Abstract
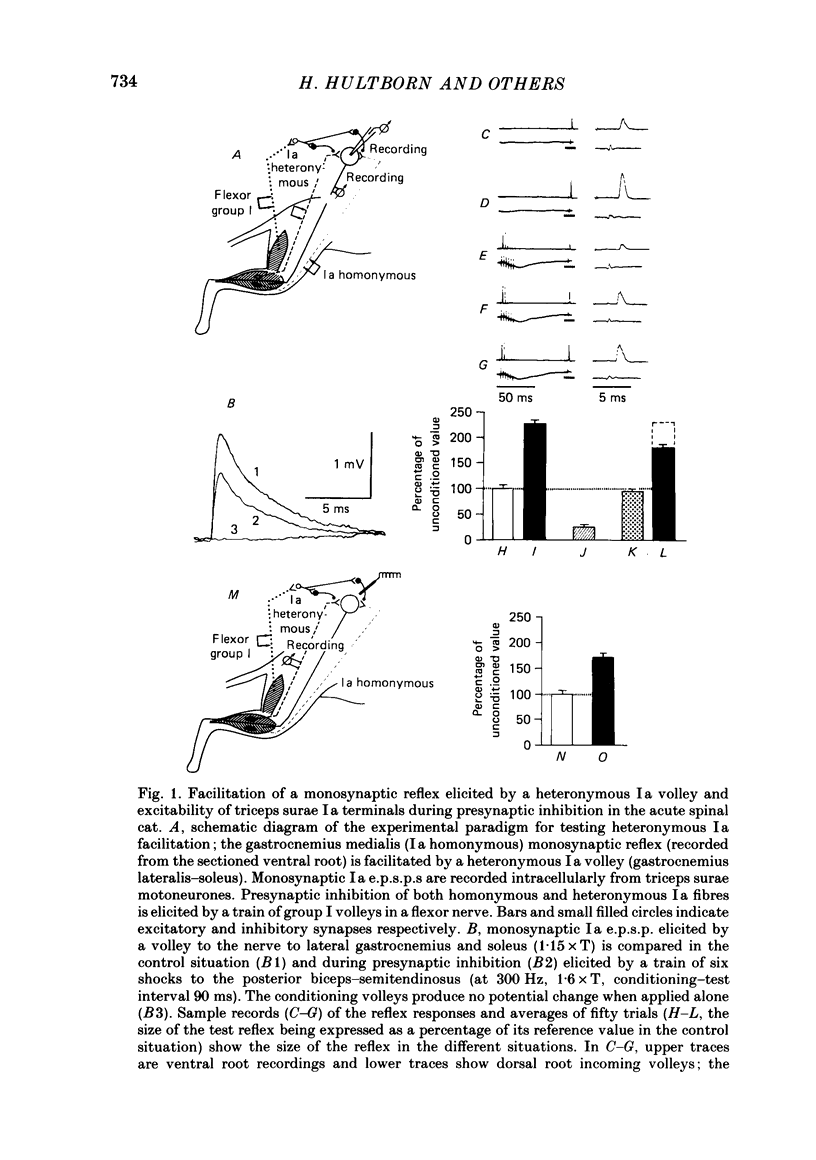
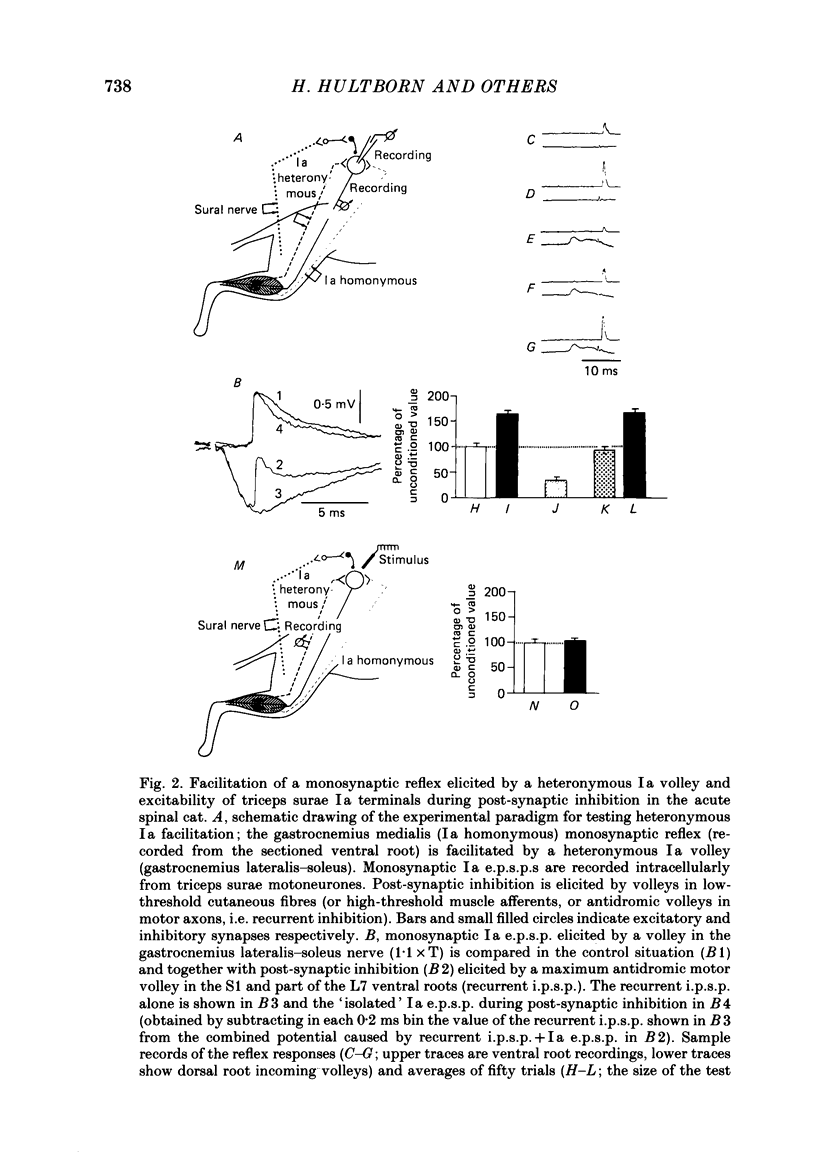
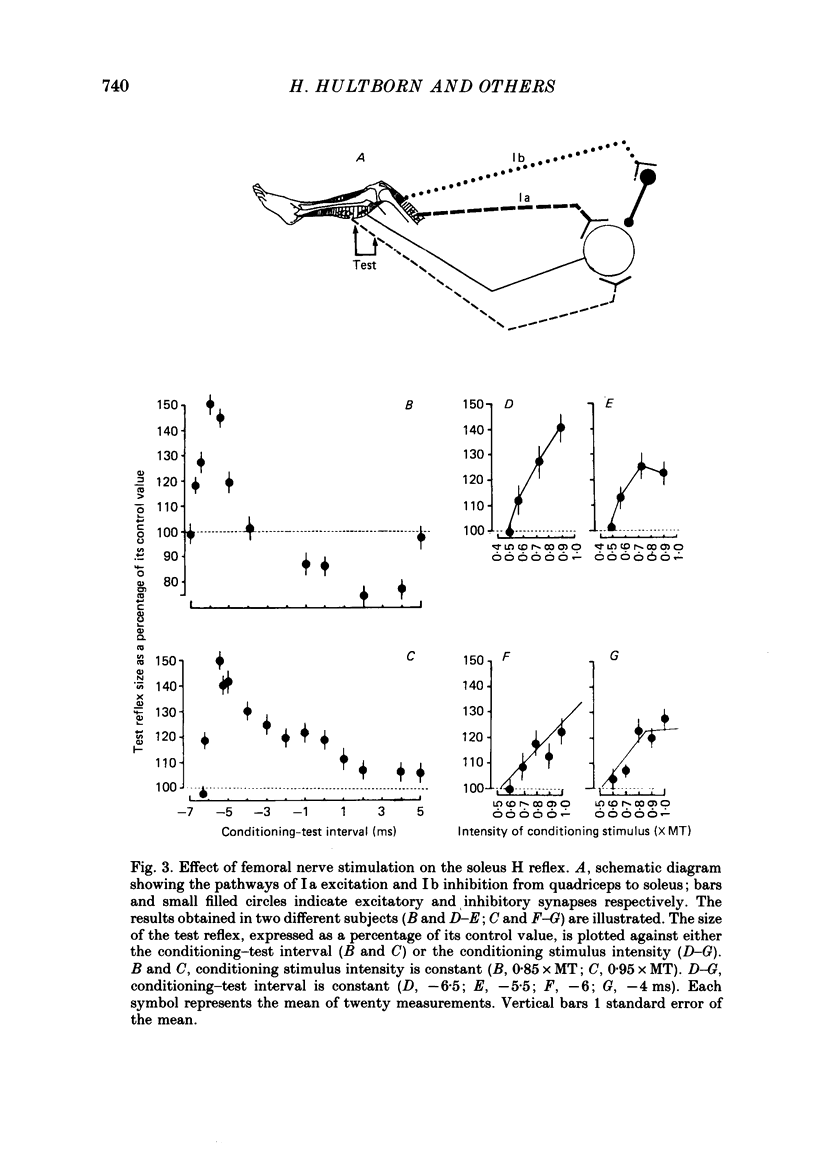
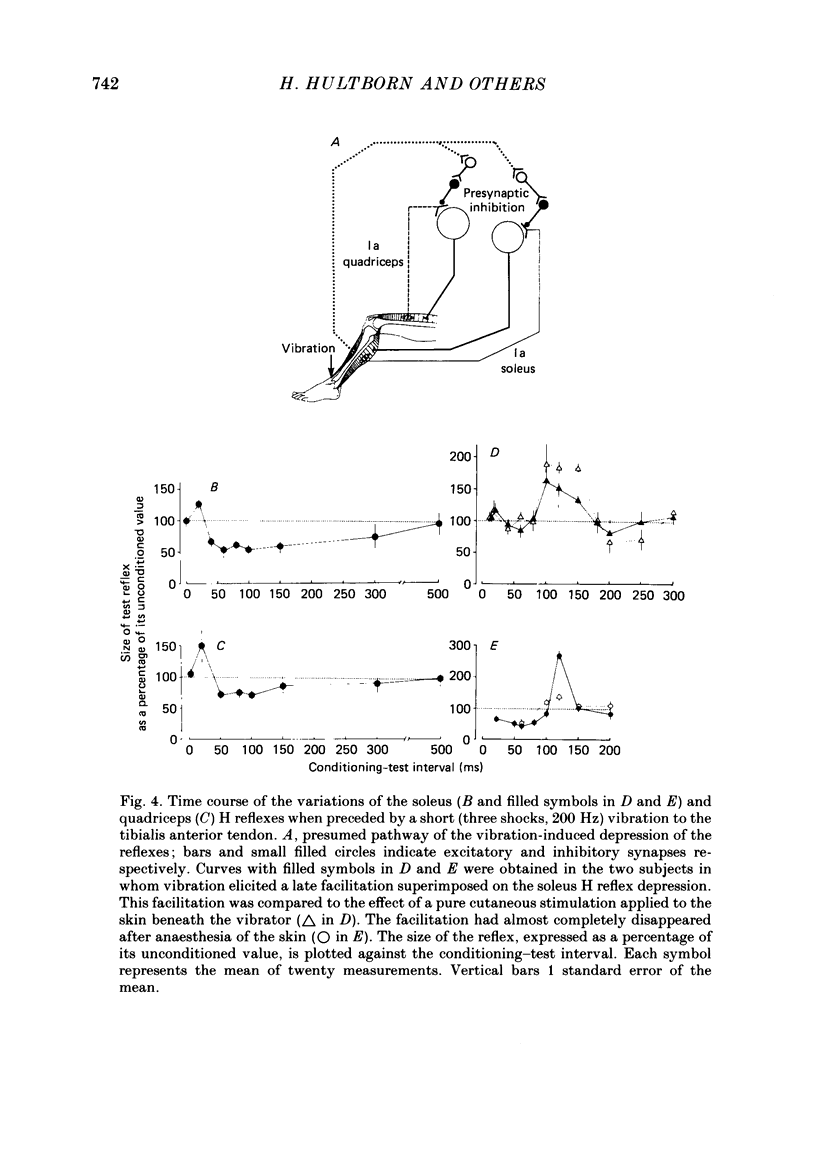
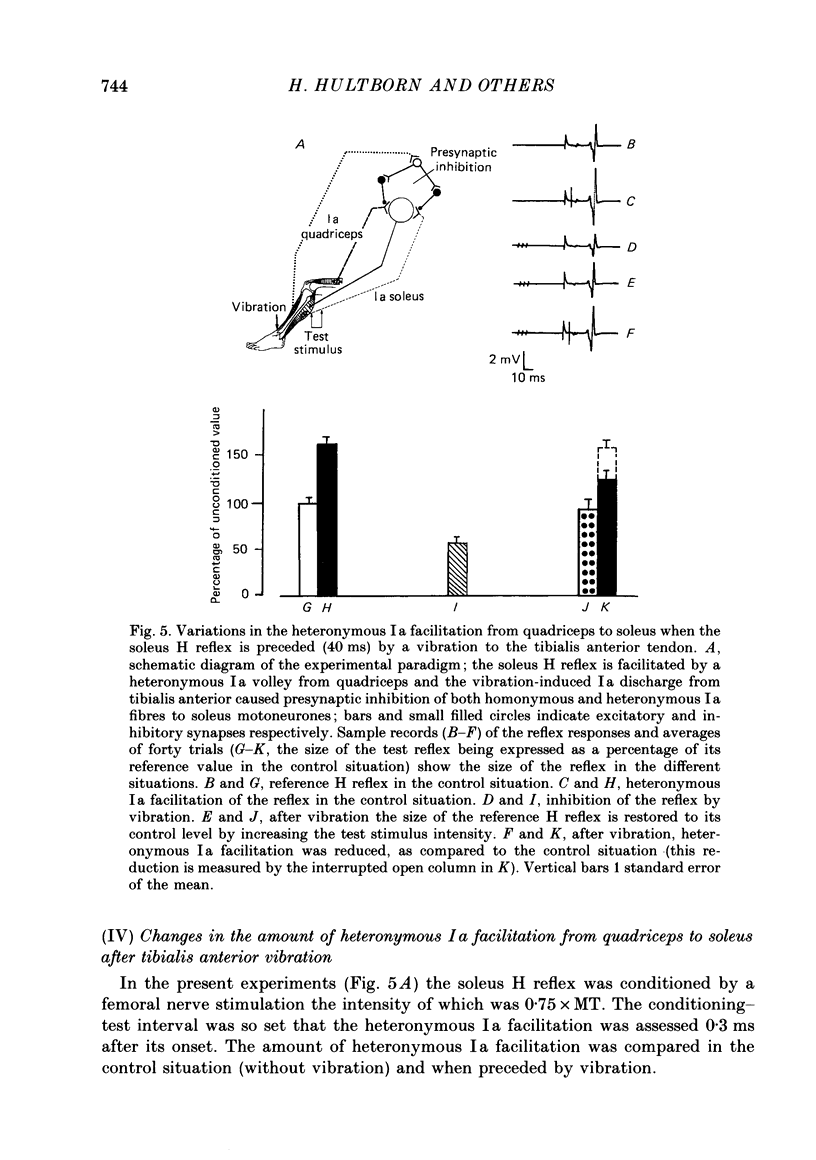
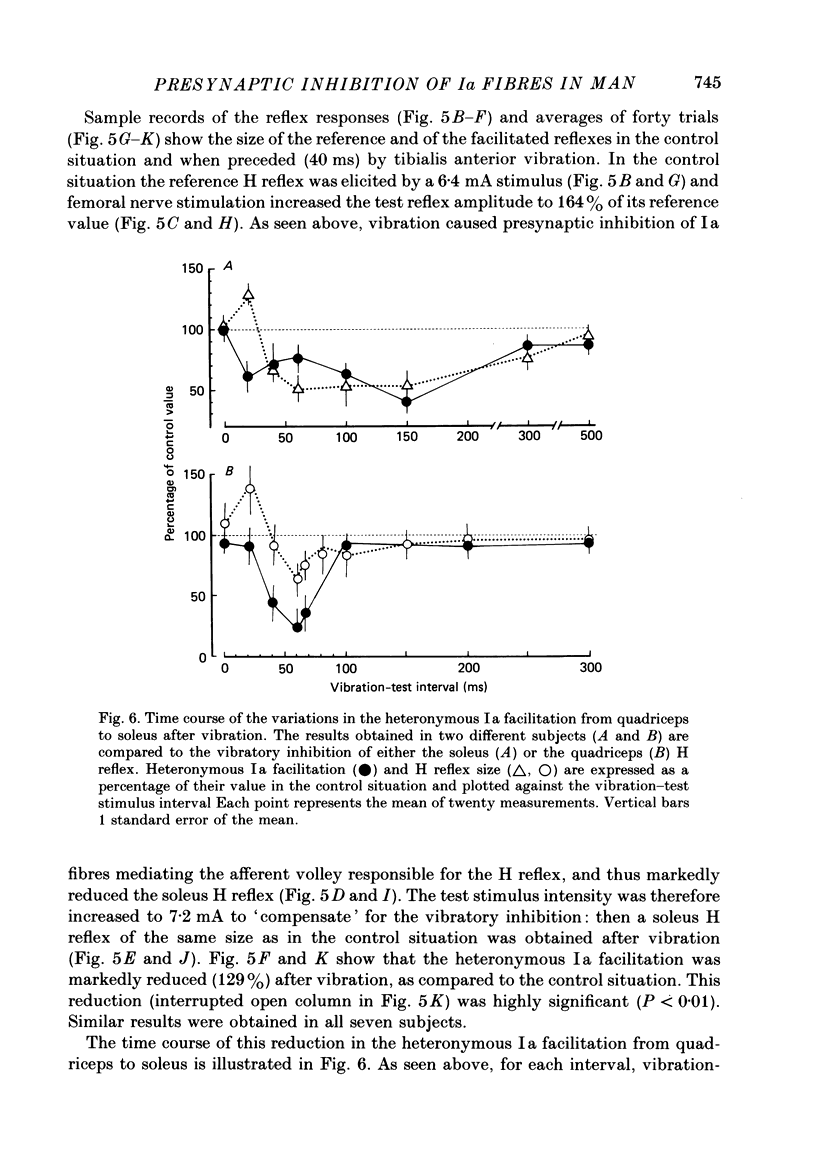
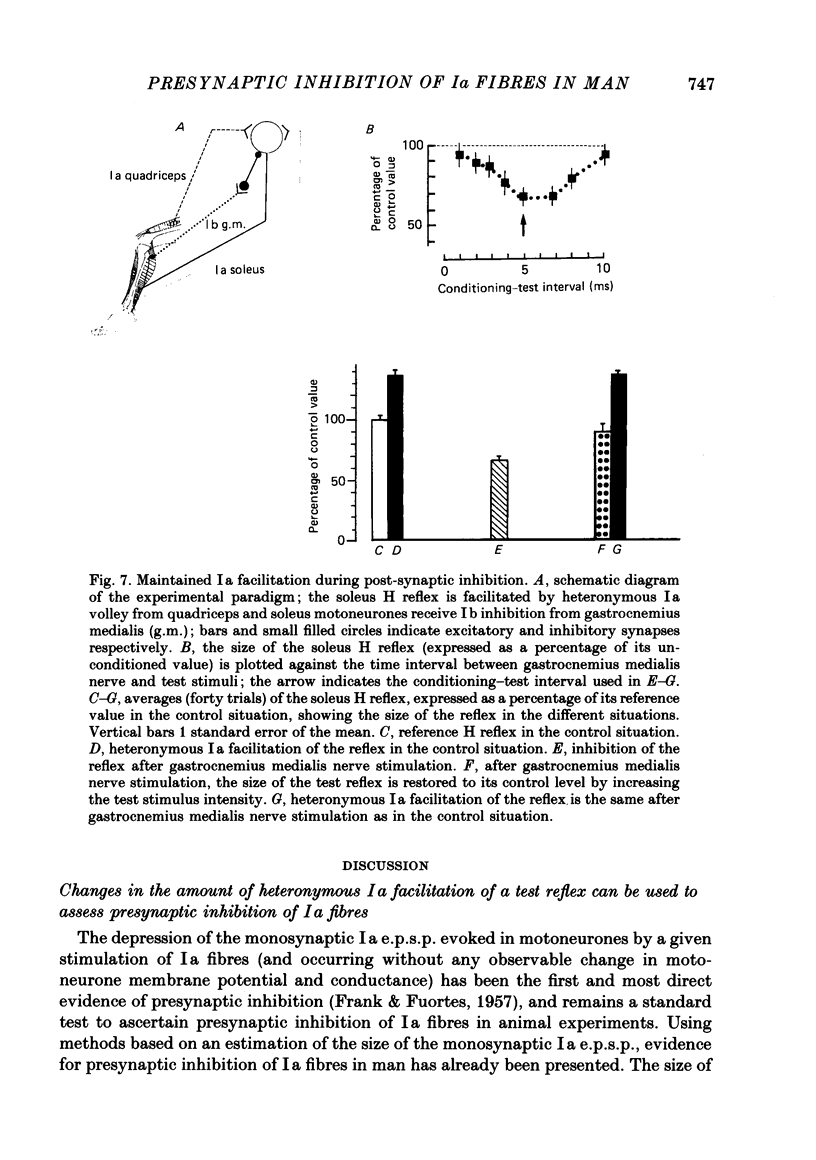
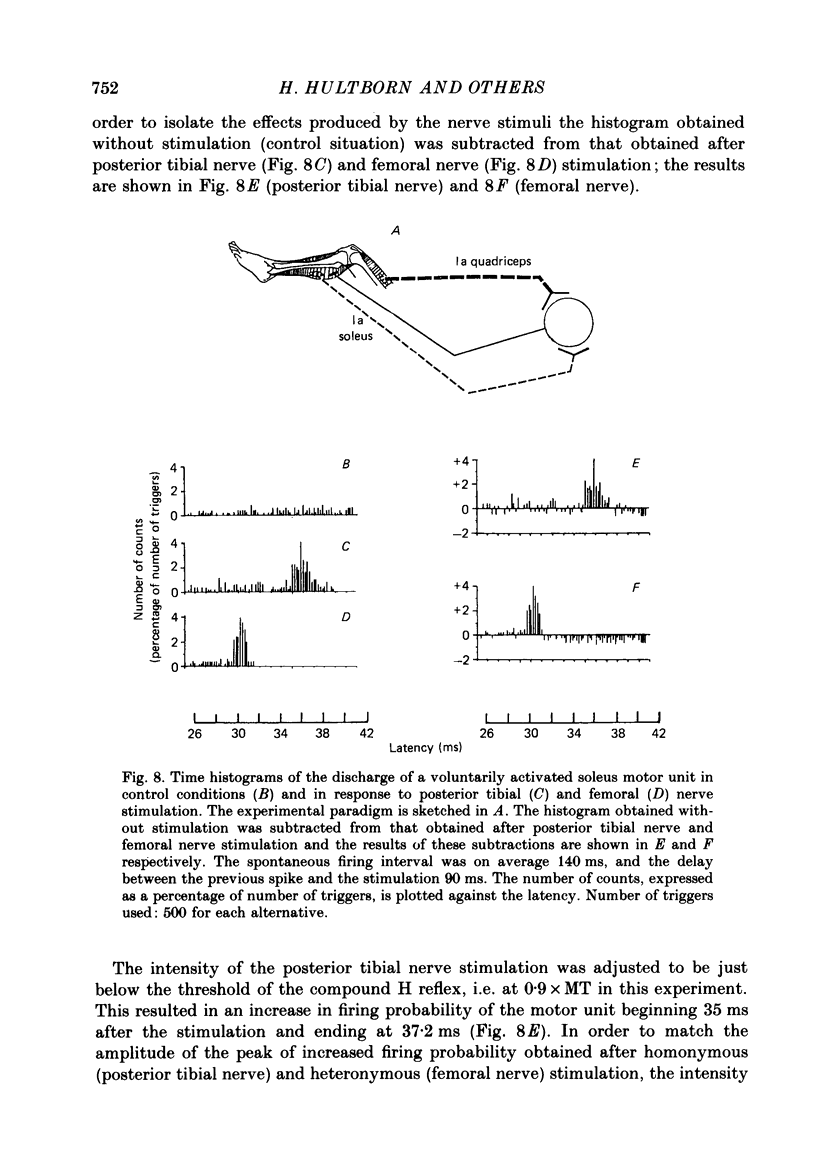
1. A method to assess changes in presynaptic inhibition of I a afferent terminals in man is proposed. The soleus H reflex was facilitated by a heteronymous I a volley from quadriceps and the amount of reflex facilitation was used to estimate the size of the conditioning I a excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.). It is argued that the size of this e.p.s.p. as measured by the resulting amount of reflex facilitation reflects the amount of presynaptic inhibition on the corresponding I a fibres. A decrease in the reflex facilitation may then be ascribed to an increase in presynaptic inhibition of the I a fibres mediating the conditioning volley. 2. That the heteronymous I a facilitation from quadriceps to soleus is caused by a purely monosynaptic e.p.s.p. is a prerequisite for the validity of the method. Experimental evidence is therefore given in an Appendix that in man the earliest part (first 0.5 ms) of this heteronymous I a facilitation is mediated through a monosynaptic pathway. Evidence is also given that this earliest facilitation is not yet contaminated by any polysynaptic effects from I a or I b afferents. 3. The validity of the method was established in animal experiments in which presynaptic inhibition of I a fibres and post-synaptic events in motoneurones could be assessed by direct tests. It was found that the amount of test reflex facilitation produced by a conditioning I a volley was decreased when I a fibres were subjected to presynaptic inhibition but remained unchanged when the motoneurone pool in which the test reflex was elicited received pure post-synaptic inhibition. 4. In man, presynaptic inhibition of I a fibres was evoked by a short-lasting (three shocks at 200 Hz) vibration applied to the tibialis anterior tendon. Such a vibratory burst reduced the efficiency of the heteronymous I a volley in facilitating the soleus H reflex. By contrast, during a pure post-synaptic inhibition of soleus motoneurones the efficiency of the conditioning volley in facilitating the test reflex remained unchanged. It is therefore argued that the amount of heteronymous I a facilitation can indeed be used to assess the amount of ongoing presynaptic inhibition exerted onto heteronymous I a fibres from the quadriceps muscle to soleus motoneurones. 5. The short-lasting tibialis anterior vibration used here evoked a long-lasting (300-500 ms) depression of soleus and quadriceps H reflexes.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby P., Verrier M. Human motoneuron responses to group 1 volleys blocked presynaptically by vibration. Brain Res. 1980 Feb 24;184(2):511–516. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90819-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmans J., Delwaide P. J., Gadea-Ciria M. Short-latency effects of low-threshold muscular afferent fibers on different motoneuronal pools of the lower limb in man. Exp Neurol. 1978 Jun;60(2):380–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Gandevia S. C., McKeon B. Monosynaptic and oligosynaptic contributions to human ankle jerk and H-reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1984 Sep;52(3):435–448. doi: 10.1152/jn.1984.52.3.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. Synaptic action during and after repetitive stimulation. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:374–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C., Hultborn H., Jespersen B. Reciprocal Ia inhibition from the peroneal nerve to soleus motoneurones with special reference to the size of the test reflex. Exp Brain Res. 1985;59(2):418–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00230924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Gail P., Lance J. W., Neilson P. D. Differential effects on tonic and phasic reflex mechanisms produced by vibration of muscles in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The convergence of monosynaptic excitatory afferents on to many different species of alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Jun 18;137(1):22–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., RALL W. Effects induced in a monosynaptic reflex path by its activation. J Neurophysiol. 1951 Sep;14(5):353–376. doi: 10.1152/jn.1951.14.5.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., SCHMIDT R. F., WILLIS W. D. Presynaptic inhibition of the spinal monosynaptic reflex pathway. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:282–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Katz R., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. A re-evaluation of the pattern of group I fibre projections in the human lower limb on using randomly alternated stimulations. Exp Brain Res. 1984;56(1):193–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00237457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Katz R., Pierrot-Deseilligny E. Descending control of reflex pathways in the production of voluntary isolated movements in man. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 12;288(1-2):375–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier E., Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Evidence for interneuronally mediated Ia excitatory effects to human quadriceps motoneurones. J Physiol. 1986 Aug;377:143–169. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Lundberg A., Phillips C. G., Thompson R. F. The pattern of monosynaptic Ia-connections to hindlimb motor nuclei in the baboon: a comparison with the cat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 May 22;221(1224):261–289. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Changes in polysynaptic Ia excitation to quadriceps motoneurones during voluntary contraction in man. Exp Brain Res. 1986;63(2):436–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00236863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultborn H., Meunier S., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Shindo M. Changes in presynaptic inhibition of Ia fibres at the onset of voluntary contraction in man. J Physiol. 1987 Aug;389:757–772. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Oligosynaptic excitation of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:411–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Pattern of 'non-reciprocal' inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:393–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R., Morin C., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Hibino R. Conditioning of H reflex by a preceding subthreshold tendon reflex stimulus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Jun;40(6):575–580. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.6.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., PORTER W. E., PARK A. M., TEASDALL R. D. Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. IV. The two-neurone reflex and identification of certain action potentials from spinal roots and cord. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1951 Jun;88(6):499–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinck H. M. Facilitation and inhibition of the human H reflex as a function of the amplitude of the control reflex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;48(2):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90305-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin C., Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Hultborn H. Evidence for presynaptic inhibition of muscle spindle Ia afferents in man. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Feb 10;44(2):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Katz R., Morin C. Evidence of Ib inhibition in human subjects. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 20;166(1):176–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrot-Deseilligny E., Morin C., Bergego C., Tankov N. Pattern of group I fibre projections from ankle flexor and extensor muscles in man. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(3-4):337–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00237499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. F. Presynaptic inhibition in the vertebrate central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1971;63:20–101. doi: 10.1007/BFb0047741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R. Reciprocal Ia inhibition during voluntary movements in man. Exp Brain Res. 1974;21(5):529–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00237171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Táboríková H., Sax D. S. Conditioning of H-reflexes by a preceding subthreshold H-reflex stimulus. Brain. 1969 Mar;92(1):203–212. doi: 10.1093/brain/92.1.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D. Excitability changes in afferent fibre terminations and their relation to slow potentials. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



