Abstract
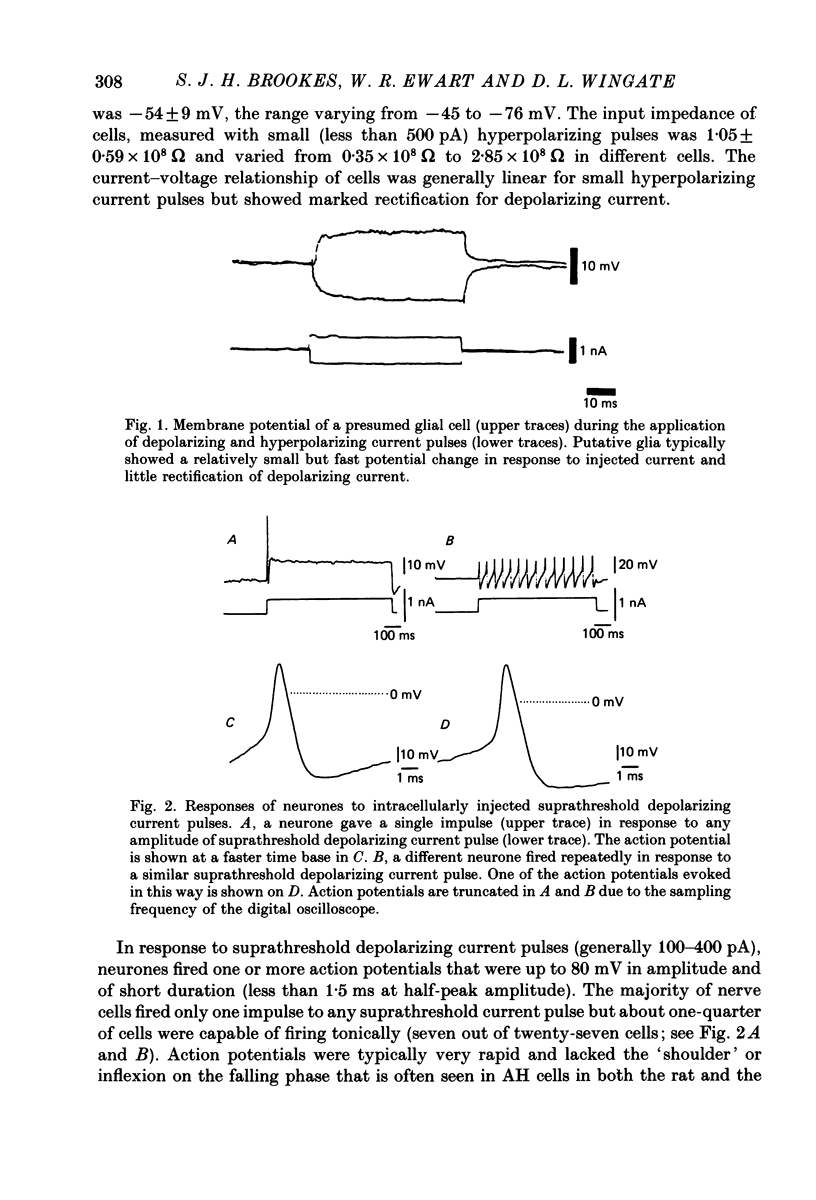
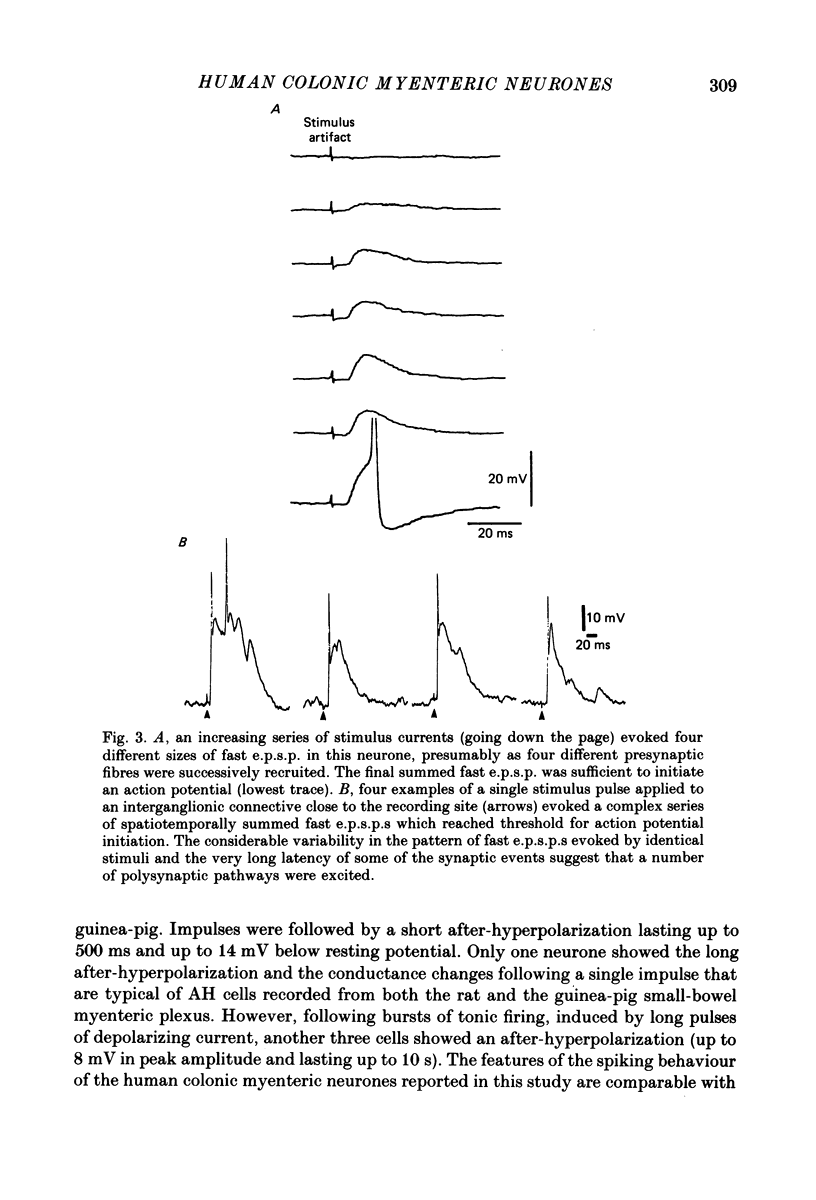
1. Intracellular recordings were made from cells in the myenteric plexus of the human colon in freshly dissected tissue obtained from patients undergoing surgery for the removal of carcinomas or diverticular bowel. 2. Twenty-seven cells from ten preparations were classified as neurones and had overshooting action potentials, an average resting potential of -54 +/- 9 mV, an average input impedance of 1.05 +/- 0.59 x 10(8) omega and a variety of synaptic inputs. 3. Twenty-three (out of twenty-five neurones tested) received nicotinic fast excitatory synaptic inputs (fast e.p.s.p.s) that were blocked reversibly by hexamethonium and mimicked by acetylcholine. These nerve cells bore a close resemblance to S cells that have been characterized in the guinea-pig small-bowel myenteric plexus. 4. One cell had a long after-hyperpolarization following its impulses and was similar to AH cells in the guinea-pig small bowel. 5. Three neurones received inhibitory synaptic inputs, up to 15 mV in amplitude, lasting up to 10 s, associated with a decrease in input impedance and with a reversal potential between -80 and -90 mV. 6. Slow excitatory synaptic potentials were only detected in the single AH cell. The slow e.p.s.p. was associated with a depolarization of up to 12 mV, an increase in excitability and an increase in the input impedance of the neurone. 7. The proportion of S and AH cells differ considerably from that reported in the guinea-pig small-bowel preparation. Possible causes of the differences are discussed.
Full text
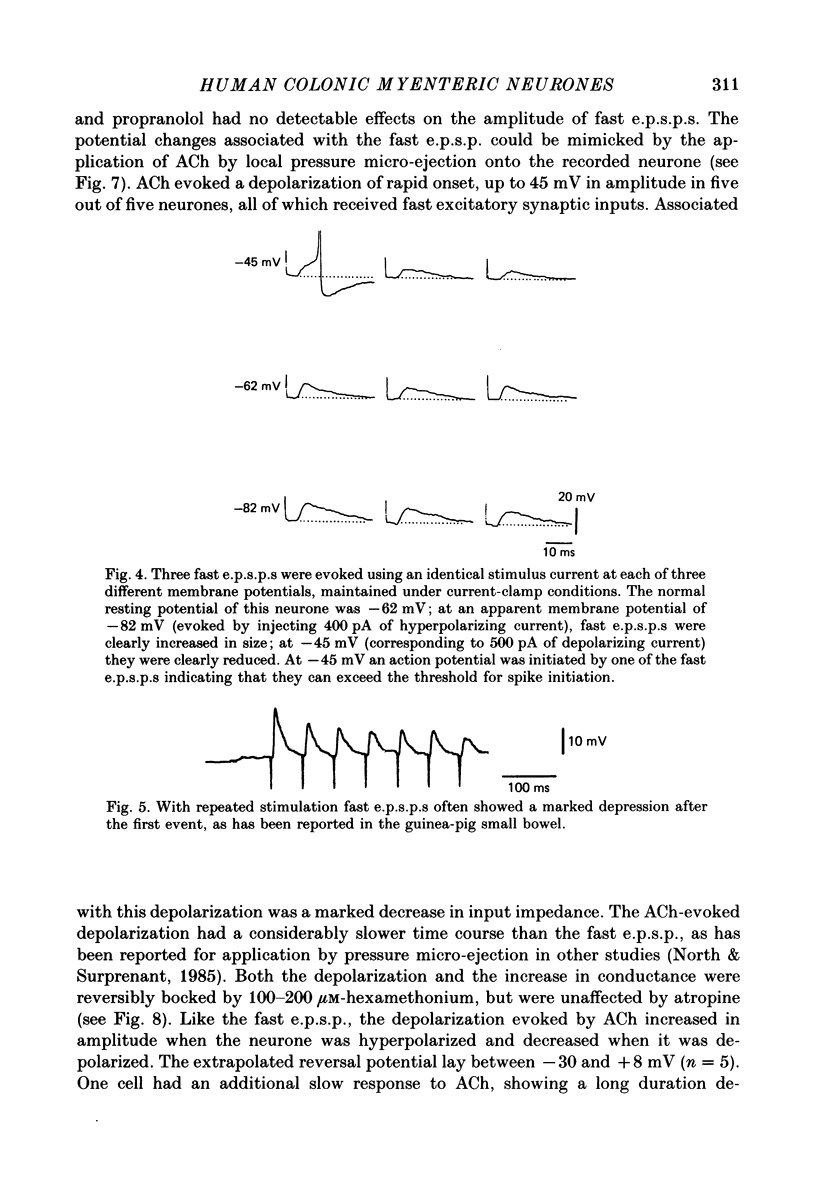
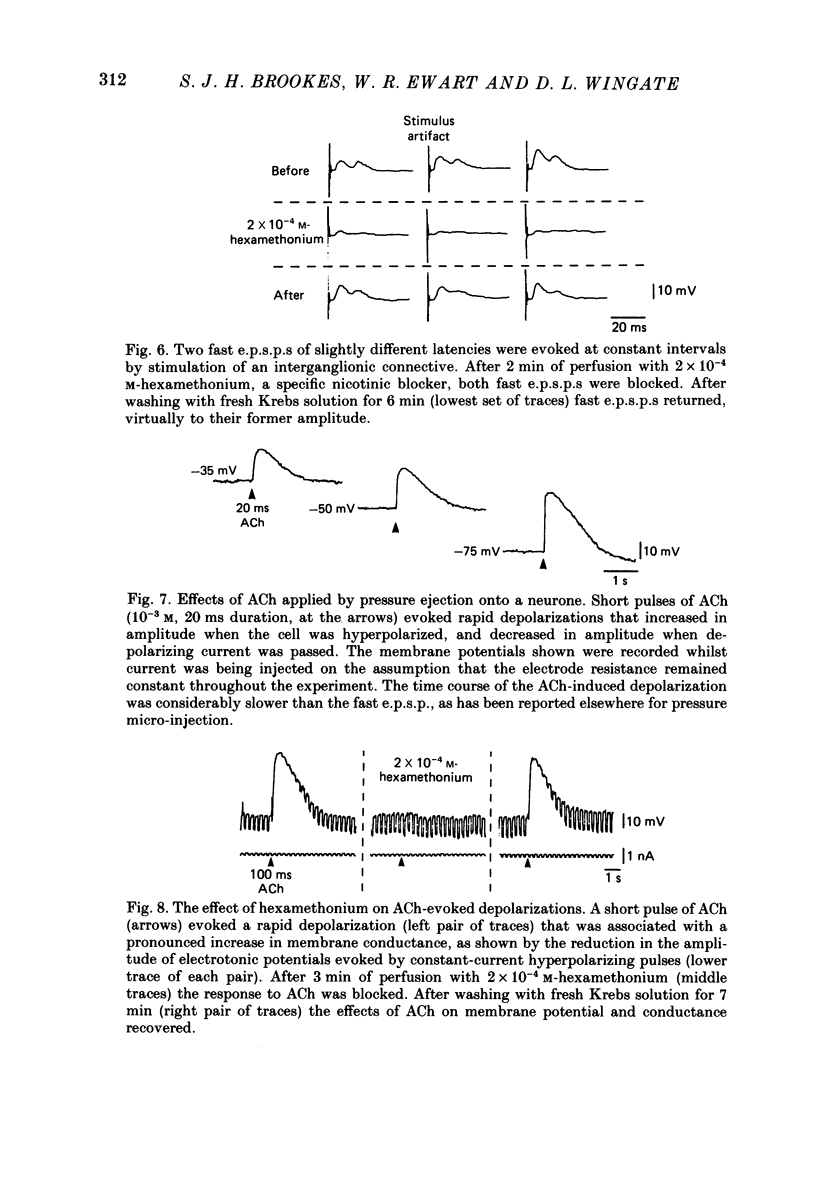
PDF







Images in this article
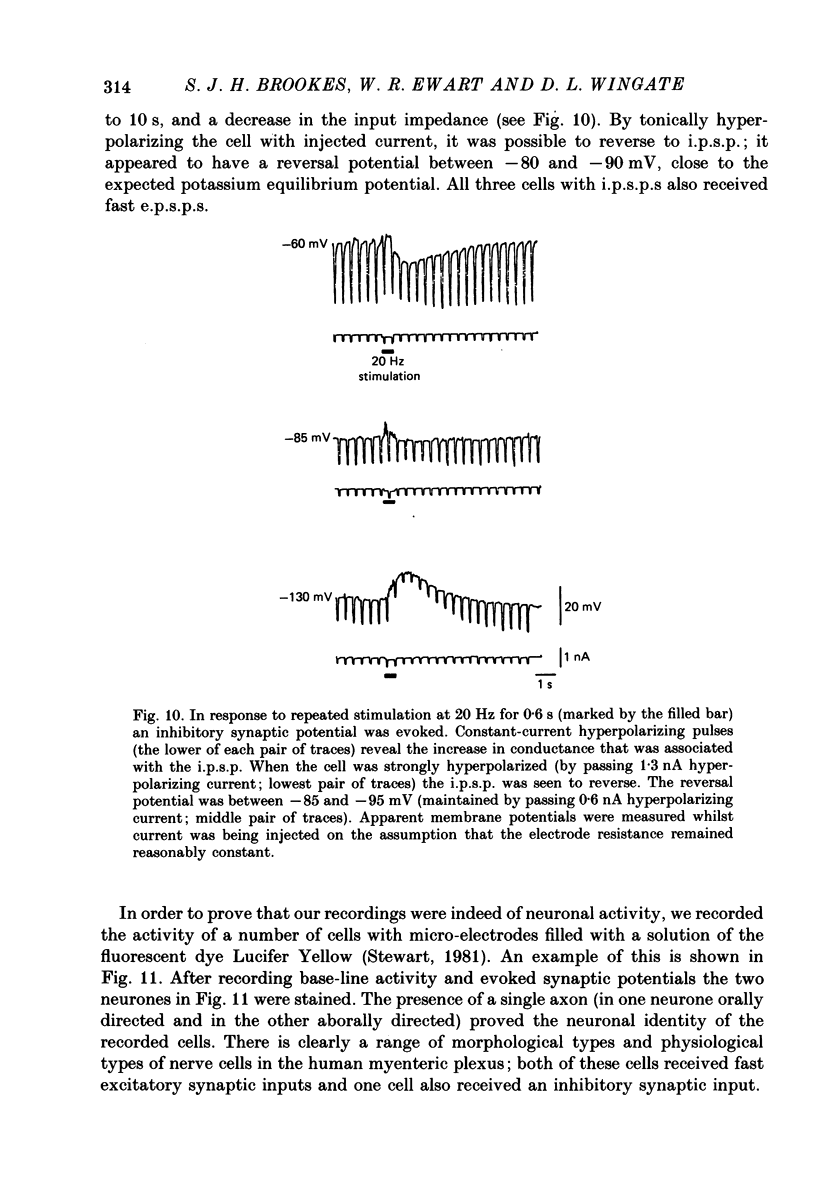
Selected References
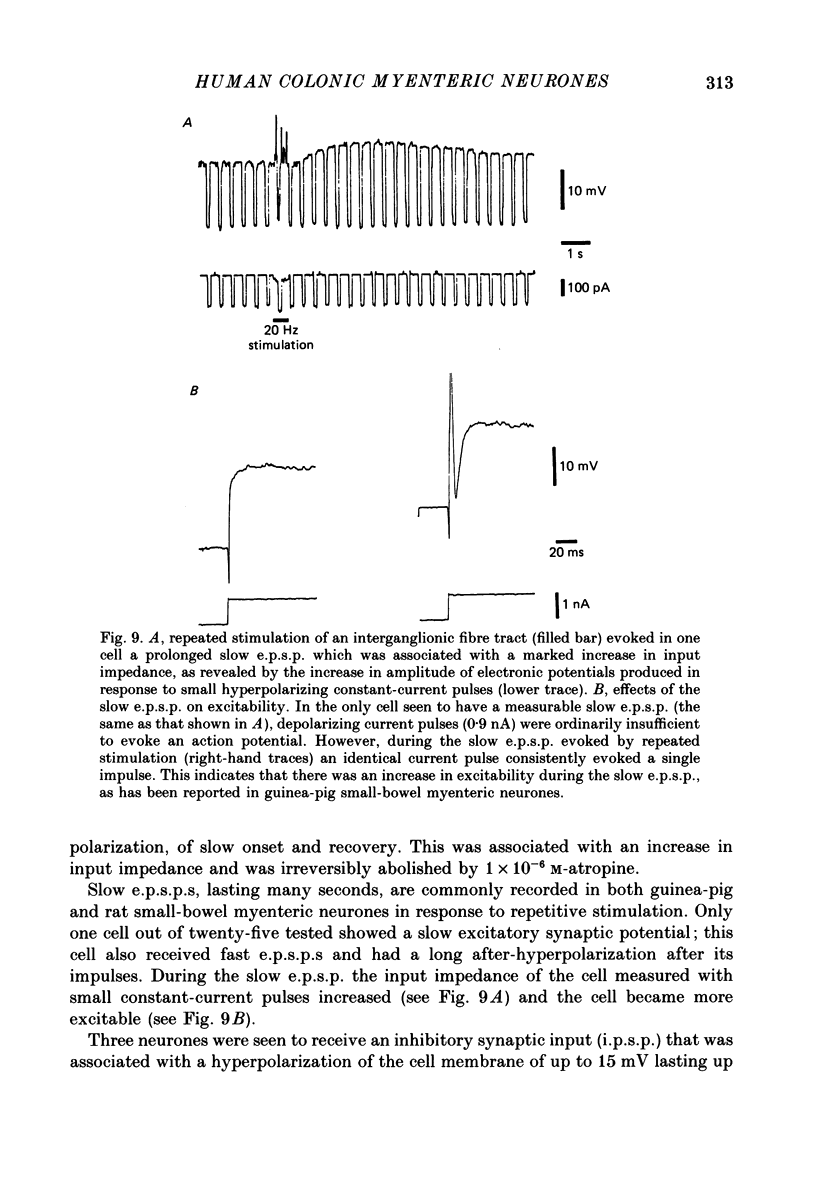
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Furukawa K., Taylor G. S., Bywater R. A. An intracellular study of myenteric neurons in the mouse colon. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;55(6):1395–1406. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.55.6.1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., McKirdy H. C. Synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):369–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Katayama Y., North R. A. Slow synaptic potentials in neurones of the myenteric plexus. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:505–516. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama T. Two types of spike generation of human Auerbach's plexus cells in culture. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Sep 1;25(2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neild T. O. The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine and possible 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists on neurones of the guinea-pig submucous plexus. Gen Pharmacol. 1981;12(4):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(81)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi R., Willard A. L. Neurons dissociated from rat myenteric plexus retain differentiated properties when grown in cell culture. I. Morphological properties and immunocytochemical localization of transmitter candidates. Neuroscience. 1985 Sep;16(1):187–199. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Electrophysiology of the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience. 1982 Feb;7(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Surprenant A. Inhibitory synaptic potentials resulting from alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkawa H., Prosser C. L. Functions of neurons in enteric plexuses of cat intestine. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1420–1426. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna S. K., Condon R., Cowles V. Colonic migrating and nonmigrating motor complexes in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 1):G355–G360. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.4.G355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. W. Lucifer dyes--highly fluorescent dyes for biological tracing. Nature. 1981 Jul 2;292(5818):17–21. doi: 10.1038/292017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Slow excitatory synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:343–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Two types of neurones lacking synaptic input in the submucous plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:363–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard A. L., Nishi R. Neurons dissociated from rat myenteric plexus retain differentiated properties when grown in cell culture. II. Electrophysiological properties and responses to neurotransmitter candidates. Neuroscience. 1985 Sep;16(1):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard A. L., Nishi R. Neurons dissociated from rat myenteric plexus retain differentiated properties when grown in cell culture. III. Synaptic interactions and modulatory effects of neurotransmitter candidates. Neuroscience. 1985 Sep;16(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D. Electrical activity from single neurons in Auerbach's plexus. Am J Physiol. 1970 Jul;219(1):159–169. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. D. Electrical discharge of single enteric neurons of guinea pig small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1973 Nov;225(5):1107–1113. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.5.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




