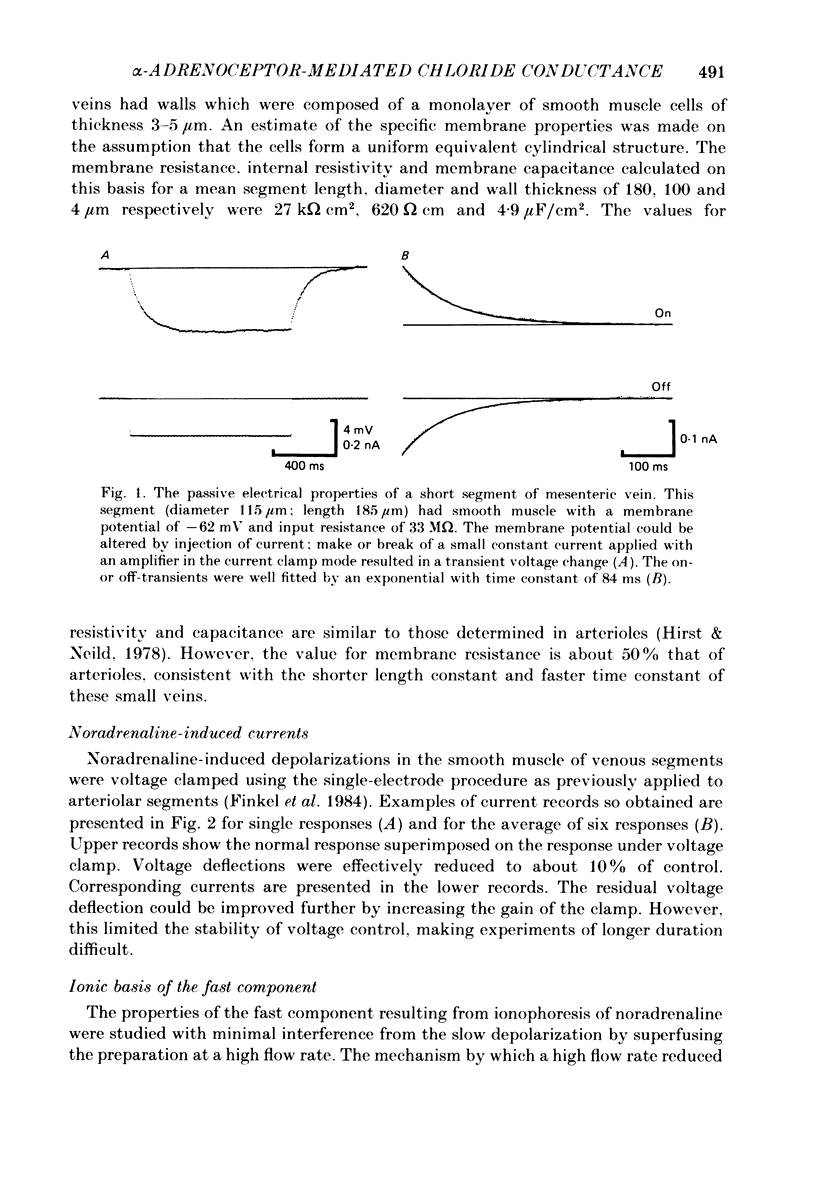
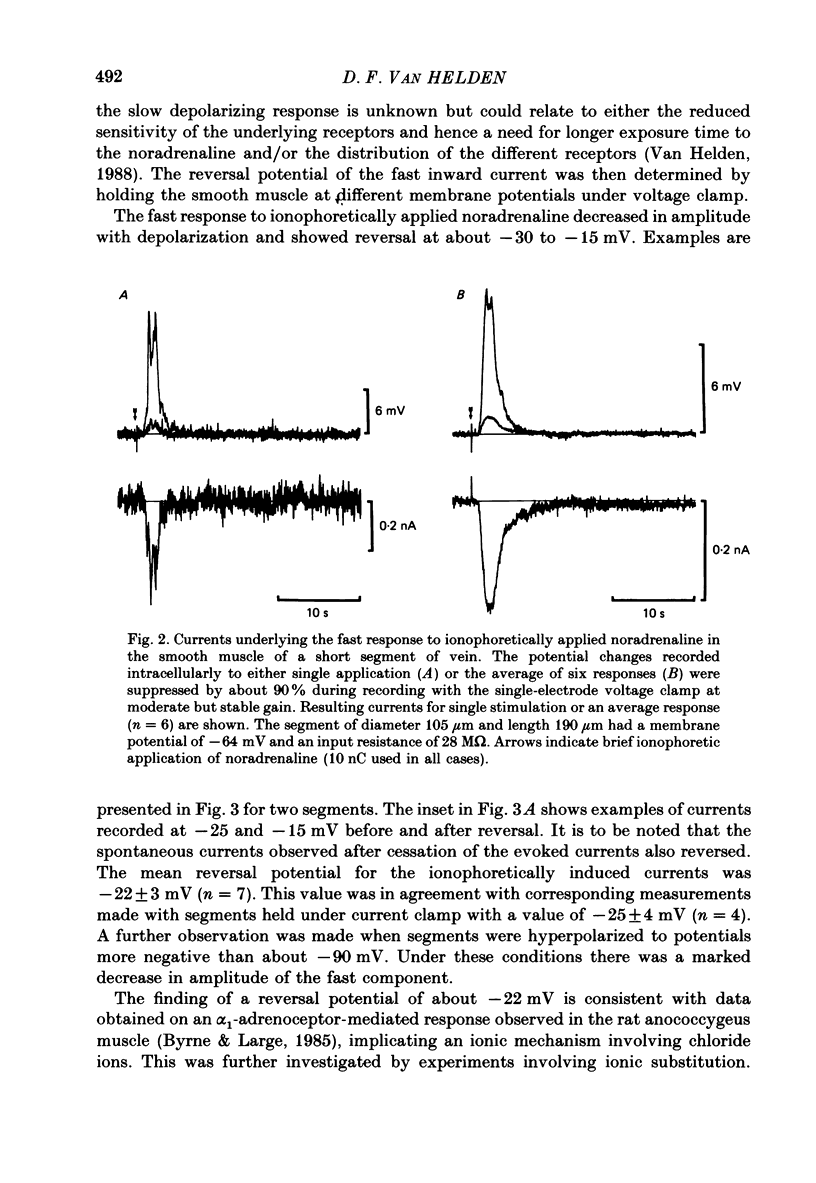
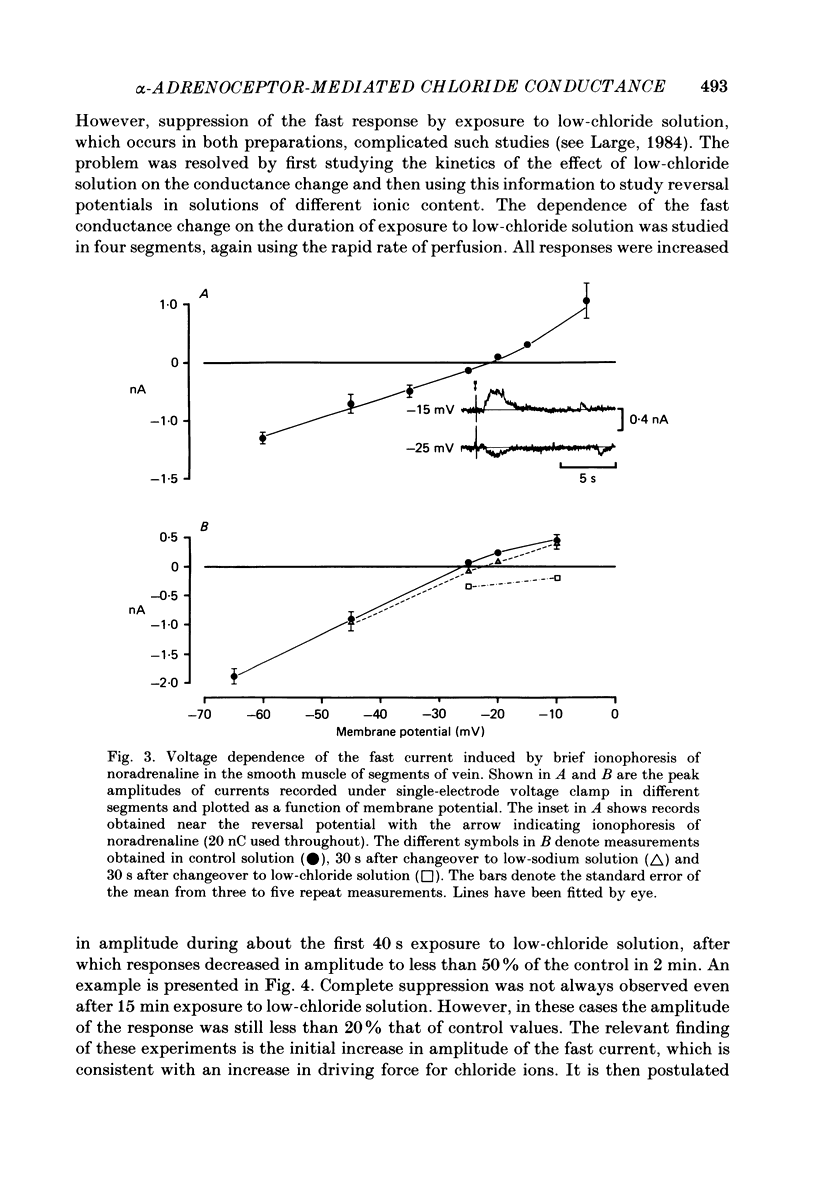
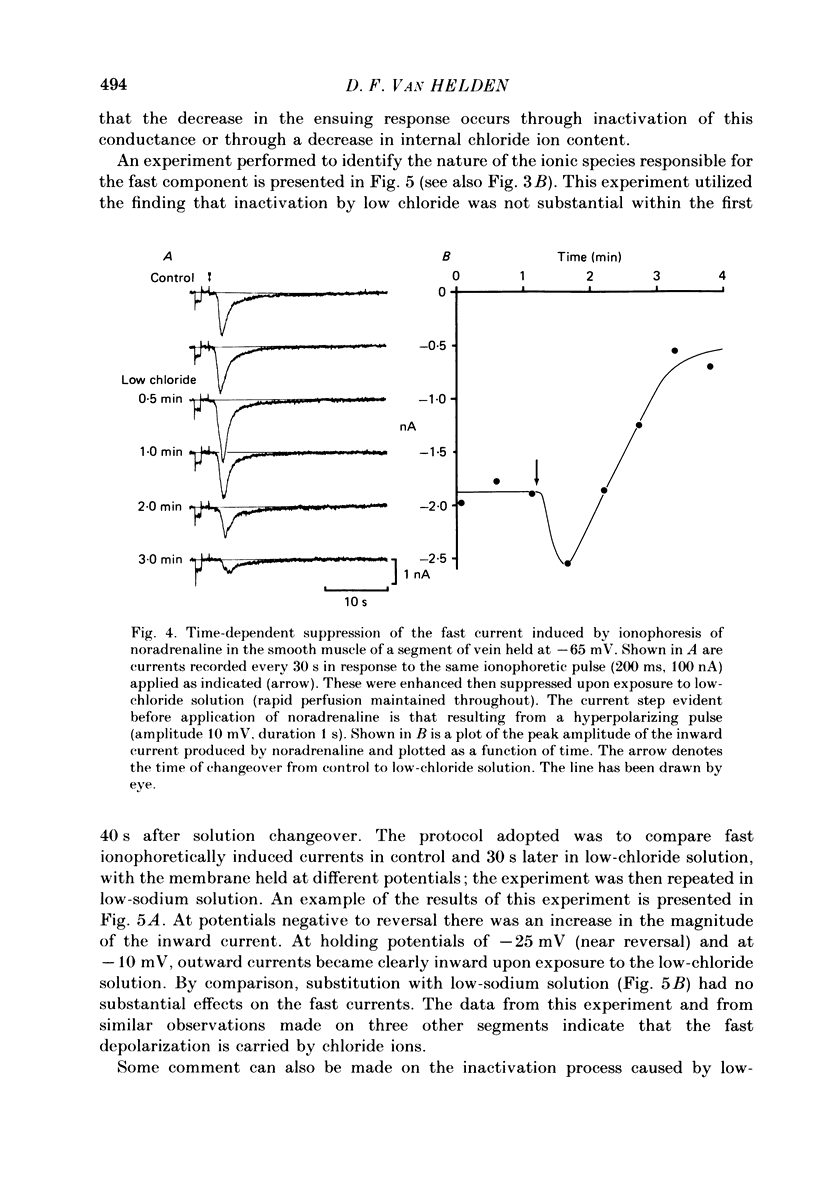
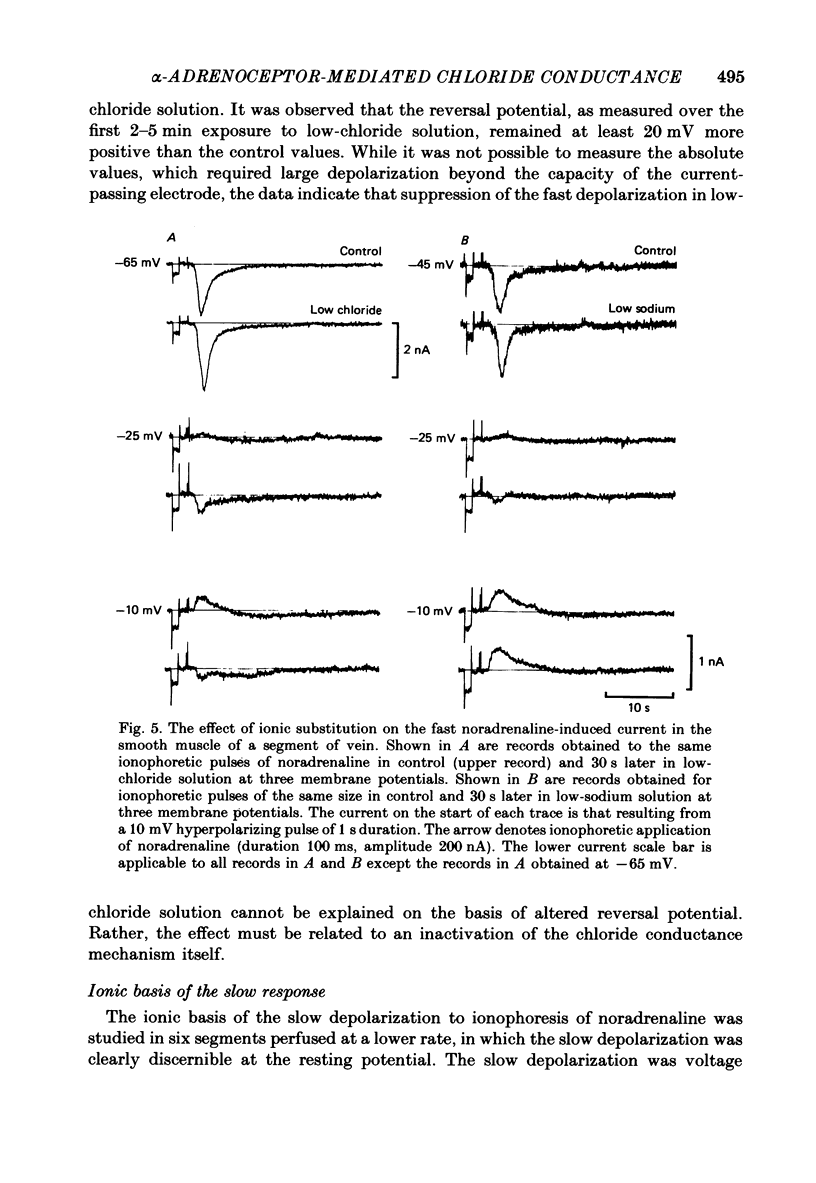
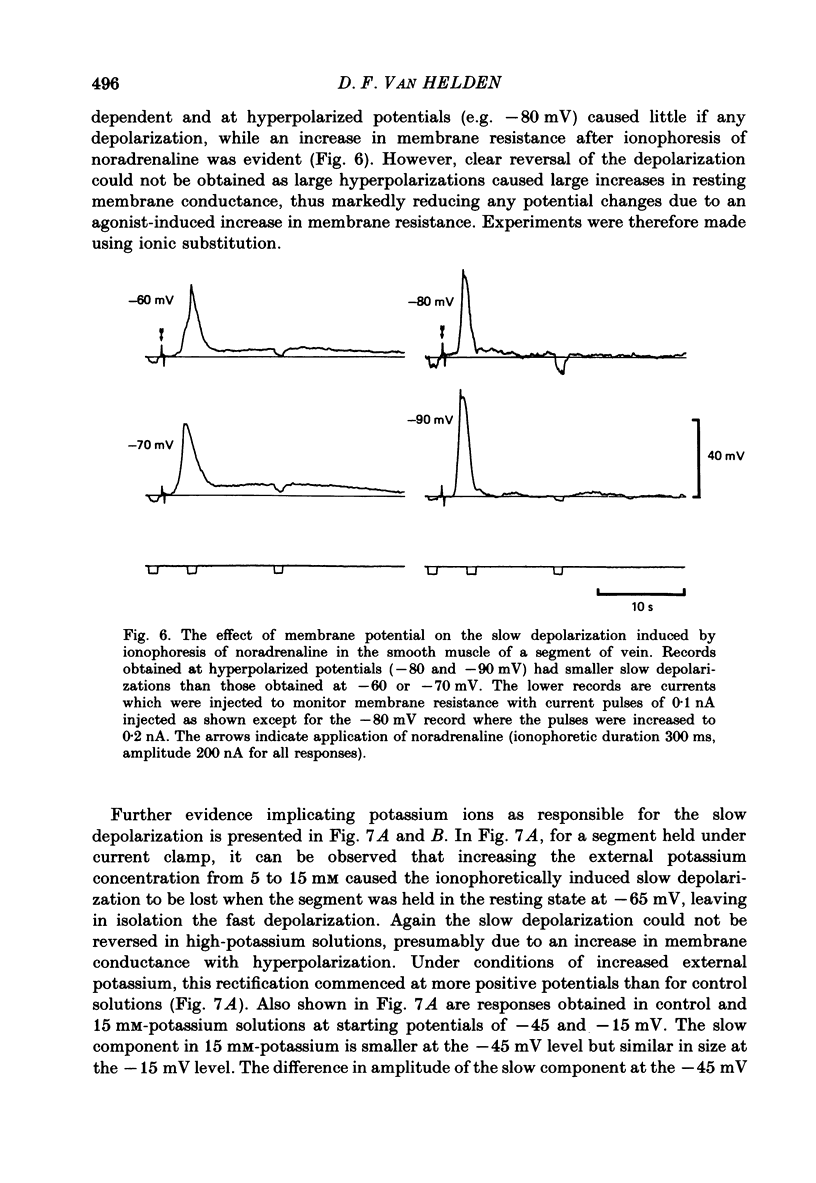
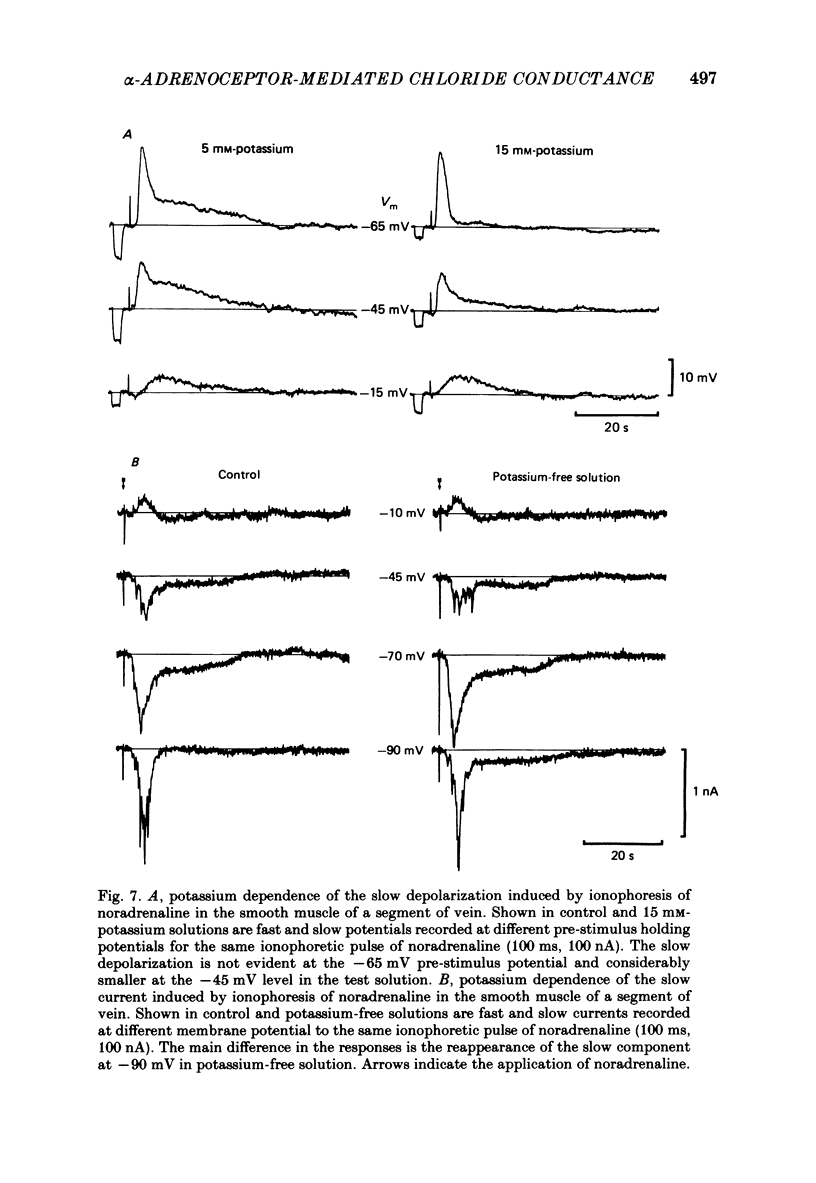
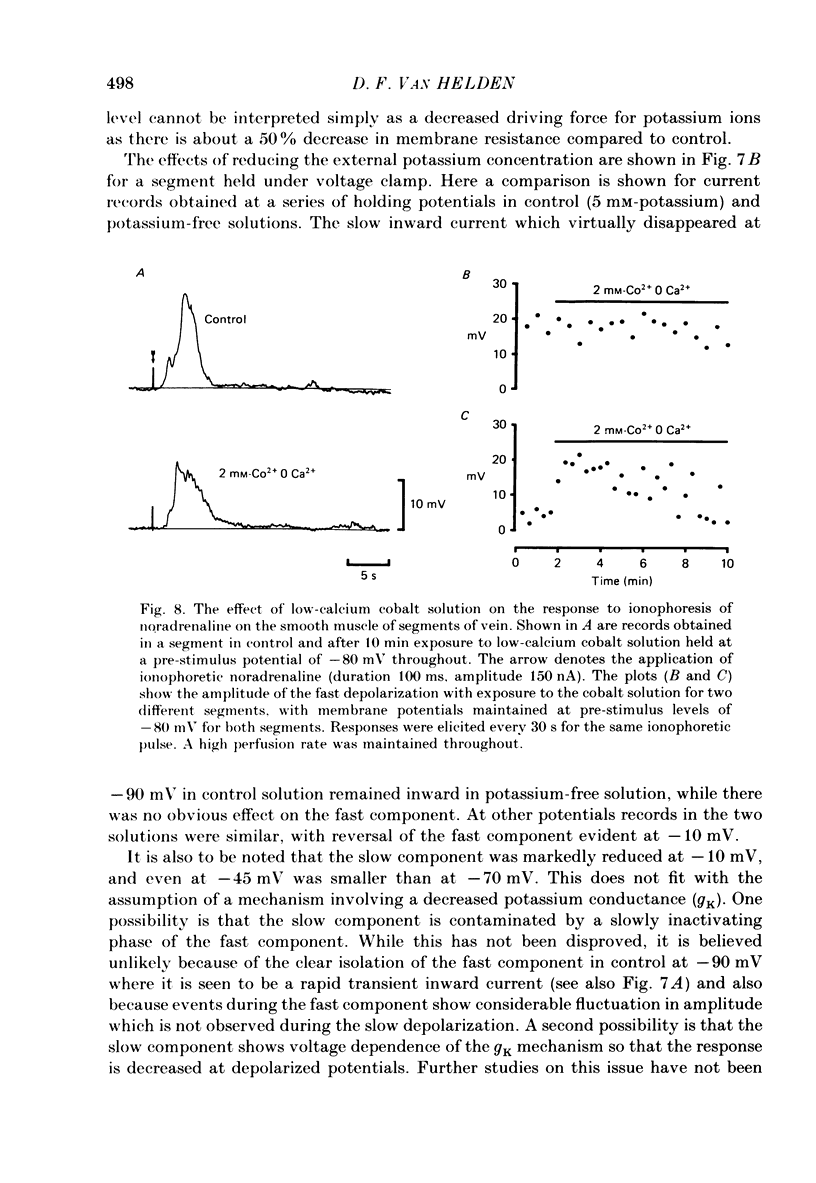
Abstract
1. The ionic basis of the depolarizing responses resulting from ionophoresis of noradrenaline onto the smooth muscle of mesenteric veins has been investigated using electrically short segments of vessel. 2. Isolated cut segments of vein were effectively isopotential as assessed by the voltage response to a step change in current. The mean input resistance and time constant of the smooth muscle were 24 M omega and 131 ms respectively. 3. Data on the noradrenaline-induced slow depolarization indicated that it resulted from a decrease in conductance to potassium ions consistent with the finding of Suzuki (1981). 4. The fast noradrenaline-induced depolarization was found to have a reversal potential of about -22 mV. 5. Exposure to low-chloride solution caused greater than 90% suppression of this fast response with a 50% reduction occurring in less than 2 min. This suppression was not due to a negative shift in reversal potential. 6. The fast response underwent a large positive shift in reversal potential directly after changeover to low-chloride solution at times when any inactivation of the response was minimal. By contrast the fast response showed no evidence implicating either sodium or calcium as charge-carrying ions. 7. It is concluded the fast depolarization is carried by chloride ions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aickin C. C., Brading A. F. Measurement of intracellular chloride in guinea-pig vas deferens by ion analysis, 36chloride efflux and micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:139–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aickin C. C., Brading A. F. Towards an estimate of chloride permeability in the smooth muscle of guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:179–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Evidence for two mechanisms of depolarization associated with alpha 1-adrenoceptor activation in the rat anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):711–721. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Szurszewski J. H. The stimulant action of noradrenaline (alpha-action) on guinea-pig myometrium compared with that of acetylcholine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Jan 29;185(1079):225–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogmans G., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Electro- and pharmacomechanical coupling in the smooth muscle cells of the rabbit ear artery. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Aug;70(2):129–148. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S., Hirst G. D., Van Helden D. F. Some properties of excitatory junction currents recorded from submucosal arterioles of guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:87–98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. An analysis of excitatory junctional potentials recorded from arterioles. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:87–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. Some properties of spontaneous excitatory junction potentials recorded from arterioles of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1980 Jun;303:43–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large W. A. The effect of chloride removal on the responses of the isolated rat anococcygeus muscle to alpha 1-adrenoceptor stimulation. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:17–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H. Effects of endogenous and exogenous noradrenaline on the smooth muscle of guinea-pig mesenteric vein. J Physiol. 1981 Dec;321:495–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Helden D. F. Electrophysiology of neuromuscular transmission in guinea-pig mesenteric veins. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:469–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström B. A. A study on the action of noradrenaline on ionic content and sodium, potassium and chloride effluxes in the rat portal vein. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Dec;89(4):522–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


