Abstract
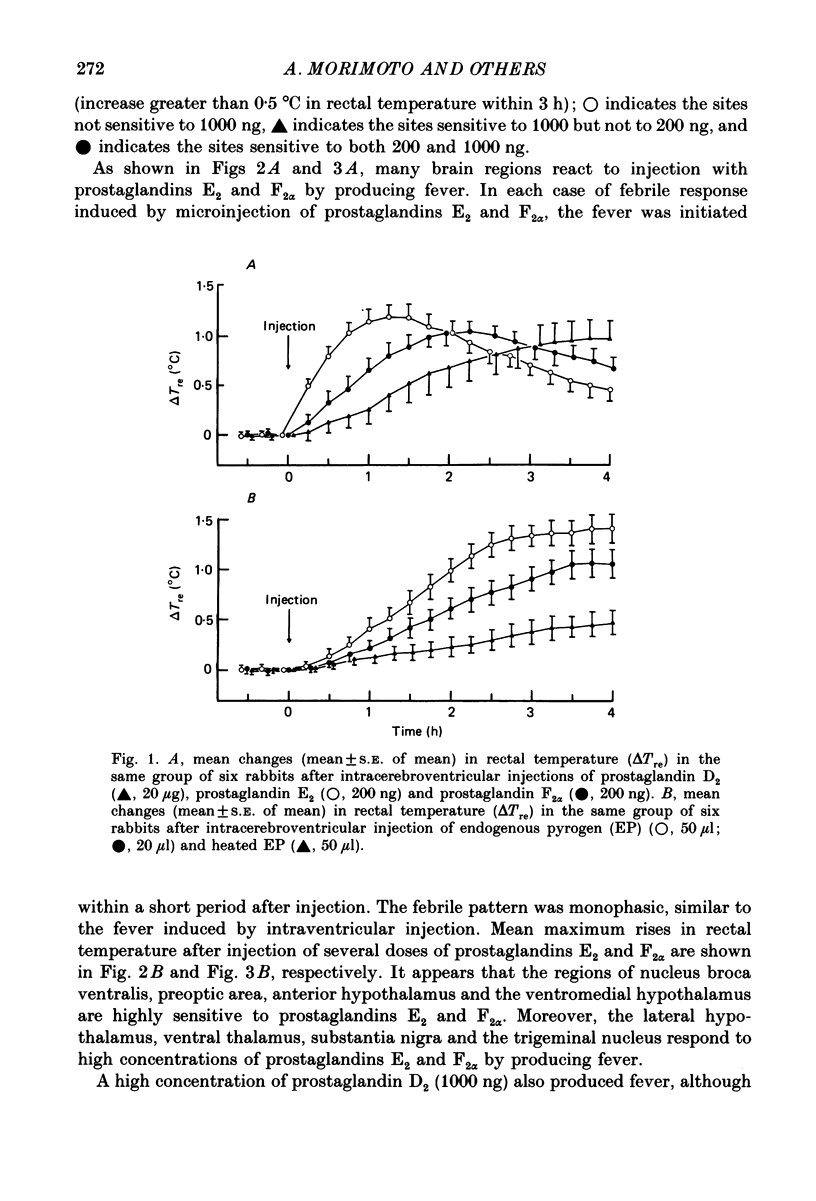
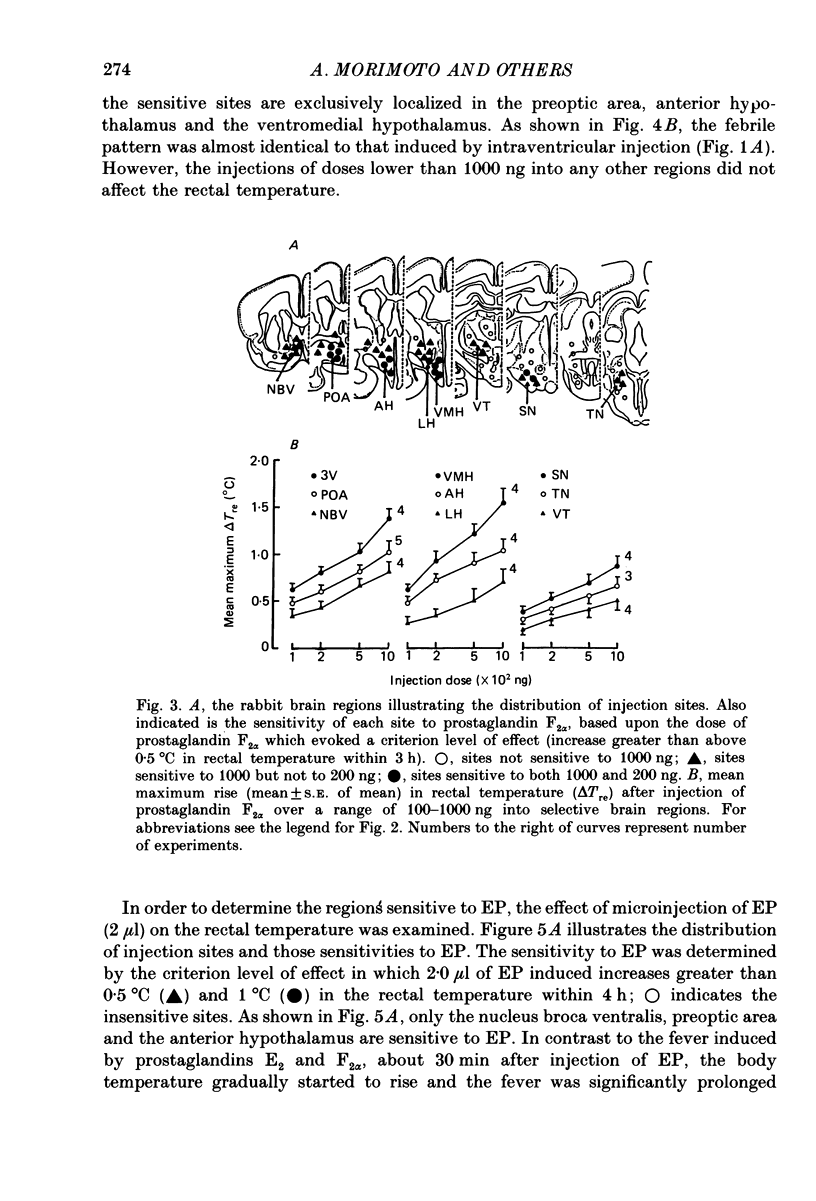
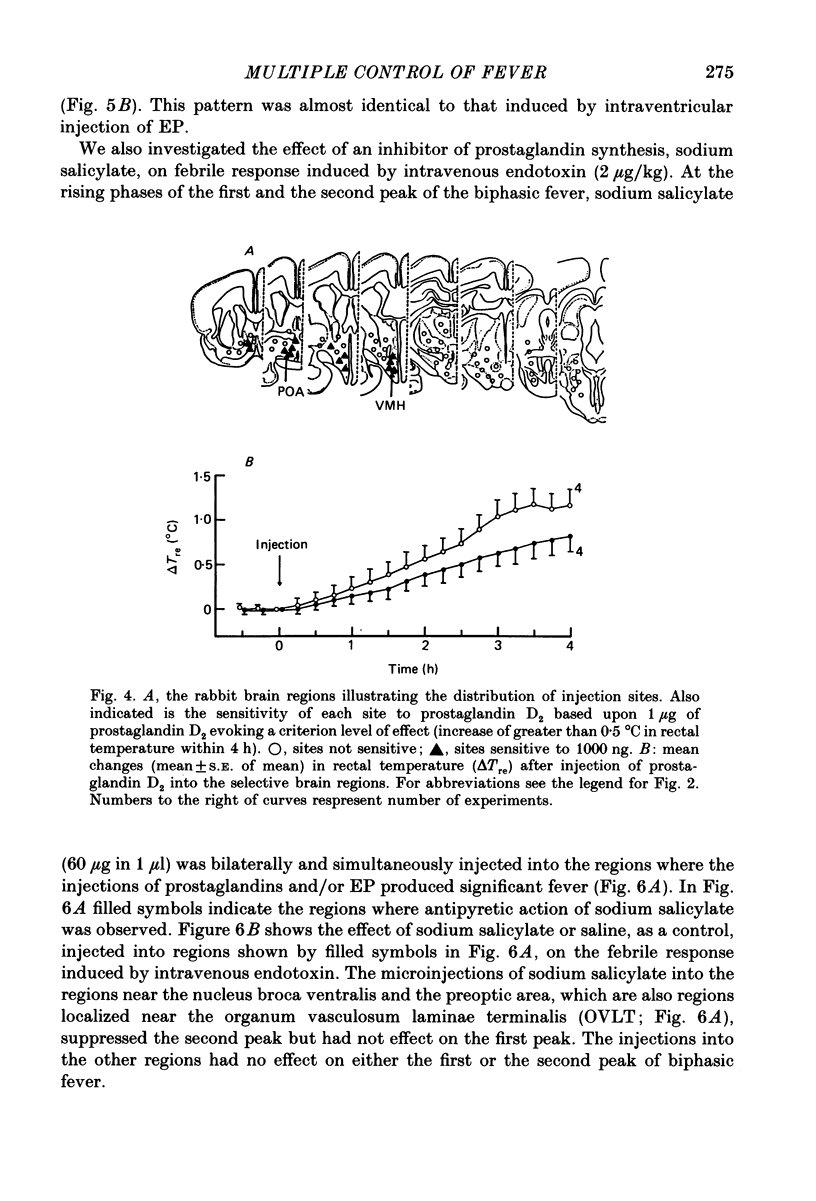
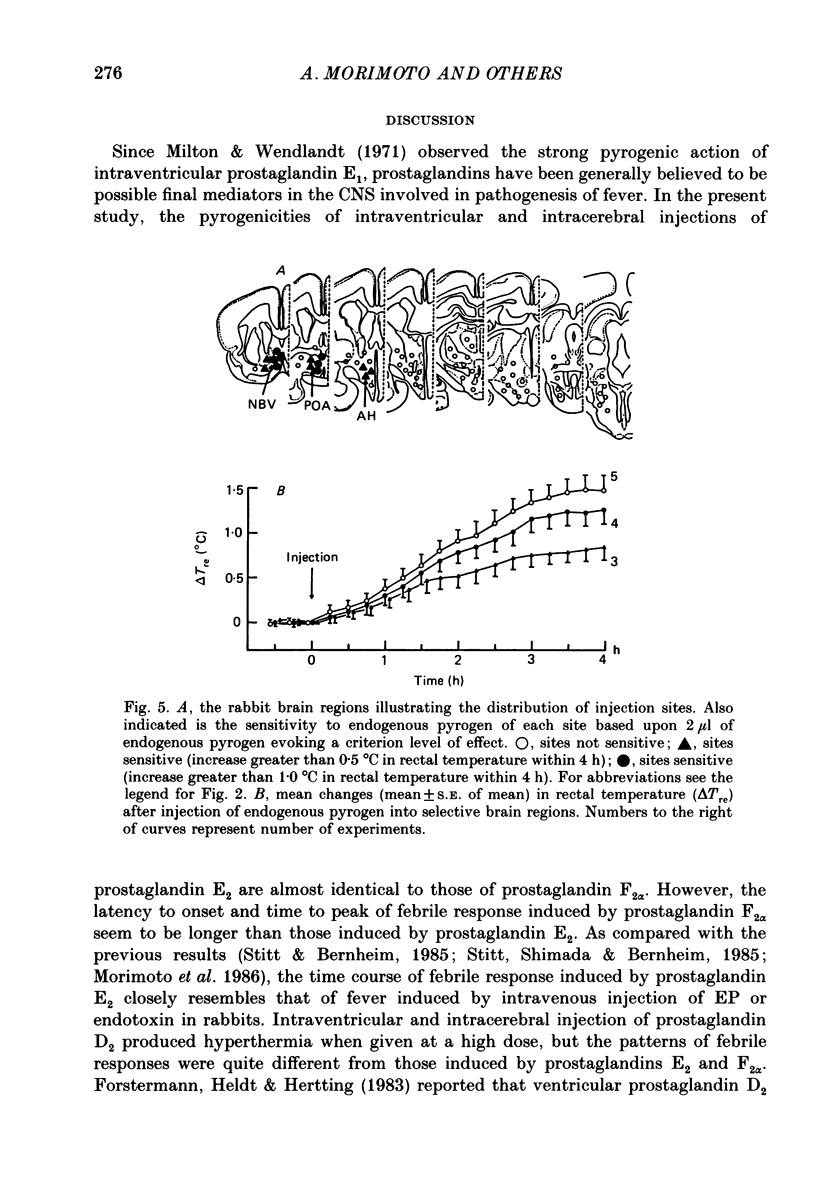
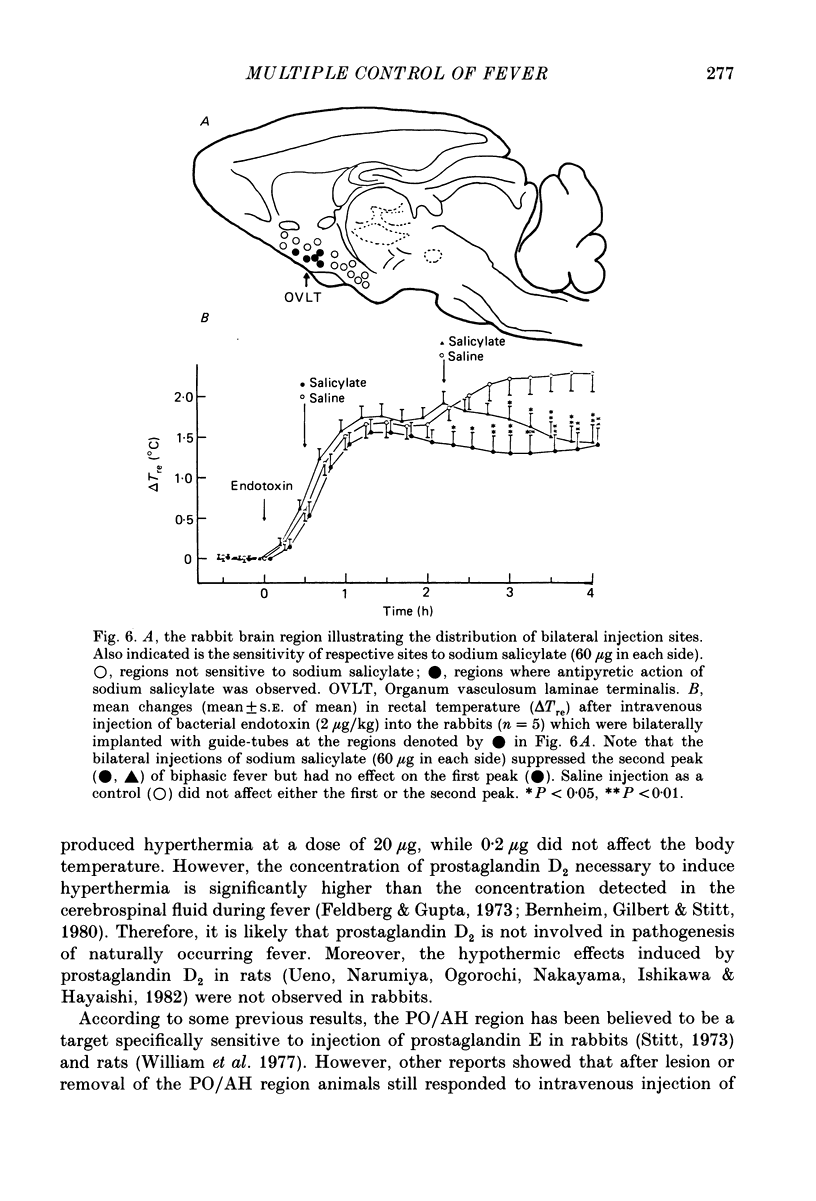
1. The effects of microinjection of prostaglandin D2, E2 and F2 alpha and of endogenous pyrogen on the rectal temperature of rabbits were extensively examined in sixty-eight brain regions and in the third cerebral ventricle. 2. Intracerebroventricular injection of both prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha produced dose-dependent fever over a range of 100-1000 ng. The selective brain regions, the nucleus broca ventralis, preoptic area, anterior hypothalamus and the ventromedial hypothalamus, responded to microinjections of a small dose (less than 200 ng) of prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha by producing fever. Furthermore, the lateral hypothalamus, ventral thalamus, substantia nigra and the trigeminal nucleus were also sensitive to high concentrations of prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha, fever being produced. It is likely that prostaglandin D2 is not involved in fever induction. 3. The ventricular injection of endogenous pyrogen also produced fever. However, brain regions sensitive to microinjection of endogenous pyrogen were exclusively localized to regions near the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis (OVLT), such as the nucleus broca ventralis and the preoptic area. In contrast to the monophasic fever induced by prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha, about 30 min after ventricular or cerebral injection of endogenous pyrogen the rectal temperature gradually started to rise and the fever was prolonged over 4 h. 4. We investigated the effect of an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, sodium salicylate, on biphasic fever induced by intravenous injection of bacterial endotoxin. The microinjections of sodium salicylate into the bilateral regions near the OVLT suppressed the second peak but had no effect on the first peak. 5. The present study clarifies that there exist two separate mechanisms of induction of biphasic fever. Correlating with the first peak of biphasic fever, prostaglandins synthesized outside the blood-brain barrier act on multiple sites in the central nervous system to induce fever. Correlating with the second peak, endogenous pyrogen acts on regions near the OVLT to synthesize and release pyrogenic prostaglandins.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATKINS E. Pathogenesis of fever. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:580–646. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim H. A., Gilbert T. M., Stitt J. T. Prostaglandin E levels in third ventricular cerebrospinal fluid of rabbits during fever and changes in body temperature. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:69–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatteis C. M., Banet M. Autonomic thermoregulation after separation of the preoptic area from the hypothalamus in rats. Pflugers Arch. 1986 May;406(5):480–484. doi: 10.1007/BF00583370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatteis C. M., Bealer S. L., Hunter W. S., Llanos-Q J., Ahokas R. A., Mashburn T. A., Jr Suppression of fever after lesions of the anteroventral third ventricle in guinea pigs. Brain Res Bull. 1983 Nov;11(5):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(83)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. E., Cranston W. I., Honour A. J. Observations on the site & mode of action of pyrogens in the rabbit brain. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(2):325–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranston W. I., Rawlins M. D. Effects of intracerebral micro-injection of sodium salicylate on temperature regulation in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):257–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Bernheim H. A. Ability of human leukocytic pyrogen to stimulate brain prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):702–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Gupta K. P. Pyrogen fever and prostaglandin-like activity in cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):41–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Kristensen F., Dubs R., Gemsa D., Weber E. Production of prostaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Weber E., Dayer J. M. Synthesis of interleukin 1/endogenous pyrogen in the brain of endotoxin-treated mice: a step in fever induction? J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1696–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Heldt R., Hertting G. Effects of intracerebroventricular administration of prostaglandin D2 on behaviour, blood pressure and body temperature as compared to prostaglandins E2 and F2 alpha. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;80(4):365–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00432122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton J. M., Trzcinka G. P. Persistence of febrile response to pyrogens after PO/AH lesions in squirrel monkeys. Am J Physiol. 1976 Dec;231(6):1638–1648. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.6.1638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Effects on body temperature of prostaglandins of the A, E and F series on injection into the third ventricle of unanaesthetized cats and rabbits. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):325–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto A., Murakami N., Nakamori T., Watanabe T. Evidence for separate mechanisms of induction of biphasic fever inside and outside the blood-brain barrier in rabbits. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:629–637. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto A., Murakami N., Nakamori T., Watanabe T. Ventromedial hypothalamus is highly sensitive to prostaglandin E2 for producing fever in rabbits. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:259–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto A., Watanabe T., Ono T., Sakata Y., Murakami N. Rat endogenous pyrogen and fever. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 2):R776–R782. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.5.R776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER C. H., EVERETT J. W., GREEN J. D. The rabbit diencephalon in stereotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Dec;101(3):801–824. doi: 10.1002/cne.901010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T., Bernheim H. A. Differences in endogenous pyrogen fevers induced by iv and icv routes in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Aug;59(2):342–347. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.2.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T. Evidence for the involvement of the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis in the febrile response of rabbits and rats. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:501–511. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T. Prosaglandin E1 fever induced in rabbits. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):163–179. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T., Shimada S. G., Bernheim H. A. Comparison of febrile responsiveness of rats and rabbits to endogenous pyrogen. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Dec;59(6):1721–1725. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.6.1721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno R., Narumiya S., Ogorochi T., Nakayama T., Ishikawa Y., Hayaishi O. Role of prostaglandin D2 in the hypothermia of rats caused by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6093–6097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. W., Rudy T. A., Yaksh T. L., Viswanathan C. T. An extensive exploration of the rat brain for sites mediating prostaglandin-induced hyperthermia. Brain Res. 1977 Jan 21;120(2):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90904-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


