Abstract
1. Currents were recorded through acetylcholine (ACh) receptor channels on clonal BC3H-1 cells in the presence of high concentrations of ACh (20-1000 microM) and carbamylcholine (180-1000 microM). 2. Channel openings at high agonist concentrations occur in clusters separated by long silent periods (seconds). Clusters, in turn, show groups of closely spaced openings separated by relatively long (hundreds of milliseconds) closed periods. The closed periods between clusters and between groups within clusters are thought to reflect two desensitized states (Sakmann, Patlak & Neher, 1980). 3. Openings within groups consist largely of long-duration openings. An excess of brief-duration openings is seen at all high agonist concentrations; most brief openings occur as isolated, solitary openings. 4. The distribution of closed periods within groups shows four exponential components with time constants separated by several fold over the range of 50 microseconds to 50 ms. 5. The distribution of closed periods within groups is analysed as a function of agonist concentration, to estimate rate constants for transitions in a hypothetical reaction scheme for receptor activation. One or two of these components (depending on agonist and agonist concentration) appear to reflect agonist binding and channel gating. It is hypothesized that the other closed-period components within groups at high agonist concentrations result from additional states of doubly liganded receptors which have closed ion channels. 6. With ACh as agonist the data indicate that binding and activation saturate at concentrations above 130 microM. The data are quantitatively consistent with measurements made at low concentrations of ACh (Sine & Steinbach, 1986b), and indicate that a four-state linear scheme is able to describe major features of ACh-receptor activation on BC3H-1 cells. The channel opening rate is estimated to be about 450 s-1 and the closing rate about 35 s-1 (-70 mV, 11 degrees C). The concentration dependence of closed durations suggests that some positive co-operativity exists in agonist binding. The dissociation constant with one ACh molecule bound is about 50 microM, and that with two bound is about 10 microM (for an ACh receptor with a closed channel). 7. Saturation is not observed with carbamylcholine, even at 1 mM. The data are consistent with data obtained at low concentrations of carbamylcholine, and are in over-all agreement with the interpretation of data obtained with ACh. The affinity for carbamylcholine is estimated to be about 20-fold lower than with ACh.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




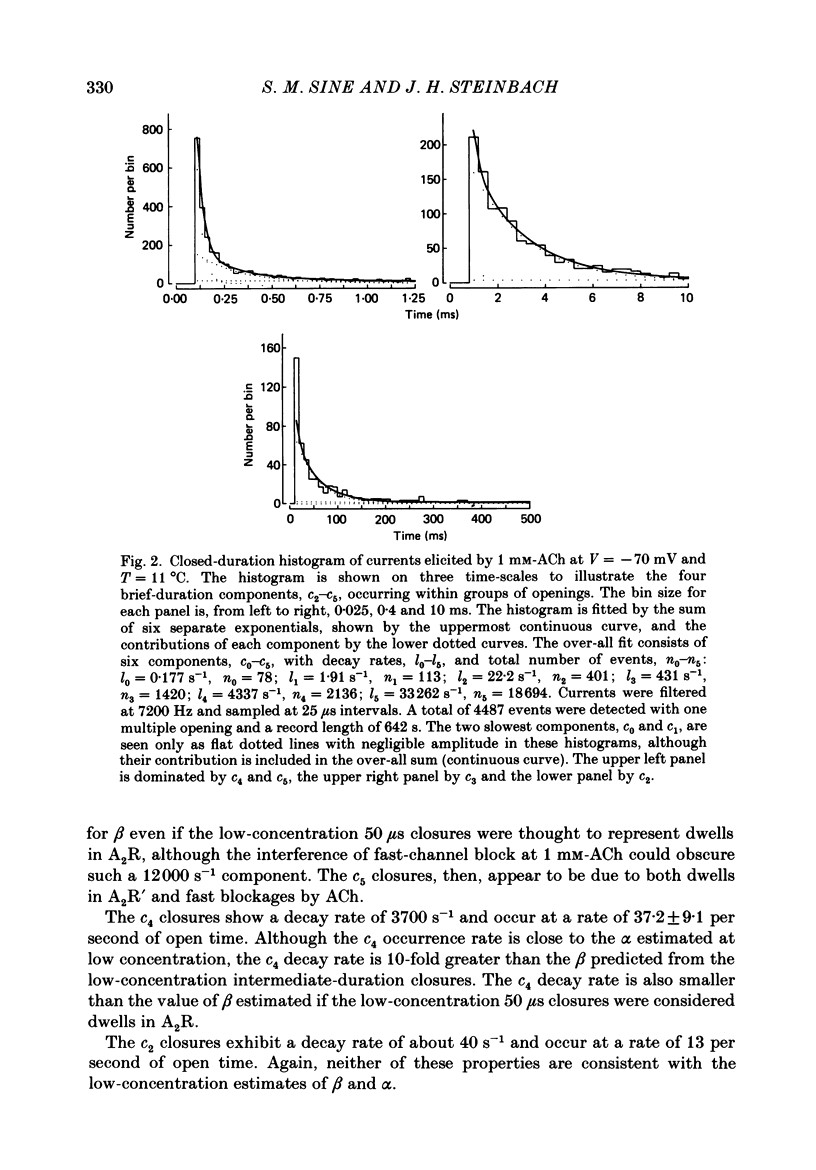


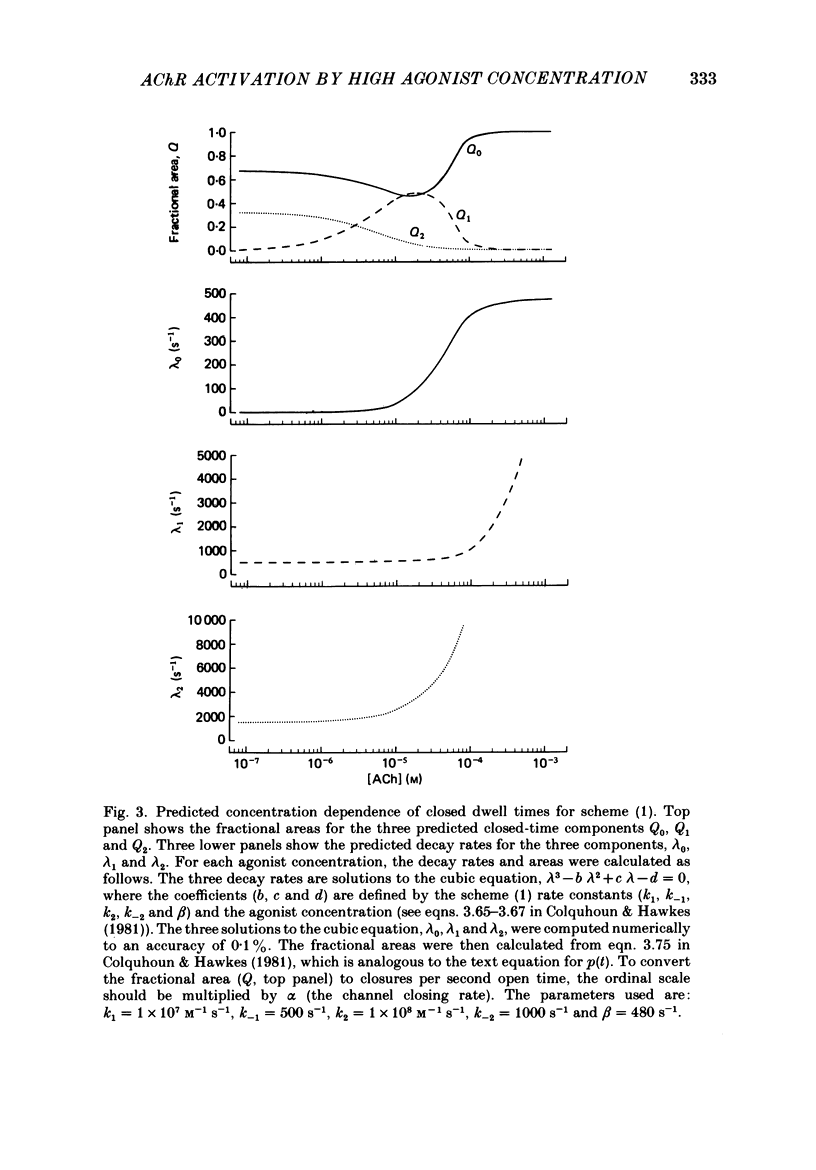

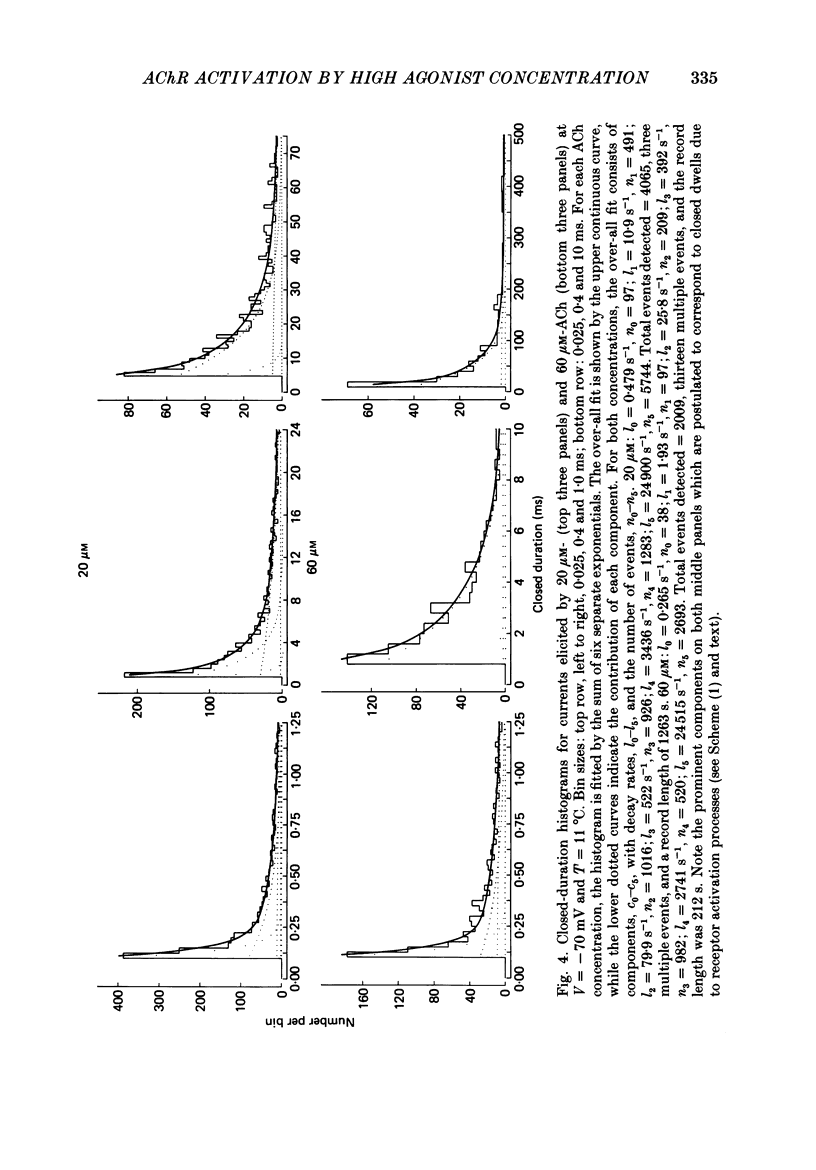
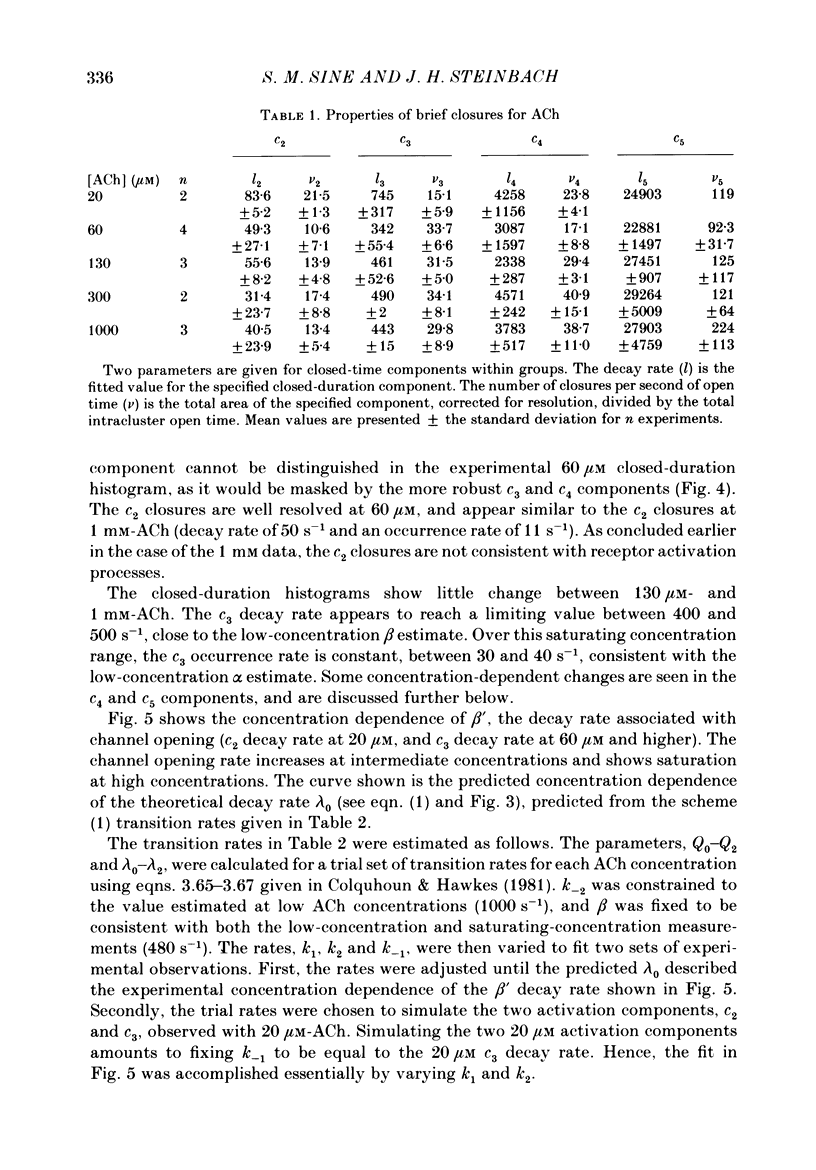








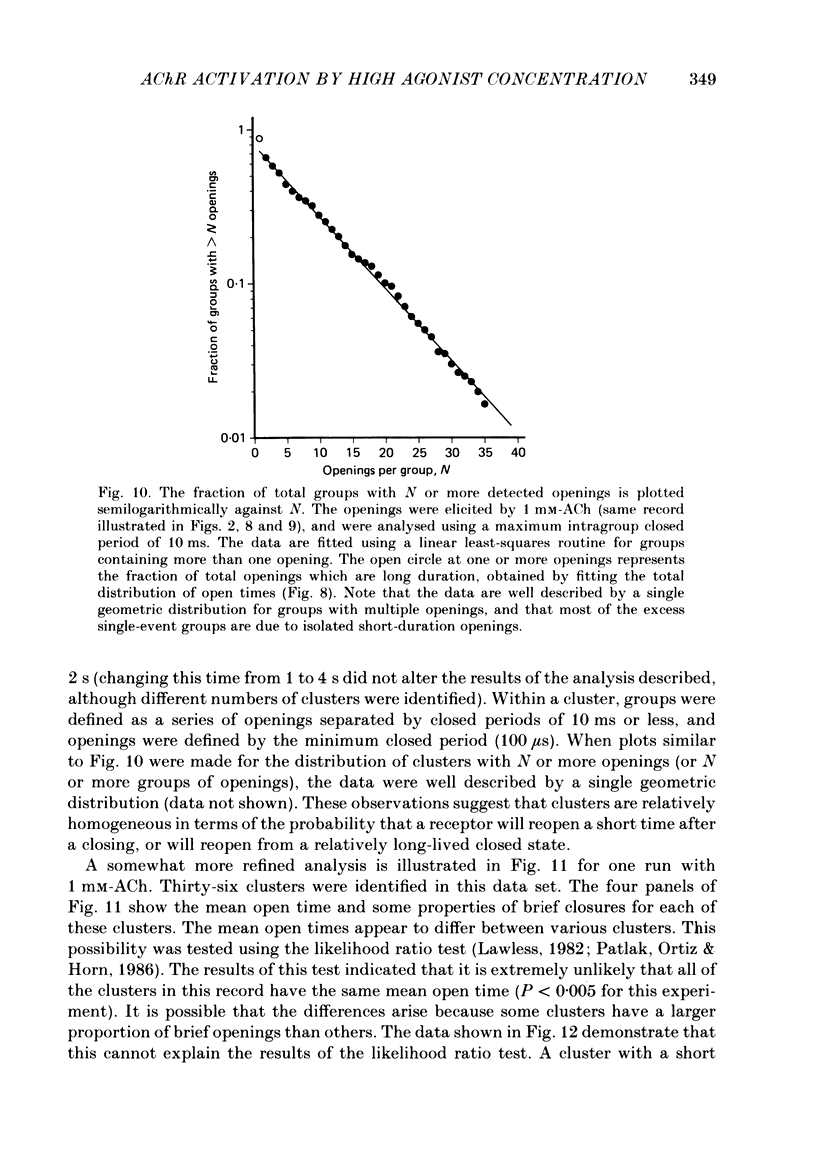
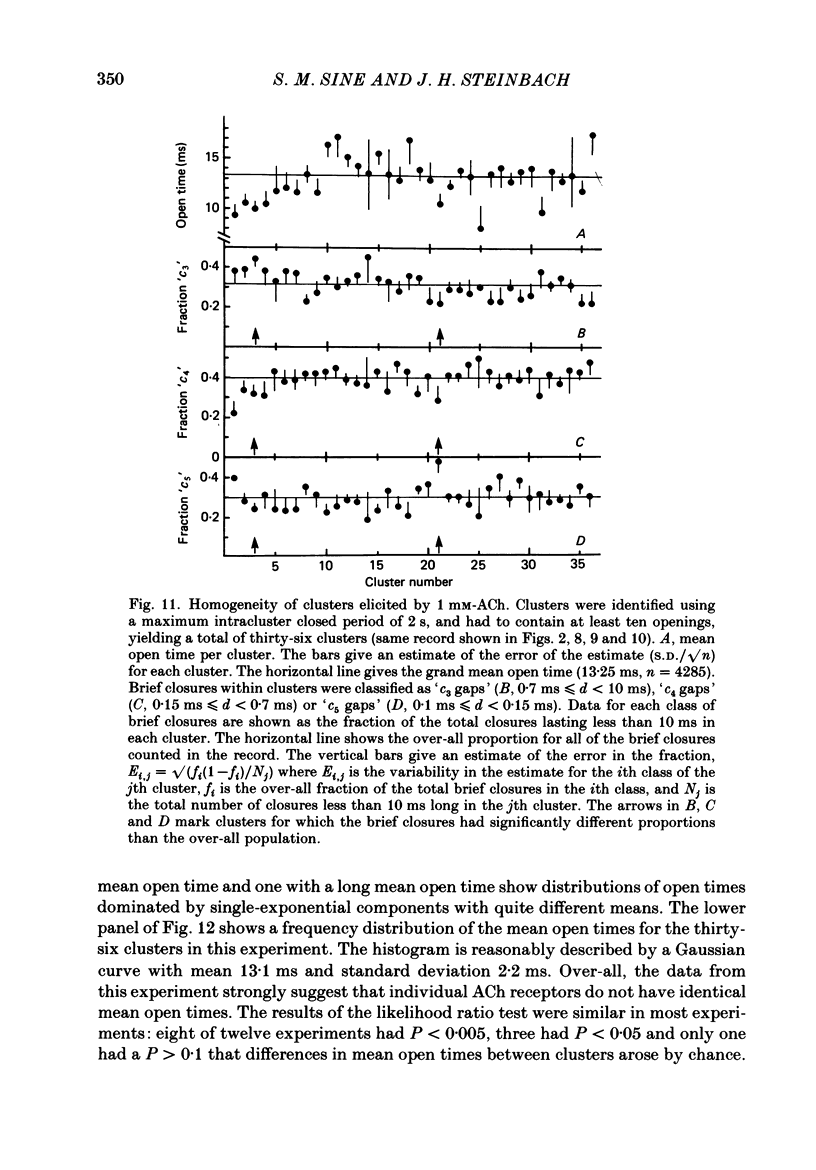
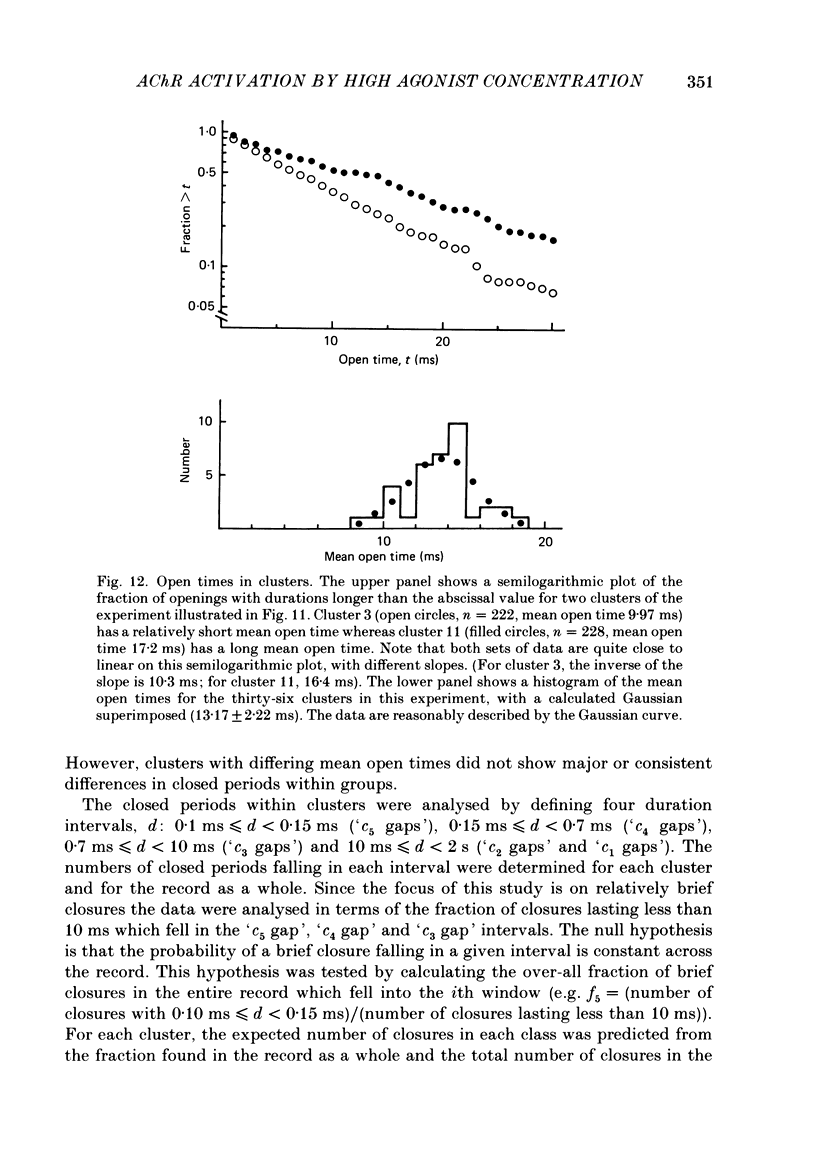








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd N. D., Cohen J. B. Kinetics of binding of [3H]acetylcholine and [3H]carbamoylcholine to Torpedo postsynaptic membranes: slow conformational transitions of the cholinergic receptor. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5344–5353. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd N. D., Cohen J. B. Kinetics of binding of [3H]acetylcholine to Torpedo postsynaptic membranes: association and dissociation rate constants by rapid mixing and ultrafiltration. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5353–5358. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash D. J., Aoshima H., Hess G. P. Acetylcholine-induced cation translocation across cell membranes and inactivation of the acetylcholine receptor: chemical kinetic measurements in the millisecond time region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3318–3322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Hawkes A. G. On the stochastic properties of single ion channels. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Mar 6;211(1183):205–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1981.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., Karlin A. Affinity labeling of one of two alpha-neurotoxin binding sites in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2039–2045. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne V. E., Steinbach J. H., Stevens C. F. An analysis of the dose-response relationship at voltage-clamped frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:421–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer F., Peper K., Sterz R. Determination of dose-response curves by quantitative ionophoresis at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:395–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. D., Dionne V. E. Single-channel acetylcholine receptor kinetics. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84144-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder T. M., Pennefather P., Quastel D. M. The time course of miniature endplate currents and its modification by receptor blockade and ethanol. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):435–468. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. A study of desensitization of acetylcholine receptors using nerve-released transmitter in the frog. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:225–250. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Cohen J. B. Permeability control by cholinergic receptors in Torpedo postsynaptic membranes: agonist dose-response relations measured at second and millisecond times. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2770–2779. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B., Ortiz M., Horn R. Opentime heterogeneity during bursting of sodium channels in frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1986 Mar;49(3):773–777. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83704-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz H., Maelicke A. Interaction of cholinergic ligands with the purified acetylcholine receptor protein. II. Kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10273–10282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Brenner H. R. Change in synaptic channel gating during neuromuscular development. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):401–402. doi: 10.1038/276401a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Patlak J., Neher E. Single acetylcholine-activated channels show burst-kinetics in presence of desensitizing concentrations of agonist. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):71–73. doi: 10.1038/286071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Acetylcholine receptor activation by a site-selective ligand: nature of brief open and closed states in BC3H-1 cells. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:357–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):175–185. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84146-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of acetylcholine receptors on clonal mammalian BC3H-1 cells by low concentrations of agonist. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:129–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Agonists block currents through acetylcholine receptor channels. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84022-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Taylor P. Relationship between reversible antagonist occupancy and the functional capacity of the acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6692–6699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Taylor P. The relationship between agonist occupation and the permeability response of the cholinergic receptor revealed by bound cobra alpha-toxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10144–10156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G., Taylor P. Ligand specificity of state transitions in the cholinergic receptor: behavior of agonists and antagonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;15(2):197–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


