Abstract
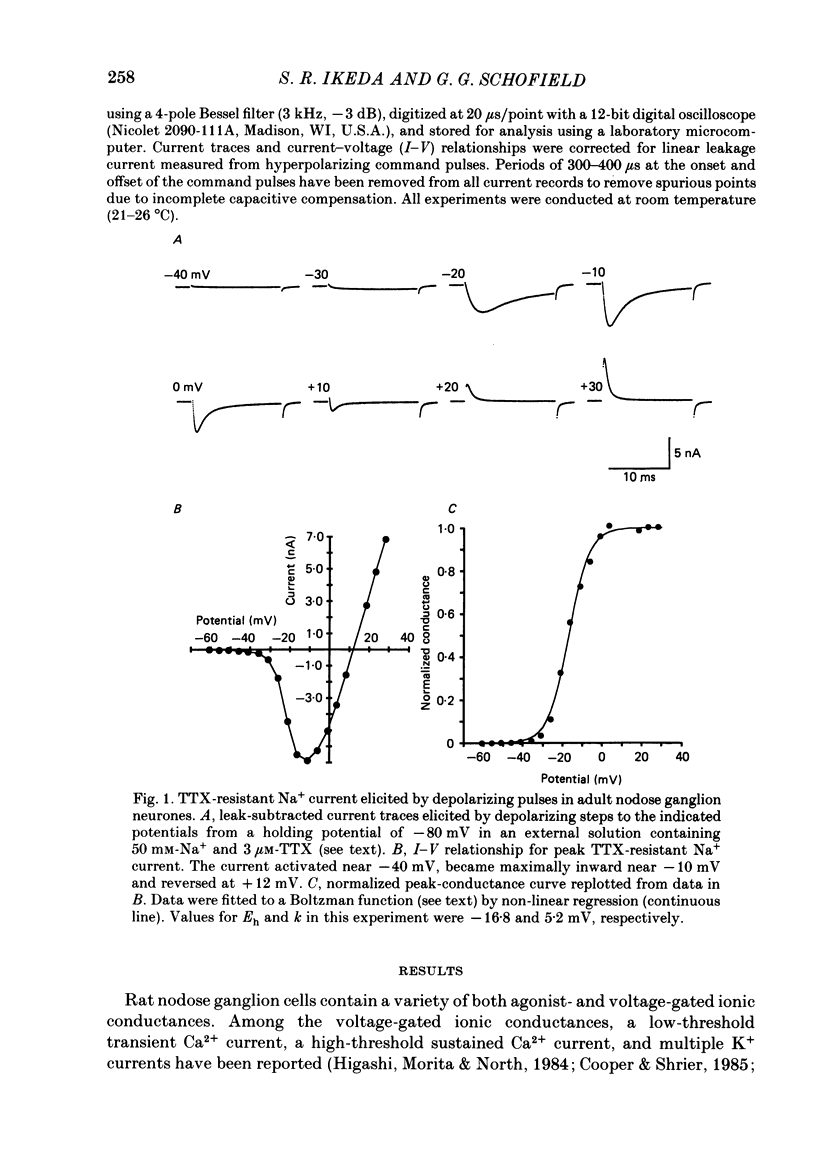
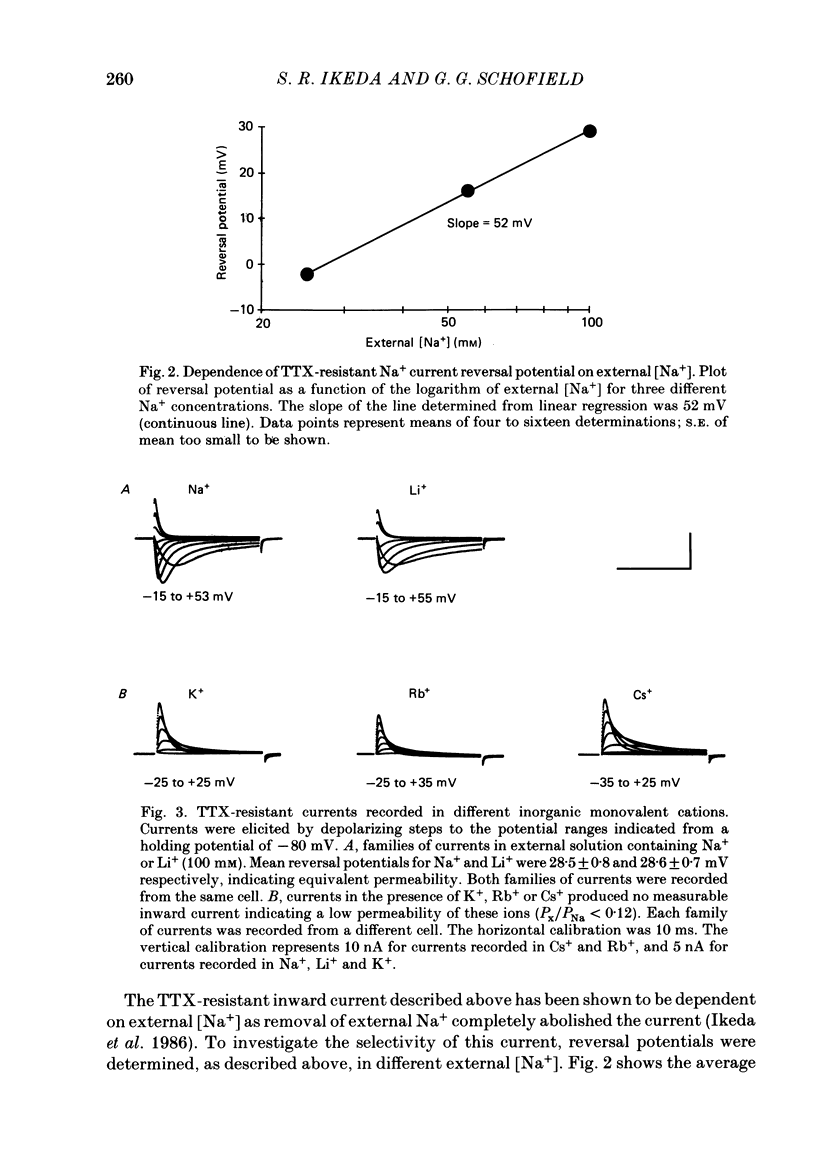
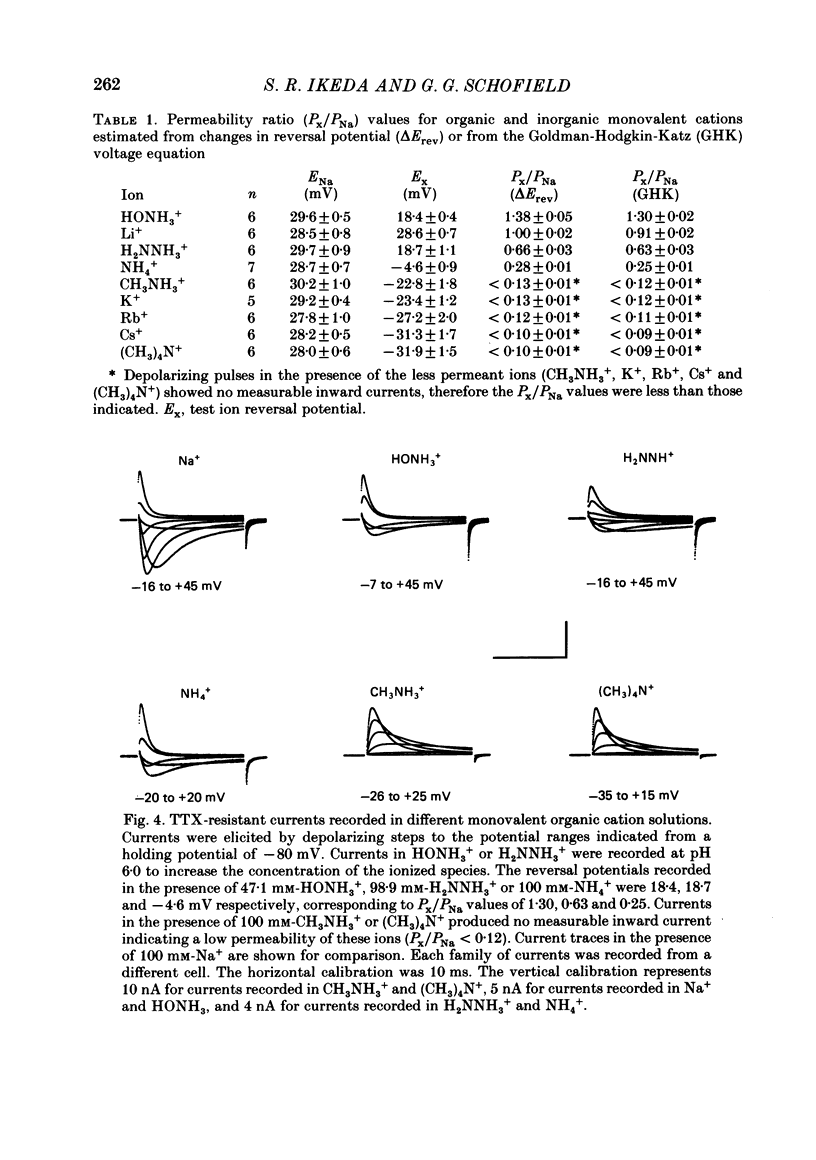
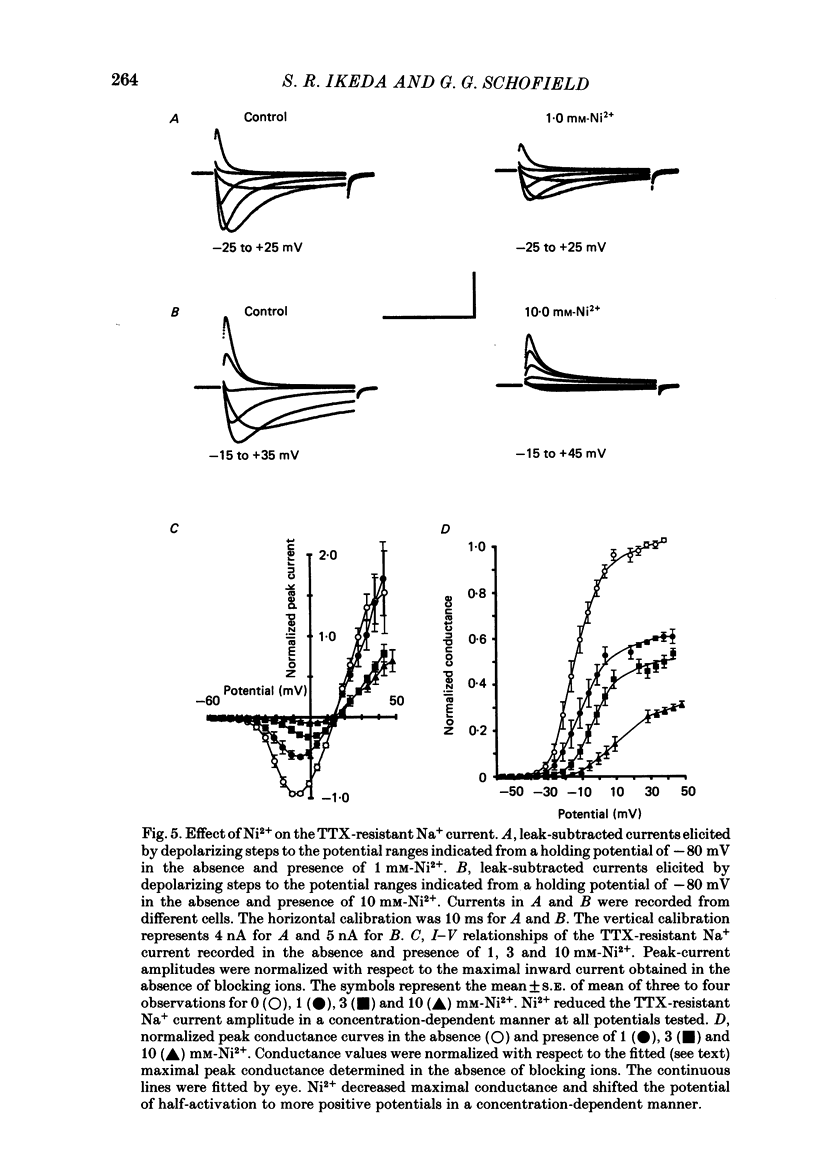
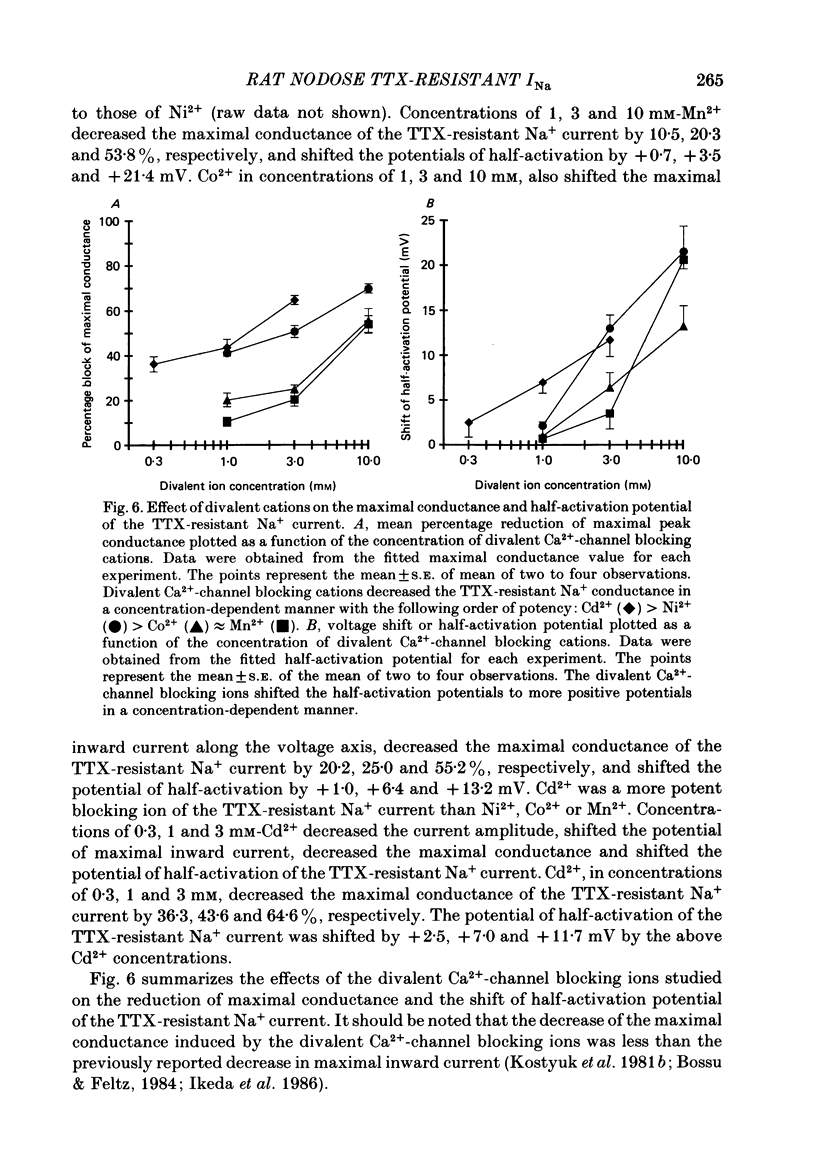
1. Monovalent cation selectivity and divalent cation sensitivity of the tetrodotoxin (TTX)-resistant Na+ current in dissociated adult rat nodose ganglion neurones were investigated using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique. 2. The TTX-resistant Na+ current was isolated using ion substitution and pharmacological agents. Under these conditions, the current reversal potential shifted 52 mV per tenfold change in external [Na+]. 3. Inorganic and organic monovalent cation permeability ratios (Px/PNa) were determined from changes in reversal potential and the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation. The Px/PNa values determined by the former method were HONH3+, 1.38; Li+, 1.00; H2NNH3+, 0.66; NH4+, 0.28; CH3NH3+, less than 0.13; K+, less than 0.13; Rb+, less than 0.12; Cs+, less than 0.10; (CH3)4N+, less than 0.10. The values determined by either method agreed within 10%. 4. The effects of Cd2+, Co2+, Mn2+ and Ni2+ on the TTX-resistant Na+ current were analysed from peak-conductance values. These ions shifted the activation of the current to more positive potentials and decreased the maximal conductance. At 3 mM concentrations, Cd2+, Ni2+, Co2+ and Mn2+ decreased the maximal conductance 64.6, 50.7, 25.0 and 20.3%, respectively. 5. The results indicate that: (a) the monovalent cation selectivity of the TTX-resistant Na+ current is similar to that of the TTX-sensitive Na+ current in other tissues; and (b) the TTX-resistant Na+ current is less sensitive to divalent cations than the Ca2+ current in these neurones. These observations suggest that the structure determining the monovalent cation permeability of the TTX-resistant Na+ current is similar to that of the TTX-sensitive Na+ current in other tissues, and that the channels carrying the TTX-resistant Na+ current are distinct from those responsible for the Ca2+ current.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W. Non-selective conductance in calcium channels of frog muscle: calcium selectivity in a single-file pore. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., McCleskey E. W., Palade P. T. A non-selective cation conductance in frog muscle membrane blocked by micromolar external calcium ions. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arhem P. Effects of some heavy metal ions on the ionic currents of myelinated fibres from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:219–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccaglini P. I., Cooper E. Electrophysiological studies of new-born rat nodose neurones in cell culture. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:429–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binstock L. Permeability of the sodium channel in Myxicola to organic cations. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Nov;68(5):551–562. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.5.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., Dupont J. L., Feltz A. IA current compared to low threshold calcium current in cranial sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Dec 4;62(2):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., Feltz A. Patch-clamp study of the tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium current in group C sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Oct 12;51(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90558-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossu J. L., Feltz A., Thomann J. M. Depolarization elicits two distinct calcium currents in vertebrate sensory neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Apr;403(4):360–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00589247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Voltage clamp experiments on internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):788–820. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper E., Shrier A. Single-channel analysis of fast transient potassium currents from rat nodose neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:199–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Fox A. P., Krasne S. Membrane patches and whole-cell membranes: a comparison of electrical properties in rat clonal pituitary (GH3) cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler J. C., Greene R., Weinreich D. Two calcium-sensitive spike after-hyperpolarizations in visceral sensory neurones of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1985 Aug;365:59–75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda J., Kameyama M. Tetrodotoxin-sensitive and tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels in tissue-cultured spinal ganglion neurons from adult mammals. Brain Res. 1980 Jan 20;182(1):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90844-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego R. The ionic basis of action potentials in petrosal ganglion cells of the cat. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:591–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Thesleff S. Studies on tetrodotoxin resistant action potentials in denervated skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Nov;83(3):382–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer E. J., Macdonald R. L. Calcium- and sodium-dependent action potentials of mouse spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Apr;47(4):641–655. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.47.4.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Morita K., North R. A. Calcium-dependent after-potentials in visceral afferent neurones of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:479–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic selectivity, saturation, and block in sodium channels. A four-barrier model. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Nov;66(5):535–560. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.5.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):637–658. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to organic cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Dec;58(6):599–619. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.6.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S. R., Schofield G. G., Weight F. F. Na+ and Ca2+ currents of acutely isolated adult rat nodose ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Mar;55(3):527–539. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.3.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Jun;18(2):997–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A. Effects of calcium and calcium-chelating agents on the inward and outward current in the membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):569–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Fedulova S. A. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-II. Calcium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2431–2437. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Veselovsky N. S., Tsyndrenko A. Y. Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons-I. Sodium currents. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2423–2430. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Akaike N., Brown A. M. Trypsin inhibits the action of tetrodotoxin on neurones. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):751–753. doi: 10.1038/265751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. D., Sutro J. B., Hille B. Voltage-dependent gating of veratridine-modified Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jan;87(1):25–46. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Hashiguchi T., Kobayashi H. Three components of active membrane current in the C-neurons of rabbit cervical nodose ganglion under voltage clamp. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Aug 30;59(2):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90198-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding B. C. Properties of toxin-resistant sodium channels produced by chemical modification in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:485–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld C. E., Wallis D. I. Properties of visceral primary afferent neurons in the nodose ganglion of the rabbit. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Aug;54(2):245–260. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Matsuda Y., Samejima A. Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium and calcium components of action potentials in dorsal root ganglion cells of the adult mouse. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Sep;41(5):1096–1106. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.5.1096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


