Abstract
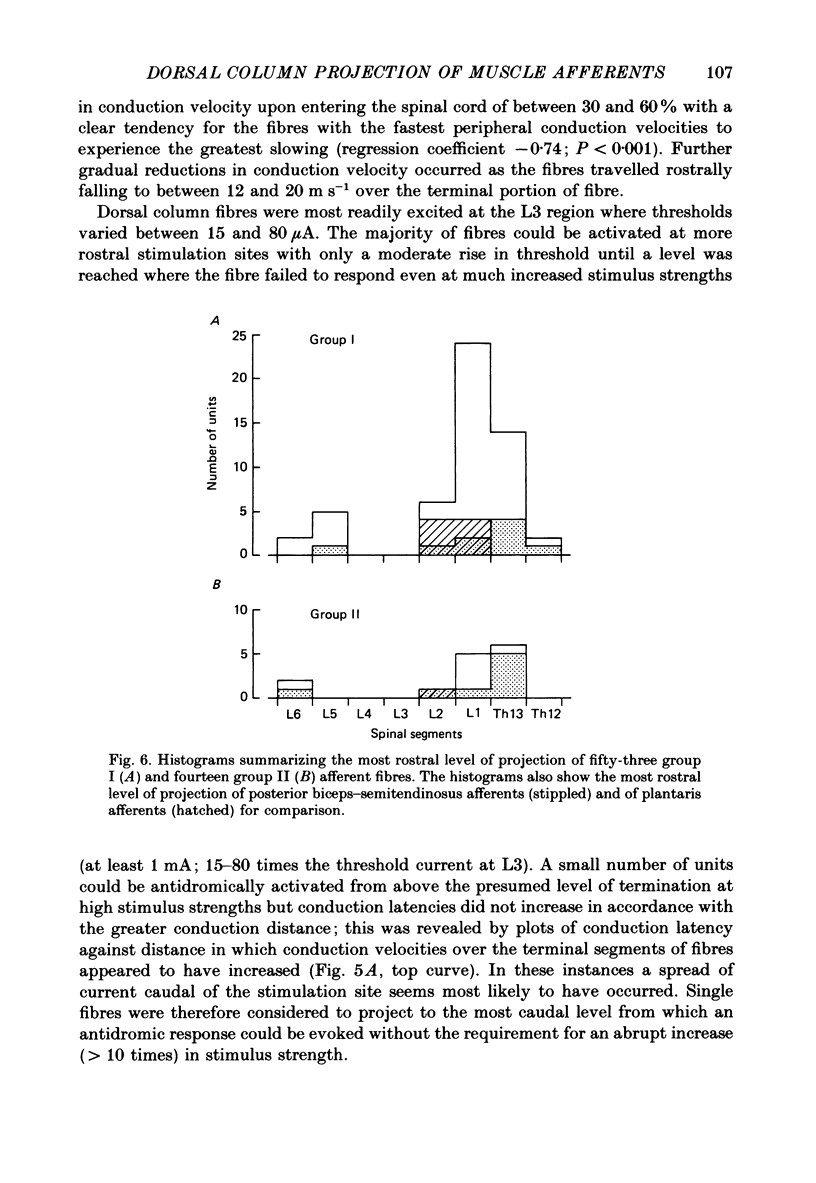
1. The extent of the projection of hindlimb muscle afferent fibres ascending the dorsal columns has been studied in barbiturate-anaesthetized cats. This has been investigated using electrical stimulation of the dorsal columns at different spinal levels while recording from (i) peripheral muscle nerves, and (ii) single muscle afferent fibres within the dorsal columns. These two approaches have produced complementary results. 2. The conduction velocity of both group I and group II afferent fibres decreased progressively after entering the dorsal columns. 3. The majority of group I and group II fibres project at least as far as L2 but leave the dorsal columns at or before the lower thoracic segments. 4. By taking advantage of the lower electrical threshold of Ia compared to Ib fibres in the hamstring nerves, it could be shown that both Ia and Ib fibres leave the dorsal columns at similar locations. 5. A small number of afferent fibres were found to project to C1. On the basis of previous work it is likely that such fibres originate from Pacinian or paciniform corpuscles.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADLEY K., ECCLES J. C. Analysis of the fast afferent impulses from thigh muscles. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):462–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. G. Cutaneous afferent fibre collaterals in the dorsal columns of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1968;5(4):293–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00235904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Clark F. J. Dorsal column projection of fibres from the cat knee joint. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):301–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallari P., Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. Post-synaptic actions of midlumbar interneurones on motoneurones of hind-limb muscles in the cat. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:675–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. J. Central projection of sensory fibers from the cat knee joint. J Neurobiol. 1972;3(2):101–110. doi: 10.1002/neu.480030202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin C. M., Jack J. J., McIntyre A. K. Properties of group I afferent fibres from semitendinosus muscle in the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):45P–46P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. An interneuronal relay for group I and II muscle afferents in the midlumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:647–674. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. Field potentials generated by group II muscle afferents in the middle lumbar segments of the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:393–413. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Jankowska E. Information processed by dorsal horn spinocerebellar tract neurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:81–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide E., Fedina L., Jansen J., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. Properties of Clarke's column neurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Sep-Oct;77(1):125–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Murphy P. R., Tripathi A. Closely coupled excitation of gamma-motoneurones by group III Muscle afferents with low mechanical threshold in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:481–498. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER E., LATIMER F., STILWELL D. Central connections for afferent fibers from the knee joint of the cat. Am J Physiol. 1949 Nov;159(2):195–198. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1949.159.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Kudo N., Sasaki S., Yamashita M., Yoshida K., Ishizuka N., Mannen H. Trajectory of group Ia and Ib fibers from the hind-limb muscles at the L3 and L4 segments of the spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Aug 8;262(2):159–194. doi: 10.1002/cne.902620202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horch K. W., Burgess P. R., Whitehorn D. Ascending collaterals of cutaneous neurons in the fasciculus gracilis of the cat. Brain Res. 1976 Nov 19;117(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90552-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. C., McINTYRE A. K. Dorsal column conduction of group I muscle afferent impulses and their relay through Clarke's column. J Neurophysiol. 1950 Jan;13(1):39–54. doi: 10.1152/jn.1950.13.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre A. K. Cortical projection of impulses in the interosseous nerve of the cat's hind limb. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):46–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSCARSSON O. Primary afferent collaterals and spinal relays of the dorsal and ventral spino-cerebellar tracts. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957 Oct 10;40(2-3):222–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1957.tb01491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit D., Burgess P. R. Dorsal column projection of receptors in cat hairy skin supplied by myelinated fibers. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Nov;31(6):849–855. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.6.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REXED B. A cytoarchitectonic atlas of the spinal cord in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Apr;100(2):297–379. doi: 10.1002/cne.901000205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


