Abstract
1. alpha-Latrotoxin (alpha-LTx) was applied to frog cutaneous pectoris muscles bathed at 1-3 degrees C in either Ringer solution, Ca2+-free Ringer solution with 1 mM-EGTA and 4 mM-Mg2+ or Ringer solution plus 4 mM-Mg2+, and its effects on miniature end-plate potential (MEPP) frequency, nerve terminal ultrastructure and uptake of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) were studied. 2. Large concentrations (2 micrograms/ml) of alpha-LTx increased MEPP rates to levels above 100/s at all junctions, but the time course of the increases depended upon the divalent cation content of the bathing solution. However, similar numbers of MEPPs (0.3-0.7 x 10(6] were recorded at all junctions during 2 h of secretion. 3. Nerve terminals exposed to alpha-LTx for 2 h lost 60-75% of their synaptic vesicles and were swollen; their presynaptic membranes were deeply infolded and they often contained many large vesicular structures. Terminals in Ringer solution retained the largest number of synaptic vesicles; terminals in Ringer solution plus Mg2+ swelled the least and contained the largest number of coated vesicles. The average number of synaptic vesicles lost was approximately equal to the average number of MEPPs recorded. 4. Few vesicles became loaded with HRP when this extracellular tracer was present in the bathing solution and the muscles were fixed near the peak of secretion. 5. When the terminals were warmed to 20 degrees C, those in the Ca2+-free solution with Mg2+ secreted additional quanta and lost almost all their residual vesicles; those in Ringer solution without Mg2+ secreted few additional quanta and retained most of their residual vesicles. 6. These results suggest that recycling was blocked at these terminals and that for each quantum secreted a vesicle became permanently incorporated into the axolemma.
Full text
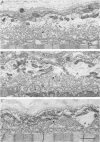
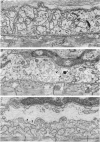
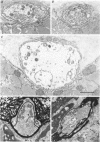
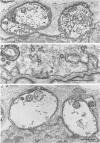
PDF


























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD I. A., MARTIN A. R. The end-plate potential in mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):74–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barrett J. N., Botz D., Chang D. B., Mahaffey D. Temperature-sensitive aspects of evoked and spontaneous transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:253–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braell W. A., Schlossman D. M., Schmid S. L., Rothman J. E. Dissociation of clathrin coats coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP: role of an uncoating ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):734–741. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Grohovaz F., Hurlbut W. P. Freeze-fracture studies of frog neuromuscular junctions during intense release of neurotransmitter. II. Effects of electrical stimulation and high potassium. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):178–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P. Ca2+-dependent recycling of synaptic vesicles at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):297–303. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P., Mauro A. Depletion of vesicles from frog neuromuscular junctions by prolonged tetanic stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jul;54(1):30–38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P., Mauro A. Turnover of transmitter and synaptic vesicles at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):499–524. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P. The effects of prolonged repetitive stimulation in hemicholinium on the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(1):163–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P. Vesicle hypothesis of the release of quanta of acetylcholine. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):396–441. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., Hurlbut W. P., Mauro A. Changes in the fine structure of the neuromuscular junction of the frog caused by black widow spider venom. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jan;52(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Quantal components of the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):560–573. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Gautron J., Israël M., Lesbats B., Manaranche R. Les compartiments d'acetylcholine de l'organe electrique de la torpille et leurs modifications par la stimulation. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1987–2002. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C., Dolezal V., Tucek S., Zemková H., Vyskocil F. Is an acetylcholine transport system responsible for nonquantal release of acetylcholine at the rodent myoneural junction? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN A., Rubin L. L., Tzeng M. C. Black widow spider venom: effect of purified toxin on lipid bilayer membranes. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1009–1011. doi: 10.1126/science.948756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesce R., Segal J. R., Ceccarelli B., Hurlbut W. P. Effects of black widow spider venom and Ca2+ on quantal secretion at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jul;88(1):59–81. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesce R., Segal J. R., Hurlbut W. P. Fluctuation analysis of nonideal shot noise. Application to the neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jul;88(1):25–57. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florey E., Kriebel M. E. Changes in acetylcholine concentration, miniature end-plate potentials and synaptic vesicles in frog neuromuscular preparations during lanthanum treatment. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1983;75(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(83)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz L. C., Mauro A. The ionic dependence of black widow spider venom action at the stretch receptor neuron and neuromuscular junction of crustaceans. J Neurobiol. 1982 Sep;13(5):385–401. doi: 10.1002/neu.480130502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frontali N., Ceccarelli B., Gorio A., Mauro A., Siekevitz P., Tzeng M. C., Hurlbut W. P. Purification from black widow spider venom of a protein factor causing the depletion of synaptic vesicles at neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):462–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorio A., Hurlbut W. P., Ceccarelli B. Acetylcholine compartments in mouse diaphragm. Comparison of the effects of black widow spider venom, electrical stimulation, and high concentrations of potassium. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):716–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimann C., Torri-Tarelli F., Fesce R., Ceccarelli B. Measurement of quantal secretion induced by ouabain and its correlation with depletion of synaptic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1953–1965. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera A. A., Grinnell A. D., Wolowske B. Ultrastructural correlates of experimentally altered transmitter release efficacy in frog motor nerve terminals. Neuroscience. 1985 Nov;16(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S. Evidence for recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):315–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J., Miledi R. Effects of lanthanum ions on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junctions. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Dec 14;179(1056):247–260. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël M., Lesbats B. Continuous determination by a chemiluminescent method of acetylcholine release and compartmentation in Torpedo electric organ synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1981 Dec;37(6):1475–1483. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb06317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël M., Manaranche R. The release of acetylcholine: from a cellular towards a molecular mechanism. Biol Cell. 1985;55(1-2):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1985.tb00403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Transmitter leakage from motor nerve endings. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Feb 11;196(1122):59–72. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Florey E. Effect of lanthanum ions on the amplitude distributions of miniature endplate potentials and on synaptic vesicles in frog neuromuscular junctions. Neuroscience. 1983 Jul;9(3):535–547. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriebel M. E., Gross C. E. Multimodal distribution of frog miniature endplate potentials in adult denervated and tadpole leg muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jul;64(1):85–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.64.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Turkanis S. A., Weakly J. N. Correlation between nerve terminal size and transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):545–556. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letinsky M. S., Fischbeck K. H., McMahan U. J. Precision of reinnervation of original postsynaptic sites in frog muscle after a nerve crush. J Neurocytol. 1976 Dec;5(6):691–718. doi: 10.1007/BF01181582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Huttner W. B., Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T. Free cytoplasmic Ca2+ and neurotransmitter release: studies on PC12 cells and synaptosomes exposed to alpha-latrotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):620–624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J. Studies on alpha-latrotoxin receptors in rat brain synaptosomes: correlation between toxin binding and stimulation of transmitter release. J Neurochem. 1982 Jun;38(6):1559–1569. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb06633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C. Dependence on multivalent cations of quantal release of transmitter induced by black widow spider venom. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C469–C476. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Hurlbut W. P. Action of black widow spider venom on quantized release of acetylcholine at the frog neuromuscular junction: dependence upon external Mg2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):991–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Rugolo M., Scott I. G., Meldolesi J. alpha-latrotoxin of black widow spider venom depolarizes the plasma membrane, induces massive calcium influx, and stimulates transmitter release in guinea pig brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7924–7928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumplin D. W., Reese T. S. Action of brown widow spider venom and botulinum toxin on the frog neuromuscular junction examined with the freeze-fracture technique. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):443–457. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal J. R., Ceccarelli B., Fesce R., Hurlbut W. P. Miniature endplate potential frequency and amplitude determined by an extension of Campbell's theorem. Biophys J. 1985 Feb;47(2 Pt 1):183–202. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(85)83891-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Interpreting power spectra from nonstationary membrane current fluctuations. Biophys J. 1981 Aug;35(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84790-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Clark A. W., Kuster T. A. Suppression by elevated calcium of black widow spider venom activity at frog neuromuscular junctions. J Neurocytol. 1977 Oct;6(5):519–539. doi: 10.1007/BF01205217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Mellman I. S., Muller W. A., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis and the recycling of plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):1–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauc L. Non vesicular release of neurotransmitter. Physiol Rev. 1982 Jul;62(3):857–893. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1982.62.3.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torri-Tarelli F., Grohovaz F., Fesce R., Ceccarelli B. Temporal coincidence between synaptic vesicle fusion and quantal secretion of acetylcholine. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1386–1399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtorta F., Madeddu L., Meldolesi J., Ceccarelli B. Specific localization of the alpha-latrotoxin receptor in the nerve terminal plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):124–132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verveen A. A., DeFelice L. J. Membrane noise. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1974;28:189–265. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(74)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyskocil F., Illés P. Non-quantal release of transmitter at mouse neuromuscular junction and its dependence on the activity of Na+-K+ ATP-ase. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Sep 16;370(3):295–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00585542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Paumgartner D. Integrated stereological and biochemical studies on hepatocytic membranes. II. Correction of section thickness effect on volume and surface density estimates. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):584–597. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Michaelson I. A., Kirkland R. J. The separation of synaptic vesicles from nerve-ending particles ('synaptosomes'). Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):293–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Roth T. F. Influence of buffer ions and divalent cations on coated vesicle disassembly and reassembly. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(2):237–250. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]