Abstract
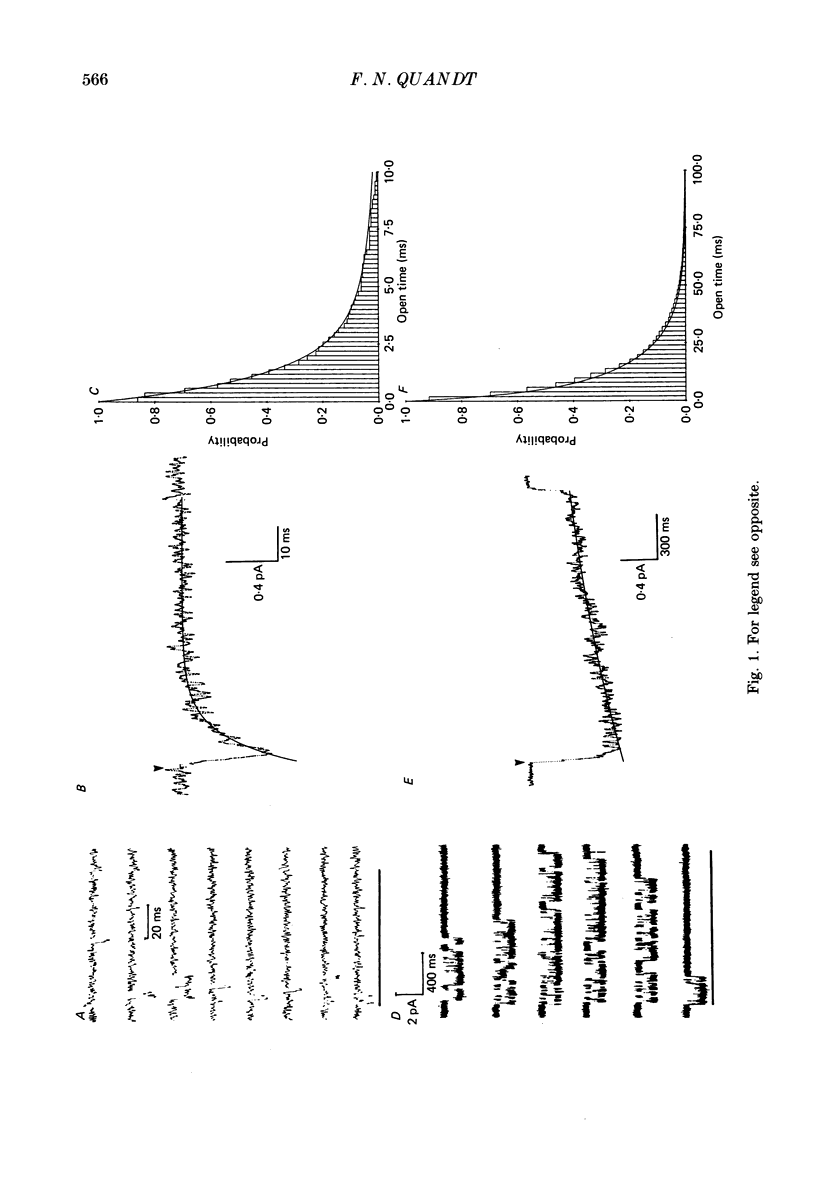
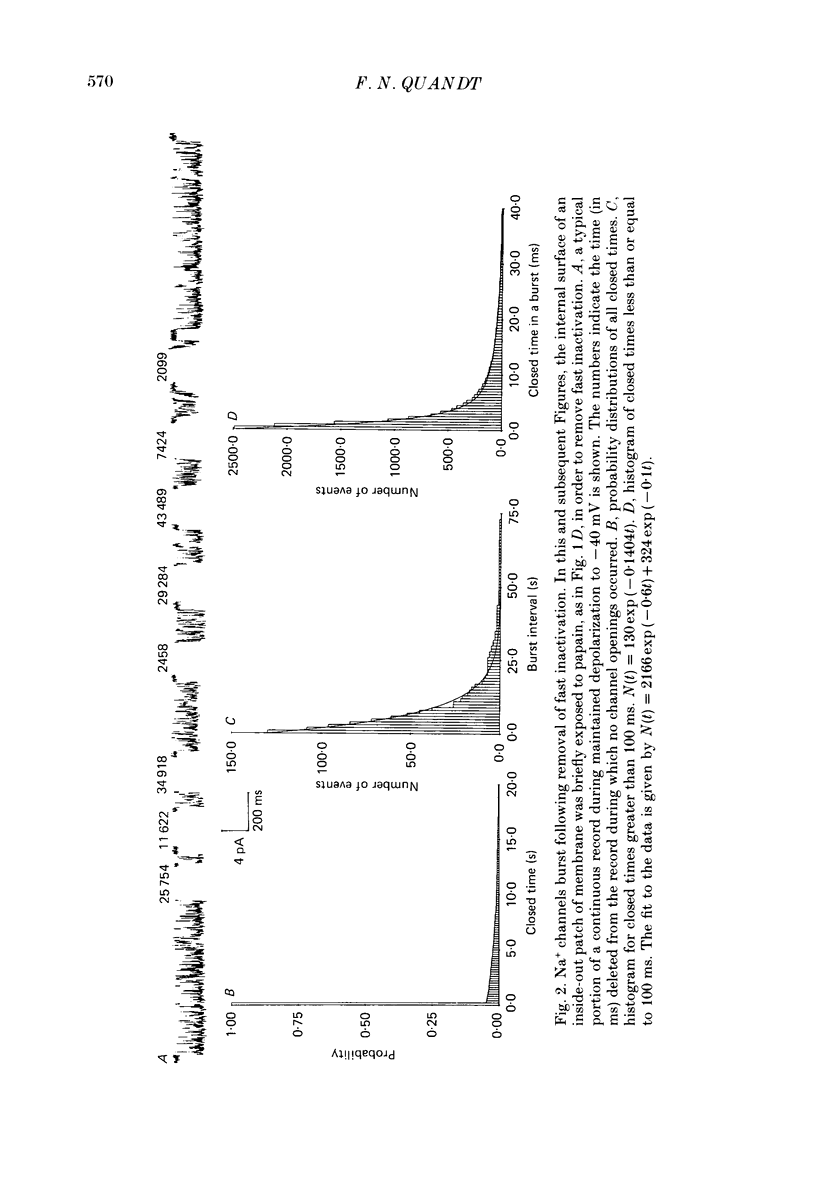
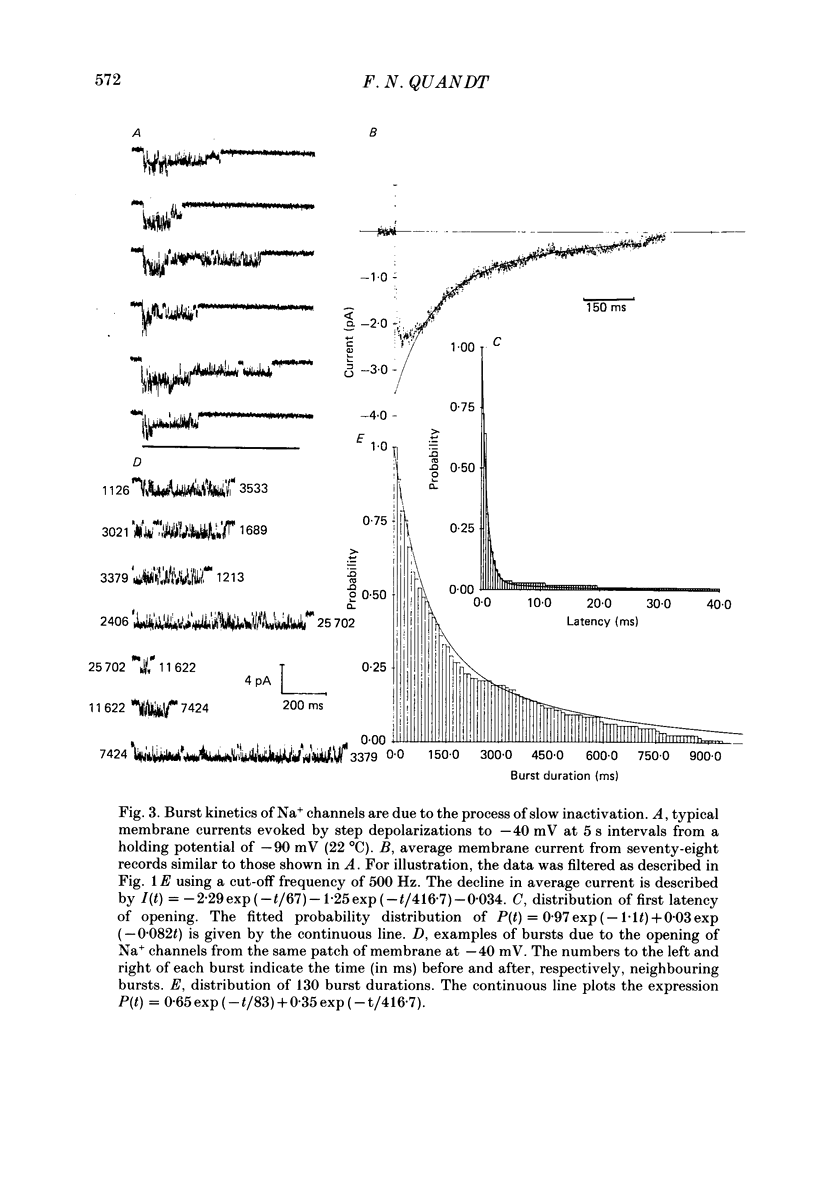
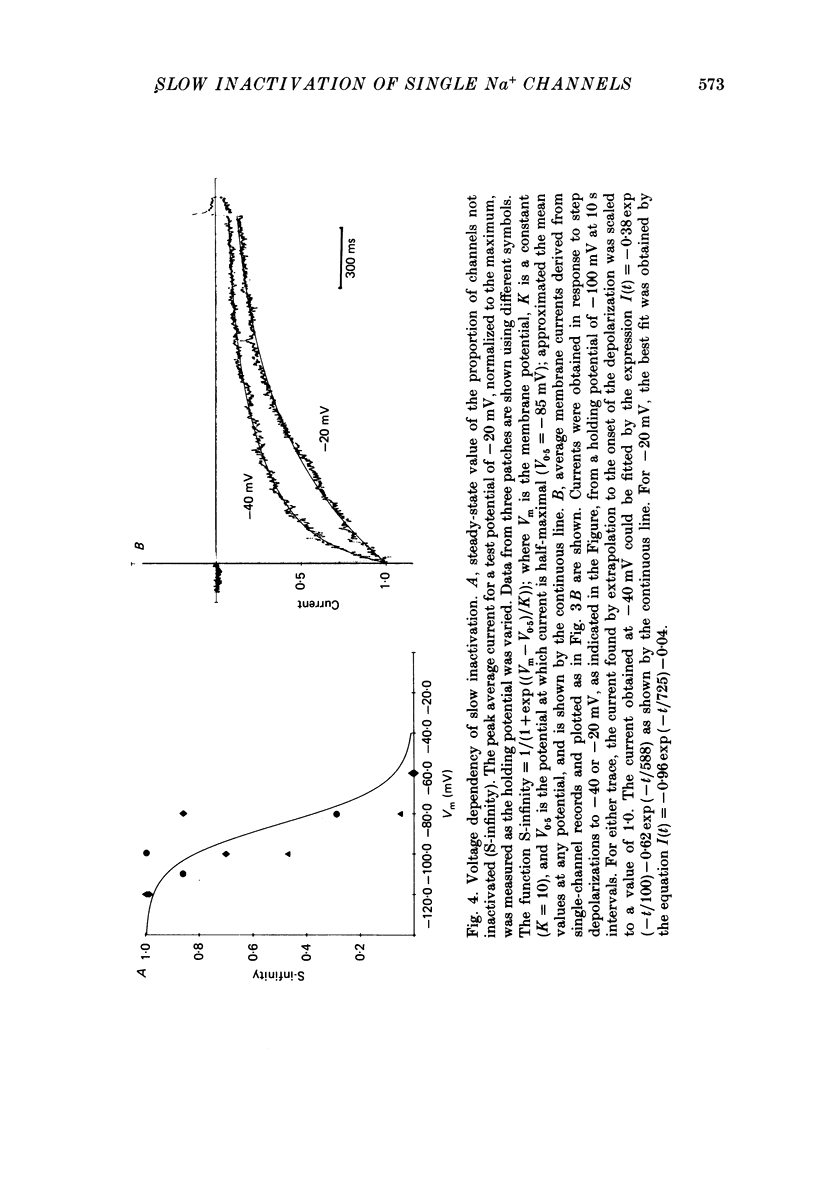
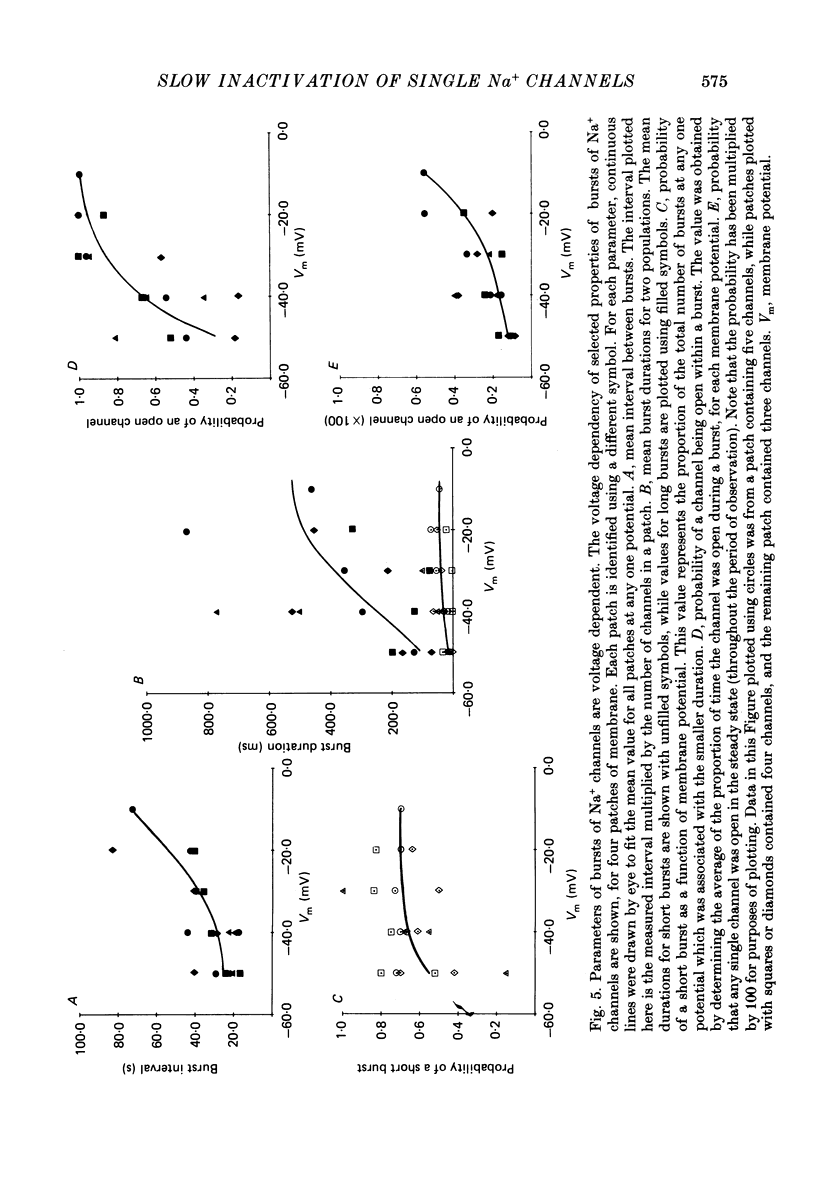
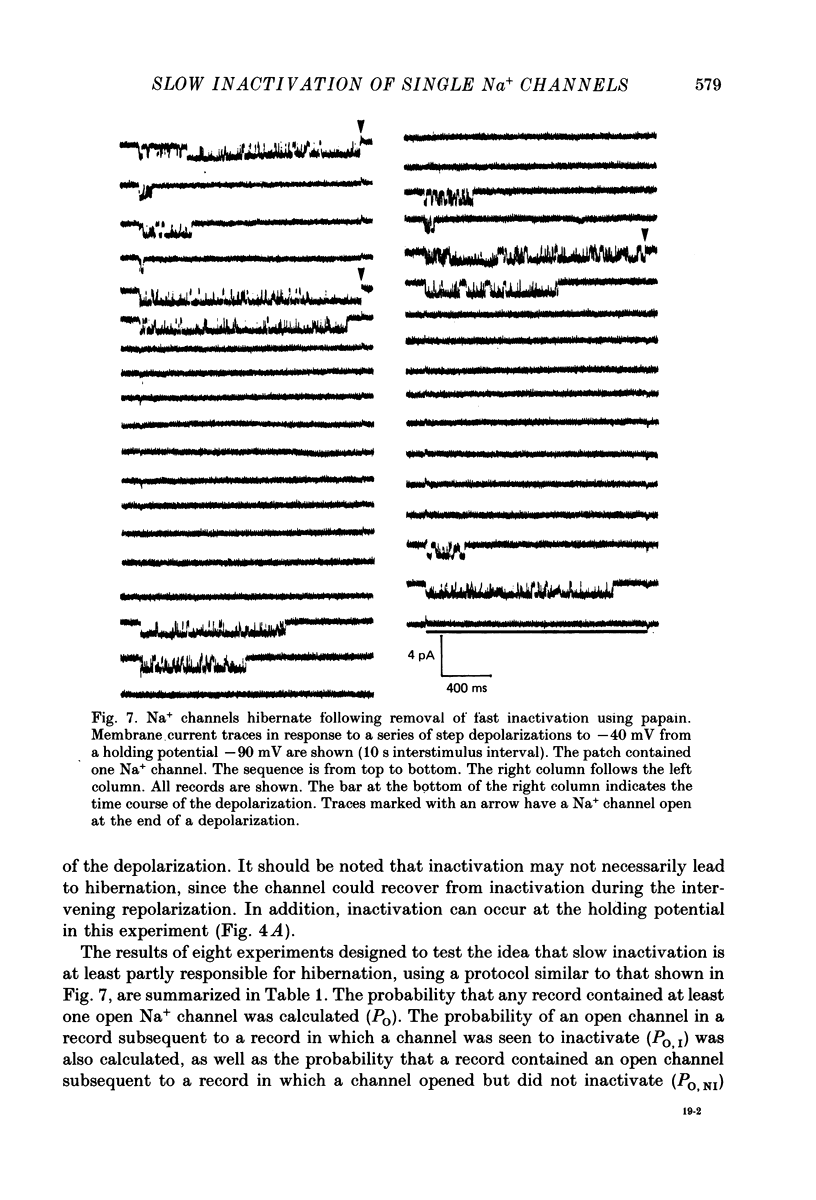
1. The kinetics of the slow inactivation process of Na+ channels were examined by recording single-channel currents from cultured neuroblastoma cells. 2. In order to directly examine slow inactivation, fast inactivation was first removed irreversibly by briefly exposing the internal surface of excised membranes to papain. Following treatment, the time constant for the inactivation of averaged membrane Na+ current increased by over two orders of magnitude, while the open time of individual channels increased by a factor of three. The two effects are consistent with the idea that papain can selectively remove fast inactivation of Na+ channels. 3. In the absence of fast inactivation, Na+ channels continued to open during maintained depolarization of the membrane to potentials less negative than -60 mV. Under these conditions, the opening occurred in bursts 50 ms to hundreds of milliseconds long, followed by silent periods lasting many seconds. The average burst length was found to be equal to the time constant of the decline in average evoked current measured at the same potential, indicating that a burst was terminated by entry of the channel into the slow inactivated state. 4. Histograms of open times revealed two populations of open states at any potential. Bursts could also be classified as either short or long bursts. Bursts appeared to be due to the gating of a single channel, and long bursts contained both types of open states, suggesting that a Na+ channel could have more than one open state. 5. The kinetics of bursts of Na+ channels were voltage dependent. As the membrane was depolarized, the burst length, interval between bursts, and open time all increased. Although the probability of an open channel during a burst increased to almost 1.0 with depolarization, any channel was open less than 0.5% of the time when measured throughout the depolarization. The increase in burst duration with depolarization would occur if the rate of slow inactivation is faster from closed states of the channel than from open states. 6. Records of membrane current evoked by a series of step depolarizations were clustered into those with openings of Na+ channels and those without openings. Records in which a channel did not inactivate during the depolarization were less likely to lead to hibernation, suggesting that this phenomenon is caused by the slow inactivation process.
Full text
PDF









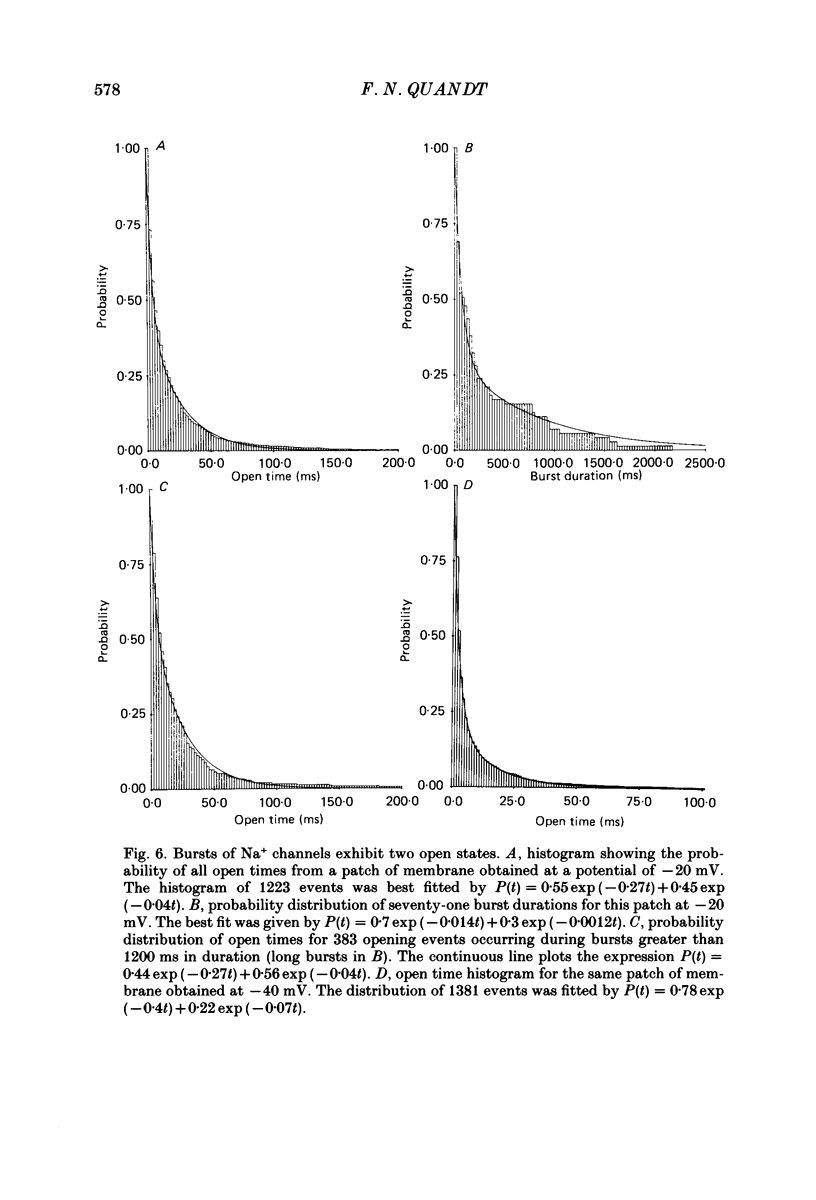






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman W. J., Jr, Palti Y. The effects of external potassium and long duration voltage conditioning on the amplitude of sodium currents in the giant axon of the squid, Loligo pealei. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Nov;54(5):589–606. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Stanfield P. R., Stühmer W. Slow changes in currents through sodium channels in frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E., Fernández J. M. Distribution and kinetics of membrane dielectric polarization. 1. Long-term inactivation of gating currents. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):21–40. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. Slow mechanism for sodium permeability inactivation in myelinated nerve fibre of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(2):283–297. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Slow changes in membrane permeability and long-lasting action potentials in axons perfused with fluoride solutions. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):707–728. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y. Inactivation of sodium channels: second order kinetics in myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(3):573–596. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins C. A., Rojas E., Suarez-Isla B. A. Activation and inactivation characteristics of the sodium permeability in muscle fibres from Rana temporaria. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:297–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of bursts of single ion channel openings and of clusters of bursts. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 24;300(1098):1–59. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fluctuations in the microsecond time range of the current through single acetylcholine receptor ion channels. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):464–466. doi: 10.1038/294464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Brodwick M. S., Oxford G. S., Rudy B. Arginine-specific reagents remove sodium channel inactivation. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):473–476. doi: 10.1038/271473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Fox A. P., Krasne S. Membrane patches and whole-cell membranes: a comparison of electrical properties in rat clonal pituitary (GH3) cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. M. Ultra-slow inactivation of the ionic currents through the membrane of myelinated nerve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 5;426(2):232–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gintant G. A., Datyner N. B., Cohen I. S. Slow inactivation of a tetrodotoxin-sensitive current in canine cardiac Purkinje fibers. Biophys J. 1984 Mar;45(3):509–512. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84187-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Vandenberg C. A., Lange K. Statistical analysis of single sodium channels. Effects of N-bromoacetamide. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):323–335. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84158-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Vandenberg C. A. Statistical properties of single sodium channels. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Oct;84(4):505–534. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.4.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Moran N., Ehrenstein G. Batrachotoxin modifies the gating kinetics of sodium channels in internally perfused neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2082–2085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Moran N., Ehrenstein G. Gating kinetics of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in neuroblastoma cells determined from single-channel measurements. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):313–322. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84157-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I., Peganov E. M., Revenko S. V., Shishkova L. D. Sodium currents in voltage clamped nerve fiber of frog under the combined action of batrachotoxin and procaine. Brain Res. 1975 Feb 14;84(3):541–546. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90771-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Worley J. F., 3rd, French R. J. Single sodium channels from rat brain incorporated into planar lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):172–175. doi: 10.1038/303172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze D. L., Lacerda A. E., Wilson D. L., Brown A. M. Cardiac Na currents and the inactivating, reopening, and waiting properties of single cardiac Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):691–719. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Calcium dependence of open and shut interval distributions from calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Nov;344:585–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuki N., Quandt F. N., Ten Eick R. E., Yeh J. Z. Characterization of the block of sodium channels by phenytoin in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Feb;228(2):523–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Garber S. S., Miller C. Batrachotoxin-activated Na+ channels in planar lipid bilayers. Competition of tetrodotoxin block by Na+. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):665–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello R., Begenisich T., Trzos W., Reed J. K. Interaction of nonylguanidine with the sodium channel. Biophys J. 1980 Sep;31(3):435–440. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)85071-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy K., Kiss T., Hof D. Single Na channels in mouse neuroblastoma cell membrane. Indications for two open states. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Dec;399(4):302–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00652757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Steinbach J. H. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B., Fox J. M., Drouin H., Schwarz W. Kinetics of the slow variation of peak sodium current in the membrane of myelinated nerve following changes of holding potential or extracellular pH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 5;426(2):245–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Removal of sodium channel inactivation in squid giant axons by n-bromoacetamide. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Mar;71(3):227–247. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M., Horn R. Opentime heterogeneity during bursting of sodium channels in frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):773–777. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83704-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M. Slow currents through single sodium channels of the adult rat heart. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jul;86(1):89–104. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M. Two modes of gating during late Na+ channel currents in frog sartorius muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Feb;87(2):305–326. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J., Horn R. Effect of N-bromoacetamide on single sodium channel currents in excised membrane patches. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Mar;79(3):333–351. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N., Narahashi T. Isolation and kinetic analysis of inward currents in neuroblastoma cells. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):249–262. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N., Narahashi T. Modification of single Na+ channels by batrachotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6732–6736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Rudy B. Destruction of the sodium conductance inactivation by a specific protease in perfused nerve fibres from Loligo. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):501–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Inactivation in Myxicola giant axons responsible for slow and accumulative adaptation phenomena. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:531–549. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Pencek T. L., Davis F. A. Slow sodium inactivation in Myxicola axons. Evidence for a second inactive state. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):771–778. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85727-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtmayer J. Behaviour of chemically modified sodium channels in frog nerve supports a three-state model of inactivation. Pflugers Arch. 1985 May;404(1):21–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00581486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P. Slow sodium inactivation in nerve after exposure to sulhydryl blocking reagents. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Feb;69(2):183–202. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J. G., Shrager P. Modification of slow sodium inactivation in nerve after internal perfusion with trypsin. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):C238–C244. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.235.5.C238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenberg C. A., Horn R. Inactivation viewed through single sodium channels. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Oct;84(4):535–564. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijverberg H. P., Pauron D., Lazdunski M. The effect of Tityus serrulatus scorpion toxin gamma on Na channels in neuroblastoma cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jul;401(3):297–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00582600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mastrigt R. Constant-step approximation of multi-exponential signals using a least-squares criterion. Comput Biol Med. 1977 Jul;7(3):231–247. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(77)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


