Abstract
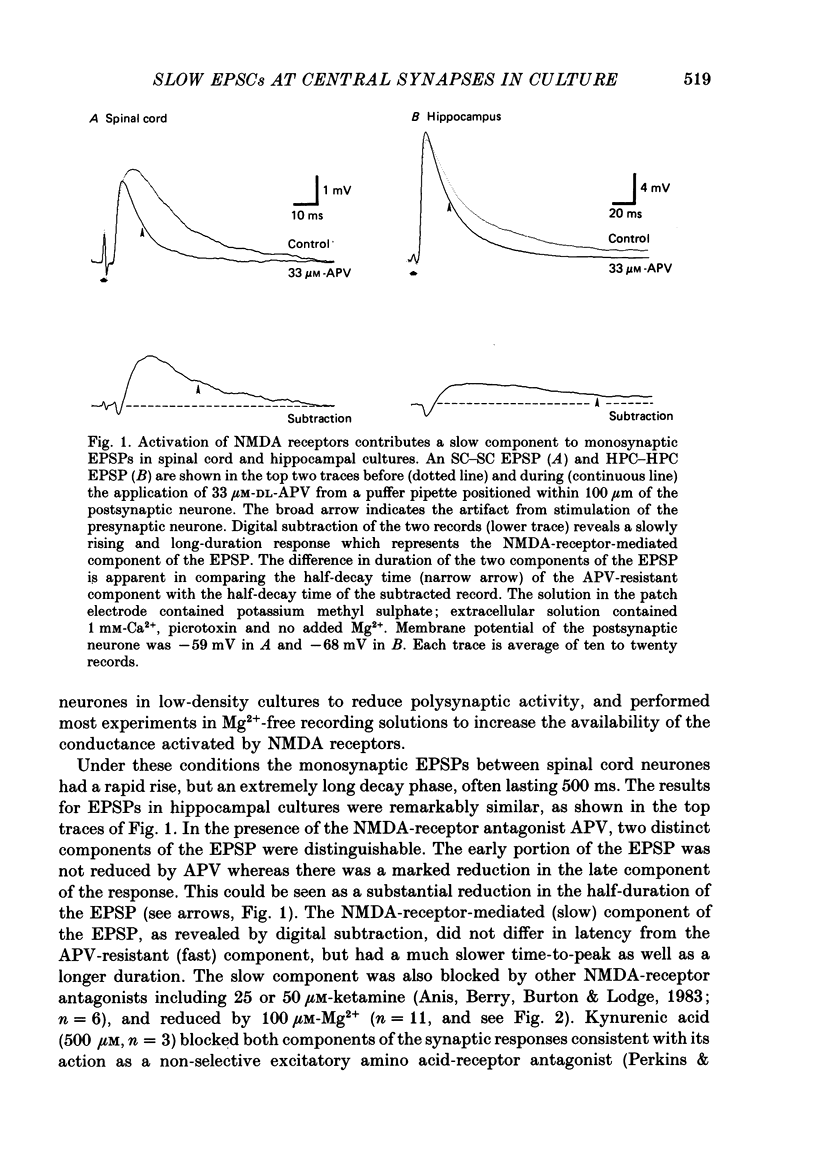
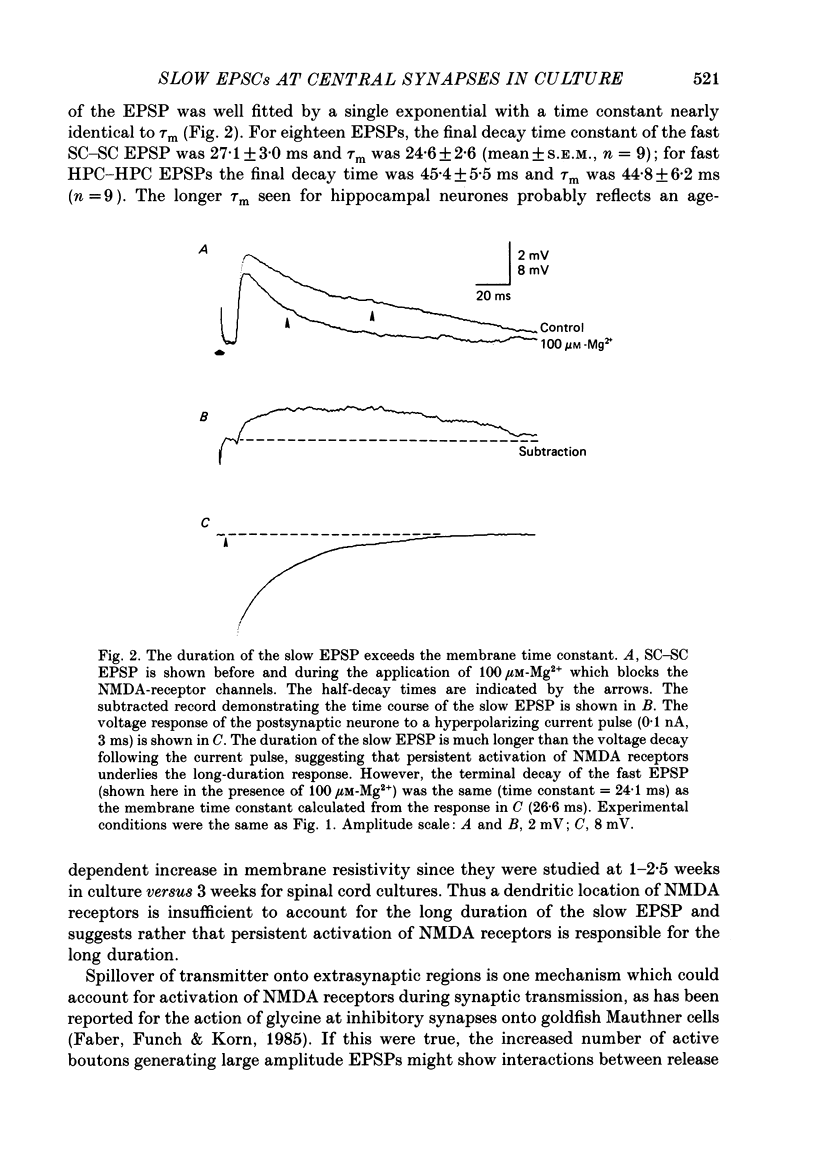
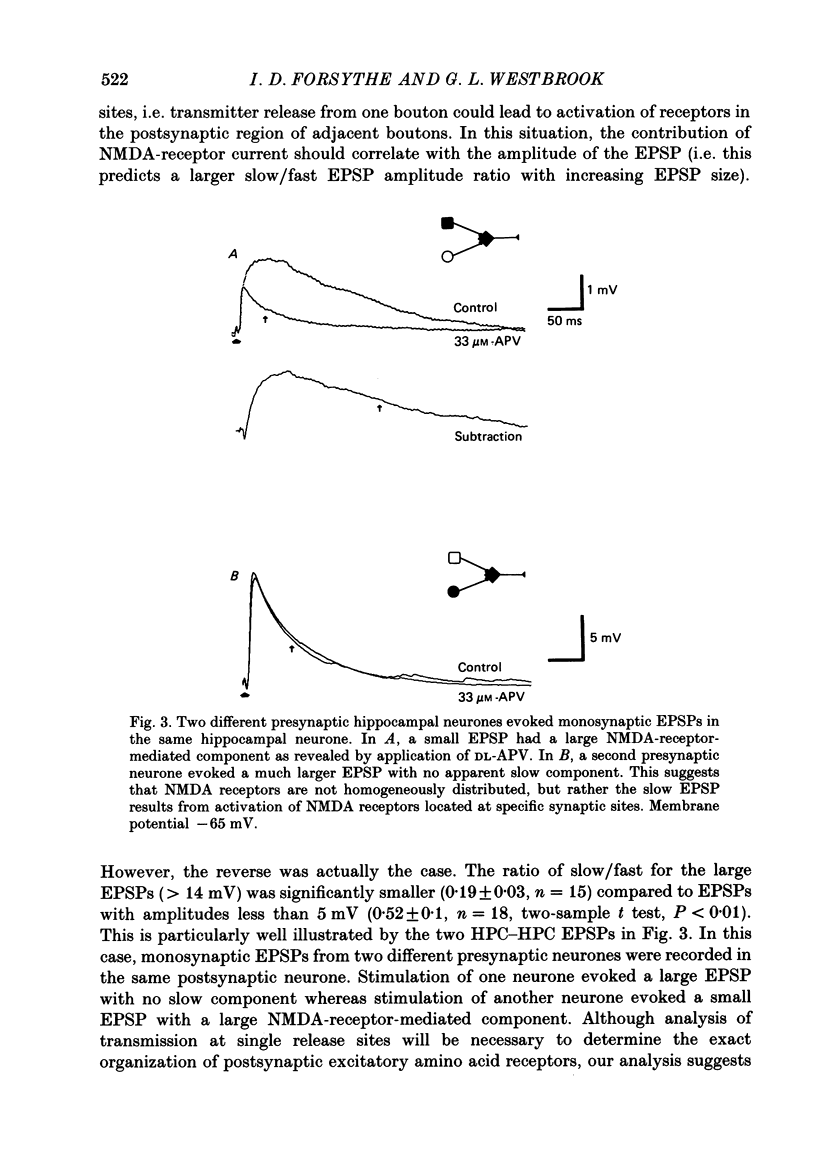
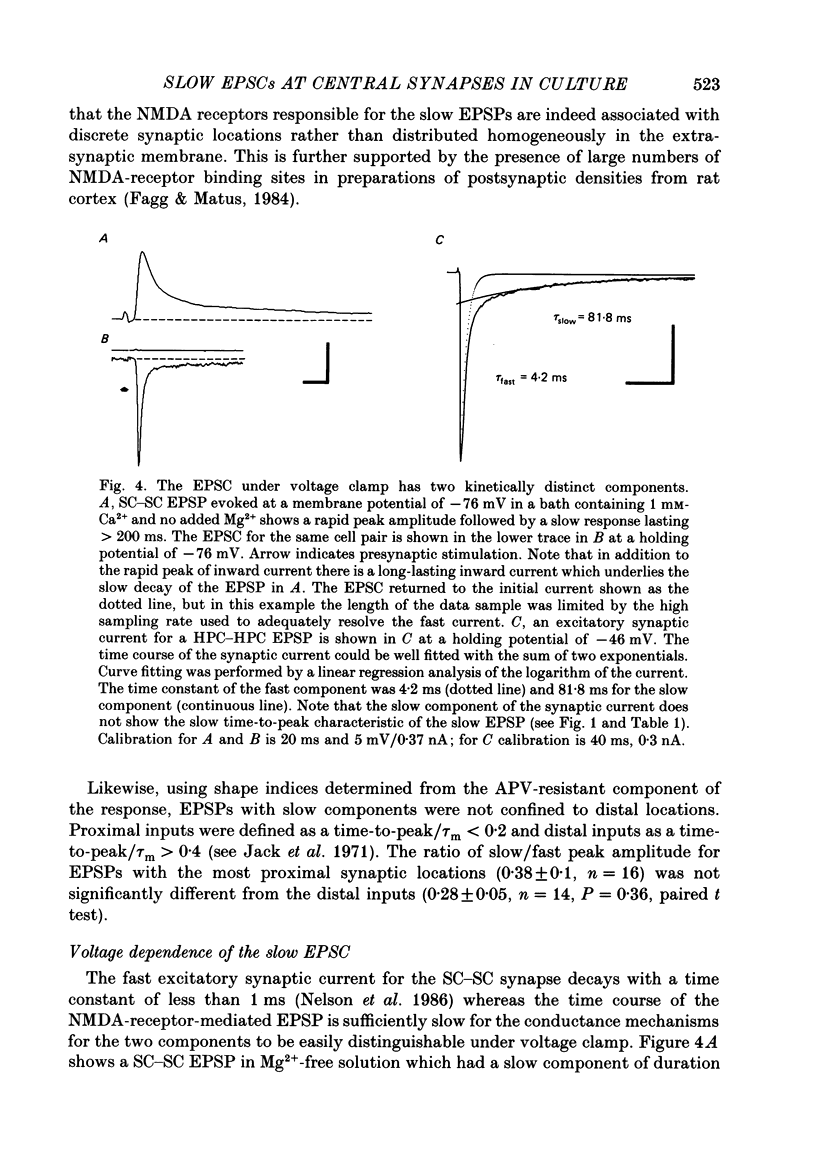
1. Monosynaptic excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) evoked between pairs of cultured neurones from either hippocampus or spinal cord were examined using the tight-seal whole-cell recording technique. 2. Using the selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-receptor antagonist, 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV), two components of the EPSP could be resolved in cultures from both brain regions. The APV-sensitive (slow) component had the same latency, but a much slower time-to-peak and longer duration than the APV-resistant (fast) component. Other NMDA antagonists such as ketamine also selectively blocked the slow component of the EPSP. 3. In Mg2+-free medium, the dual-component EPSP had a duration lasting up to 500 ms, greatly exceeding the membrane time constant of the postsynaptic neurone, suggesting that persistent activation of NMDA receptors was responsible for the long duration of the APV-sensitive component. 4. Under voltage clamp the excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) also showed fast and slow components, both of which had a reversal potential near 0 mV in physiological saline. The synaptic current could be fitted with a sum of two exponentials with a decay time constant for the slow EPSC near 80 ms. The slow current contributed approximately 50% of the total charge transfer during the EPSC. 5. In Mg2+-containing medium, the peak of the fast component was voltage insensitive, whereas the synaptic current measured at a latency of 10-50 ms was voltage dependent with a region of negative slope conductance at membrane potentials hyperpolarized to -30 mV. 6. Raising [Ca2+]o from 1 to 20 mM resulted in a shift of the reversal potential of the APV-sensitive component from near 0 mV to + 10 mV, but the reversal potential of the fast component remained near 0 mV. This suggests that conductances with different ionic permeability underlie the two components of the EPSC and that the slow component is highly permeable to Ca2+ as well as to monovalent cations. 7. Our results demonstrate that two functionally distinct excitatory amino acid receptor channels are simultaneously activated by transmitter release from a single presynaptic neurone. The conductance mechanism underlying the slow component of the EPSP displays the voltage dependence and Ca2+ permeability expected for NMDA-receptor channels. We suggest that the available conductance generating the slow EPSP may be sufficient, even at low firing rates, to influence excitability on both a short-term and more long-lasting basis.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. The permeability of endplate channels to monovalent and divalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):493–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker G. A., Cowan W. M. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977 May 13;126(3):397–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90594-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chad J. E., Eckert R. Calcium domains associated with individual channels can account for anomalous voltage relations of CA-dependent responses. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):993–999. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84244-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. Multiple-conductance channels activated by excitatory amino acids in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):525–528. doi: 10.1038/325525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Dual-component amino-acid-mediated synaptic potentials: excitatory drive for swimming in Xenopus embryos. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:35–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Excitatory amino acid receptors in Xenopus embryo spinal cord and their role in the activation of swimming. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:527–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber D. S., Funch P. G., Korn H. Evidence that receptors mediating central synaptic potentials extend beyond the postsynaptic density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Matus A. Selective association of N-methyl aspartate and quisqualate types of L-glutamate receptor with brain postsynaptic densities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6876–6880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S., Redman S. J. The synaptic current evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group 1a axons. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:615–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong A. H., Lanthorn T. H., Cotman C. W. Kynurenic acid inhibits synaptic and acidic amino acid-induced responses in the rat hippocampus and spinal cord. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 22;273(1):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H., Abraham W. C., Huang Y. Y. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus using depolarizing current pulses as the conditioning stimulus to single volley synaptic potentials. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):774–780. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00774.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Quantitative studies on some antagonists of N-methyl D-aspartate in slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):381–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. Post-synaptic potentiation: interaction between quanta of acetylcholine at the skeletal neuromuscular synapse. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):427–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herron C. E., Lester R. A., Coan E. J., Collingridge G. L. Frequency-dependent involvement of NMDA receptors in the hippocampus: a novel synaptic mechanism. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):265–268. doi: 10.1038/322265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Miller S., Porter R., Redman S. J. The time course of minimal excitory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones by group Ia afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J. An electrical description of the motoneurone, and its application to the analysis of synaptic potentials. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):321–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Brown T. H. Interpretation of voltage-clamp measurements in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):464–486. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. NMDA-receptor activation increases cytoplasmic calcium concentration in cultured spinal cord neurones. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):519–522. doi: 10.1038/321519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Porietis A. V., Wojtowicz J. M. L-Aspartic acid induces a region of negative slope conductance in the current-voltage relationship of cultured spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 8;237(1):248–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., MacDermott A. B., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. Agonist- and voltage-gated calcium entry in cultured mouse spinal cord neurons under voltage clamp measured using arsenazo III. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3230–3244. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03230.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Mixed-agonist action of excitatory amino acids on mouse spinal cord neurones under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:29–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The action of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid on mouse spinal neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:65–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Pun R. Y., Westbrook G. L. Synaptic excitation in cultures of mouse spinal cord neurones: receptor pharmacology and behaviour of synaptic currents. J Physiol. 1986 Mar;372:169–190. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. J., Fischbach G. D. Excitatory synaptic transmission between interneurons and motoneurons in chick spinal cord cell cultures. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3284–3289. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03284.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. L-glutamate has higher affinity than other amino acids for [3H]-D-AP5 binding sites in rat brain membranes. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):460–462. doi: 10.1038/307460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Stone T. W. An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 9;247(1):184–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S., Koh J., Choi D. W. Zinc selectively blocks the action of N-methyl-D-aspartate on cortical neurons. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):589–593. doi: 10.1126/science.2883728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Christian C. N., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. II. Synaptic activity and circuit behavior. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1151–1162. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman S. M., Samaie M. Physiology of excitatory synaptic transmission in cultures of dissociated rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Sep;54(3):701–713. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.3.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt T. E. Mediation of thalamic sensory input by both NMDA receptors and non-NMDA receptors. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):263–265. doi: 10.1038/322263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., West D. C., Lodge D. An N-methylaspartate receptor-mediated synapse in rat cerebral cortex: a site of action of ketamine? Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):479–481. doi: 10.1038/313479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook G. L., Mayer M. L. Micromolar concentrations of Zn2+ antagonize NMDA and GABA responses of hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):640–643. doi: 10.1038/328640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook G. L., Mayer M. L., Namboodiri M. A., Neale J. H. High concentrations of N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) selectively activate NMDA receptors on mouse spinal cord neurons in cell culture. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3385–3392. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03385.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigström H., Gustafsson B. A possible correlate of the postsynaptic condition for long-lasting potentiation in the guinea pig hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Feb 24;44(3):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


