Abstract
1. The single 'giga-seal' patch-electrode technique (Hamill, Marty, Neher, Sakmann & Sigworth, 1981) was used to record whole-cell currents in the GH3 rat anterior pituitary cell line. 2. GH3 cells have a rapidly inactivating, voltage-dependent K+ current that is selectively inhibited by 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) but not by tetraethylammonium chloride (TEA). 3. The majority of the Ca2+-activated K+ current in these cells is blocked by TEA with an inhibitory concentration that is half-maximal at 1 mM. An additional Ca2+-activated K+ current is also present that is relatively resistant to TEA and is blocked by the polypeptide apamin. The apamin-sensitive component represents less than 18% of the total Ca2+-activated K+ current at 0 mV. 4. The time course of the slowly declining components of the Ca2+-activated K+ tail currents measured at the -50 mV holding potential was usually biexponential with time constants of 0.21 +/- 0.02 and 1.75 +/- 0.23 s (mean +/- S.E. of mean, n = 14). Both of the two slowly decaying components contribute to the TEA- and apamin-sensitive currents. 5. It is concluded that GH3 cells have at least two pharmacologically distinct Ca2+-activated K+ currents and a 4-AP-sensitive voltage-dependent K+ current.
Full text
PDF


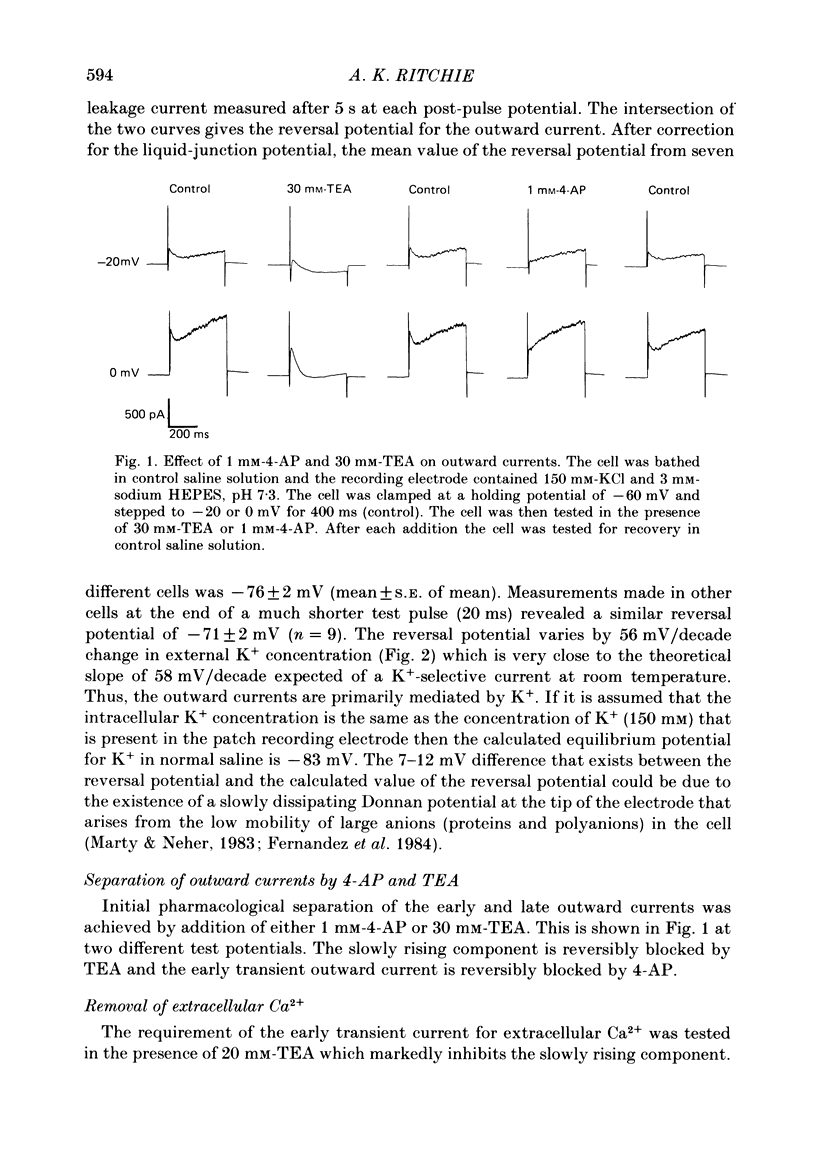
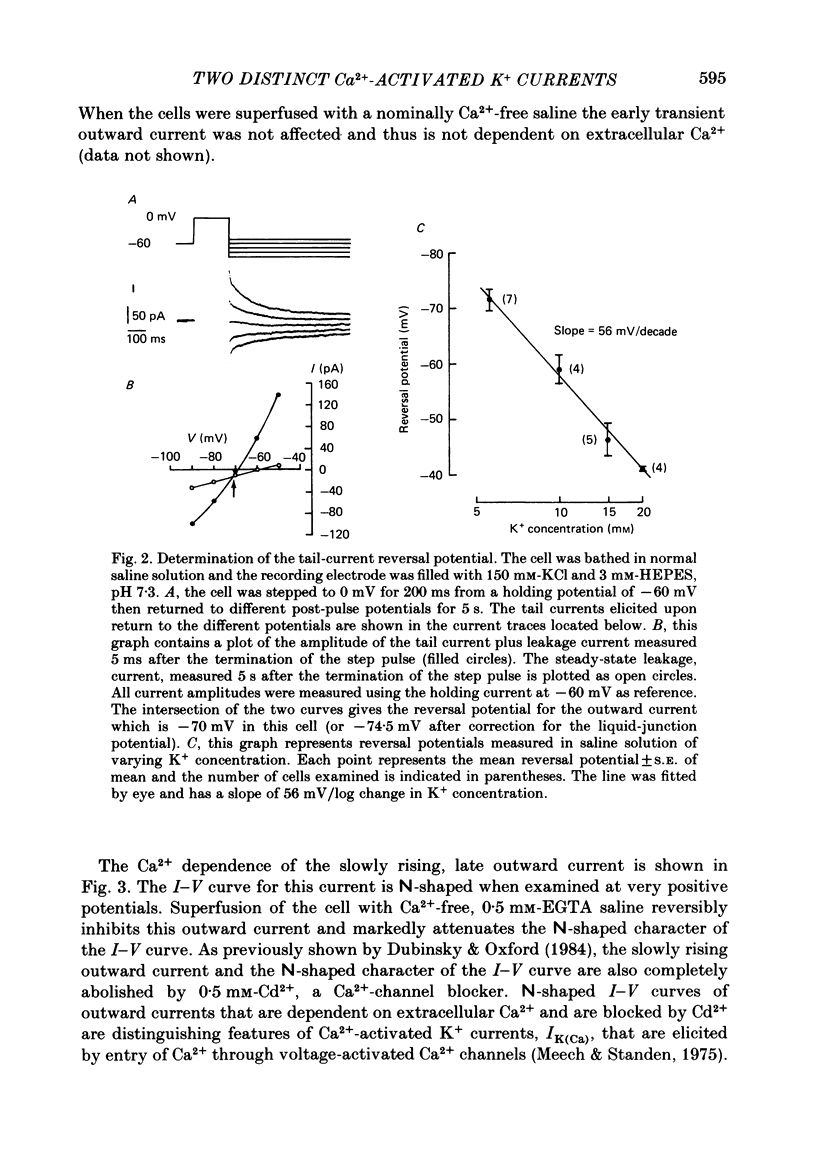
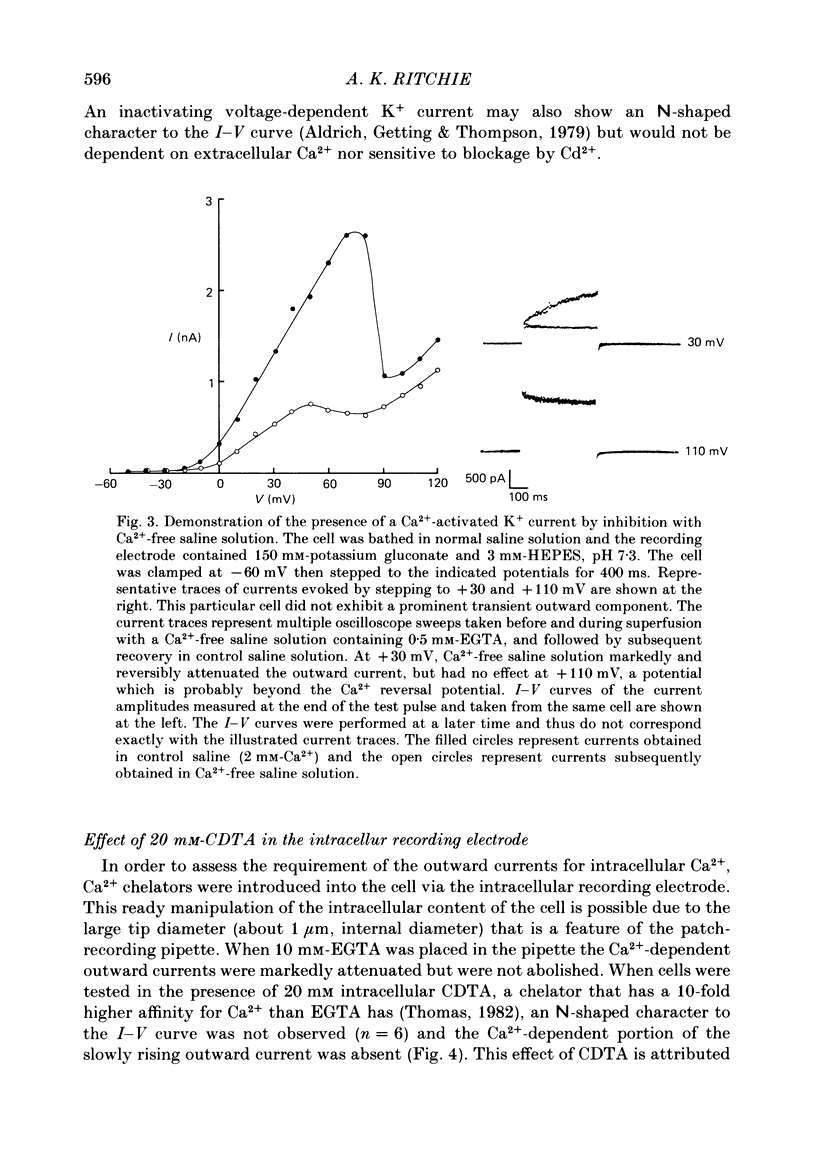
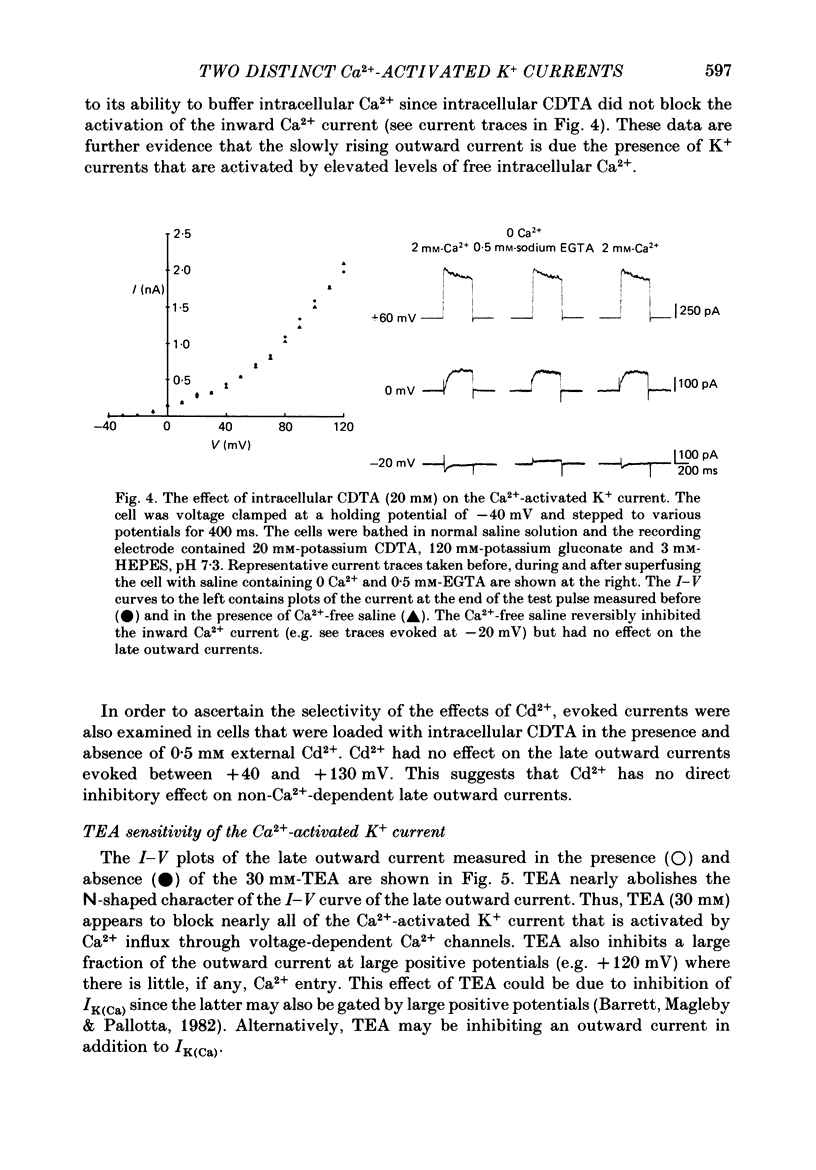
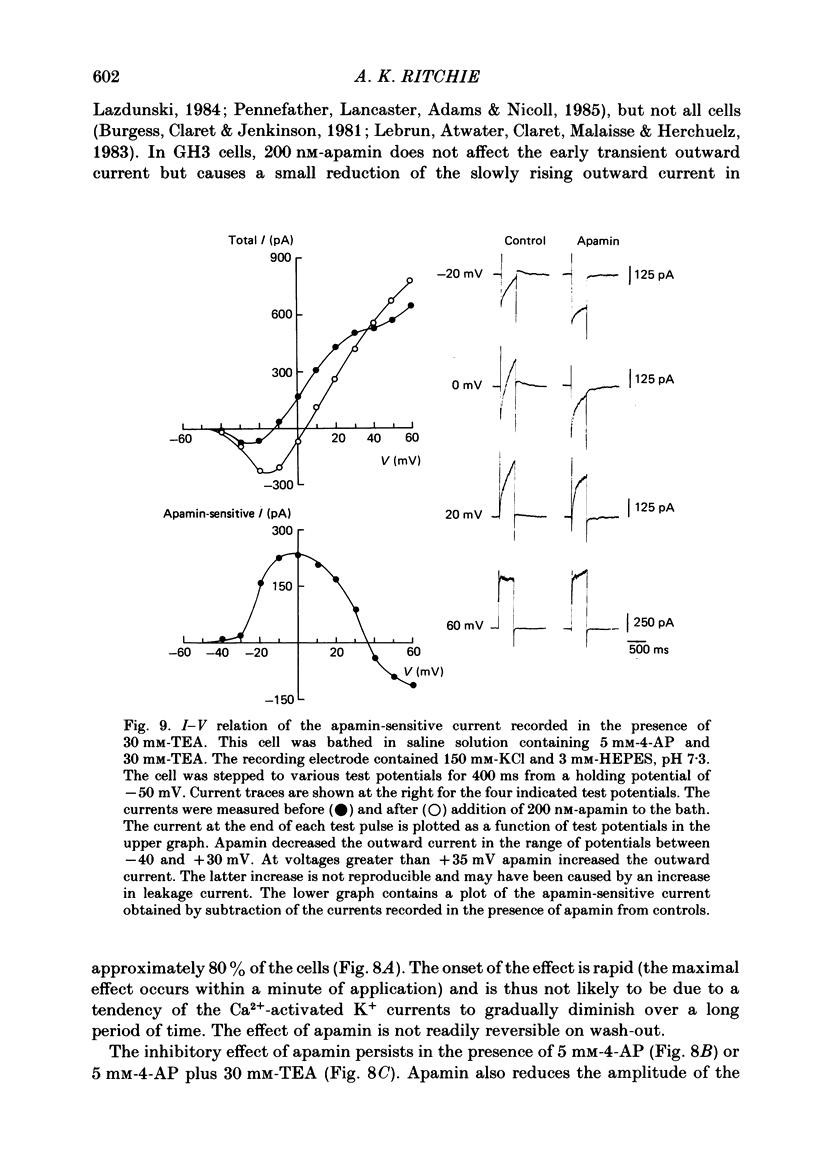

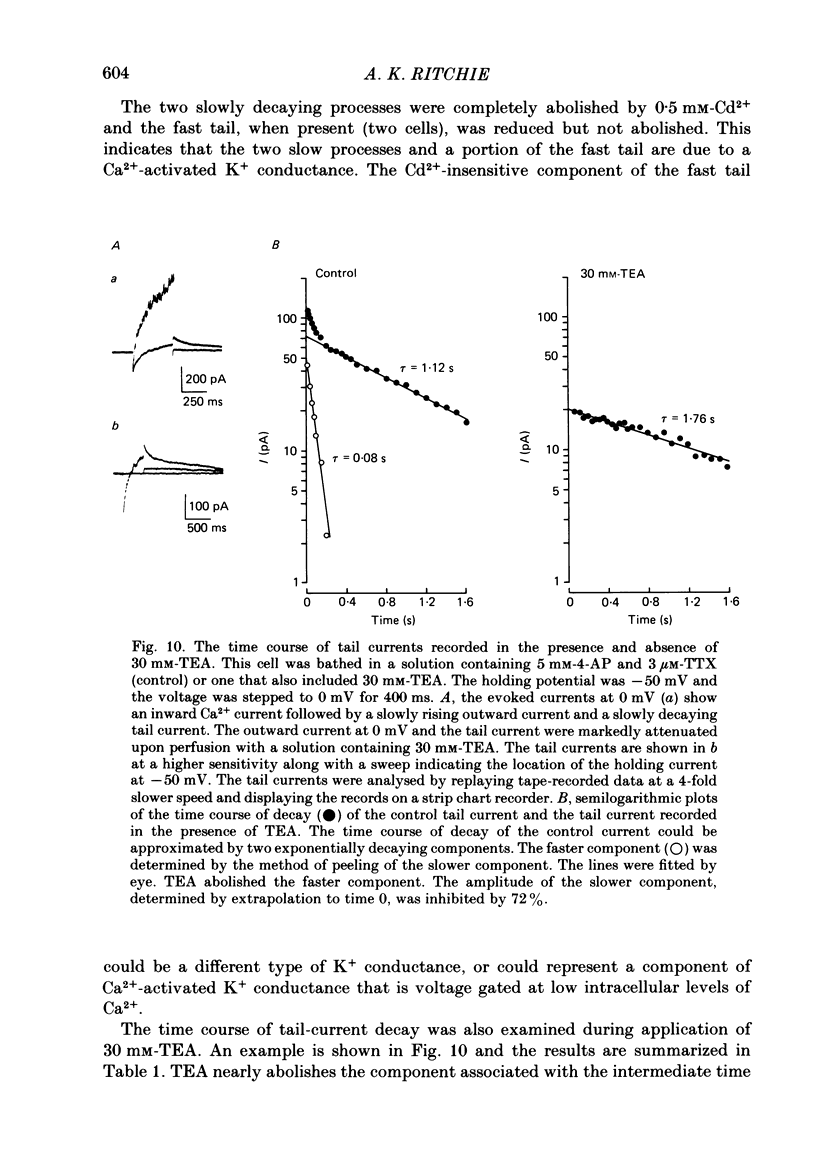
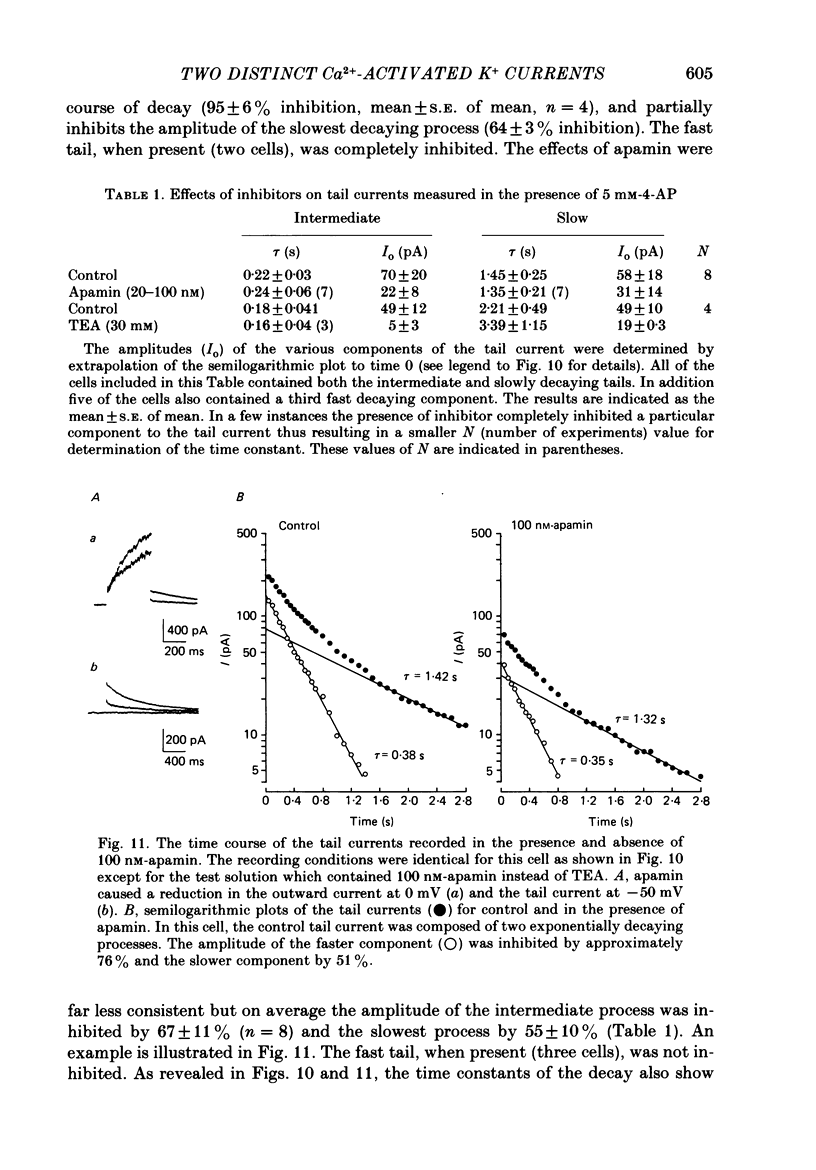




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Smith S. J., Thompson S. H. Ionic currents in molluscan soma. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:141–167. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich R. W., Jr, Getting P. A., Thompson S. H. Inactivation of delayed outward current in molluscan neurone somata. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barish M. E., Thompson S. H. Calcium buffering and slow recovery kinetics of calcium-dependent outward current in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:201–219. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barros F., Katz G. M., Kaczorowski G. J., Vandlen R. L., Reuben J. P. Calcium currents in GH3 cultured pituitary cells under whole-cell voltage-clamp: inhibition by voltage-dependent potassium currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1108–1112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Ion conductance and selectivity of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Jul;84(1):1–23. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Constanti A., Adams P. R. Ca-activated potassium current in vertebrate sympathetic neurons. Cell Calcium. 1983 Dec;4(5-6):407–420. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;213(1):21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Eckert R. Two components of Ca-dependent potassium current in identified neurons of Aplysia californica. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Apr;403(4):353–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00589246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky J. M., Oxford G. S. Ionic currents in two strains of rat anterior pituitary tumor cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):309–339. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufy B., Barker J. L. Calcium-activated and voltage-dependent potassium conductances in clonal pituitary cells. Life Sci. 1982 May 31;30(22):1933–1941. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90475-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Fox A. P., Krasne S. Membrane patches and whole-cell membranes: a comparison of electrical properties in rat clonal pituitary (GH3) cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. A patch-clamp study of potassium channels and whole-cell currents in acinar cells of the mouse lacrimal gland. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:179–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. High-conductance K+ channel in pancreatic islet cells can be activated and inactivated by internal calcium. J Membr Biol. 1985;83(1-2):169–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01868748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of calcium channels in rat clonal pituitary cells with patch electrode voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:231–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of single calcium channel currents in rat clonal pituitary cells. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:649–661. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Hartung K. Properties of a Ca2+ activated K+ conductance in Helix neurones investigated by intracellular Ca2+ ionophoresis. Pflugers Arch. 1982 May;393(3):248–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00584078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Romey G., Duval D., Vincent J. P., Lazdunski M. Apamin as a selective blocker of the calcium-dependent potassium channel in neuroblastoma cells: voltage-clamp and biochemical characterization of the toxin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1308–1312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume J. R., Giles W. Ionic currents in single isolated bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Feb;81(2):153–194. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczorowski G. J., Vandlen R. L., Katz G. M., Reuben J. P. Regulation of excitation-secretion coupling by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH): evidence for TRH receptor-ion channel coupling in cultured pituitary cells. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):109–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01870679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Spontaneous calcium action potentials in a clonal pituitary cell line and their relationship to prolactin secretion. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):741–742. doi: 10.1038/258741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun P., Atwater I., Claret M., Malaisse W. J., Herchuelz A. Resistance to apamin of the Ca2+-activated K+ permeability in pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 5;161(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80726-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Armstrong C. M. Na and Ca channels in a transformed line of anterior pituitary cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Mar;83(3):371–394. doi: 10.1085/jgp.83.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D. R., Armstrong C. M. Properties of two types of calcium channels in clonal pituitary cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Jan;87(1):161–182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. G., Segal M., Barker J. L. A Ca-dependent Cl- conductance in cultured mouse spinal neurones. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):567–570. doi: 10.1038/311567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa S., Miyazaki S. I. Electrical excitability in the rat clonal pituitary cell and its relation to hormone secretion. Jpn J Physiol. 1979;29(4):411–426. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.29.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. K. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates a calcium-activated potassium current in a rat anterior pituitary cell line. J Physiol. 1987 Apr;385:611–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Lazdunski M. The coexistence in rat muscle cells of two distinct classes of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels with different pharmacological properties and different physiological functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):669–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sand O., Haug E., Gautvik K. M. Effects of thyroliberin and 4-aminopyridine on action potentials and prolactin release and synthesis in rat pituitary cells in culture. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Mar;108(3):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. Tetraethylammonium ions and the potassium permeability of excitable cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1983;97:1–67. doi: 10.1007/BFb0035345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Conduction, Blockade and Gating in a Ca -activated K Channel Incorporated into Planar Lipid Bilayers. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84114-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Lecar H., Adler M. Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84522-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolum J. C., Gorman A. L. Time dependence of the calcium-activated potassium current. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):297–302. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84729-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


