Abstract
1. The passive permeability of the blood-retinal barrier (b.r.b.) to the water-soluble non-electrolytes, sucrose and mannitol, was determined using a multiple time point-graphical approach as has been used in the assessment of blood-brain barrier (b.b.b.) permeability. 2. The calculated permeability surface area product for the b.r.b. for sucrose was 0.44 (+/- 0.081 S.E. of mean) X 10(-5) ml g-1 s-1 (n = 20) and for mannitol was 1.25 (+/- 0.30) X 10(-5) ml g-1 s-1 (n = 18). These values are similar and comparable to those found for the capillaries in the brain (P greater than 0.05) and significantly different from zero (P less than 0.01). 3. Data on the concentrations of sucrose in different parts of the eye show that the permeability of the blood-retinal barrier, rather than the more permeable blood-aqueous barrier permeability, was being measured by our technique.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alm A., Törnquist P. The uptake index method applied to studies on the blood-retinal barrier. I. A methodological study. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Sep;113(1):73–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
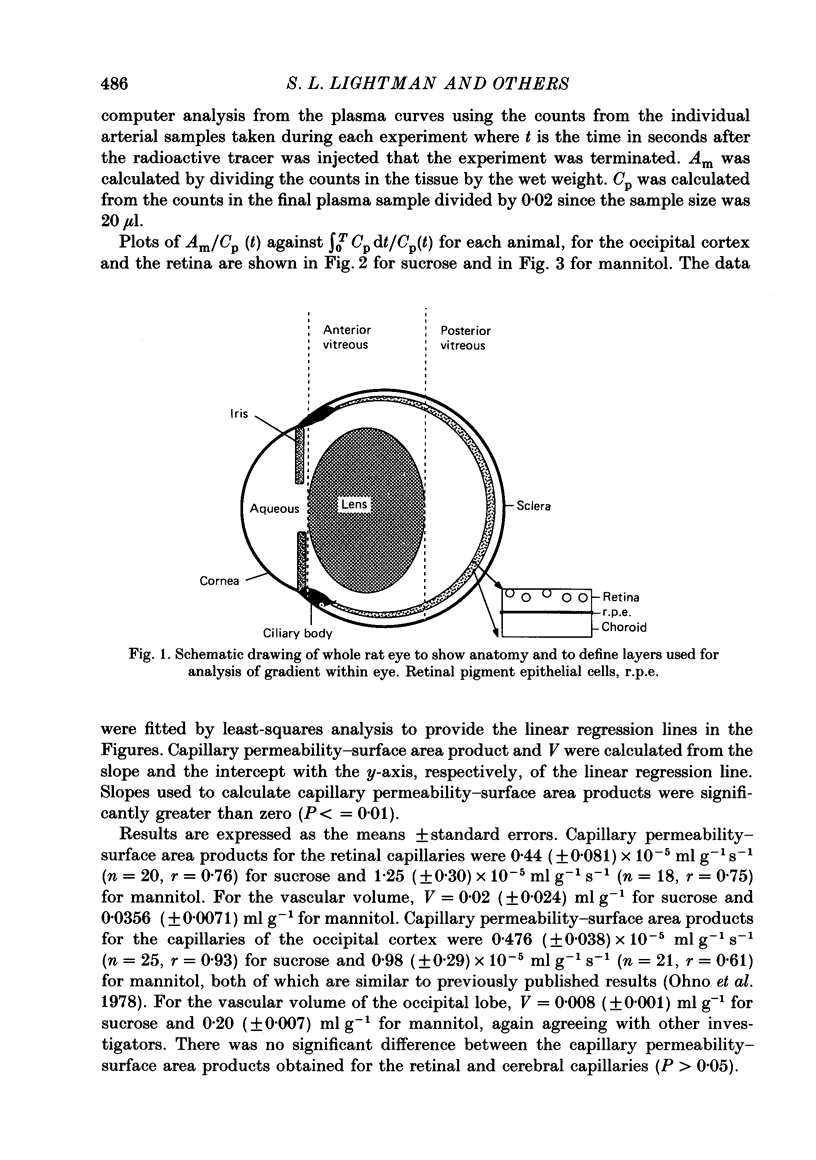
- Ames A., 3rd, Nesbett F. B. Intracellular and extracellular compartments of mammalian central nervous tissue. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):215–238. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E. The influx of amino acids into the brain of the rat in vivo: the essential compared with some non-essential amino acids. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Feb 27;183(1070):59–70. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Kleeman C. R. Stability of the potassium content of cerebrospinal fluid and brain. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):519–528. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Vaz J. G. The blood-retinal barriers. Doc Ophthalmol. 1976 Oct 15;41(2):287–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00146764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Vaz J. The blood-ocular barriers. Surv Ophthalmol. 1979 Mar-Apr;23(5):279–296. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(79)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMattio J., Zadunaisky J. A. Glucose transport into the ocular compartments of the rat. Exp Eye Res. 1981 May;32(5):517–532. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(81)80001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis S. R., Betz A. L. Sucrose permeability of the blood-retinal and blood-brain barriers. Effects of diabetes, hypertonicity, and iodate. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Jul;27(7):1095–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjedde A. High- and low-affinity transport of D-glucose from blood to brain. J Neurochem. 1981 Apr;36(4):1463–1471. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasansky A. The pathway between hyaloid blood and retinal neurons in the toad. Structural observations and permeability to tracer substances. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):617–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Pettigrew K. D., Rapoport S. I. Lower limits of cerebrovascular permeability to nonelectrolytes in the conscious rat. Am J Physiol. 1978 Sep;235(3):H299–H307. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1978.235.3.H299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak C. S., Blasberg R. G., Fenstermacher J. D. Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1983 Mar;3(1):1–7. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1983.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson J. E., Green K. Aqueous humor dynamics: experimental studies. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Mar;15(3):277–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna G. S., Bradbury M. W., Cavanagh J. Permeability of the blood-brain barrier after portocaval anastomosis in the rat. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 23;138(3):550–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90692-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törnquist P., Alm A., Bill A. Studies on ocular blood flow and retinal capillary permeability to sodium in pigs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Jul;106(3):343–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törnquist P., Alm A. Carrier-mediated transport of amino acids through the blood-retinal and the blood-brain barriers. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1986;224(1):21–25. doi: 10.1007/BF02144127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Törnquist P. Capillary permeability in cat choroid, studied with the single injection technique (II). Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Aug;106(4):425–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



