Abstract
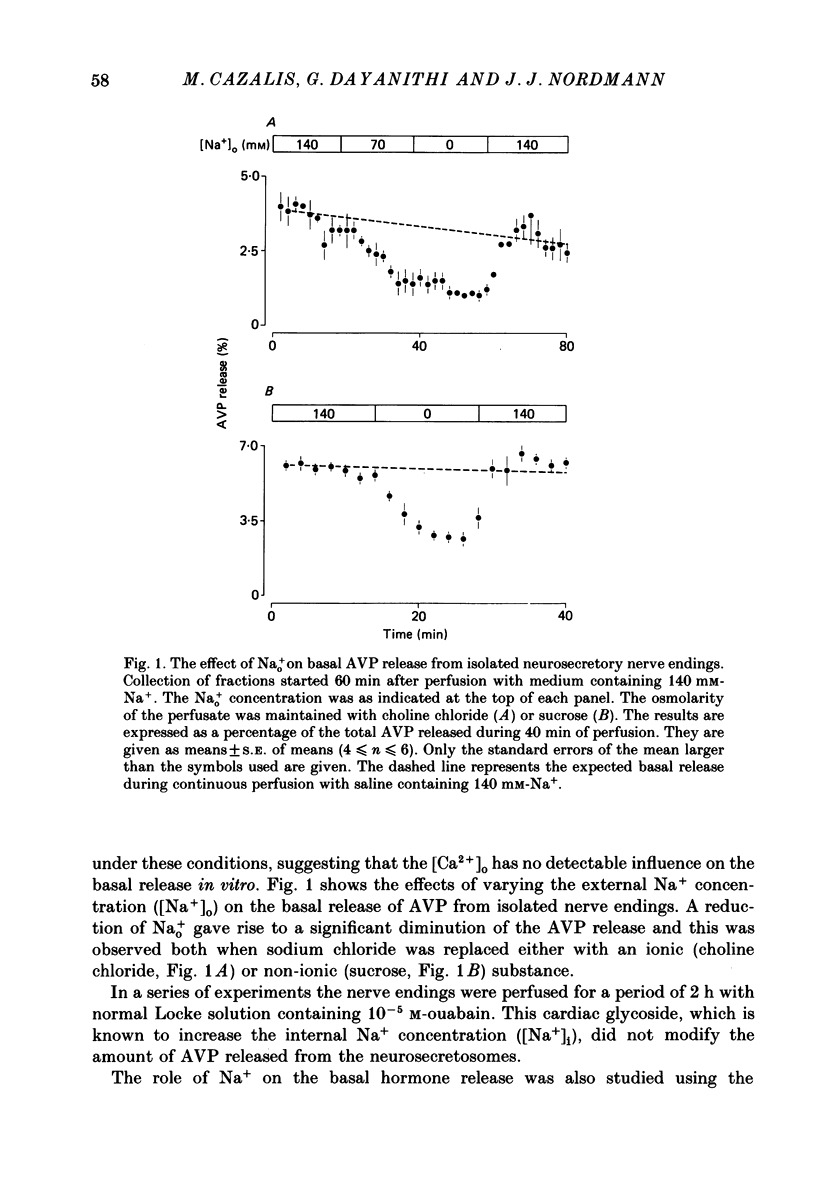
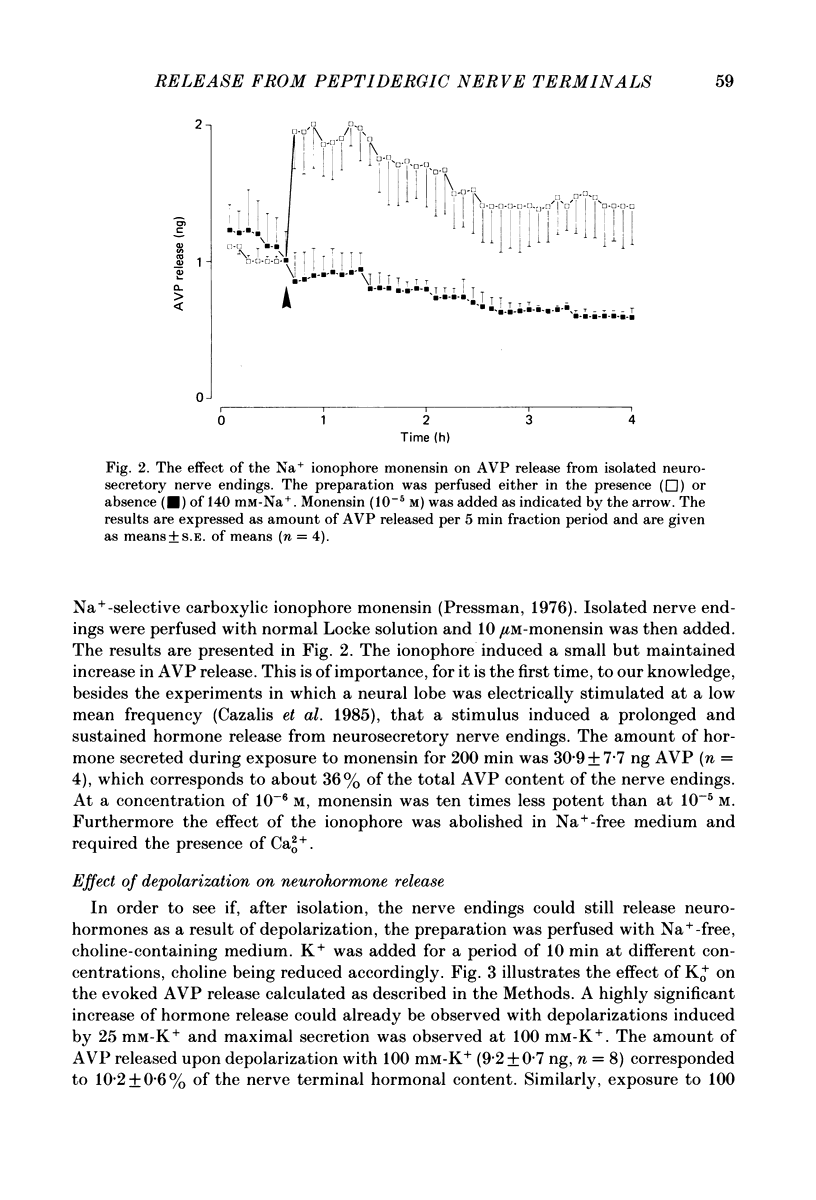
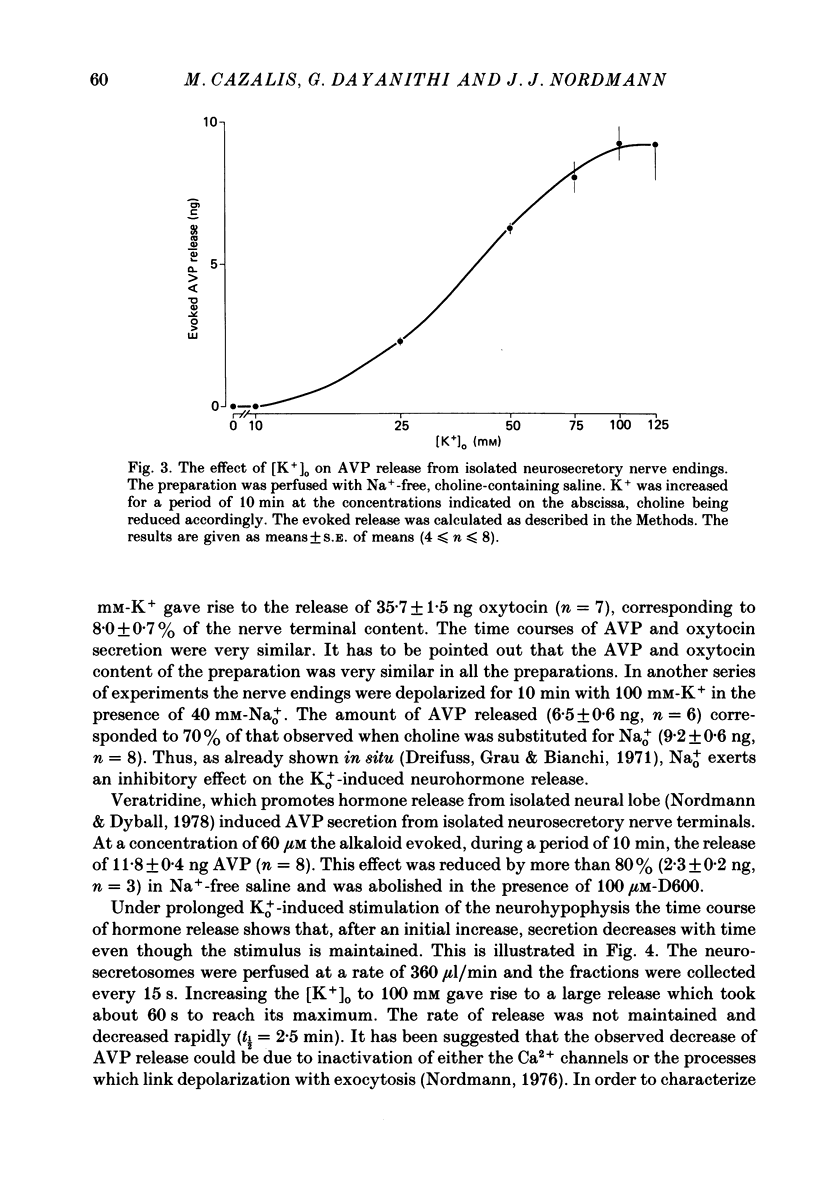
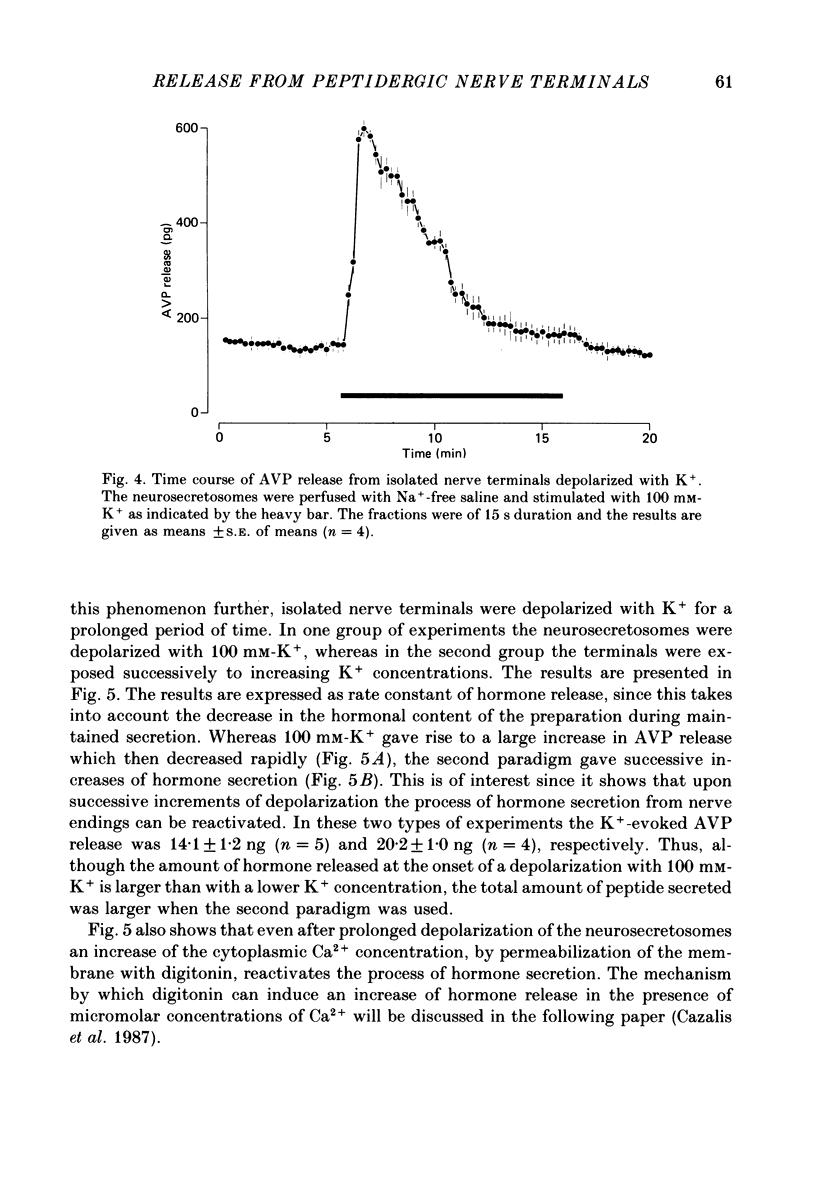
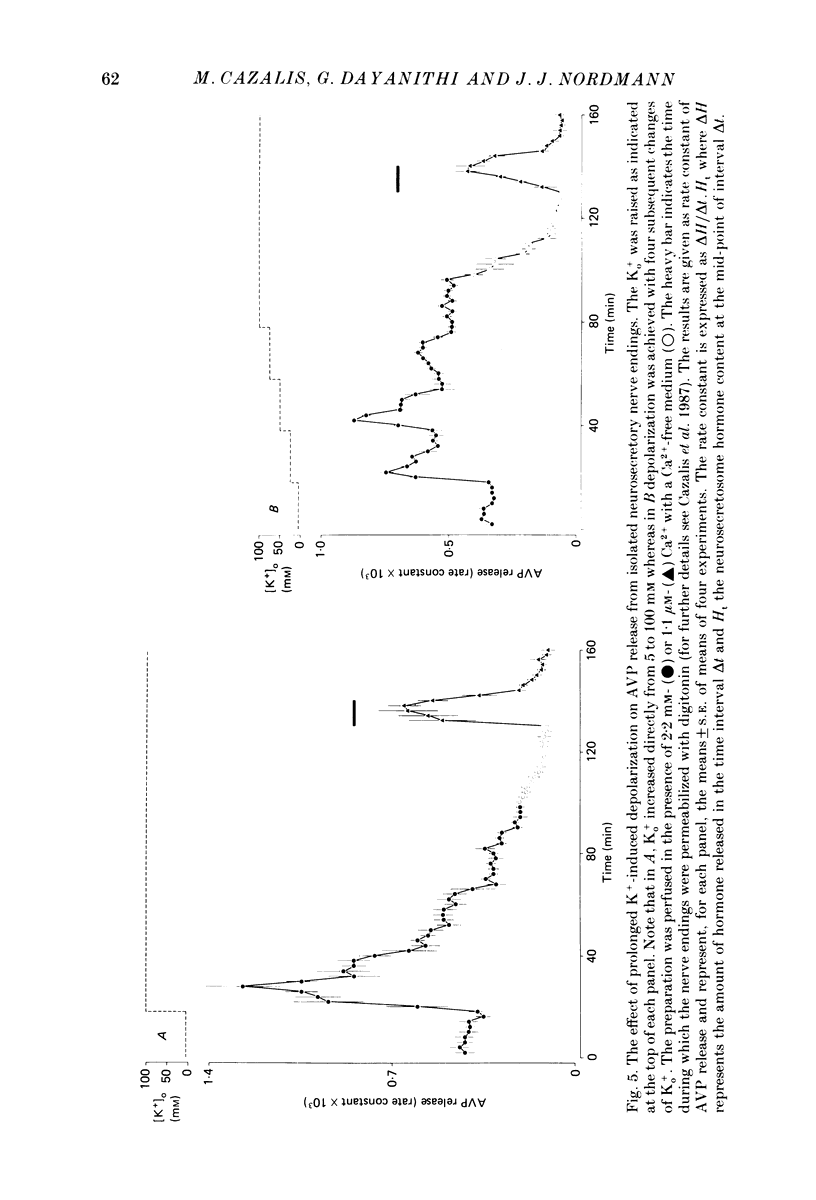
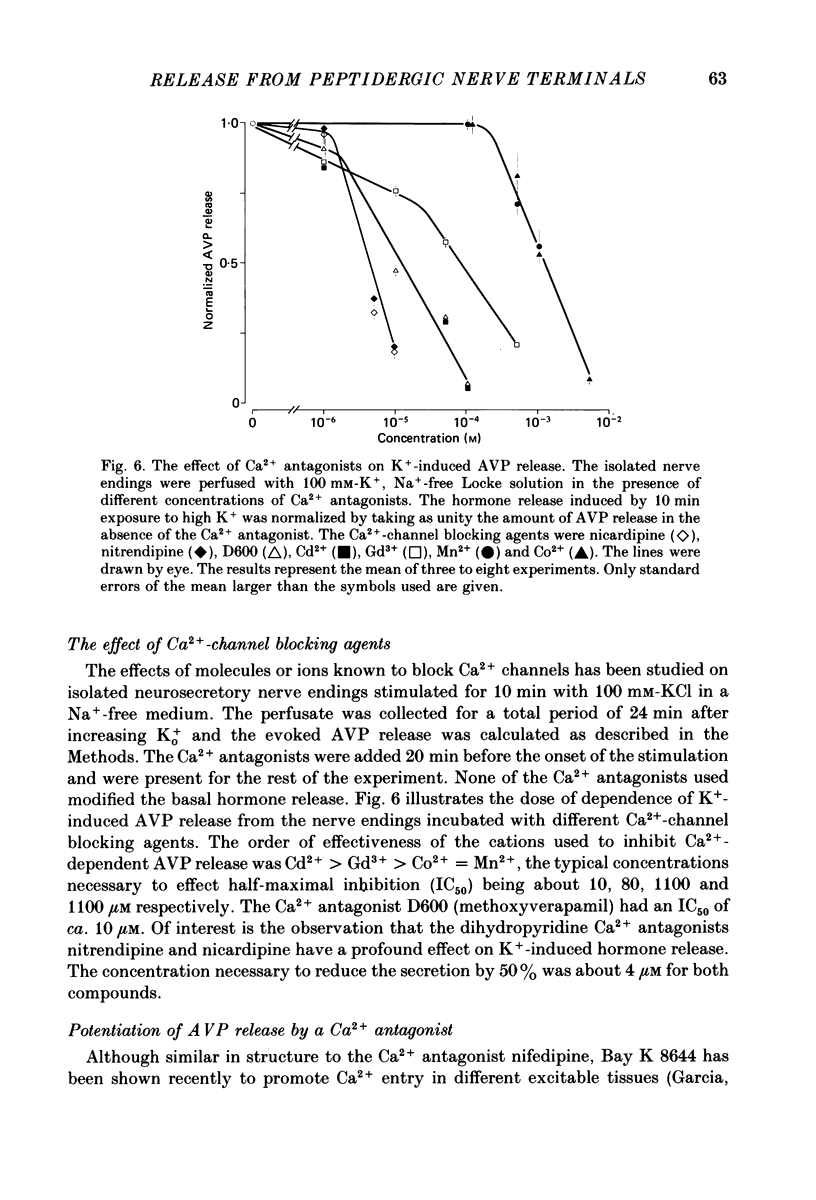
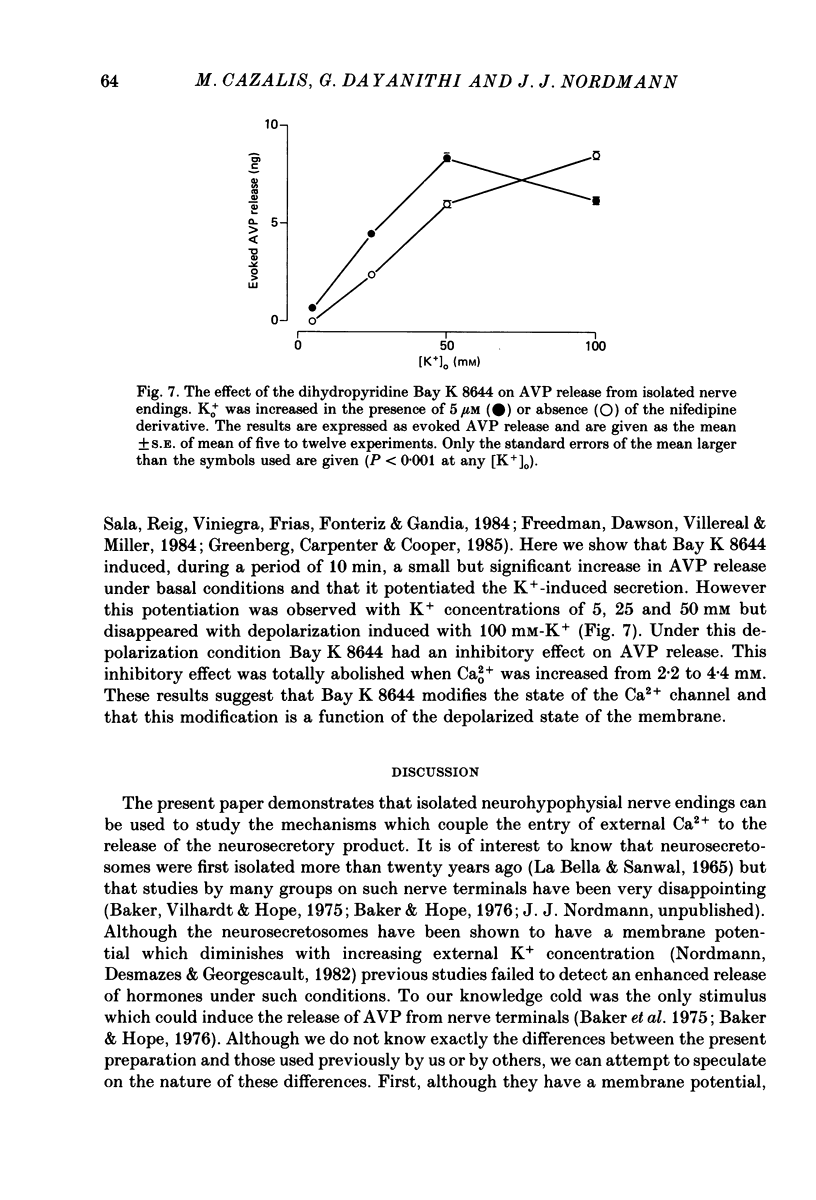
1. Isolated neurosecretory nerve endings were prepared from rat neurohypophyses. The amount of vasopressin (AVP) and oxytocin released was measured by radioimmunoassay. 2. The amount of hormone release under resting conditions was not affected by external calcium (Ca2+o). Secretion decreased by ca. 50% when external sodium (Na+o) was replaced by choline or sucrose. 3. Ouabain did not modify the basal AVP release. 4. The Na+ ionophore monensin increased the release of AVP only in the presence of Na+o. This increase was maintained during prolonged exposure to the ionophore and occurred in the presence of Ca2+o only. 5. In the presence of Ca2+o, the amount of evoked hormone release was dependent on the external K+ concentration. Half-maximal activation was achieved with ca. 40 mM-K+. The K+-induced secretion was potentiated in Na+-free solution. 6. Prolonged 100 mM-K+-induced depolarization in the presence of Ca2+o gave rise to a large increase in hormone secretion which decreased with time (t1/2 = 2.5 min). The release could be reactivated after permeabilization of the nerve terminals in the presence of micromolar concentrations of Ca2+. 7. A stepwise paradigm in which Ko+ is incrementally increased to 25, 50, 75 and then 100 mM released more AVP than a prolonged exposure to 100 mM-K+. 8. Veratridine increased the amount of AVP released. This effect was considerably reduced in the absence of Nao+ and abolished in the presence of D600. 9. The depolarization-induced AVP release was blocked by different Ca2+-antagonists. Their effectiveness was nitrendipine = nicardipine greater than Cd2+ greater than Gd3+ greater than Co2+ = Mn2+. 10. The dihydropyridine Bay K 8644 potentiated both the basal and the K+-evoked AVP release. Its maximal effect was obtained with 25-50 mM-Ko+. 11. In conclusion, the isolated neurohypophysial terminals which have both Na+ and Ca2+ channels and release AVP and oxytocin upon depolarization might be an excellent system to study further the mechanisms leading to secretion of neurohormones.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Effects of manganese and other agents on the calcium uptake that follows depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. V., Hope D. B. The effect of gradual changes in temperature on the release of hormones from nerve endings isolated from bovine neural lobes. J Neurochem. 1976 Jul;27(1):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. V., Vilhardt H., Hope D. B. Cold-induced release of hormones and proteins from nerve endings isolated from bovine neural lobes. J Neurochem. 1975 May;24(5):1091–1093. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb03684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne G. W., Trifaró J. M. The gadolinium ion: a potent blocker of calcium channels and catecholamine release from cultured chromaffin cells. Neuroscience. 1982 Jul;7(7):1615–1622. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brethes D., Dayanithi G., Letellier L., Nordmann J. J. Depolarization-induced Ca2+ increase in isolated neurosecretory nerve terminals measured with fura-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1439–1443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazalis M., Dayanithi G., Nordmann J. J. Requirements for hormone release from permeabilized nerve endings isolated from the rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:71–91. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazalis M., Dayanithi G., Nordmann J. J. The role of patterned burst and interburst interval on the excitation-coupling mechanism in the isolated rat neural lobe. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:45–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay J. R., Shrier A. Effects of D-600 on sodium current in squid axons. J Membr Biol. 1984;79(3):211–214. doi: 10.1007/BF01871060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., POISNER A. M. CALCIUM MOVEMENT IN THE NEUROHYPOPHYSIS OF THE RAT AND ITS RELATION TO THE RELEASE OF VASOPRESSIN. J Physiol. 1964 Jul;172:19–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., POISNER A. M. STIMULUS-SECRETION COUPLING IN A NEUROSECRETORY ORGAN: THE ROLE OF CALCIUM IN THE RELEASE OF VASOPRESSIN FROM THE NEUROHYPOPHYSIS. J Physiol. 1964 Jul;172:1–18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell L. C., Barr E. M., Leslie S. W. 45Ca2+ uptake into rat whole brain synaptosomes unaltered by dihydropyridine calcium antagonists. J Neurochem. 1983 Nov;41(5):1455–1459. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellmann H. D., Boudier J. A., Couraud F., Cau P., Boudier J. L. Voltage-sensitive Na+ channels in the neurohypophysis of the rat as demonstrated by 125I-labelled scorpion toxin. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jan 31;35(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Grau J. D., Bianchi R. E. Antagonism between Ca and Na ions at neurohypophysial nerve terminals. Experientia. 1971;27(11):1295–1296. doi: 10.1007/BF02136696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifuss J. J., Grau J. D., Nordmann J. J. Effects on the isolated neurohypophysis of agents which affect the membrane permeability to calcium. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):96P–98P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyball R. E., Nordmann J. J. Reactivation by veratridine of hormone release from the K+-depolarized rat neurophypophysis [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):65P–66P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyeart J. J., Hinkle P. M. The calcium agonist Bay K 8644 stimulates secretion from a pituitary cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):991–996. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S. B., Dawson G., Villereal M. L., Miller R. J. Identification and characterization of voltage-sensitive calcium channels in neuronal clonal cell lines. J Neurosci. 1984 Jun;4(6):1453–1467. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-06-01453.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galper J. B., Catterall W. A. Inhibition of sodium channels by D600. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;15(1):174–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García A. G., Sala F., Reig J. A., Viniegra S., Frías J., Fontériz R., Gandía L. Dihydropyridine BAY-K-8644 activates chromaffin cell calcium channels. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):69–71. doi: 10.1038/309069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Carpenter C. L., Cooper E. C. Stimulation of calcium uptake in PC12 cells by the dihydropyridine agonist BAY K 8644. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):990–993. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Pelzer D., Trube G., Trautwein W. Does the organic calcium channel blocker D600 act from inside or outside on the cardiac cell membrane? Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):287–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00581411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Calcium-dependence of catecholamine release from bovine adrenal medullary cells after exposure to intense electric fields. J Membr Biol. 1982;68(2):107–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01872259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F. S., Sanwal M. Isolation of nerve endings from the posterior pituitary gland. Electron microscopy of fractions obtained by centrifugation. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):179–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos J. R., Nordmann J. J., Cooke I. M., Stuenkel E. L. Single channels and ionic currents in peptidergic nerve terminals. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):410–412. doi: 10.1038/319410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos J. R., Nordmann J. J. Ionic channels and hormone release from peptidergic nerve terminals. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:53–72. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee R., Jr, Schneider J. E. Inhibition of high affinity synaptosomal uptake systems by verapamil. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):877–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiri H., Erulkar S. D., Lerman T., Rahamimoff R. The action of the sodium ionophore, monensin, or transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. Brain Res. 1981 Jan 5;204(1):204–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90665-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. F. Hormone storage in individual neurosecretory granules of the pituitary gland: A quantitative ultrastructural approach to hormone storage in the neural lobe. J Endocrinol. 1976 Feb;68(02):209–224. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0680209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. F., Nordmann J. J., Dyball R. E. Structure-function correlation in mammalian neurosecretion. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1978;18:1–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscholl E., Racké K., Traut A. Gadolinium ions inhibit exocytotic vasopressin release from the rat neurohypophysis. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:419–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller J. R., Thorn N. A., Torp-Pedersen C. Effects of calcium and sodium on vasopressin release in vitro induced by a prolonged potassium stimulation. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1975 May;79(1):51–59. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0790051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Desmazes J. P., Georgescauld D. The relationship between the membrane potential of neurosecretory nerve endings, as measured by a voltage-sensitive dye, and the release of neurohypophysial hormones. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):731–737. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90078-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Dyball R. E. Effects of veratridine on Ca fluxes and the release of oxytocin and vasopressin from the isolated rat neurohypophysis. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):297–304. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J. Evidence for calcium inactivation during hormone release in the rat neurohypophysis. J Exp Biol. 1976 Dec;65(3):669–683. doi: 10.1242/jeb.65.3.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J. Stimulus-secretion coupling. Prog Brain Res. 1983;60:281–304. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64397-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J. Ultrastructural morphometry of the rat neurohypophysis. J Anat. 1977 Feb;123(Pt 1):213–218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Weatherby T. M., Haylett B. A. Ultrastructural changes in isolated peptidergic nerve terminals induced by digitonin permeabilization and K+ stimulation in the sinus gland of the crab, Cardisoma carnifex. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;246(2):365–371. doi: 10.1007/BF00215899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B., Dyball R. E. Electrophysiological differentiation of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr;196(1125):367–384. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H., Haller E. W. Further studies on the capacity of the neurohypophysis to release vasopressin. Endocrinology. 1968 Aug;83(2):251–262. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby I. A., Kongsamut S., Freedman S. B., Miller R. J. The effects of dihydropyridines on neurotransmitter release from cultured neuronal cells. Life Sci. 1984 Sep 17;35(12):1289–1295. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchard S. J., Lattanzio F. A., Jr, Rubin R. W., Pressman B. C. Stimulation of catecholamine secretion from cultured chromaffin cells by an ionophore-mediated rise in intracellular sodium. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):531–539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terakawa S. Ca-K bi-ionic action potential in squid giant axons. J Membr Biol. 1981;63(1-2):41–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01969444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


