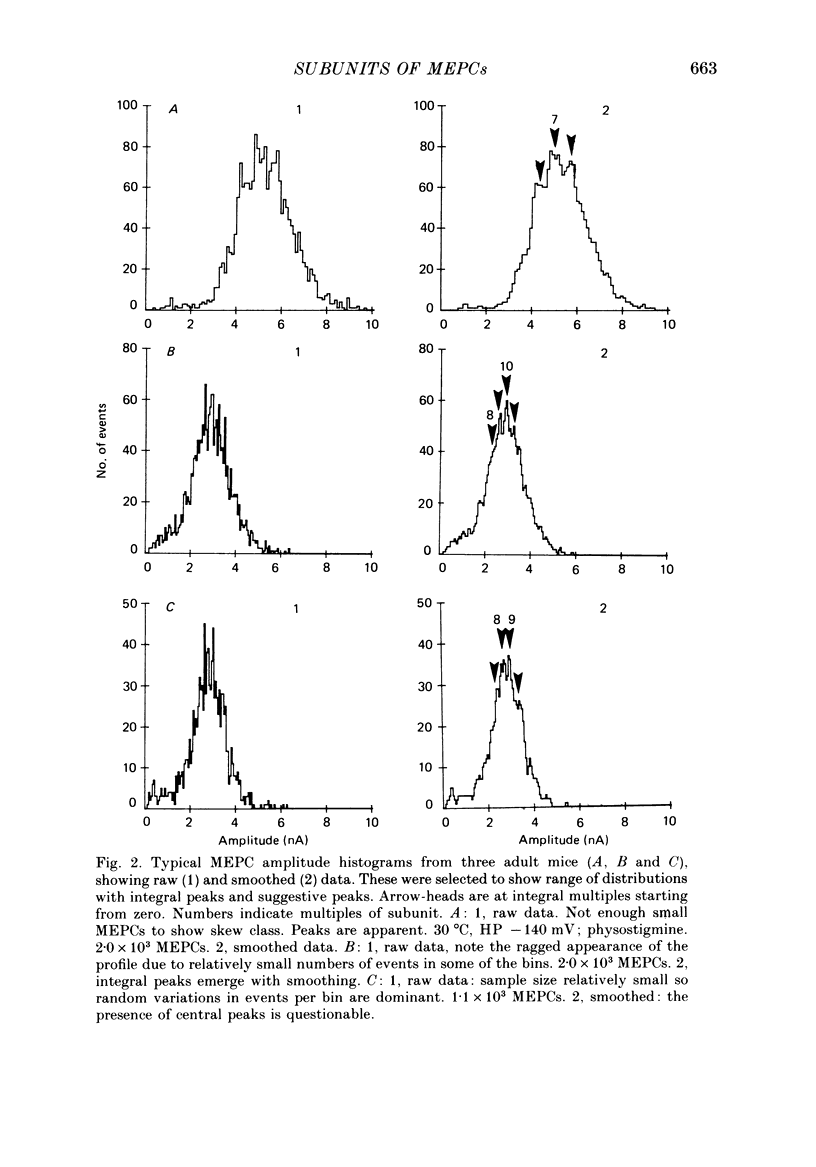
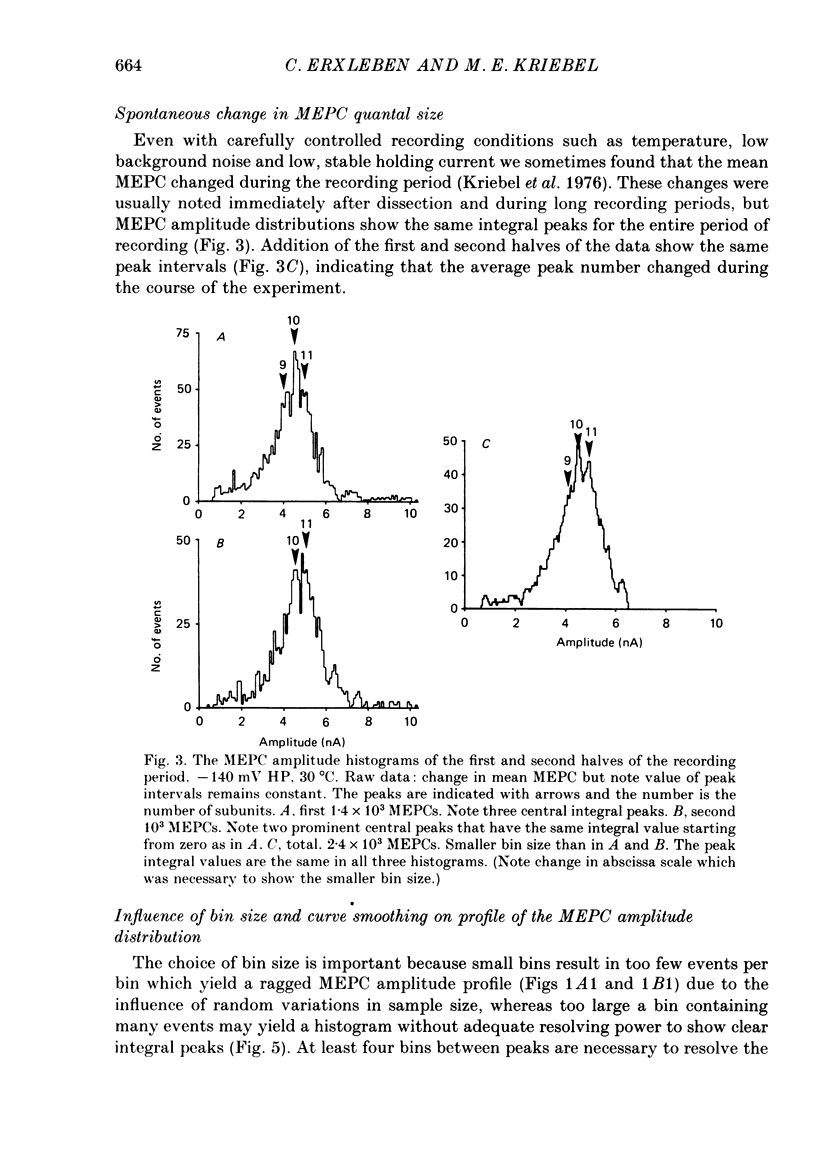
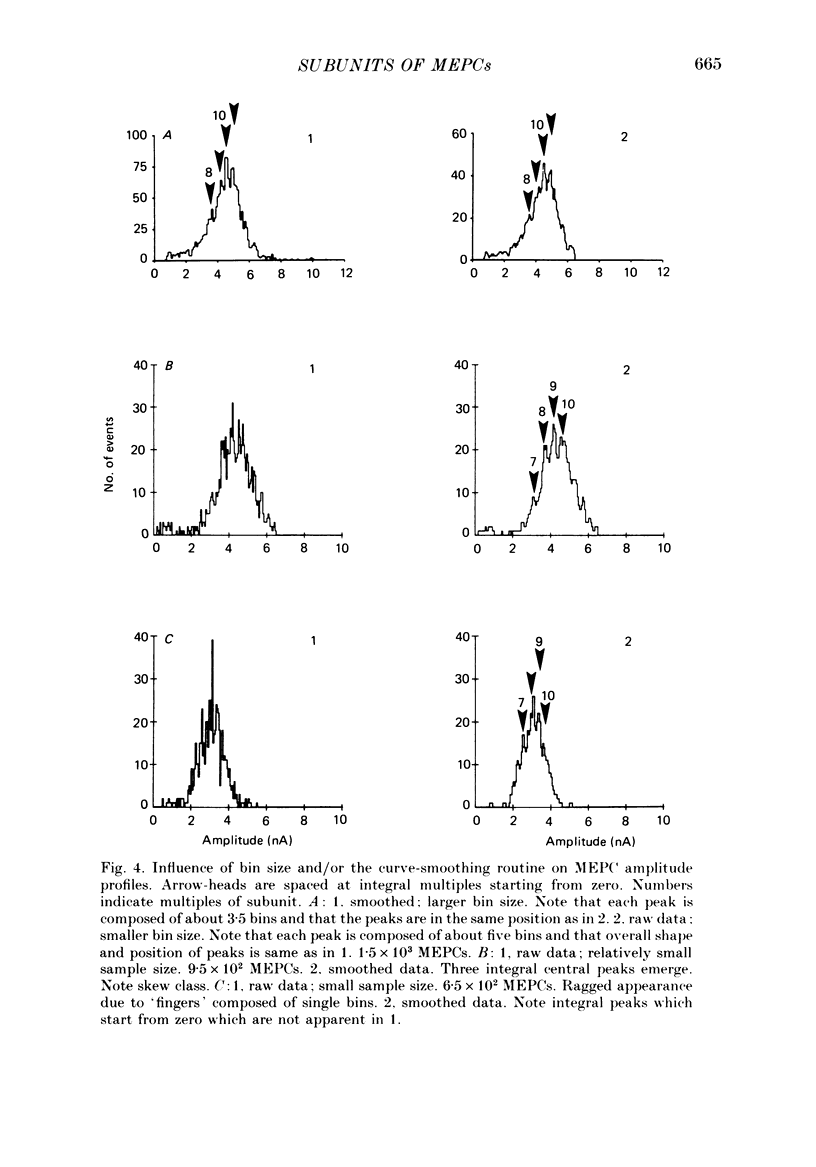
1. Adult, neonate and young mouse diaphragm muscle fibres were voltage clamped with a two-electrode clamp. Miniature end-plate currents (MEPCs) were recorded on magnetic tape and analysed with a computer. The MEPC amplitude, charge, rise time, time-to-peak, decay time constant and root mean square (r.m.s.) noise level were determined for each MEPC. 2. The MEPC amplitude and charge distributions showed integral peaks starting from zero. Peaks were enhanced by selecting MEPCs with uniform time characteristics, with low noise, with increased sample size, with a curve smoothing routine and/or with a selected bin size. 3. Integral peaks were found in histograms from neonate, young and old mice. The ratio of sub-MEPCs to bell MEPCs decreased during neonatal development. 4. The size of the peak intervals was the same in all preparations of the same developmental stage. The adult modal peak varied between 8 and 12 times the subunit value, but peak intervals were similar (0.44 +/- 0.04 nA). 5. Changes in the holding potential or the bath temperature, or addition of an anticholinesterase agent, changed the peak interval. 6. The number of peaks in the overall MEPC amplitude and area-to-peak (charge) histogram profiles were usually the same. 7. Integral peaks on MEPC amplitude profiles, notches and steps on the MEPC rising phase and changes in the overall MEPC profiles are explained by a subunit composition of the quantum of transmitter release.
Full text
PDF



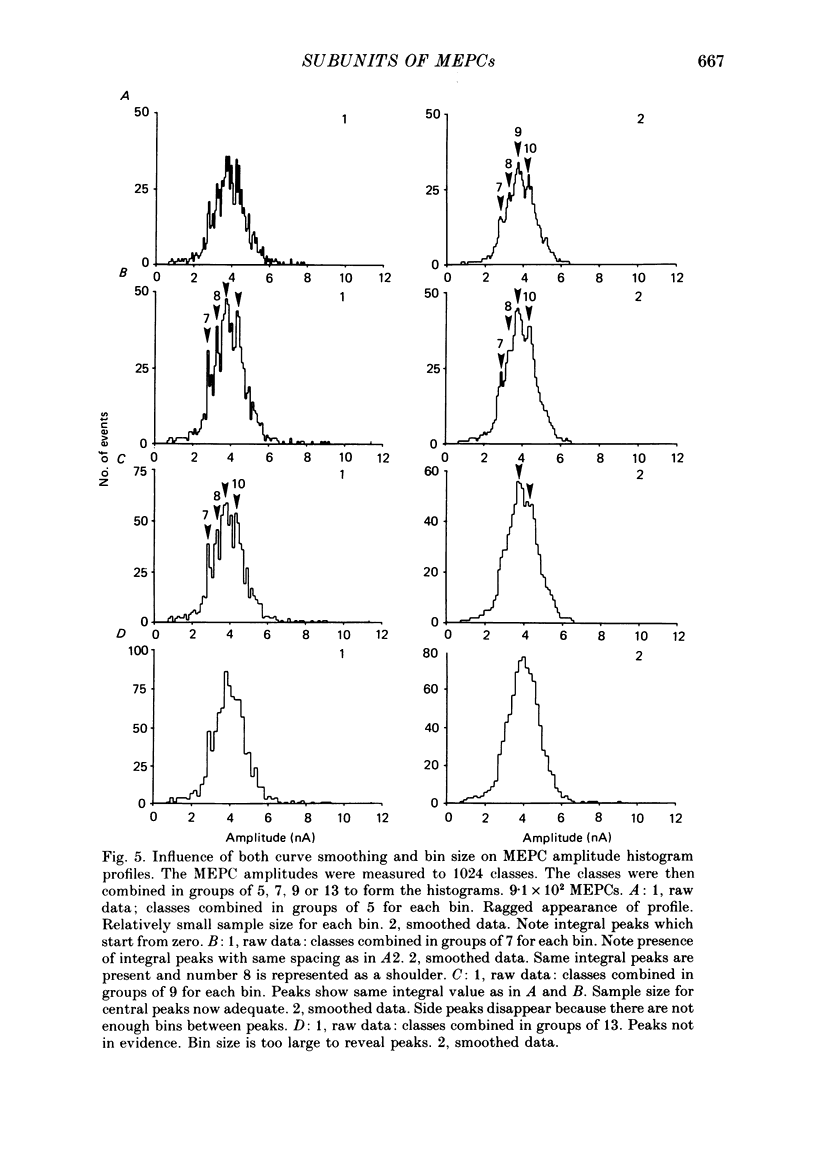
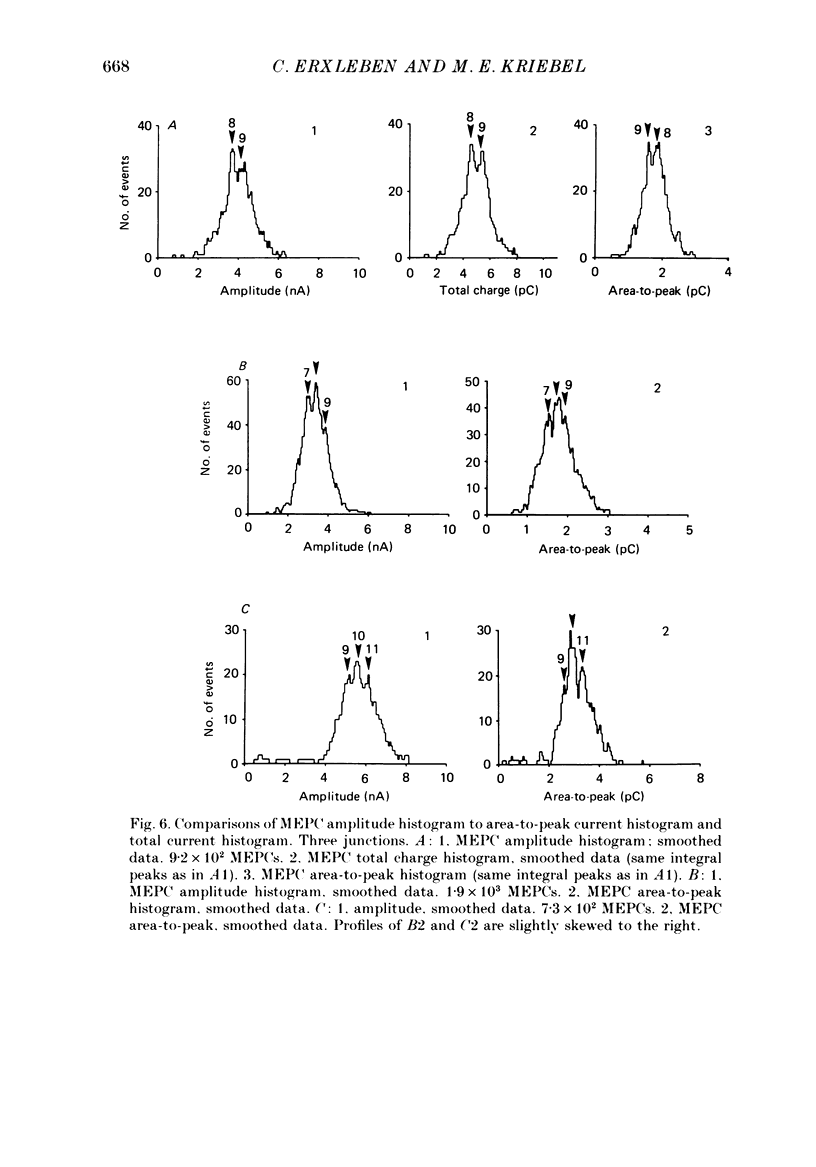
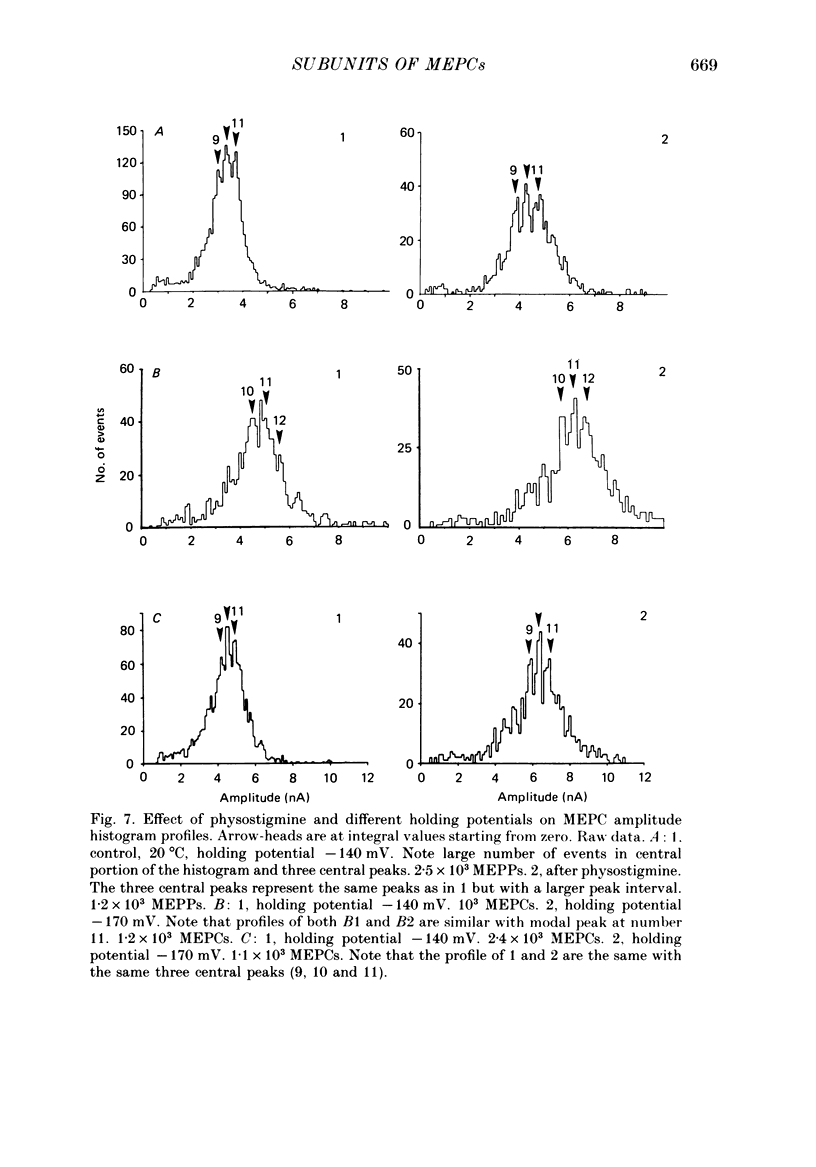

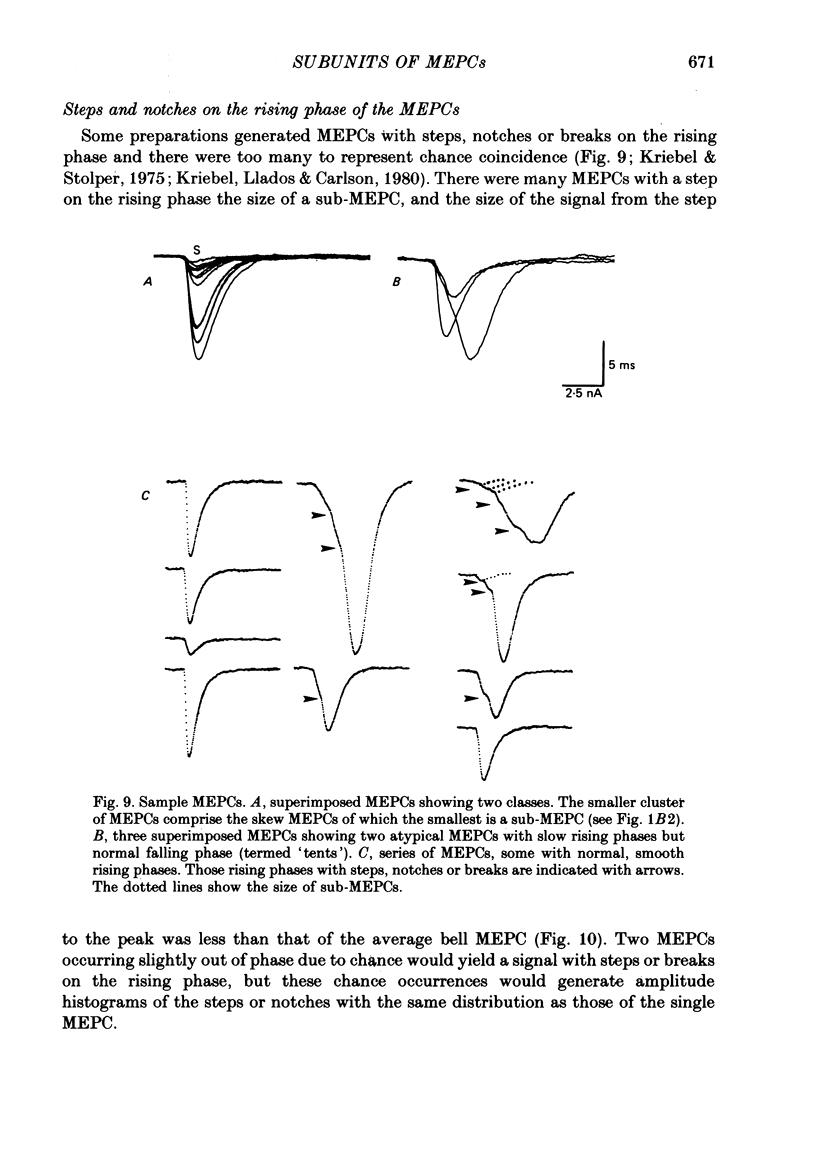




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at mammalian neural muscular junctions. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):61–73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan S. Sub-miniature end-plate potentials at untreated frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(1):145–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. G., Kriebel M. E., Muniak C. G. The effect of temperature on the amplitude distributions of miniature endplate potentials in the mouse diaphragm. Neuroscience. 1982 Oct;7(10):2537–2549. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. G., Kriebel M. E. Neostigmine increases the size of subunits composing the quantum of transmitter release at mouse neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:489–502. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke J. D., Quastel D. M. Transmitter release by mammalian motor nerve terminals in response to focal polarization. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):377–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csicsaky M., Papadopoulos R., Wiegand H. Detection of sub-miniature endplate potentials by harmonic analysis. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Oct-Nov;15(2):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Miledi R. Characteristics of transmitter release at regenerating frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(3):571–594. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M., Miledi R. Lack of correspondence between the amplitudes of spontaneous potentials and unit potentials evoked by nerve impulses at regenerating neuromuscular junctions. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):126–128. doi: 10.1038/newbio232126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erxleben C., Kriebel M. E. Characteristics of spontaneous miniature and subminiature end-plate currents at the mouse neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:645–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiekers J. F. Concentration-dependent effects of neostigmine on the endplate acetylcholine receptor channel complex. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):502–514. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00502.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füldner H. H., Stadler H. 31P-NMR analysis of synaptic vesicles. Status of ATP and internal pH. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. J., Miledi R. The effect of type D botulinum toxin on frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1971 Sep;217(2):497–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Estimates of quantal content during 'chemical potentiation' of transmitter release. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Aug 31;205(1160):369–378. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Florey E. Effect of lanthanum ions on the amplitude distributions of miniature endplate potentials and on synaptic vesicles in frog neuromuscular junctions. Neuroscience. 1983 Jul;9(3):535–547. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Gross C. E. Multimodal distribution of frog miniature endplate potentials in adult denervated and tadpole leg muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jul;64(1):85–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Hanna R., Muniak C. Synaptic vesicle diameters and synaptic cleft widths at the mouse diaphragm in neonates and adults. Brain Res. 1986 Jun;392(1-2):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(86)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Llados F., Carlson C. G. Effect of the Ca++ ionophore X-537A and a heat challenge on the distribution of mouse MEPP amplitude histograms. J Physiol (Paris) 1980 Sep;76(5):435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Llados F., Matteson D. R. Histograms of the unitary evoked potential of the mouse diaphragm show multiple peaks. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:211–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Llados F., Matteson D. R. Spontaneous subminature end-plate potentials in mouse diaphragm muscle: evidence for synchronous release. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):553–581. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E. Small mode miniature end plate potentials are increased and evoked in fatigued preparations and in high Mg2+ saline. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 16;148(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90726-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Stolper D. R. Non-Poisson distribution in time of small- and large-mode miniature end-plate potentials. Am J Physiol. 1975 Nov;229(5):1321–1329. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.5.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llados F., Matteson D. R., Kriebel M. E. beta-Bungarotoxin preferentially blocks one class of miniature endplate potentials. Brain Res. 1980 Jun 23;192(2):598–602. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90914-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Miller D. C. Is the quantum of transmitter release composed of subunits? A critical analysis in the mouse and frog. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:267–287. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Kreibel M. E., Llados F. A statistical model supports the subunit hypothesis of quantal relsease. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Dec;15(2-3):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)96104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Kriebel M. E., Llados F. A statistical model indicates that miniature end-plate potentials and unitary evoked end-plate potentials are composed of subunits. J Theor Biol. 1981 Jun 7;90(3):337–363. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muniak C. G., Kriebel M. E., Carlson C. G. Changes in MEPP and EPP amplitude distributions in the mouse diaphragm during synapse formation and degeneration. Brain Res. 1982 Oct;281(2):123–138. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(82)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. J., Pappas G. D., Kriebel M. E. The fine structure of identified frog neuromuscular junctions in relation to synaptic activity. Brain Res. 1978 Apr 14;144(2):213–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vautrin J., Mambrini J. Caractéristiques du potentiel unitaire de plaque motrice de la grenouille. J Physiol (Paris) 1981 May;77(9):999–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernig A., Stirner H. Quantum amplitude distributions point to functional unity of the synaptic 'active zone'. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):820–822. doi: 10.1038/269820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K., Redman S. The recovery of a random variable from a noisy record with application to the study of fluctuations in synaptic potentials. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Aug;2(4):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


