Abstract
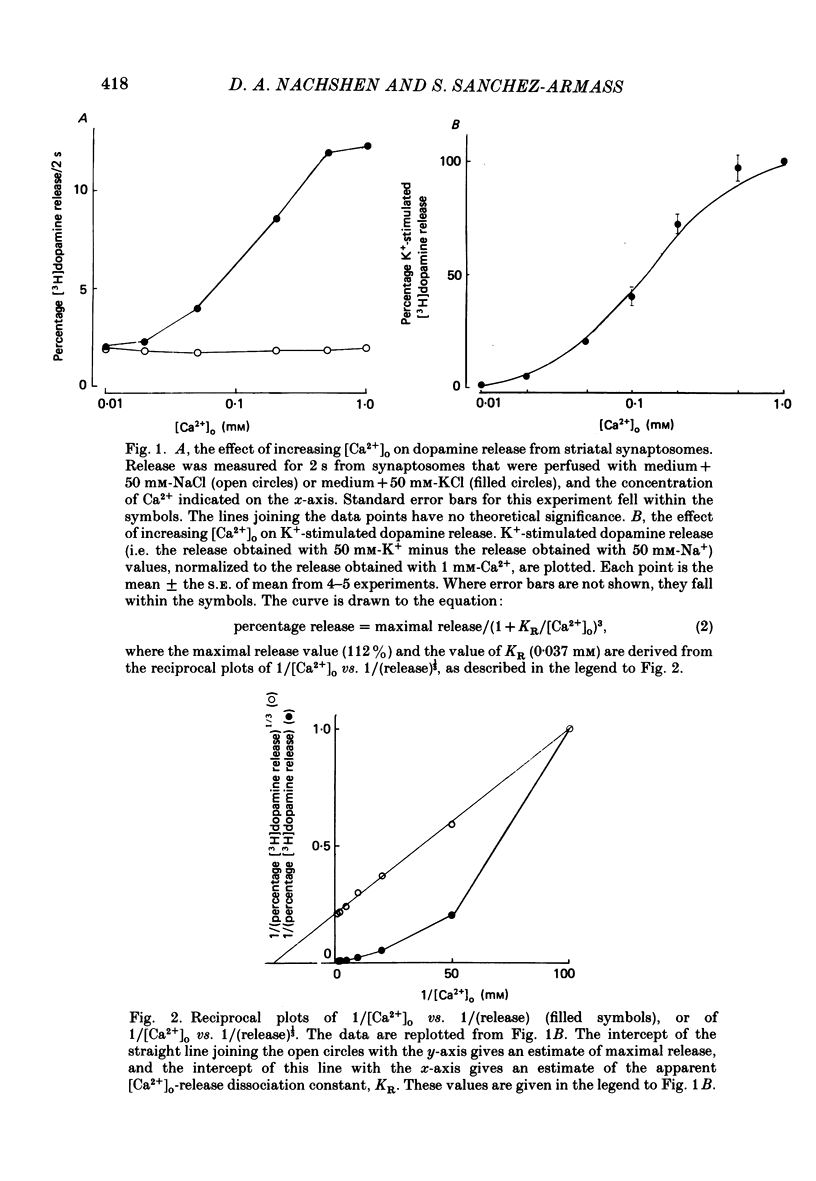
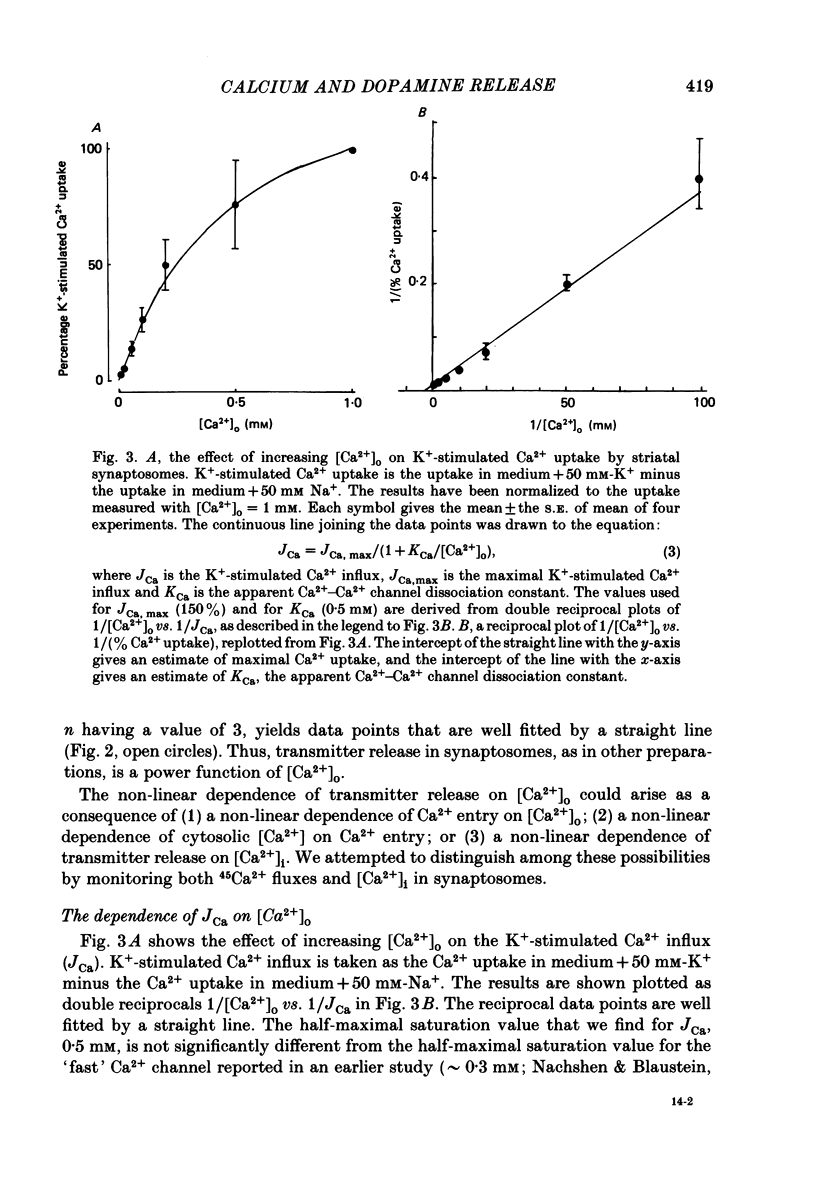
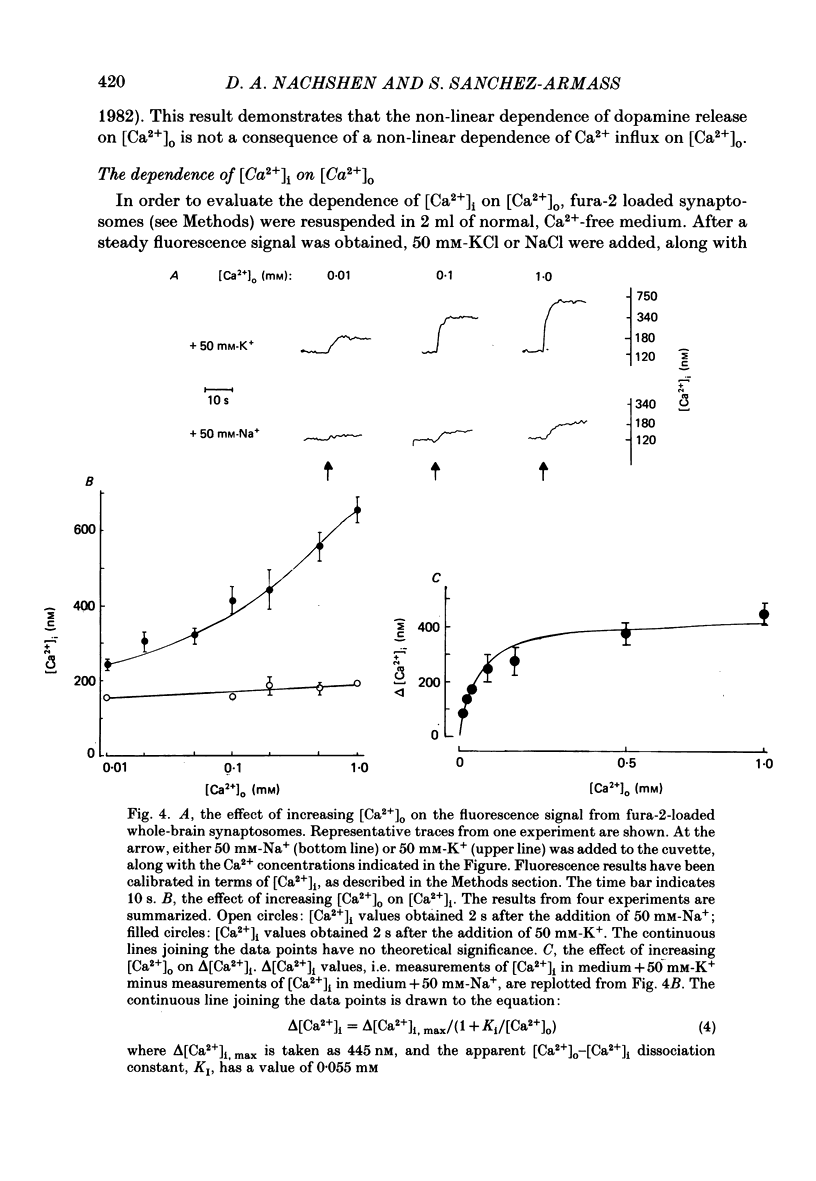
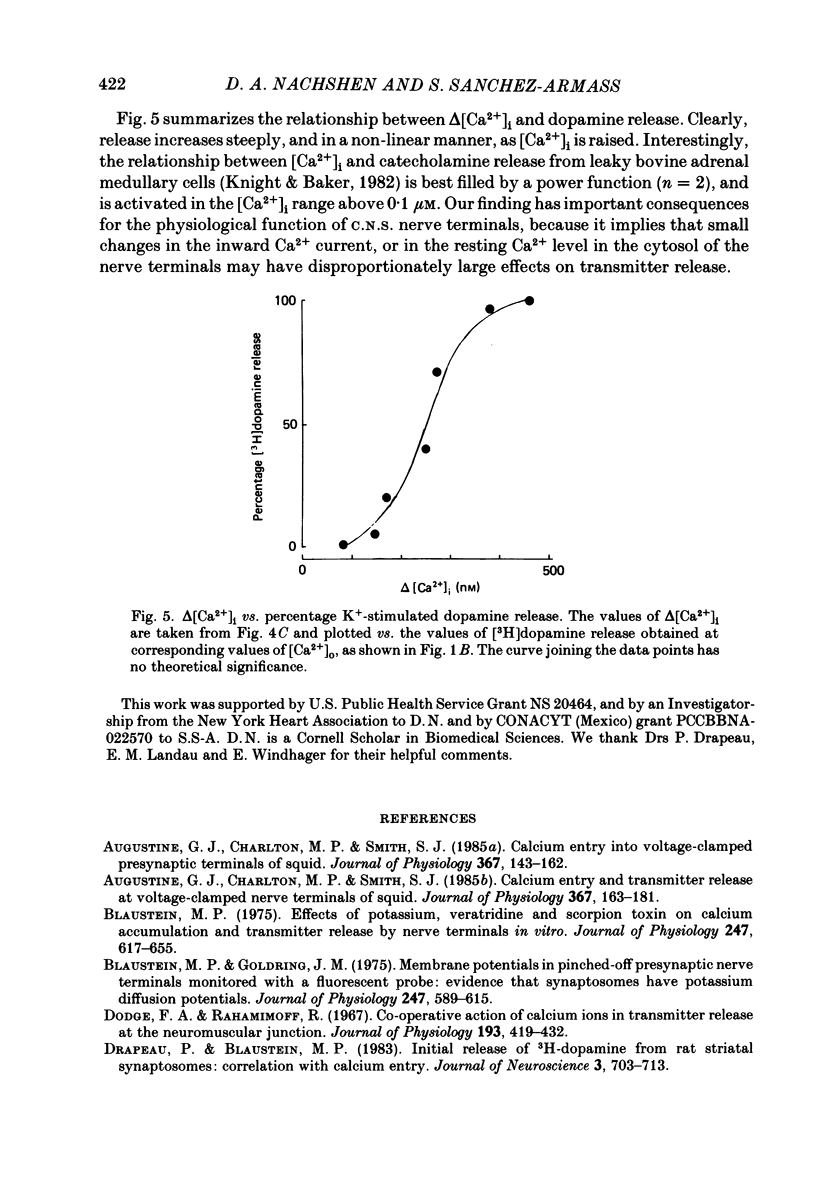
1. The release of [3H]dopamine from isolated presynaptic nerve terminals (synaptosomes) prepared from rat striata was measured as a function of the external Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]o). 2. In synaptosomes depolarized by the addition of 50 mM-K+, release of [3H]dopamine increased in a highly non-linear manner with [Ca2+]o. The release could be described as a third power function of [Ca2+]o. 3. Both 45Ca2+ influx and the change in the free cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i, measured with the fluorescent Ca2+ indicator fura-2) that were evoked by depolarization increased in a linear manner with [Ca2+]o. 4. These results suggest that non-linearity in the [Ca2+]o dependence of transmitter release originates in a co-operative relation between [Ca2+]i and exocytosis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P., Smith S. J. Calcium entry and transmitter release at voltage-clamped nerve terminals of squid. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:163–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P., Smith S. J. Calcium entry into voltage-clamped presynaptic terminals of squid. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:143–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Effects of potassium, veratridine, and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):617–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Goldring J. M. Membrane potentials in pinched-off presynaptic nerve ternimals monitored with a fluorescent probe: evidence that synaptosomes have potassium diffusion potentials. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):589–615. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau P., Blaustein M. P. Initial release of [3H]dopamine from rat striatal synaptosomes: correlation with calcium entry. J Neurosci. 1983 Apr;3(4):703–713. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-04-00703.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Jones S. F., Landau E. M. On the mechanism by which calcium and magnesium affect the release of transmitter by nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1968 May;196(1):75–86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Blaustein M. P. Some properties of potassium-stimulated calcium influx in presynaptic nerve endings. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Dec;76(6):709–728. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.6.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A. Regulation of cytosolic calcium concentration in presynaptic nerve endings isolated from rat brain. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:87–101. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Sanchez-Armass S., Weinstein A. M. The regulation of cytosolic calcium in rat brain synaptosomes by sodium-dependent calcium efflux. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:17–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A., Delgado-Escueta A. V. Rapid preparation of synaptosomes from mammalian brain using nontoxic isoosmotic gradient material (Percoll). J Neurochem. 1984 Oct;43(4):1114–1123. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Augustine G. J., Charlton M. P. Transmission at voltage-clamped giant synapse of the squid: evidence for cooperativity of presynaptic calcium action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):622–625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


