Abstract
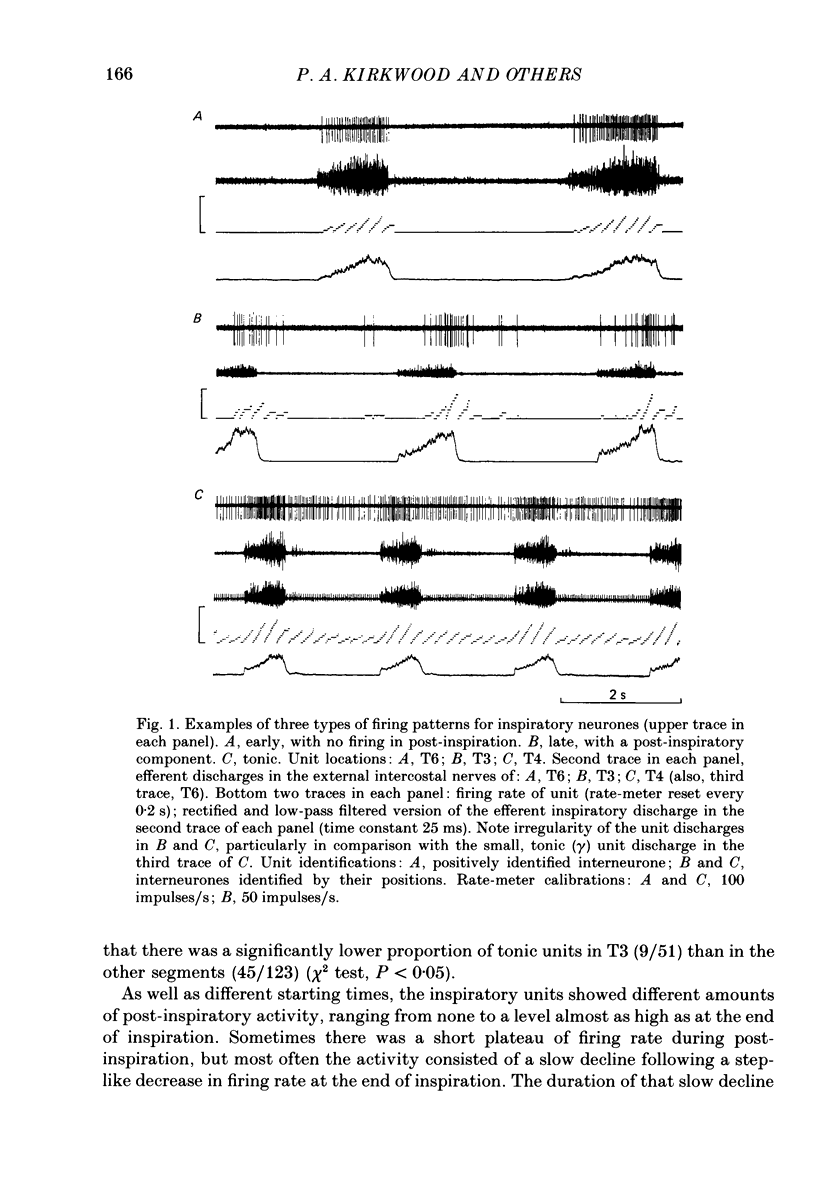
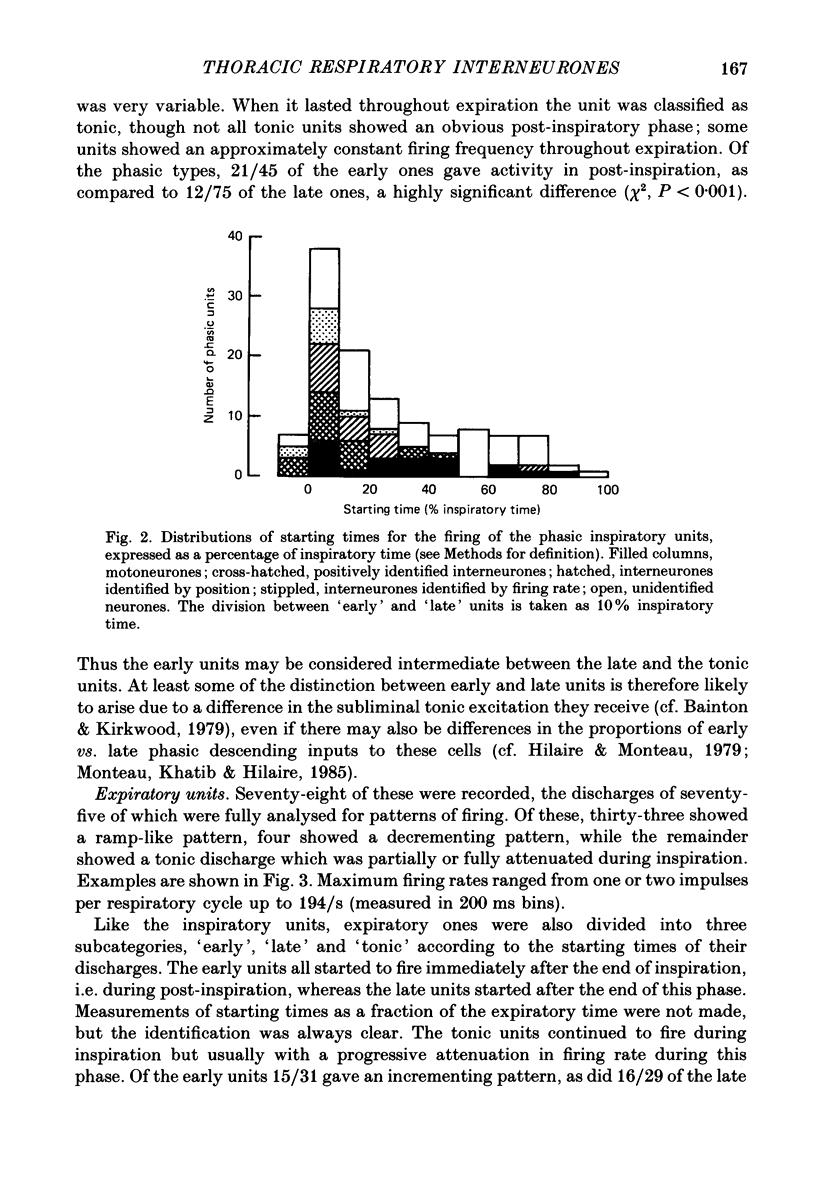
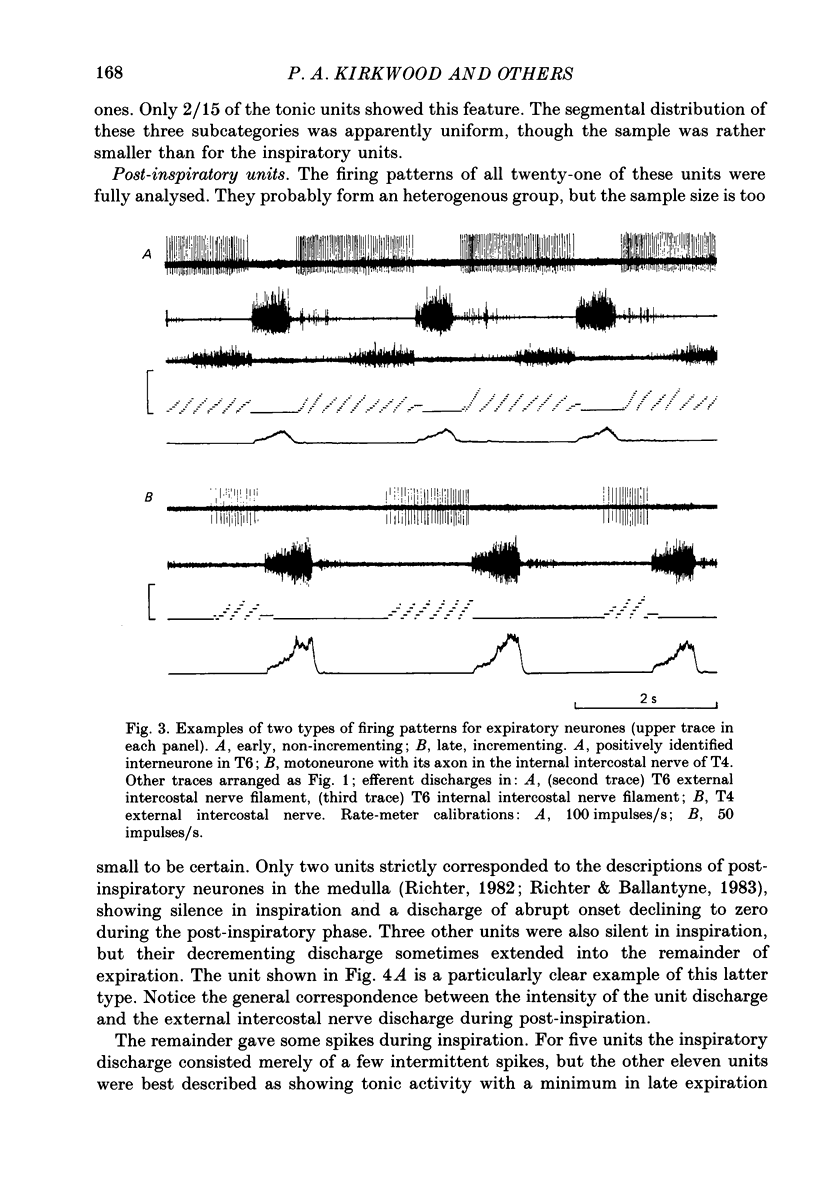
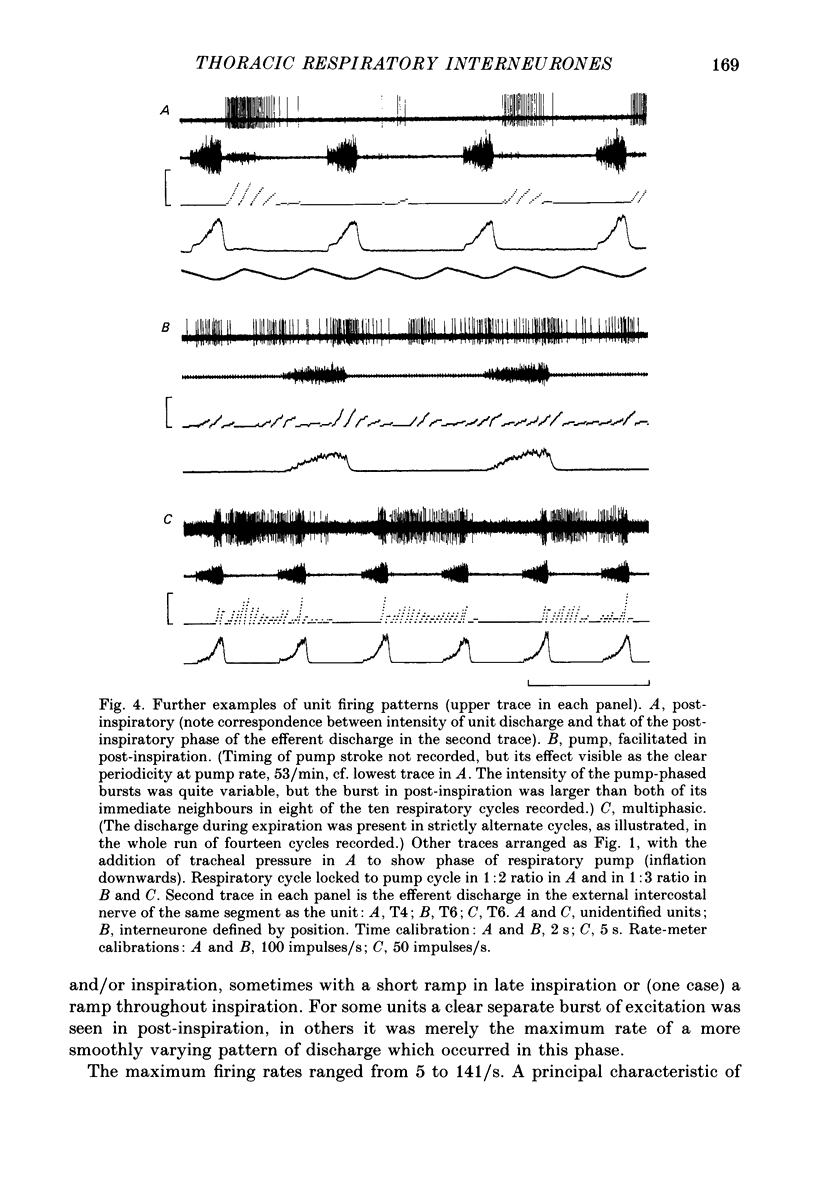
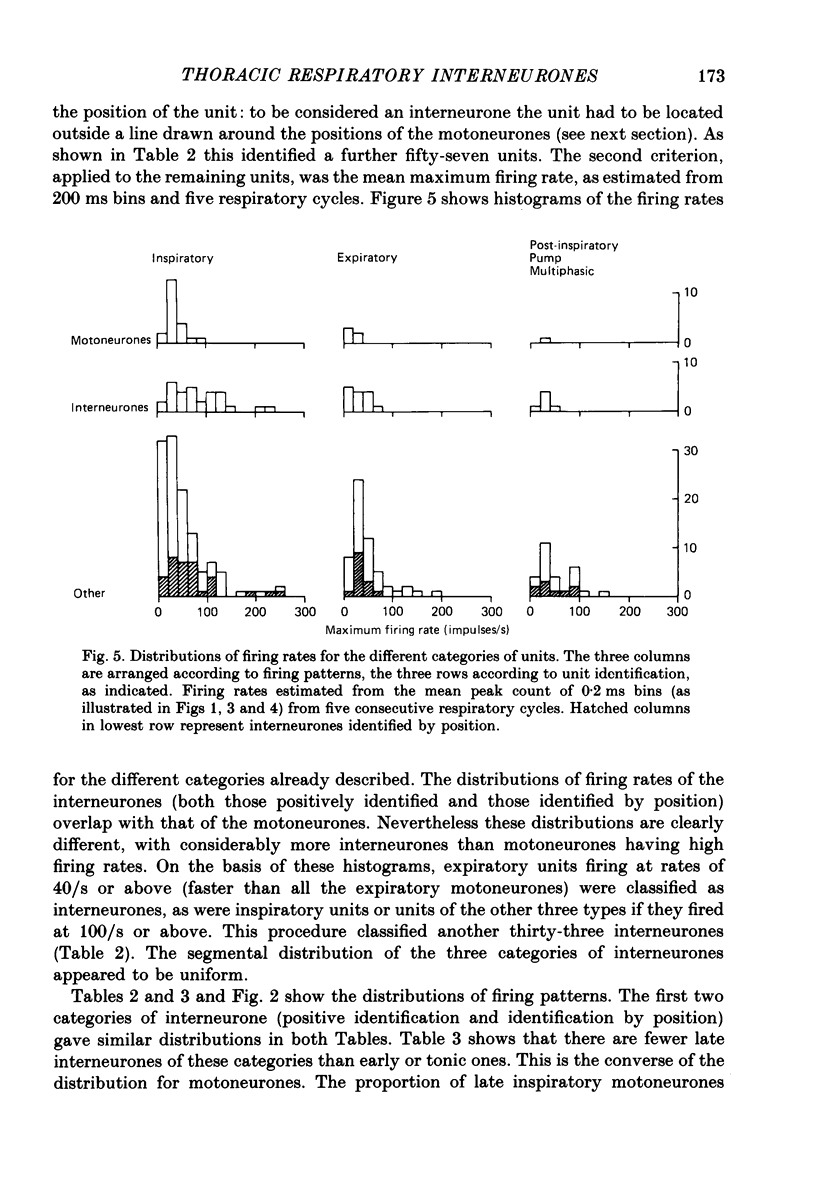
1. The discharges of spontaneously firing neurones, whose activity was modulated in phase with the central respiratory cycle, were recorded in the thoracic ventral horn (T3-T9) of anaesthetized, paralysed cats. 2. Out of 310 neurones, forty-six were positively identified as motoneurones by antidromic activation or spike-triggered averaging, fifty-four were positively identified as interneurones by antidromic activation from other spinal cord segments and ninety were indirectly identified as interneurones by virtue of their positions or firing rates as compared to the motoneurones. 3. Units were classified as inspiratory (64%), expiratory (25%) or post-inspiratory (7%) according to the times of their maximum firing rates. The remaining 4% consisted of units whose discharges were either strongly locked to the respiratory pump cycle or did not fit into the other categories. All but one of the motoneurones were classified as inspiratory or expiratory. 4. Inspiratory and expiratory units were further classified as early, late or tonic according to the starting times of their discharges in the respiratory cycle. The interneurones (both positively and indirectly identified) included more of the early and tonic categories and more fast-firing units than did the motoneurones in both the inspiratory and expiratory groups. 5. The locations of the motoneurones corresponded to the known positions of the intercostal and interchondral motor nuclei, including clear segregation of inspiratory and expiratory populations. The locations of neither the interneurones nor the unidentified units were segregated according to their firing patterns. These neurones were concentrated in the medial half of the ventral horn and were found generally more dorsally than the positions of the motoneurones, though their positions overlapped considerably with this group. 6. The axons of the positively identified interneurones were identified from one to five segments caudally and mostly contralaterally, but were not traced to their terminations. Some axons were located by microstimulation and found to run in the ventral or ventromedial white matter. Conduction velocities covered a wide range, 8 to around 100 m/s, mean 53 m/s. 7. Preliminary calculations indicate that there may be almost 10 times more respiratory thoracic interneurones as respiratory bulbospinal neurones.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF











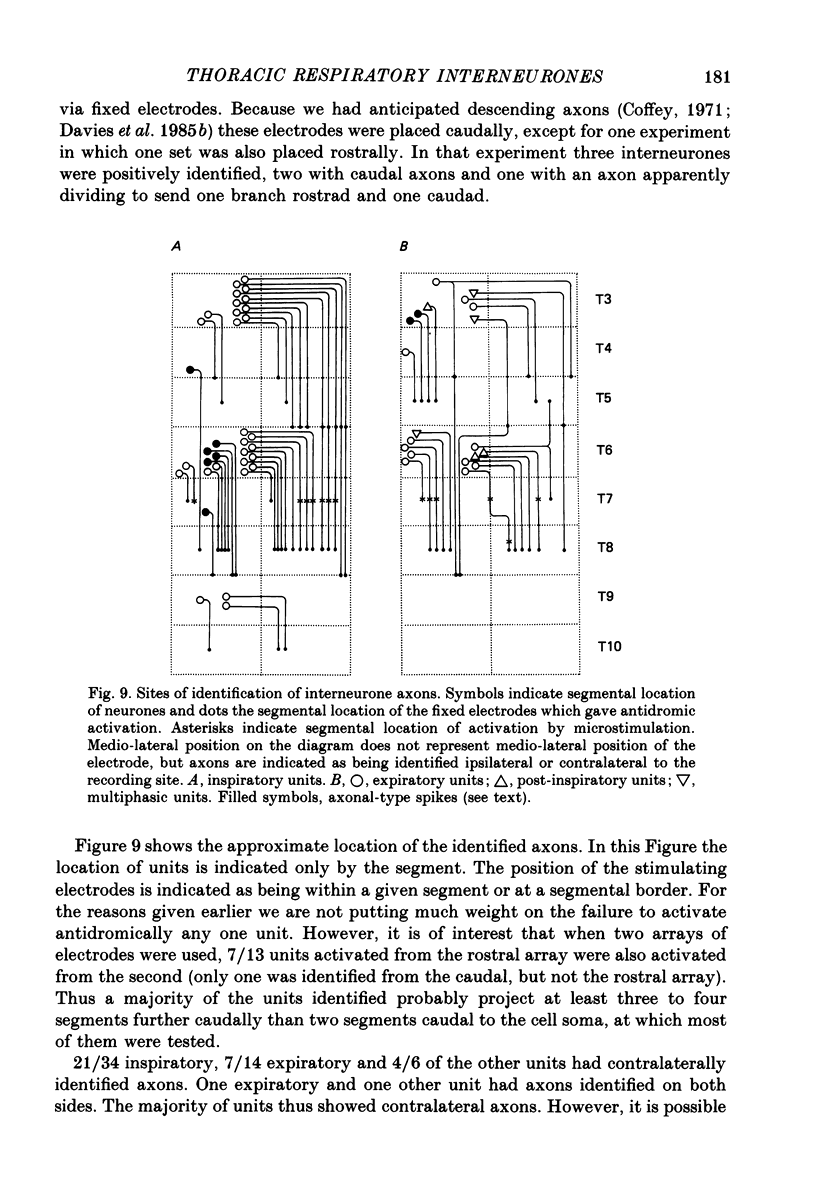
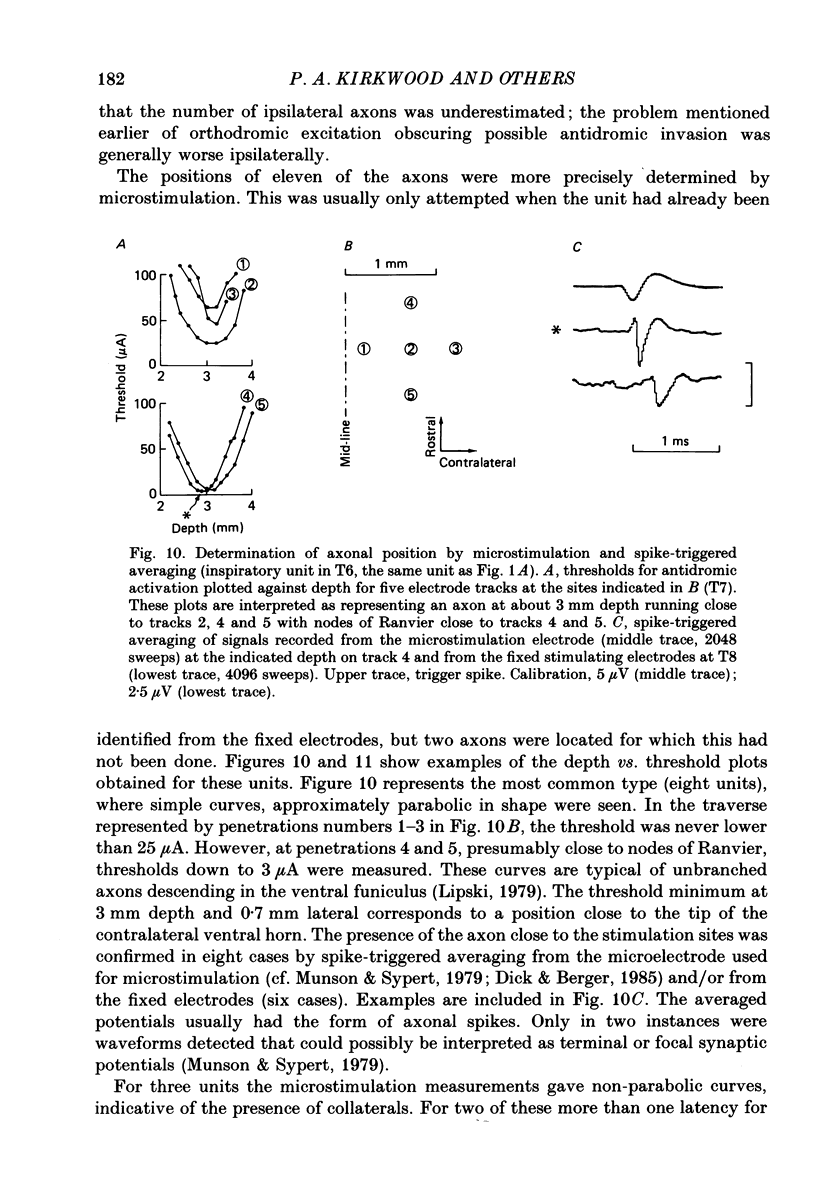
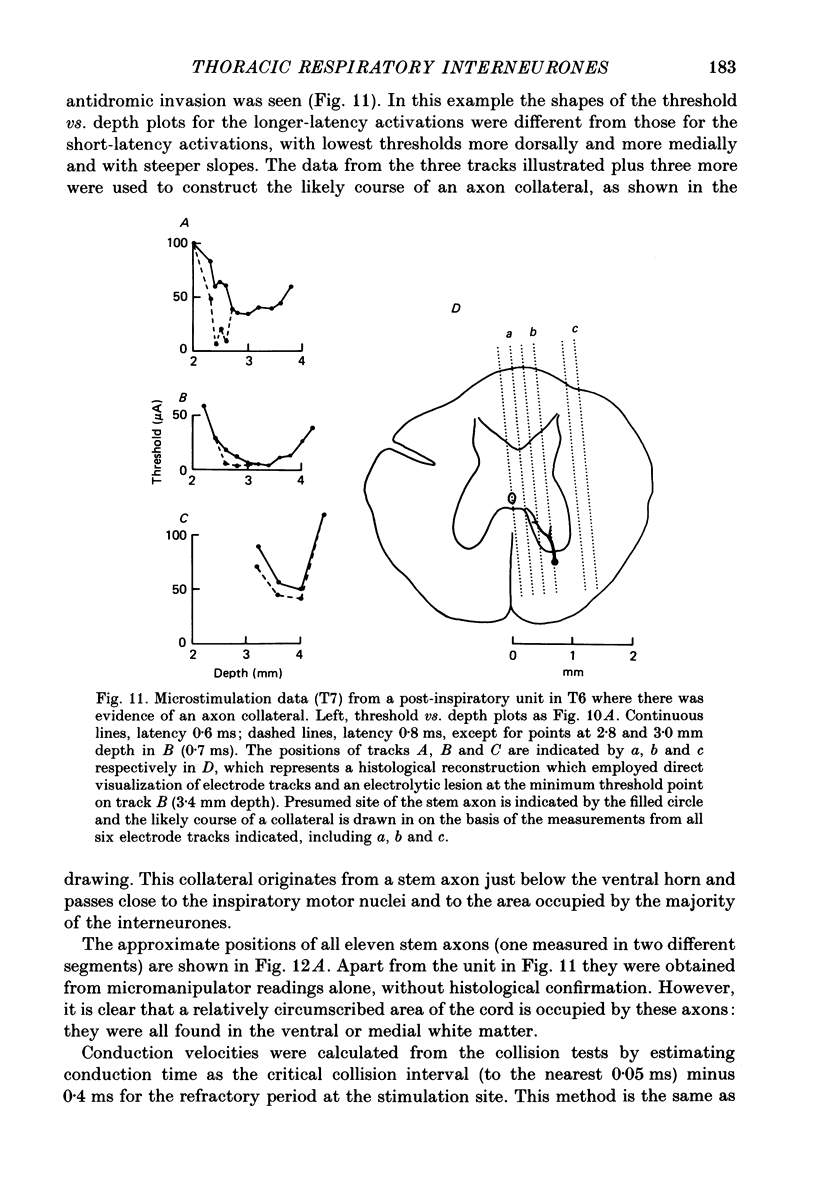
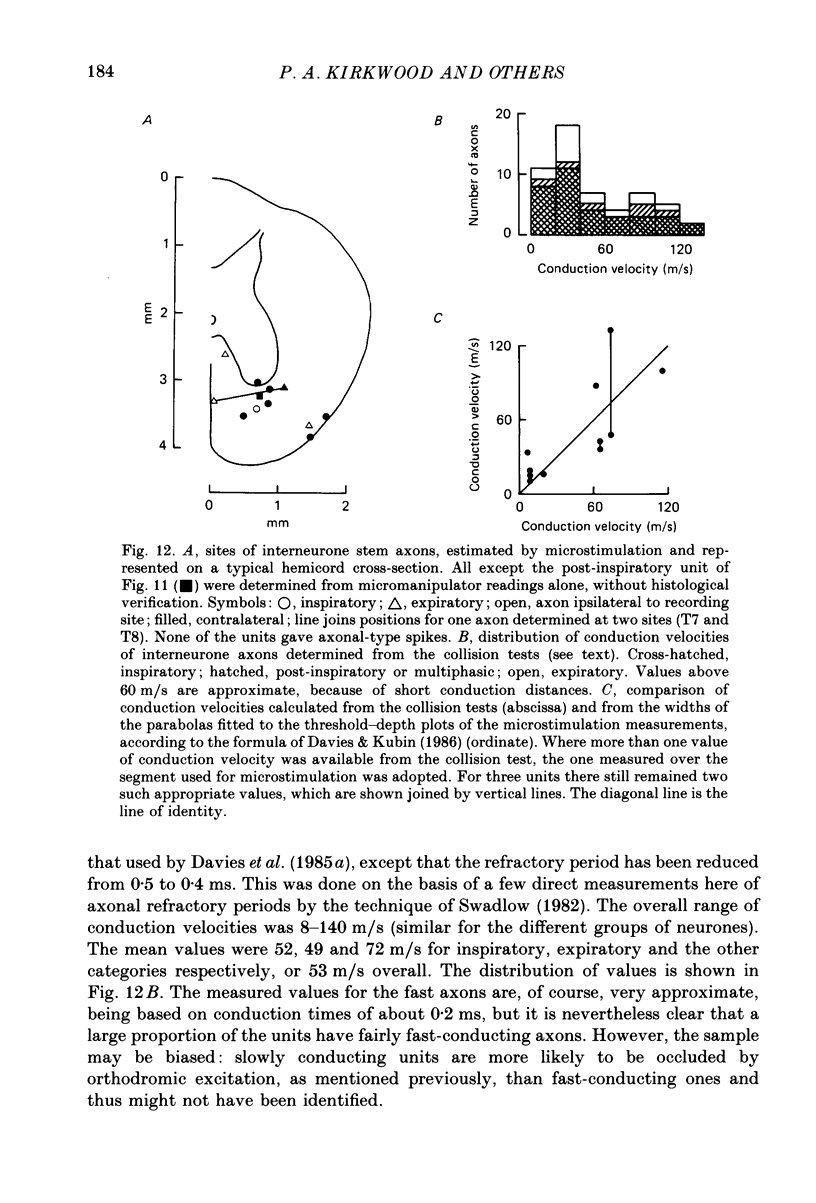








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aminoff M. J., Sears T. A. Spinal integration of segmental, cortical and breathing inputs to thoracic respiratory motoneurones. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):557–575. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Sears T. A. Medullary activation of intercostal fusimotor and alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1970 Aug;209(3):739–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki M., Mori S., Kawahara K., Watanabe H., Ebata N. Generation of spontaneous respiratory rhythm in high spinal cats. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 24;202(1):51–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP P. O., BURKE W., DAVIS R. The identification of single units in central visual pathways. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:409–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton C. R., Kirkwood P. A. The effect of carbon dioxide on the tonic and the rhythmic discharges of expiratory bulbospinal neurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:291–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballantyne D., Richter D. W. The non-uniform character of expiratory synaptic activity in expiratory bulbospinal neurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:433–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barman S. M., Gebber G. L. Basis for synchronization of sympathetic and phrenic nerve discharges. Am J Physiol. 1976 Nov;231(5 Pt 1):1601–1607. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.5.1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger A. J. Dorsal respiratory group neurons in the medulla of cat: spinal projections, responses to lung inflation and superior laryngeal nerve stimulation. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 28;135(2):231–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. Responses of single thoracic respiratory neurons to electrical stimulation of suprasegmental respiratory areas. Exp Neurol. 1975 May;47(2):199–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90250-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWNMAN C. B. Skeletal muscle reflexes of splanchnic and intercostal nerve origin in acute spinal and decerebrate cats. J Neurophysiol. 1955 May;18(3):217–235. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. G., Kirkwood P. A., Romaniuk J. R., Sears T. A. Effects of sagittal medullary section on high-frequency oscillation in rabbit phrenic neurogram. Respir Physiol. 1986 Jun;64(3):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(86)90121-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. G., Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. The detection of monosynaptic connexions from inspiratory bulbospinal neurones to inspiratory motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:33–62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. G., Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. The distribution of monosynaptic connexions from inspiratory bulbospinal neurones to inspiratory motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:63–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. O., Kubin L. Projection of pulmonary rapidly adapting receptors to the medulla of the cat: an antidromic mapping study. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:63–86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decima E. E., von Euler C., Thoden U. Intercostal-to-phrenic reflexes in the spinal cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Apr;75(4):568–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick T. E., Berger A. J. Axonal projections of single bulbospinal inspiratory neurons revealed by spike-triggered averaging and antidromic activation. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Jun;53(6):1590–1603. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.6.1590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. L., Loewy A. D., Speck D. F. Projections from the ventral respiratory group to phrenic and intercostal motoneurons in cat: an autoradiographic study. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):1993–2000. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-01993.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Schlag J. D. Determination of antidromic excitation by the collision test: problems of interpretation. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellon R. F. The marking of electrode tip positions in nervous tissue. J Physiol. 1971;214 (Suppl):12P–12P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
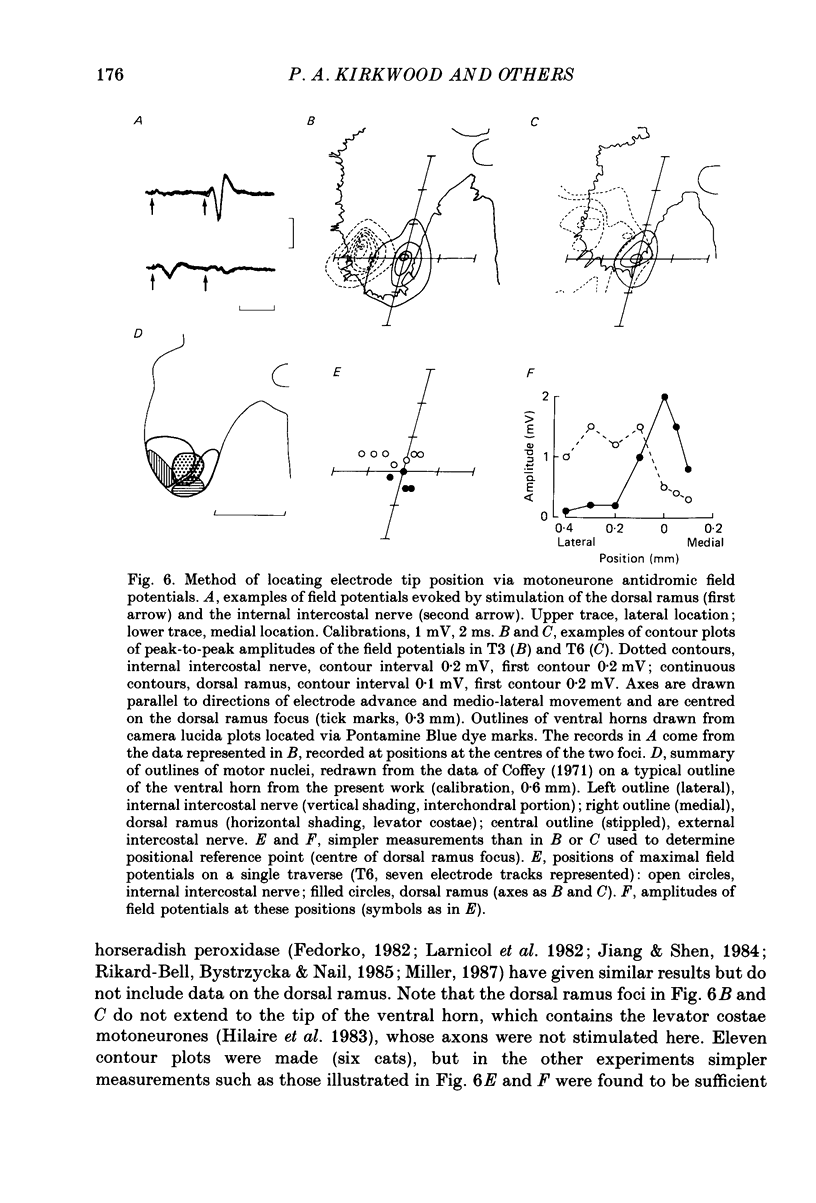
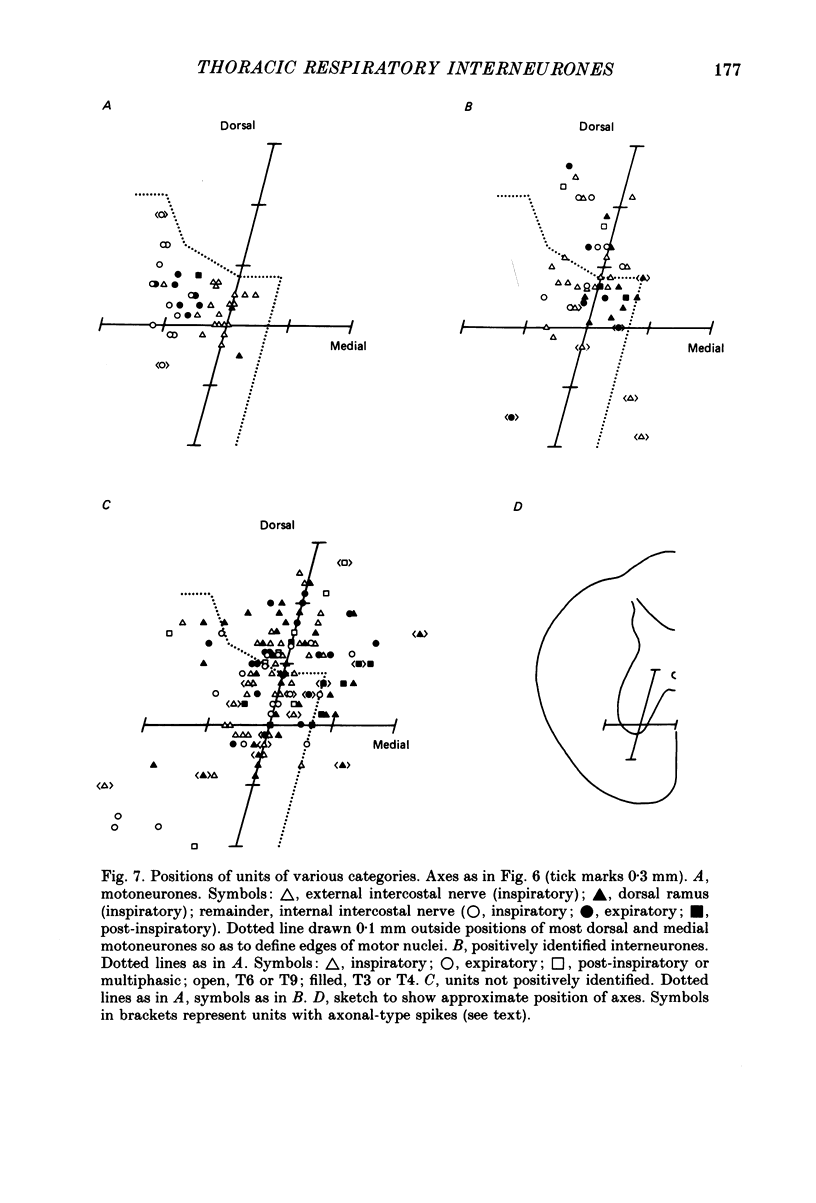
- Hilaire G. G., Nicholls J. G., Sears T. A. Central and proprioceptive influences on the activity of levator costae motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilaire G., Khatib M., Monteau R. Spontaneous respiratory activity of phrenic and intercostal Renshaw cells. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 23;43(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilaire G., Monteau R. Facteurs déterminant l'order de recrutement des motoneurones phréniques. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(7):765–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. Excitatory post-synaptic potentials from single muscle spindle afferents in external intercostal motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:287–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. Spike triggered averaging for the measurement of single unit conduction velocities. J Physiol. 1975 Feb;245(2):58P–59P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Stagg D., Westgaard R. H. The spatial distribution of synchronization of intercostal motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:137–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Tuck D. L., Westgaard R. H. Variations in the time course of the synchronization of intercostal motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:105–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Westgaard R. H. Recurrent inhibition of intercostal motoneurones in the cat. J Physiol. 1981;319:111–130. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A., Westgaard R. H. Restoration of function in external intercostal motoneurones of the cat following partial central deafferentation. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:225–251. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larnicol N., Rose D., Marlot D., Duron B. Anatomical organization of cat intercostal motor nuclei as demonstrated by HRP retrograde labelling. J Physiol (Paris) 1982 Aug;78(2):198–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J. Antidromic activation of neurones as an analytic tool in the study of the central nervous system. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Jun;4(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., Duffin J. An electrophysiological investigation of propriospinal inspiratory neurons in the upper cervical cord of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1986;61(3):625–637. doi: 10.1007/BF00237589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S., Duffin J. The neuronal determinants of respiratory rhythm. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;27(2):101–182. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin B. J. Propriospinal and supraspinal projections to the motor nuclei in the cat spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Apr;144(4):475–500. doi: 10.1002/cne.901440406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D. Localization of motoneurons innervating individual abdominal muscles of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Feb 22;256(4):600–606. doi: 10.1002/cne.902560412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteau R., Khatib M., Hilaire G. Central determination of recruitment order: intracellular study of phrenic motoneurons. Neurosci Lett. 1985 May 23;56(3):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90266-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson J. B., Sypert G. W. Properties of single central Ia afferent fibres projecting to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:315–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON J. R. Single unit activity in medullary respiratory centers of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Sep;22:590–598. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.5.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W. Generation and maintenance of the respiratory rhythm. J Exp Biol. 1982 Oct;100:93–107. doi: 10.1242/jeb.100.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikard-Bell G. C., Bystrzycka E. K., Nail B. S. The identification of brainstem neurones projecting to thoracic respiratory motoneurones in the cat as demonstrated by retrograde transport of HRP. Brain Res Bull. 1985 Jan;14(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk J. R., Budzinska K. Effects of a midsagittal lesion of the rabbit medulla. II. Vagal modulation of respiratory activity. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1985 Nov-Dec;21(6):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. EFFERENT DISCHARGES IN ALPHA AND FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF INTERCOSTAL NERVES OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:295–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. SOME PROPERTIES AND REFLEX CONNEXIONS OF RESPIRATORY MOTONEURONES OF THE CAT'S THORACIC SPINAL CORD. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS T. A. THE SLOW POTENTIALS OF THORACIC RESPIRATORY MOTONEURONES AND THEIR RELATION TO BREATHING. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:404–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRAGUE J. M. Motor and propriospinal cells in the thoracic and lumbar ventral horn of the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1951 Aug;95(1):103–123. doi: 10.1002/cne.900950107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMI T. Organization of spinal respiratory neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Jun 24;109:561–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUMI T. SPINAL RESPIRATORY NEURONS AND THEIR REACTION TO STIMULATION OF INTERCOSTAL NERVES. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1963 Oct 25;278:172–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00362689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinoda Y., Yamaguchi T., Futami T. Multiple axon collaterals of single corticospinal axons in the cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Mar;55(3):425–448. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swadlow H. A. Antidromic activation: measuring the refractory period at the site of axonal stimulation. Exp Neurol. 1982 Feb;75(2):514–519. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(82)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. The contribution of the intercostal muscles to the effort of respiration in man. J Physiol. 1960 May;151:390–402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viala D., Freton E. Evidence for respiratory and locomotor pattern generators in the rabbit cervico-thoracic cord and for their interactions. Exp Brain Res. 1983;49(2):247–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00238584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal P. P., Graf W., Berthoz A. The orientation of the cervical vertebral column in unrestrained awake animals. I. Resting position. Exp Brain Res. 1986;61(3):549–559. doi: 10.1007/BF00237580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


