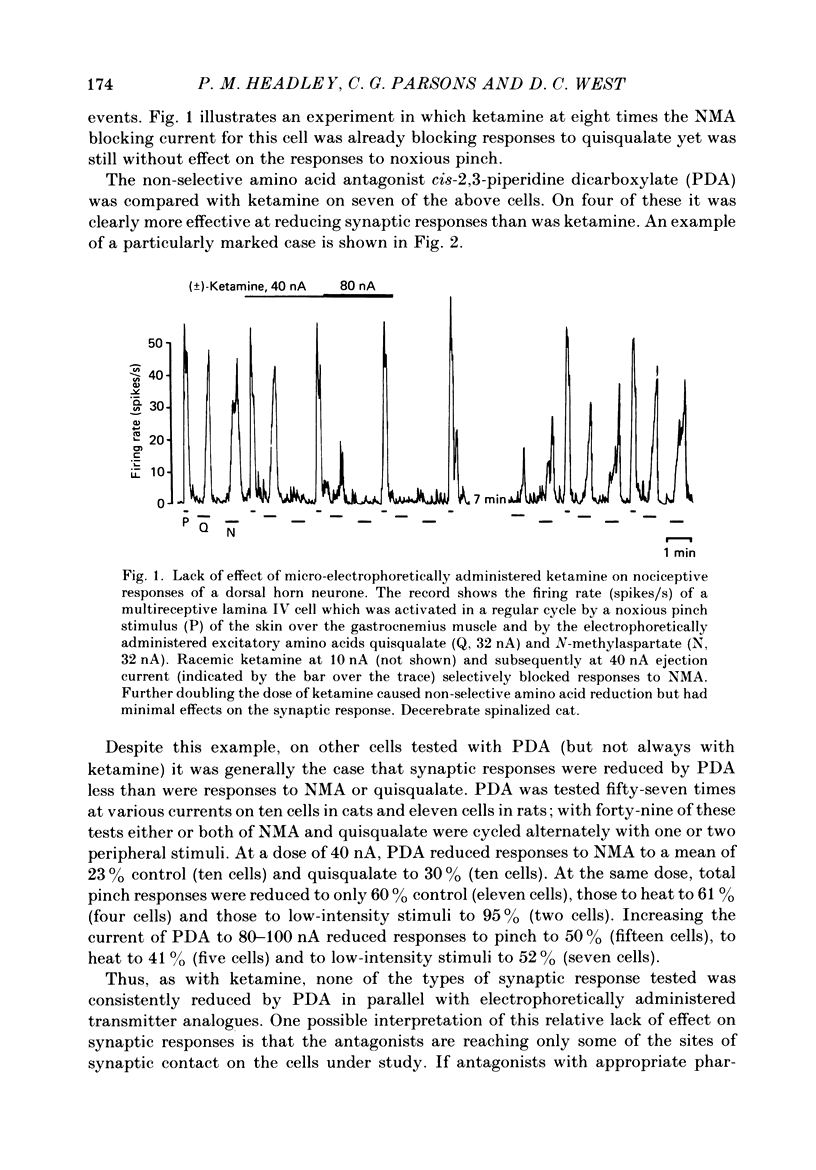
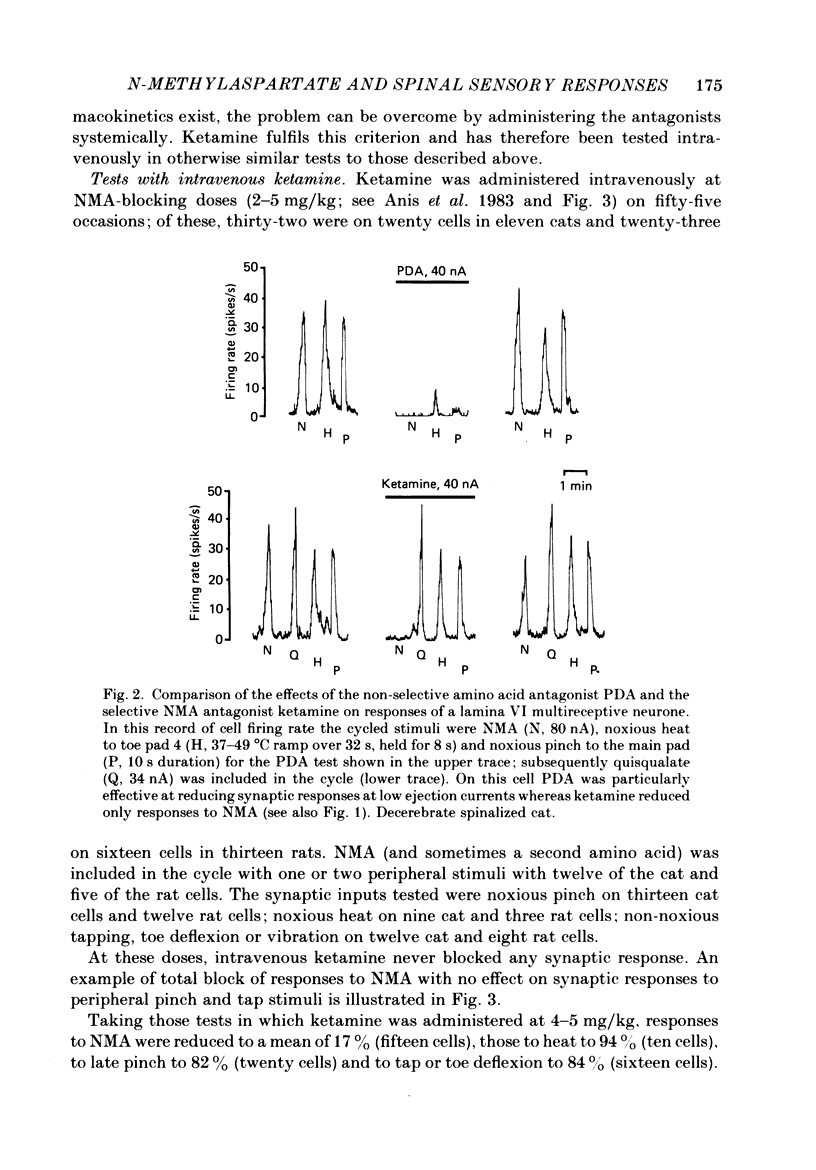
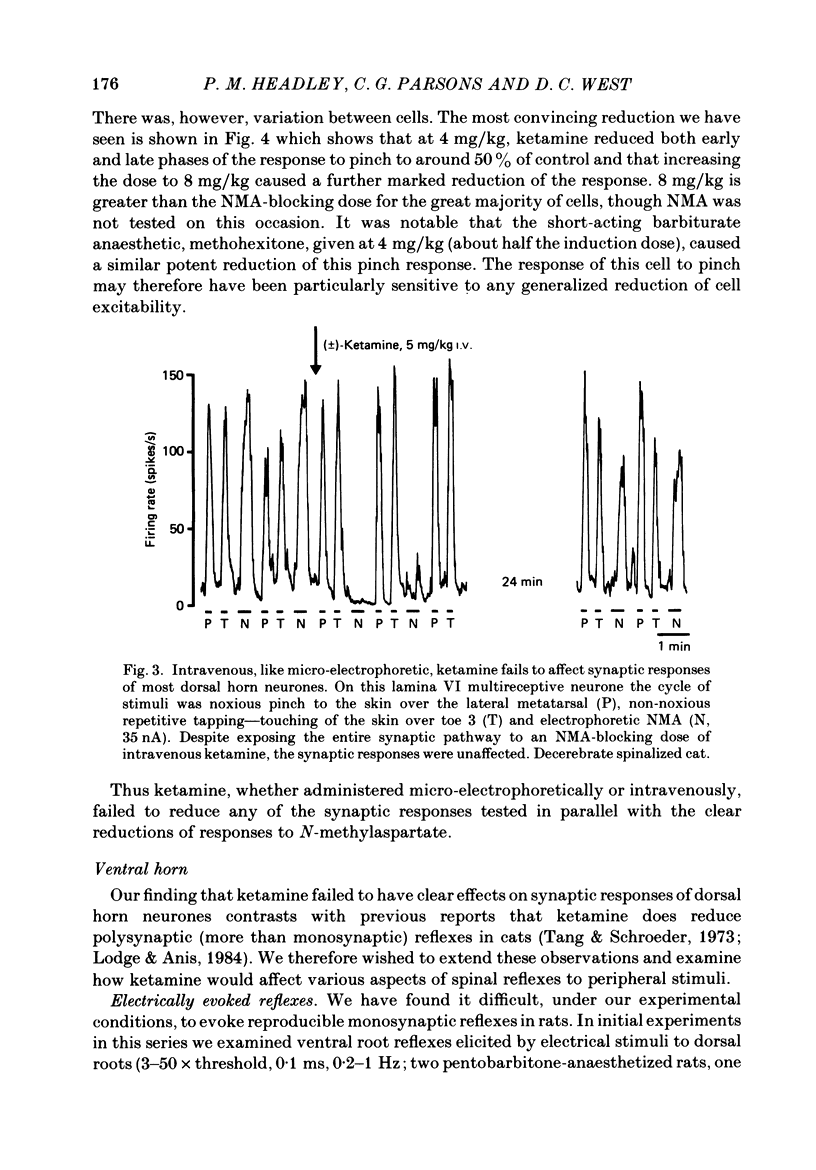
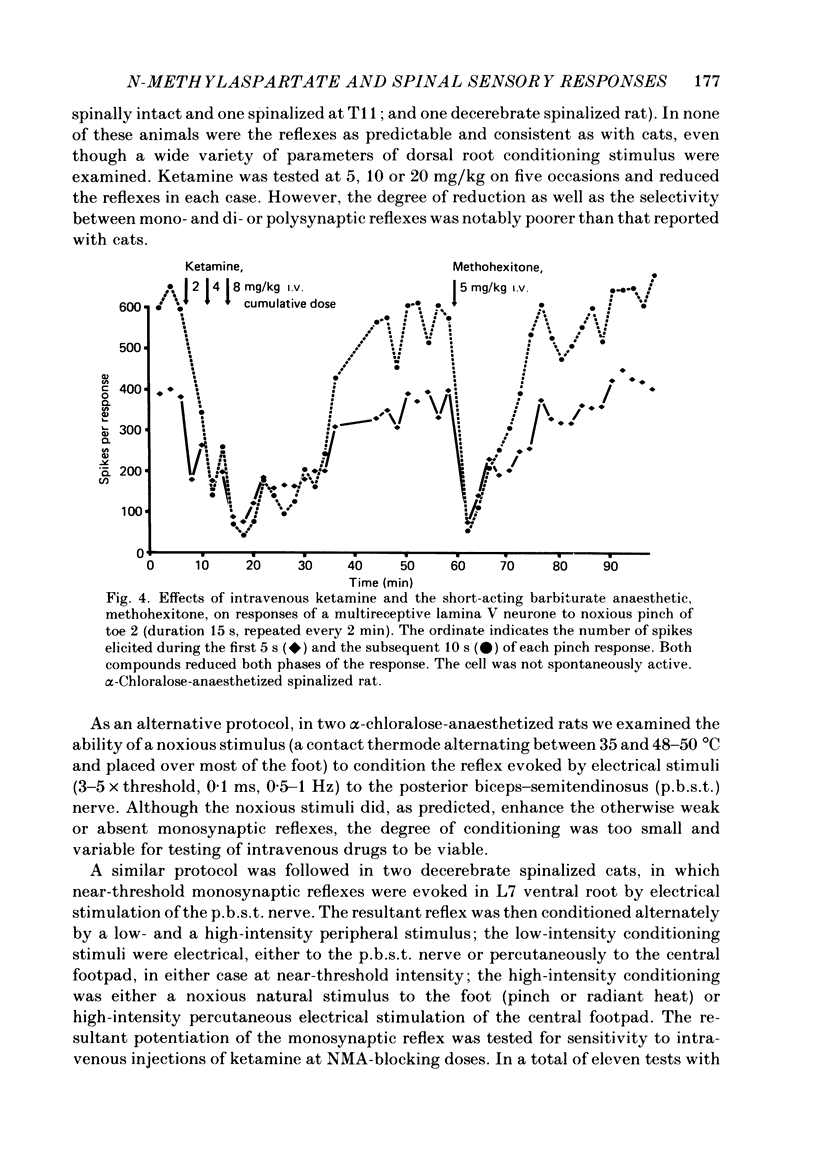
Abstract
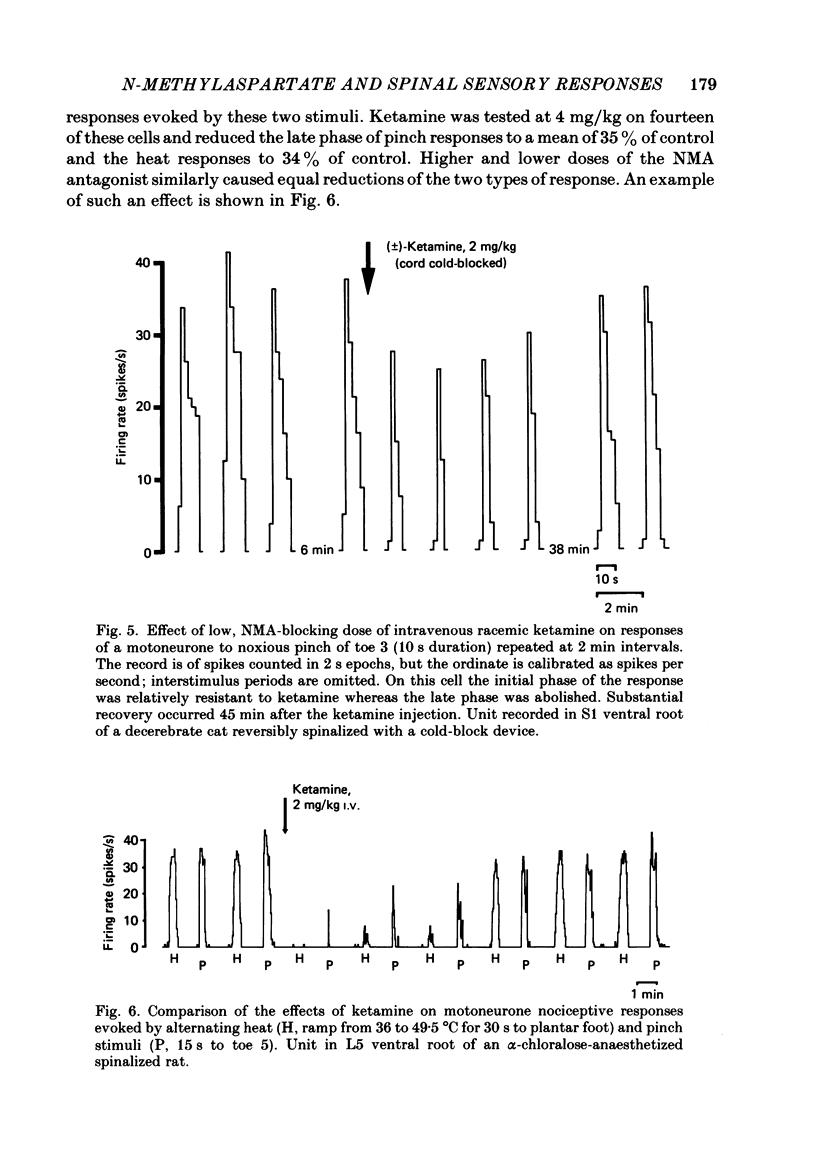
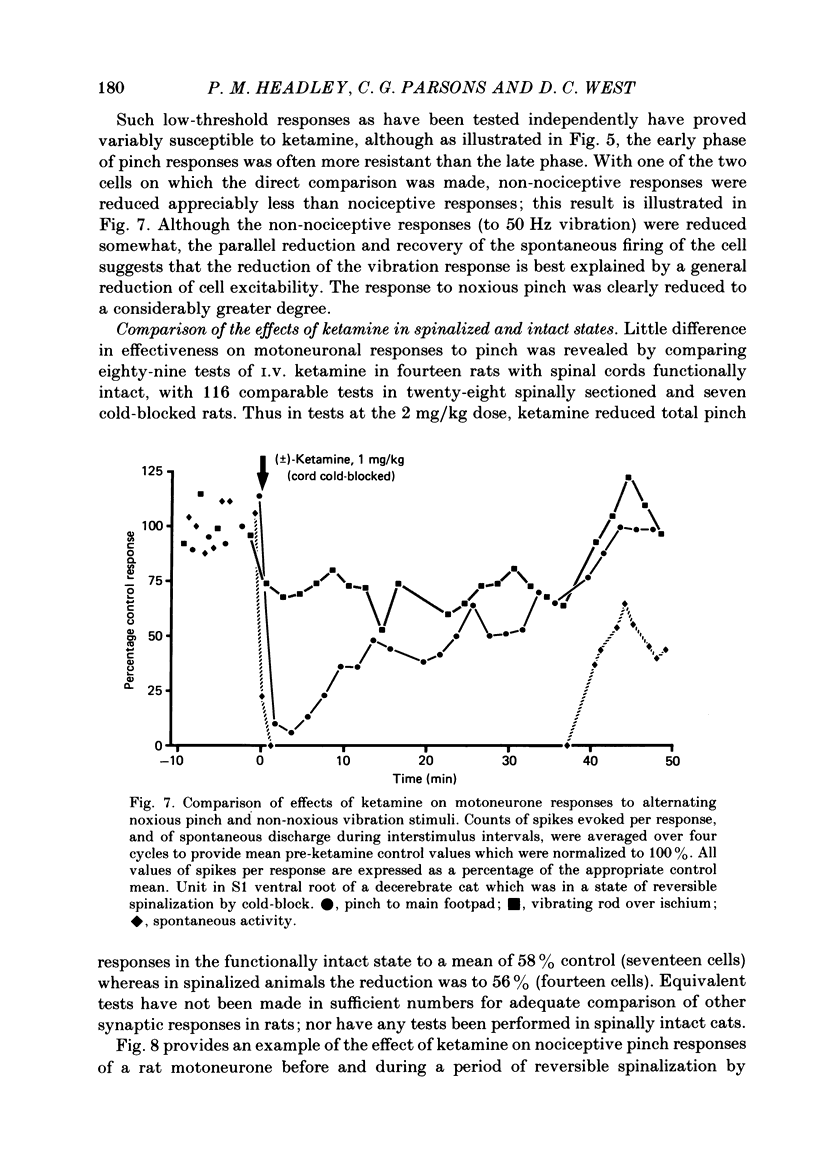
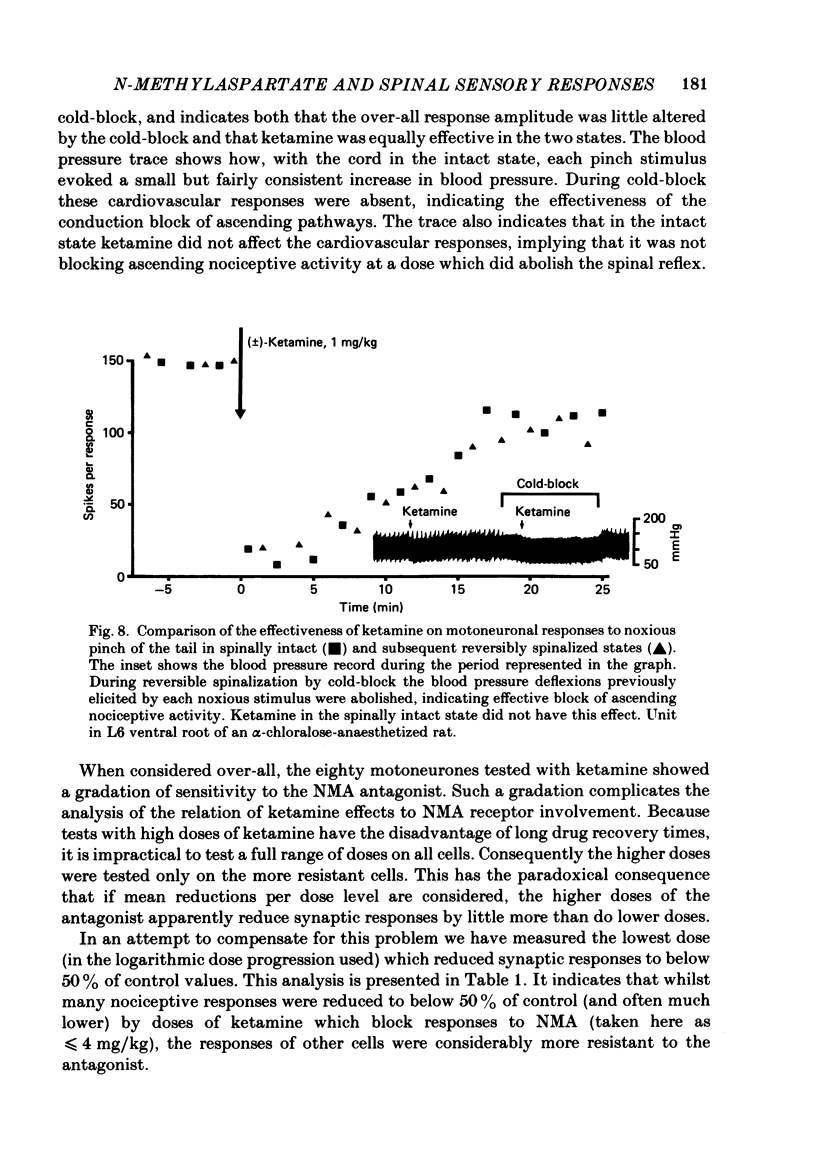
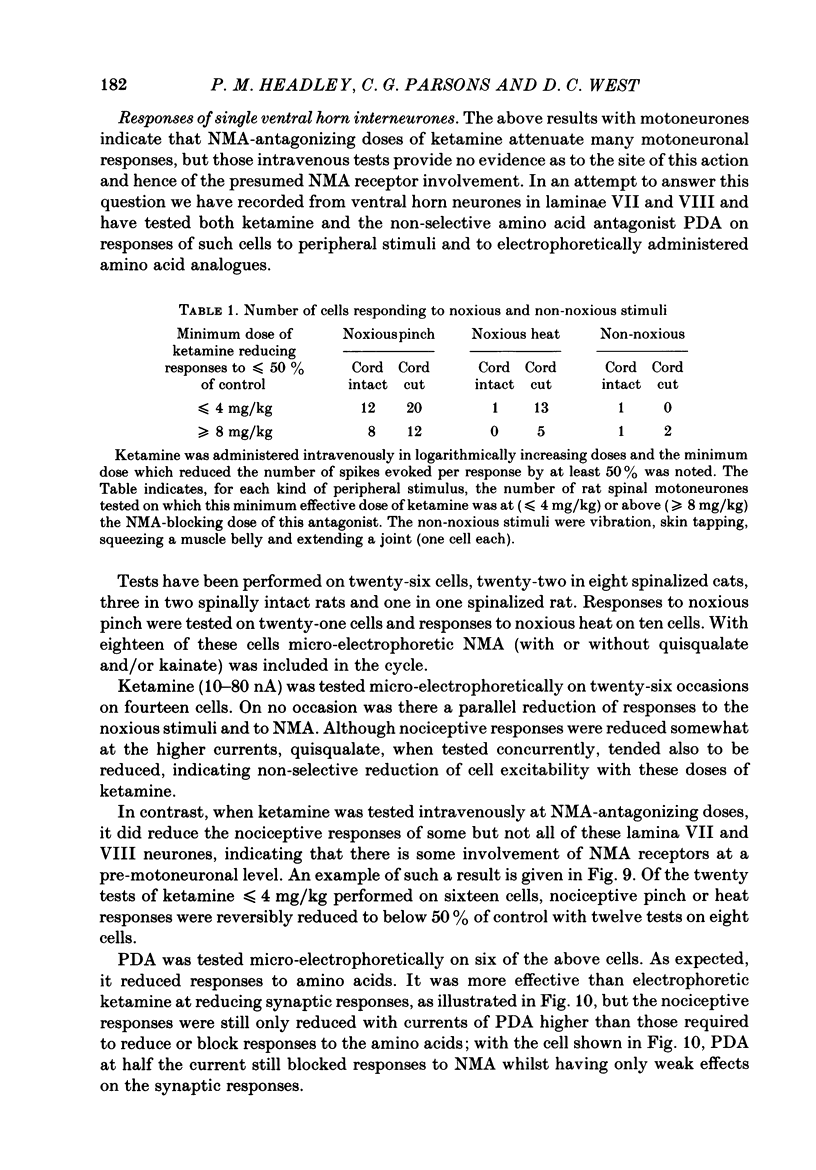
1. Single-cell recordings were made from neurones in various spinal laminae in anaesthetized or decerebrated, spinalized or intact rats and cats. Cells were activated by controlled peripheral sensory stimuli which mimicked natural conditions and with some cells also by micro-electrophoretically administered excitatory amino acid analogues. Such responses were tested with amino acid antagonists administered both micro-electrophoretically and intravenously. 2. With cells in the dorsal horn, the dissociative anaesthetic ketamine, administered either micro-electrophoretically or intravenously at doses which selectively reduce responses to N-methylaspartate, had no consistent effect on any of the sensory responses examined. 3. The non-selective amino acid antagonist cis-2,3-piperidine dicarboxylate was somewhat more effective at reducing sensory responses. 4. With motoneurones, intravenous N-methylaspartate-blocking doses of ketamine consistently reduced nociceptive responses. Non-nociceptive responses were less affected. 5. With ventral horn interneurones, intravenous but not micro-electrophoretic ketamine reduced nociceptive responses on about half the cells tested. 6. These results are interpreted in terms of the physiological role of the N-methylaspartate class of excitatory amino acid receptor in mediating responses in the ventral but not dorsal horn of the spinal cord to peripheral somatic stimuli.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahuja B. R. Analgesic effect of intrathecal ketamine in rats. Br J Anaesth. 1983 Oct;55(10):991–995. doi: 10.1093/bja/55.10.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry S. C., Dawkins S. L., Lodge D. Comparison of sigma- and kappa-opiate receptor ligands as excitatory amino acid antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Martin M. R., Watkins J. C., Davies J., Dray A. D-alpha-Aminoadipate as a selective antagonist of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation of mammalian spinal neurones. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):743–745. doi: 10.1038/270743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biscoe T. J., Headley P. M., Lodge D., Martin M. R., Watkins J. C. The sensitivity of rat spinal interneurones and renshaw cells to L-glutamate and L-aspartate. Exp Brain Res. 1976 Dec 22;26(5):547–551. doi: 10.1007/BF00238827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Dray A. Effects of D-alpha-aminoadipate on physiologically evoked responses of cat dorsal horn neurones. Experientia. 1979 Mar 15;35(3):353–354. doi: 10.1007/BF01964348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. Antagonism of excitatory amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation of spinal neurones by cis-2,3-piperidine dicarboxylate. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):1305–1307. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Role of excitatory amino acid receptors in mono- and polysynaptic excitation in the cat spinal cord. Exp Brain Res. 1983;49(2):280–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00238587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Selective antagonism of amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation in the cat spinal cord. J Physiol. 1979 Dec;297(0):621–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Griersmith B. T., Headley P. M., Maher J. B. The need to control skin temperature when using radiant heat in tests of analgesia. Exp Neurol. 1978 Sep 1;61(2):471–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Quantitative studies on some antagonists of N-methyl D-aspartate in slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):381–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Headley P. M., Parsons C. G., West D. C. Comparison of mu, kappa and sigma preferring agonists for effects on spinal nociceptive and other responses in rats. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Salt T. E. An ionophoretic study of the responses of rat caudal trigeminal nucleus neurones to non-noxious mechanical sensory stimuli. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:65–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Anis N. A. Effects of ketamine and three other anaesthetics on spinal reflexes and inhibitions in the cat. Br J Anaesth. 1984 Oct;56(10):1143–1151. doi: 10.1093/bja/56.10.1143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D., Headley P. M., Curtis D. R. Selective antagonism by D-alpha-aminoadipate of amino acid and synaptic excitation of cat spinal neurons. Brain Res. 1978 Sep 8;152(3):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D., Lodge D. Ketamine acts as a non-competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist on frog spinal cord in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 1985 Oct;24(10):999–1003. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(85)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. S., Croucher M. J., Czuczwar S. J., Collins J. F., Curry K., Joseph M., Stone T. W. A comparison of the anticonvulsant potency of (+/-) 2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid and (+/-) 2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoic acid. Neuroscience. 1983 Aug;9(4):925–930. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt T. E., Hill R. G. Excitatory amino acids as transmitter candidates of vibrissae afferent fibres to the rat trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Mar 10;22(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt T. E., Hill R. G. Pharmacological differentiation between responses of rat medullary dorsal horn neurons to noxious mechanical and noxious thermal cutaneous stimuli. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 14;263(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang A. H., Schroeder L. A. Spinal-cord depressant effects of ketamine and etoxadrol in the cat and the rat. Anesthesiology. 1973 Jul;39(1):37–43. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197307000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., West D. C., Lodge D. An N-methylaspartate receptor-mediated synapse in rat cerebral cortex: a site of action of ketamine? Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):479–481. doi: 10.1038/313479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turski L., Schwarz M., Turski W. A., Klockgether T., Sontag K. H., Collins J. F. Muscle relaxant action of excitatory amino acid antagonists. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Feb 4;53(3):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90558-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. F., Way W. L., Trevor A. J. Ketamine--its pharmacology and therapeutic uses. Anesthesiology. 1982 Feb;56(2):119–136. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198202000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


