Abstract
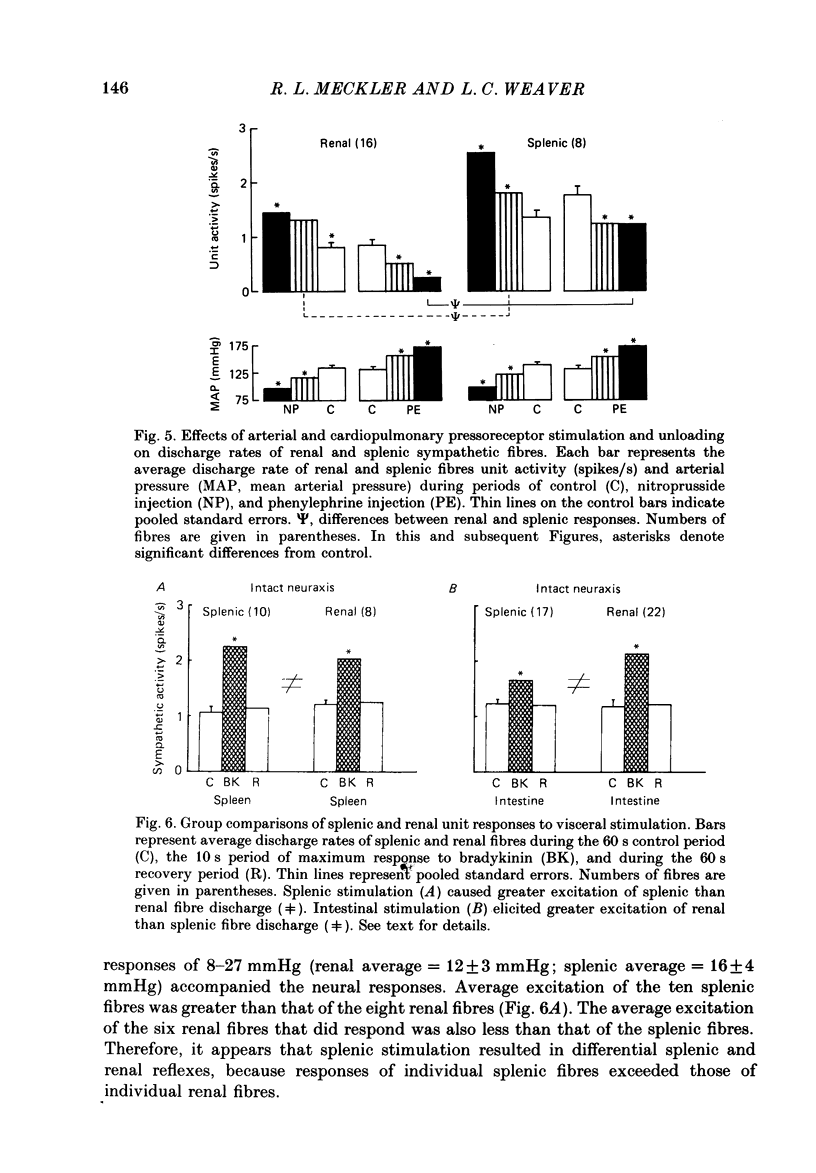
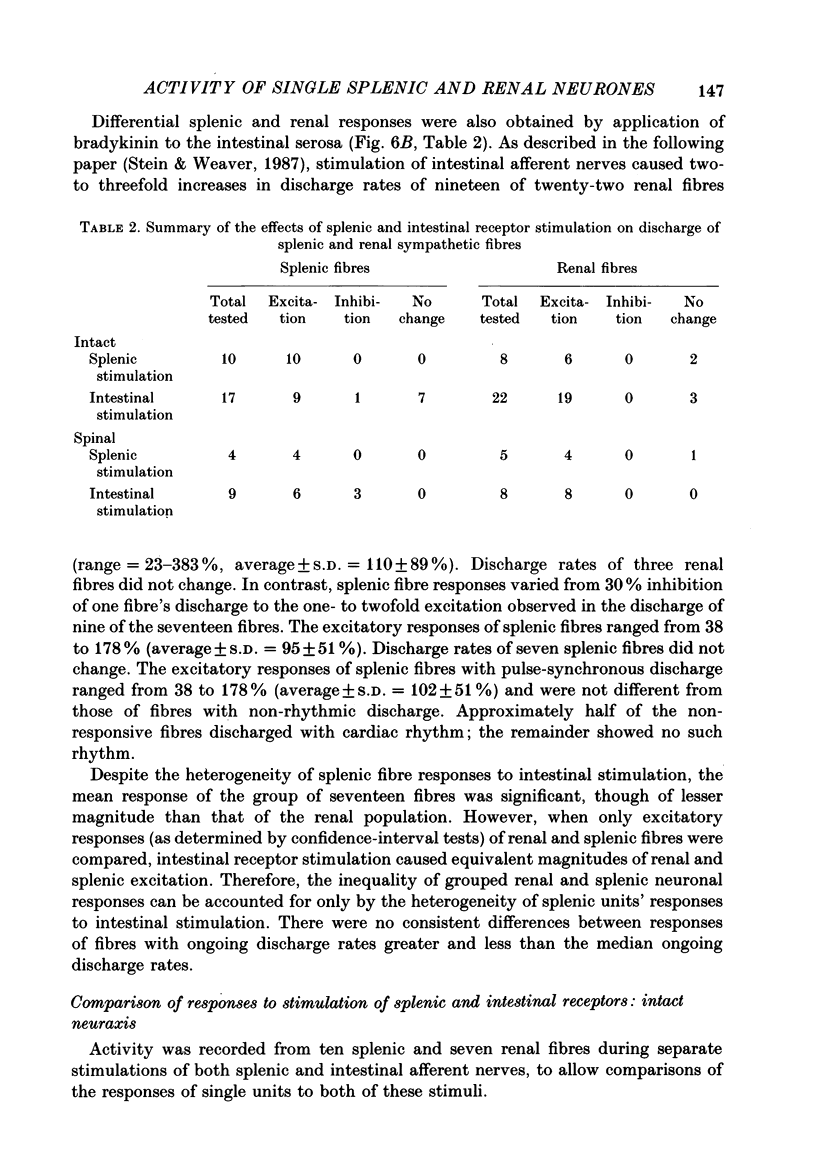
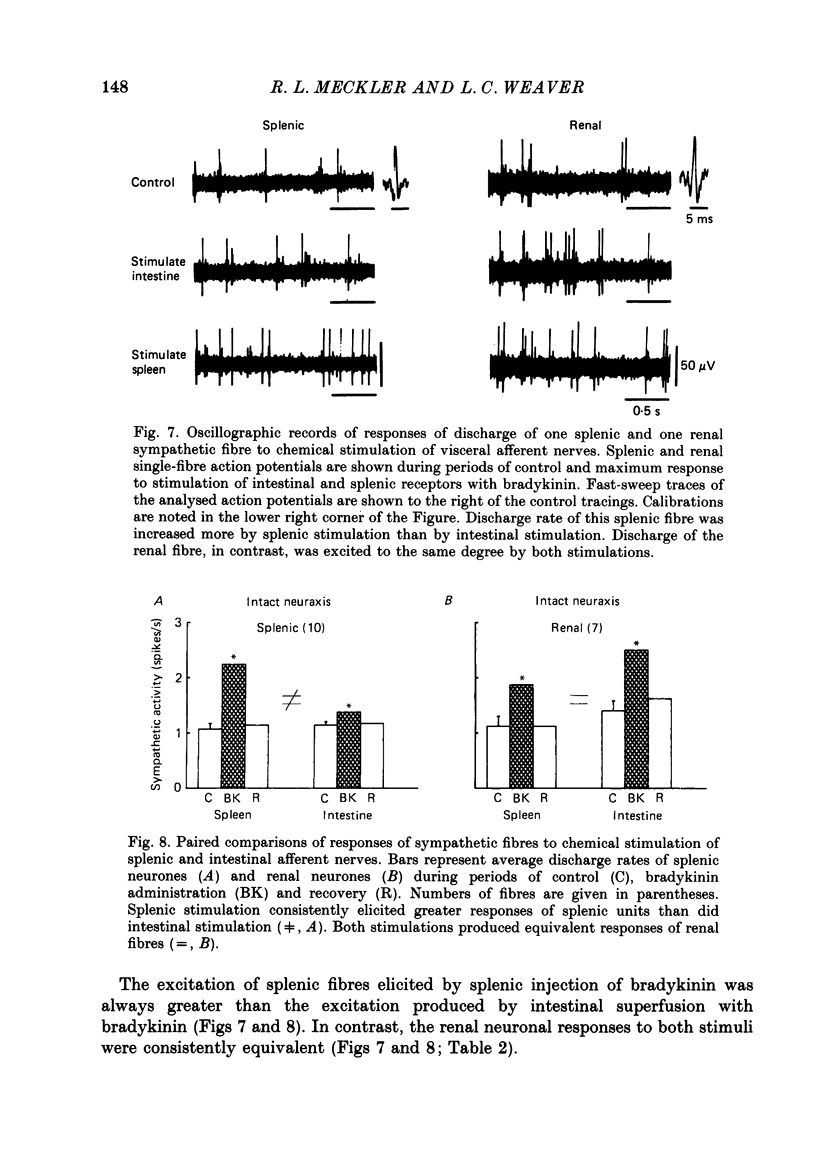
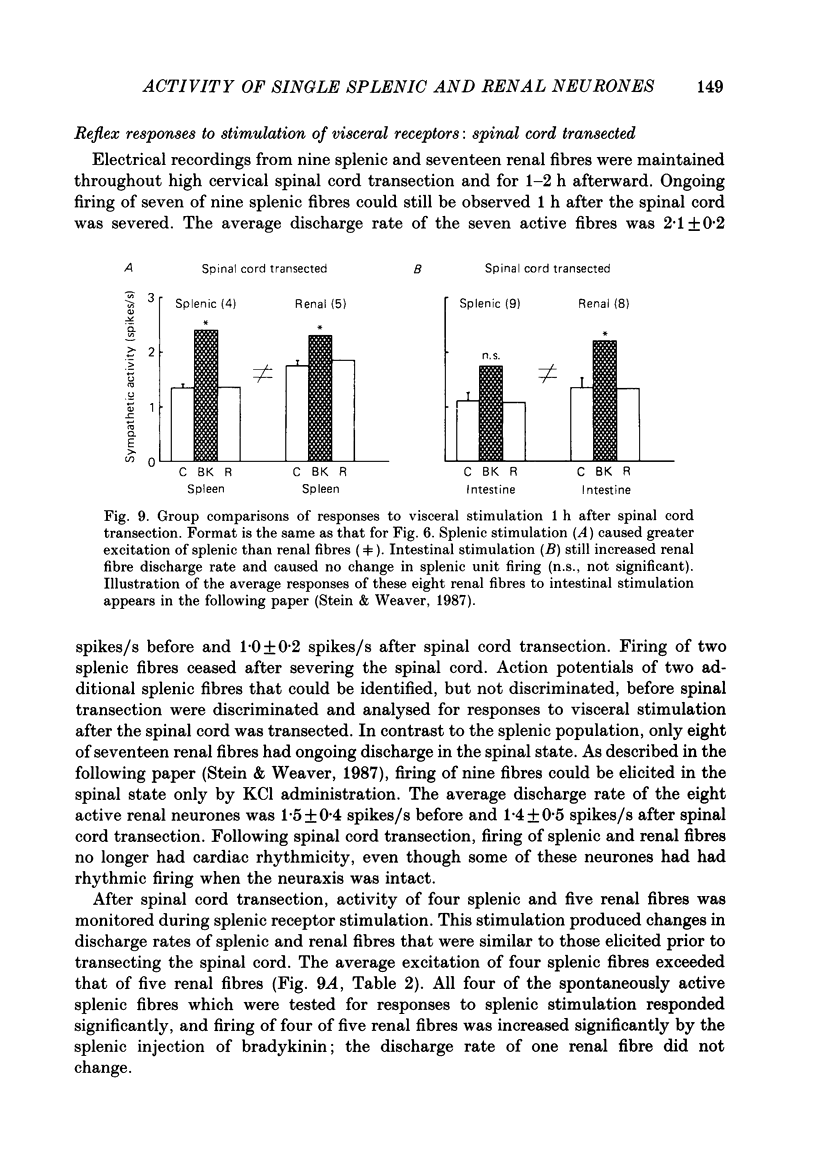
1. Electrical discharge of thirty-nine single splenic and renal postganglionic nerve fibres was recorded in artificially respired, chloralose-anaesthetized cats. 2. Ongoing discharge rates, averaged over 10 s periods, did not differ between renal and splenic fibres. All neurones of both groups had irregular discharge frequencies. 3. Half of the splenic population and all renal fibres had cardiac-related discharge patterns. Of those tested for respiratory-related firing, 30% of the splenic fibres and 69% of the renal fibres exhibited this pattern. 4. Firing of splenic fibres was less inhibited than that of renal fibres by stimulation of pressoreceptors with phenylephrine-induced increases in blood pressure. Firing of splenic fibres also was less excited than that of renal fibres by unloading pressoreceptors with depressor doses of sodium nitroprusside. 5. Chemical stimulation of splenic afferent nerves with bradykinin consistently elicited greater increases in splenic than renal nerve discharge by causing large increases in firing of all splenic fibres and smaller excitatory responses in 75% of the renal fibres. 6. Application of bradykinin to the intestinal serosa produced greater increases in renal than splenic nerve discharge by consistently causing increased firing of renal fibres and by causing excitation, inhibition, or no change in splenic fibre discharge. 7. Responses of splenic and renal fibres to stimulation of splenic and intestinal afferent nerves after spinal cord transection were similar to those responses elicited when the neuraxis was intact. 8. In conclusion, the differential reflex responses of splenic and renal neuronal populations can be due to the heterogeneity or to the intensity of responses within a neuronal population.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D., Bronk D. W., Phillips G. Discharges in mammalian sympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1932 Feb 8;74(2):115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1932.sp002832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H., Jänig W., Rieckmann C., Szulczyk P. Baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes in postganglionic neurones supplying skeletal muscle and hairy skin. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1980 Oct;2(3):223–240. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(80)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calaresu F. R., Tobey J. C., Heidemann S. R., Weaver L. C. Splenic and renal sympathetic responses to stimulation of splenic receptors in cats. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 2):R856–R865. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.247.5.R856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway C. V., Stark R. D. Vascular responses of the spleen to rapid haemorrhage in the anaesthetized cat. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):169–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor M., Jänig W., Wiprich L. Cardiac and respiratory rhythmicities in cutaneous and muscle vasoconstrictor neurones to the cat's hindlimb. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Sep 16;370(3):299–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00585543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F., Kidd C., Malpus C. M., Penna P. E. The effects of stimulation of the left atrial receptors on sympathetic efferent nerve activity. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):243–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meckler R. L., Weaver L. C. Splenic, renal, and cardiac nerves have unequal dependence upon tonic supraspinal inputs. Brain Res. 1985 Jul 8;338(1):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss G., Polosa C. The relation between end-tidal CO2 and discharge patterns of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Brain Res. 1977 Feb 18;122(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90293-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. D., Weaver L. C. Multi- and single-fibre mesenteric and renal sympathetic responses to chemical stimulation of intestinal receptors in cats. J Physiol. 1988 Feb;396:155–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. G., Gebber tgl Baroreceptor mechanisms controlling sympathetic nervous rhythms of central origin. Am J Physiol. 1975 Apr;228(4):1002–1003. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.4.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. C., Fry H. K., Meckler R. L., Oehl R. S. Multisegmental spinal sympathetic reflexes originating from the heart. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):R345–R352. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.245.3.R345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


