Abstract
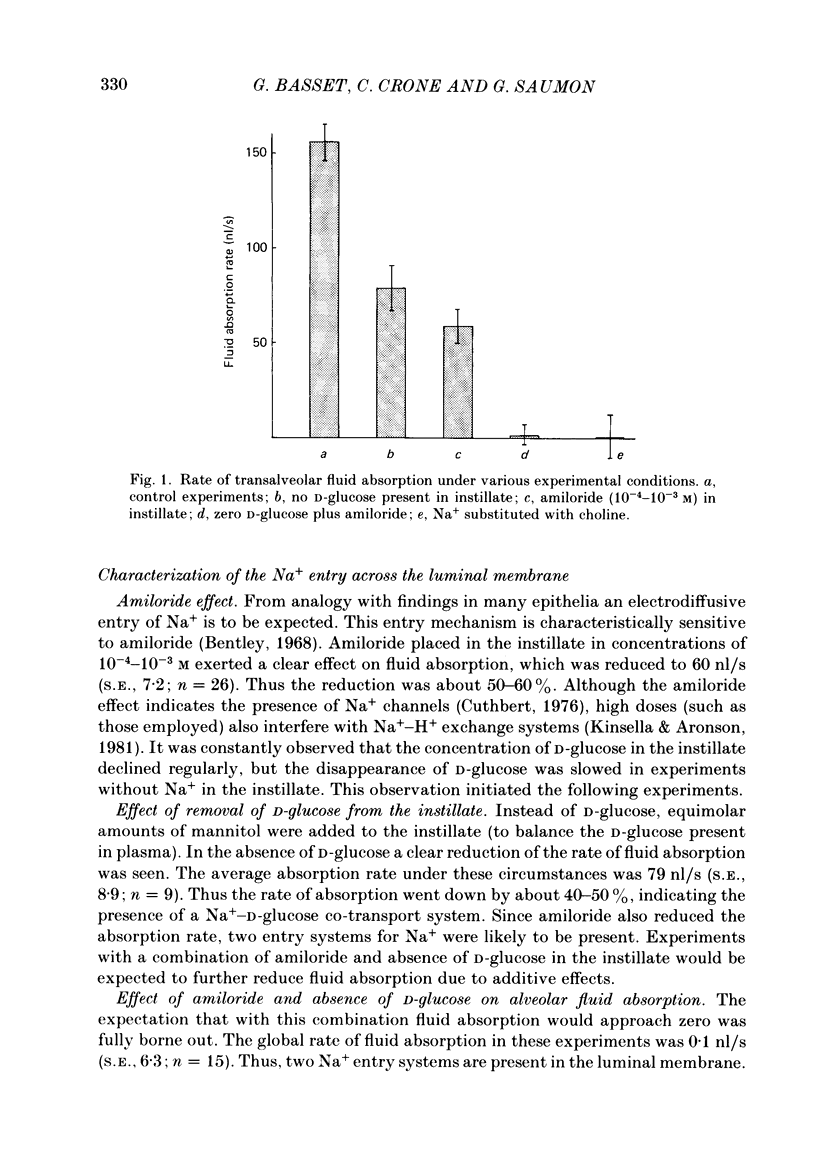
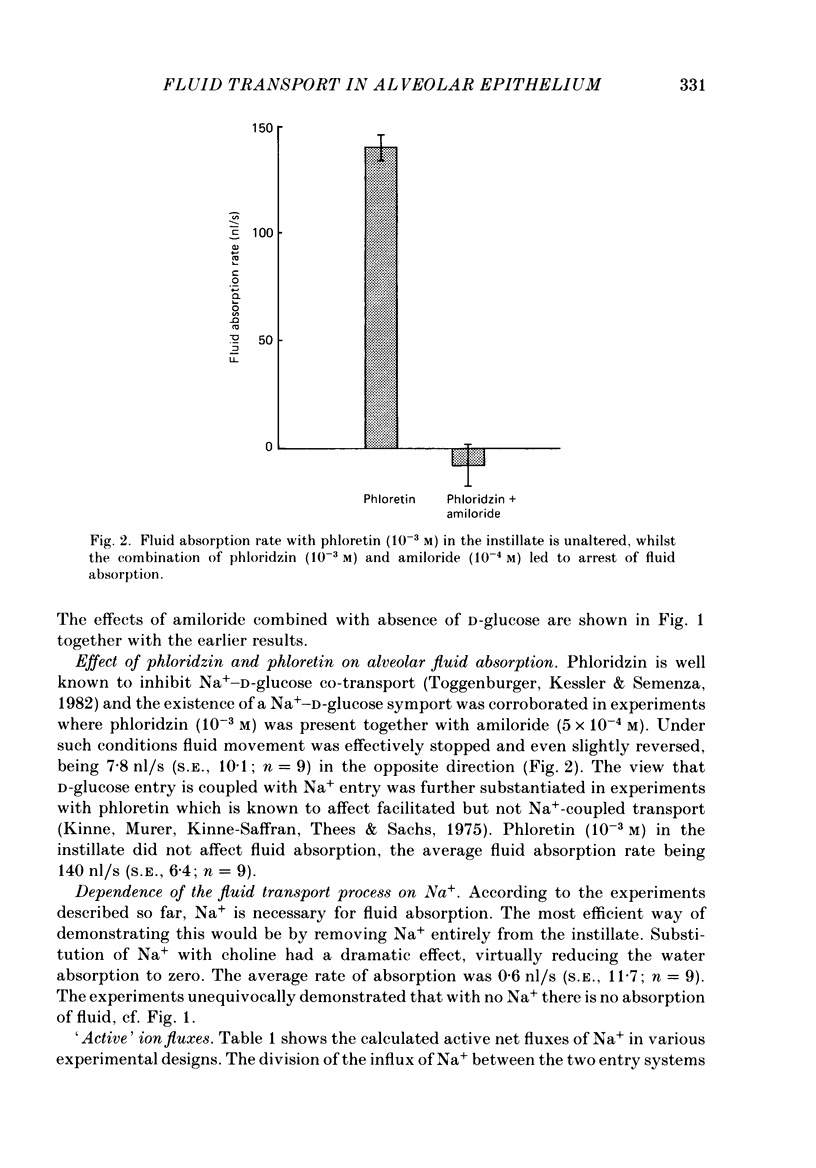
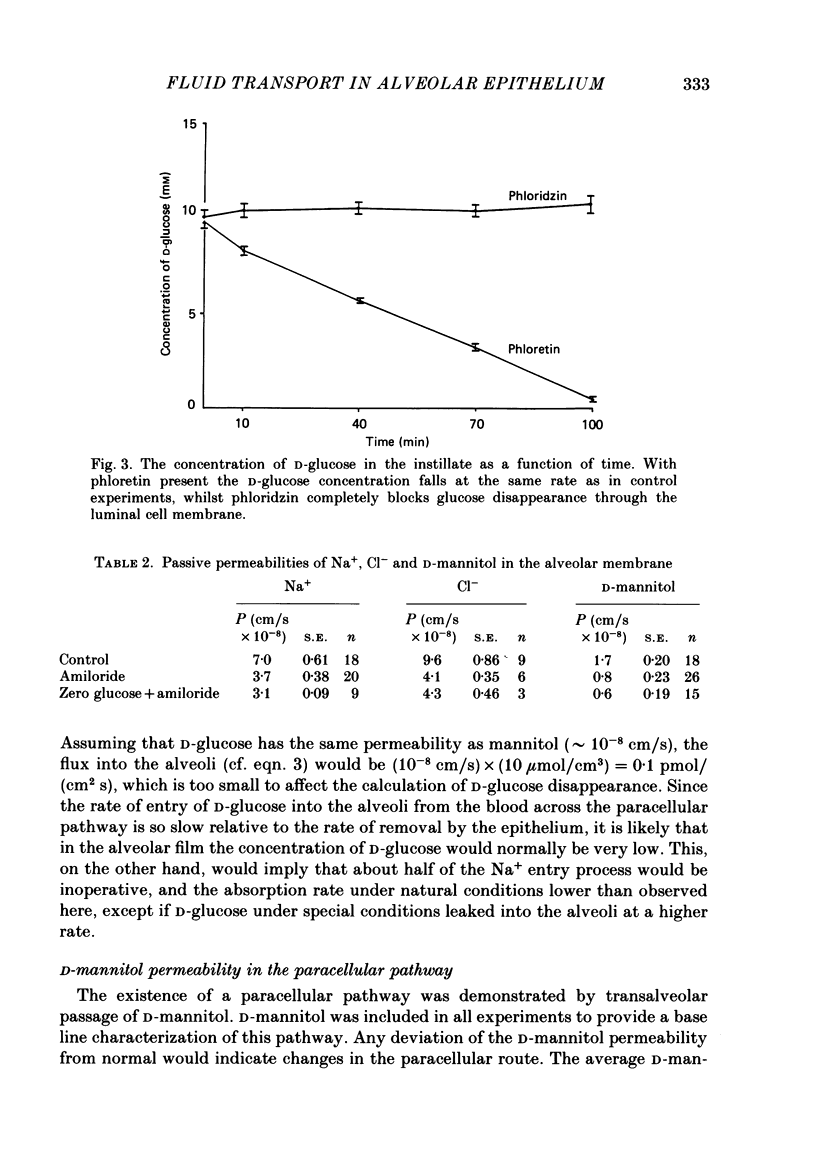
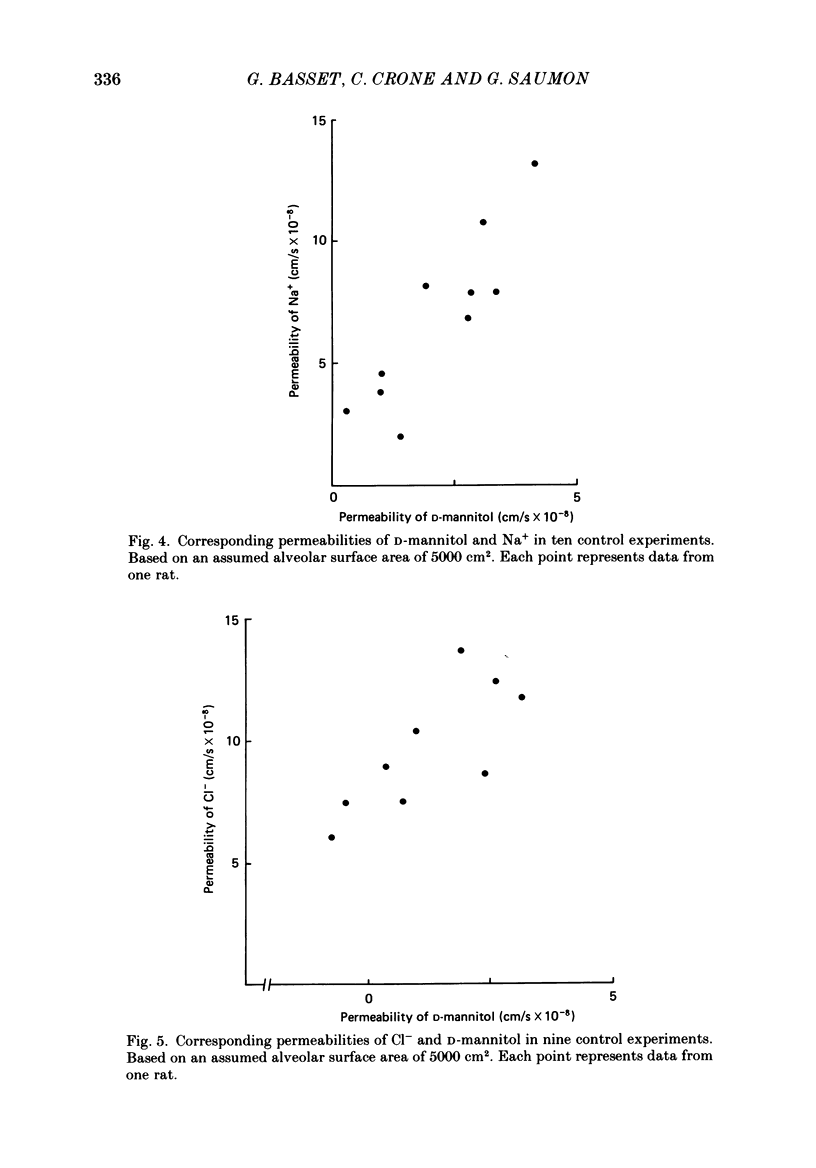
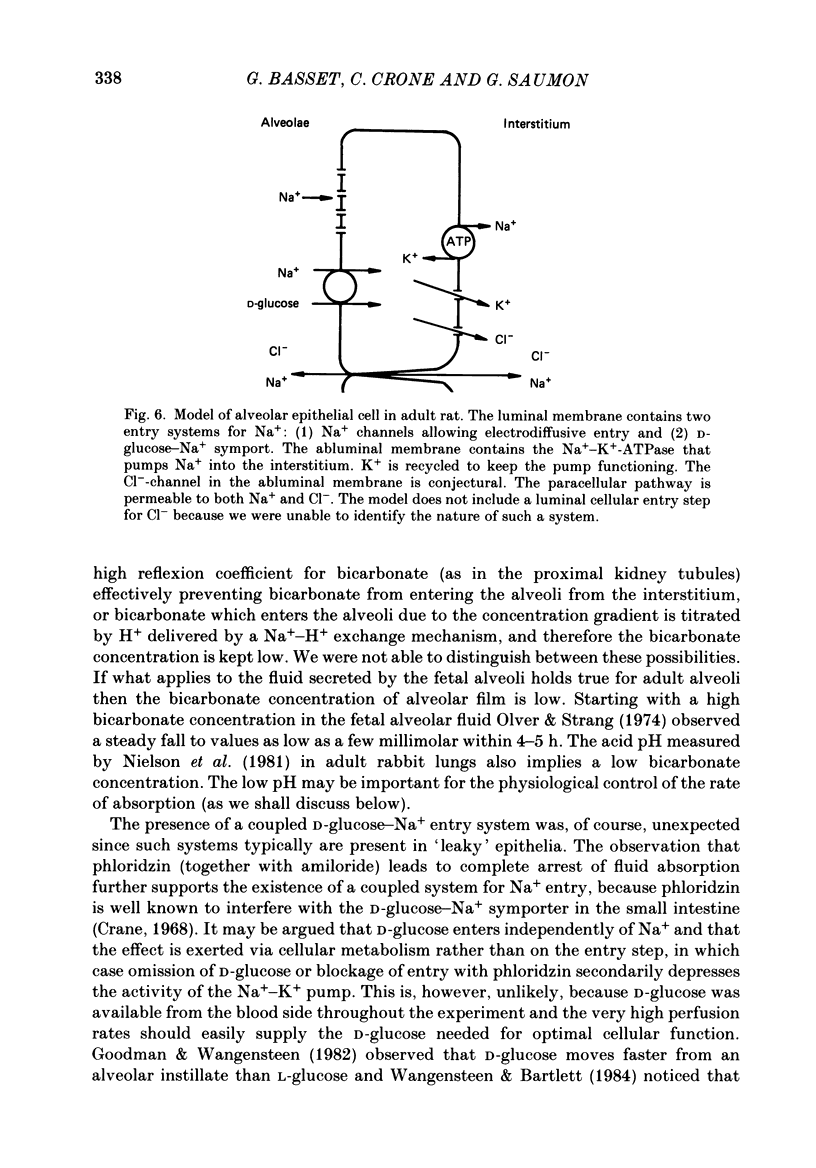
1. The purpose of the investigation was to characterize the luminal membrane and the paracellular pathway of rat lung alveolar epithelium. Experiments were performed on lungs in situ instilled with isotonic, buffered Ringer solution and perfused with blood from a donor rat using cross-circulation technique. 2. The rate of active Na+ transport was 4.4 pmol/(cm2s). The fluid absorption was 156 nl/s, and was unaffected by the presence of protein in the instillate (166 nl/s). In the absence of Na+, fluid absorption was zero. Amiloride (10(-3) M) reduced fluid absorption by 60%. Amiloride, combined with absence of D-glucose, arrested fluid absorption completely. Phloridzin at the luminal side reduced fluid absorption whilst phloretin had no effect. Amiloride together with phloridzin (10(-3) M) also arrested absorption. Thus, there are two entry systems for Na+ in the luminal membrane: Na+ channels and a Na+-D-glucose symport. These results show that alveolar fluid absorption is due to cellular activity. 3. Substitution of Cl- with gluconate not only stopped fluid absorption, but led to slight reversal of net fluid movement. 4. Passive unidirectional flux of Na+, determined with 22Na+, was 9.9 pmol/(cm2s) and that of Cl-, determined with 36Cl-, was 12.4 pmol/(cm2s). These fluxes were based on an assumed alveolar surface area of 5000 cm2. Transference numbers calculated from these figures are close to those in free solution, suggesting a neutral or weakly charged intercellular junctional pathway. The D-mannitol permeability in the paracellular pathway was 1.7 X 10(-8) cm/s. 5. It is a consequence of the proposed mechanism for fluid absorption that it becomes inoperative if the normally high reflexion coefficients for Na+ and Cl- are lowered in pathological states. In such conditions pulmonary oedema may develop depending on the net balance of passive mechanical and colloid-osmotic forces. 6. An explanation of the reversal of fluid transport at the time of birth is presented.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson P. S. Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:545–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset G., Crone C., Saumon G. Significance of active ion transport in transalveolar water absorption: a study on isolated rat lung. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:311–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. Amiloride: a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyenbach K. W., Frömter E. Electrophysiological evidence for Cl secretion in shark renal proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F282–F295. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F. Transport of H+ and of ionic weak acids and bases. J Membr Biol. 1983;72(1-2):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF01870311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. J., Olver R. E., Ramsden C. A., Strang L. B., Walters D. V. Effects of adrenaline and of spontaneous labour on the secretion and absorption of lung liquid in the fetal lamb. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:137–152. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruus K., Kristensen P., Larsen E. H. Pathways for chloride and sodium transport across toad skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1976 Mar;97(1):31–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1976.tb10233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall E. D., Kim K. J. Transport of water and solutes across bullfrog alveolar epithelium. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Jun;50(6):1263–1271. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.50.6.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. Importance of guanidinium groups of blocking sodium channels in epithelia. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):945–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Transcellular cross-talk between epithelial cell membranes. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):683–685. doi: 10.1038/300683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Koch M. J., Schultz S. G. Ion transport by rabbit colon. I. Active and passive components. J Membr Biol. 1976;27(3):297–316. doi: 10.1007/BF01869142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Diamond J. Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):9–13. doi: 10.1038/newbio235009a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Fleischer R. S., Crandall E. D. Evidence for active Na+ transport by cultured monolayers of pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C78–C83. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Wangensteen D. Alveolar epithelium permeability to small solutes: developmental changes. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jan;52(1):3–8. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R. Ion transport mechanisms in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mammalian nephron. Physiol Rev. 1985 Jul;65(3):760–797. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.3.760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greger R., Schlatter E. Mechanism of NaCl secretion in the rectal gland of spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias). I. Experiments in isolated in vitro perfused rectal gland tubules. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Sep;402(1):63–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00584833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEFOED-JOHNSEN V., USSING H. H. The nature of the frog skin potential. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Jun 2;42(3-4):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Amiloride inhibition of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F374–F379. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen E. H., Rasmussen B. E. Chloride channels in toad skin. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):413–434. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Butt A. G., Bowler M. J., Leader J. P., Macknight A. D. Effects of anions on cellular volume and transepithelial Na+ transport across toad urinary bladder. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(1-2):119–137. doi: 10.1007/BF01868744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Diamond J. M. Na+ transport by rabbit urinary bladder, a tight epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1976 Aug 27;28(1):1–40. doi: 10.1007/BF01869689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maetz J. Transport of ions and water across the epithelium of fish gills. Ciba Found Symp. 1976;(38):133–159. doi: 10.1002/9780470720202.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel L. J. Actions of external hypertonic urea, ADH, and theophylline on transcellular and extracellular solute permeabilities in frog skin. J Gen Physiol. 1975 May;65(5):599–615. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.5.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel L. J., Curran P. F. Response of the frog skin to steady-state voltage clamping. I. The shunt pathway. J Gen Physiol. 1972 May;59(5):503–518. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.5.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Widdicombe J. H., Sanders M. J., Misfeldt D. S., Berry L. C., Jr Transepithelial transport by pulmonary alveolar type II cells in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6033–6037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthay M. A., Landolt C. C., Staub N. C. Differential liquid and protein clearance from the alveoli of anesthetized sheep. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Jul;53(1):96–104. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.53.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson D. W., Goerke J., Clements J. A. Alveolar subphase pH in the lungs of anesthetized rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand I. C., Olver R. E., Reynolds E. O., Strang L. B. Permeability of lung capillaries and alveoli to non-electrolytes in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(2):303–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olver R. E. Fluid balance across the fetal alveolar epithelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 May;127(5 Pt 2):S33–S36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olver R. E., Schneeberger E. E., Walters D. V. Epithelial solute permeability, ion transport and tight junction morphology in the developing lung of the fetal lamb. J Physiol. 1981 Jun;315:395–412. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olver R. E., Strang L. B. Ion fluxes across the pulmonary epithelium and the secretion of lung liquid in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):327–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spenney J. G., Flemstrom G., Shoemaker R. L., Sachs G. Quantitation of conductance pathways in antral gastric mucosa. J Gen Physiol. 1975 May;65(5):645–662. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.5.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. E., Gaar K. A., Jr Estimation of equivalent pore radii of pulmonary capillary and alveolar membranes. Am J Physiol. 1970 Apr;218(4):1133–1140. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.4.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toggenburger G., Kessler M., Semenza G. Phlorizin as a probe of the small-intestinal Na+,D-glucose cotransporter. A model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 14;688(2):557–571. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangensteen D., Bartlett M. D- and L-glucose transport across the pulmonary epithelium. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Dec;57(6):1722–1730. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.6.1722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangensteen O. D., Wittmers L. E., Jr, Johnson J. A. Permeability of the mammalian blood-gas barrier and its components. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):719–727. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R. Morphological basis of alveolar-capillary gas exchange. Physiol Rev. 1973 Apr;53(2):419–495. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.2.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yablonski M. E., Lifson N. Mechanism of production of intestinal secretion by elevated venous pressure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):904–915. doi: 10.1172/JCI108367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



