Abstract
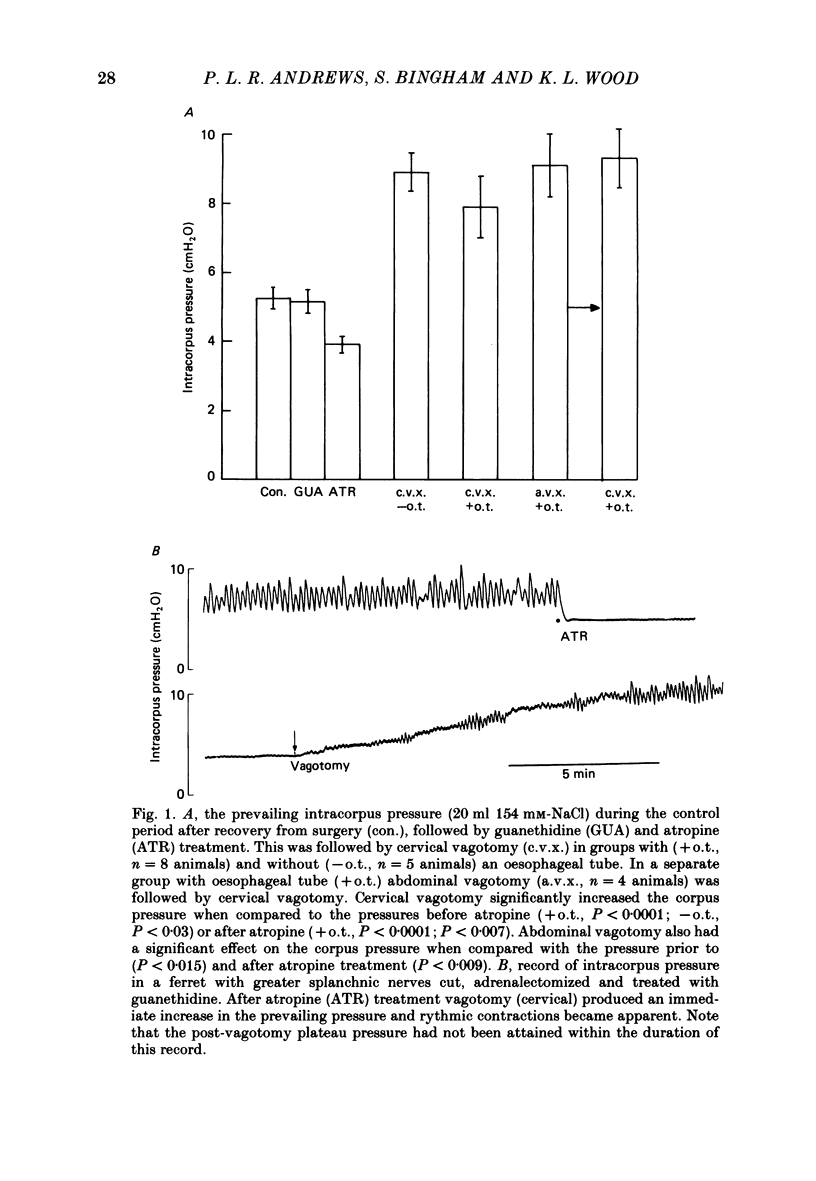
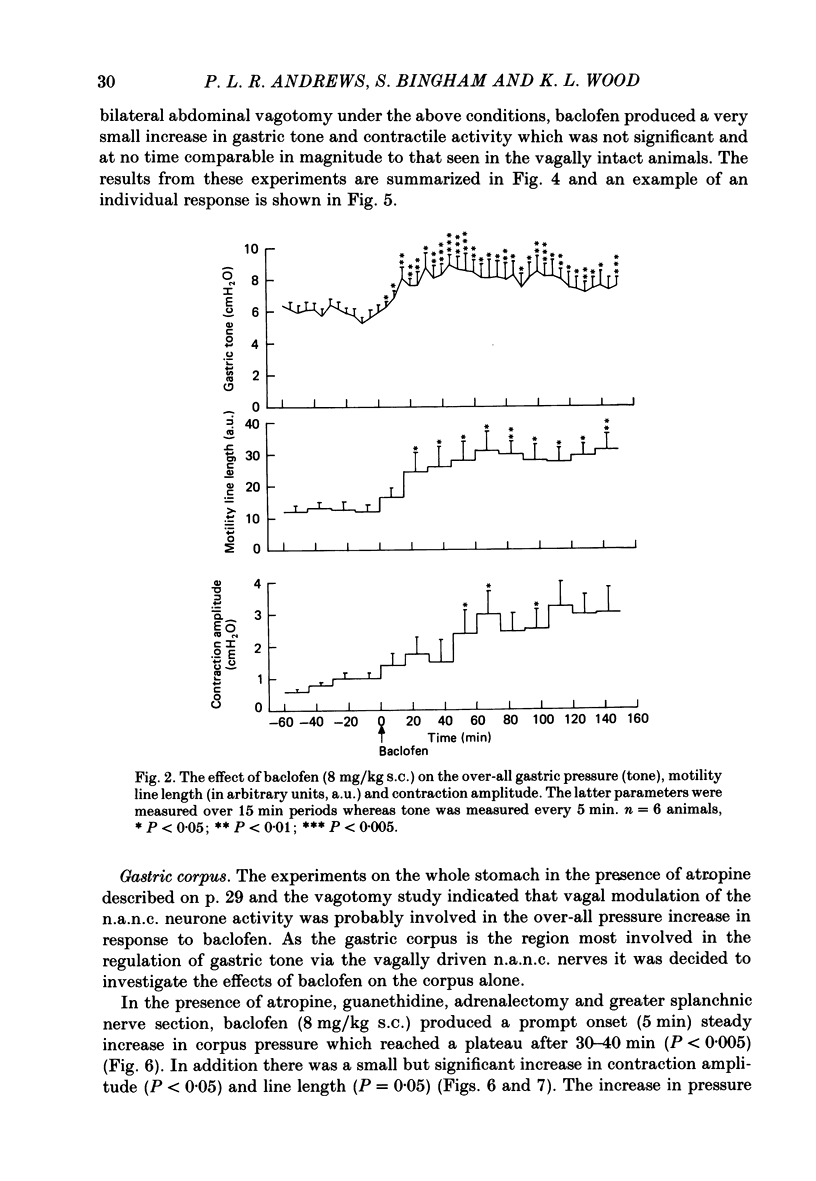
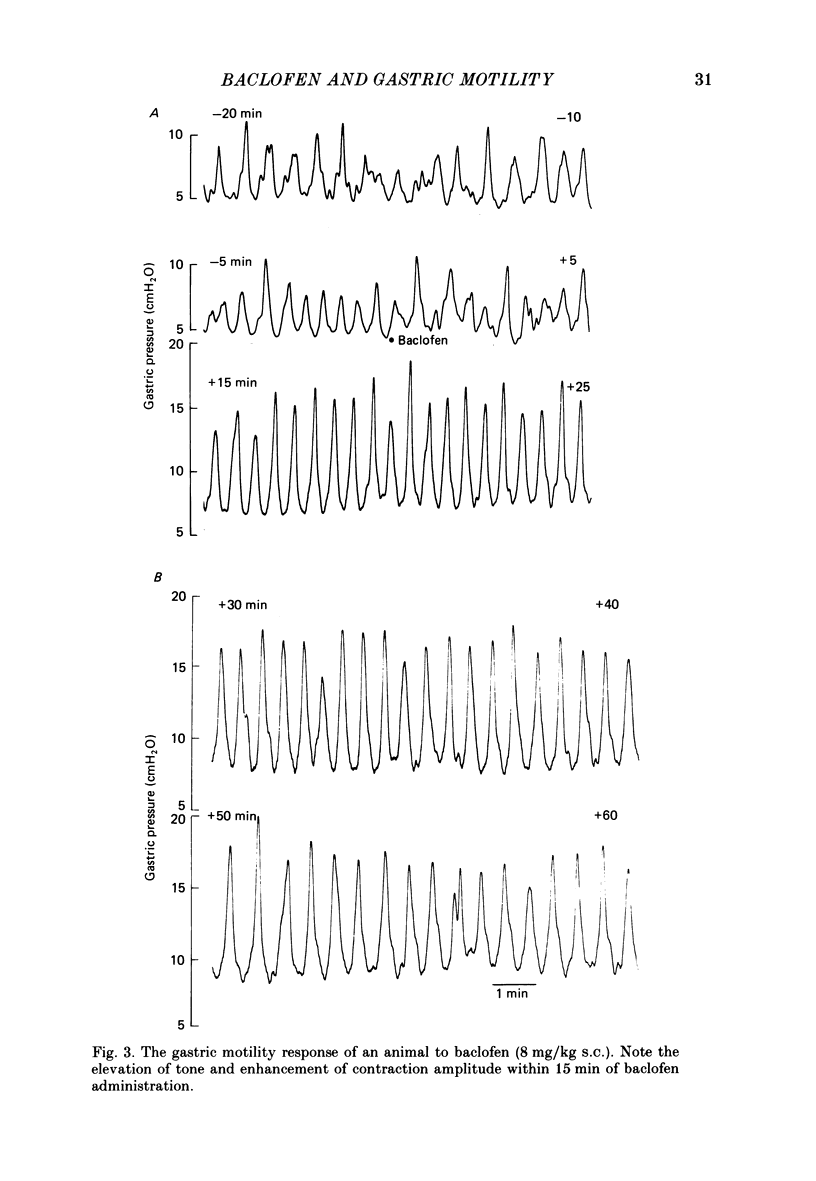
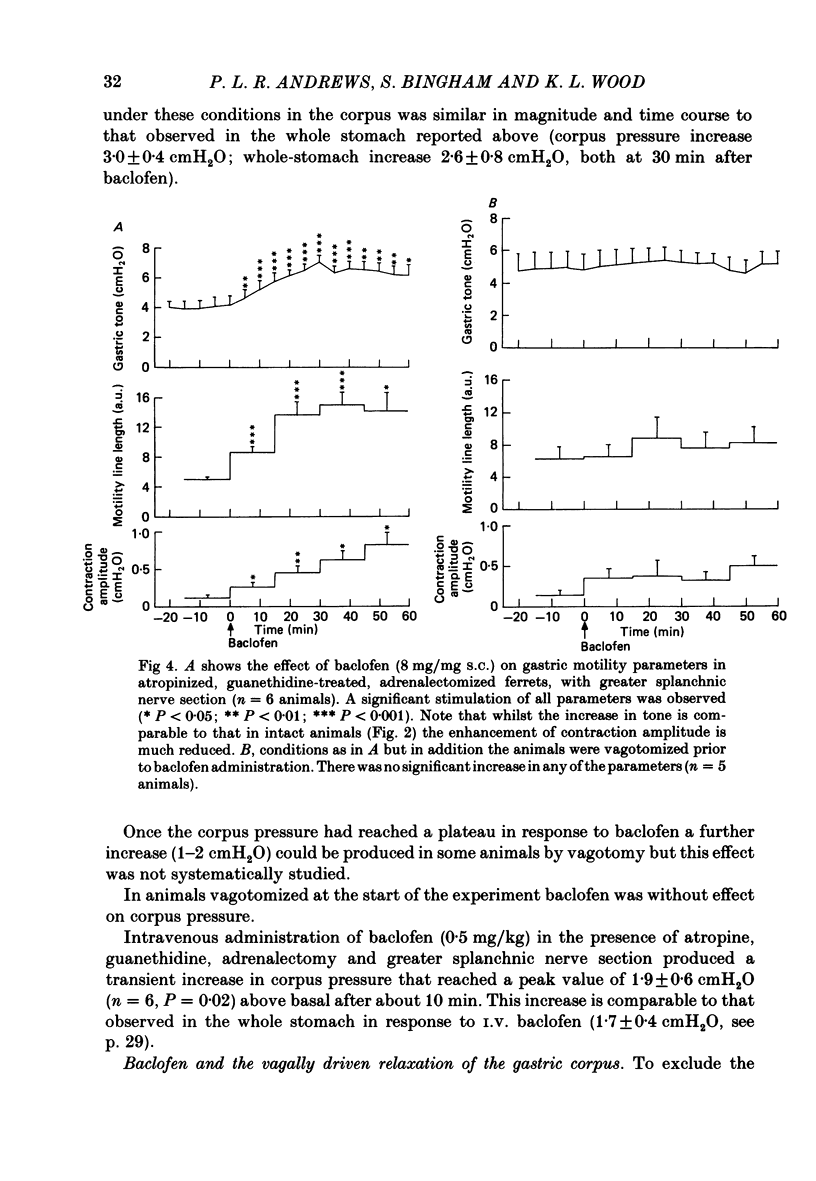
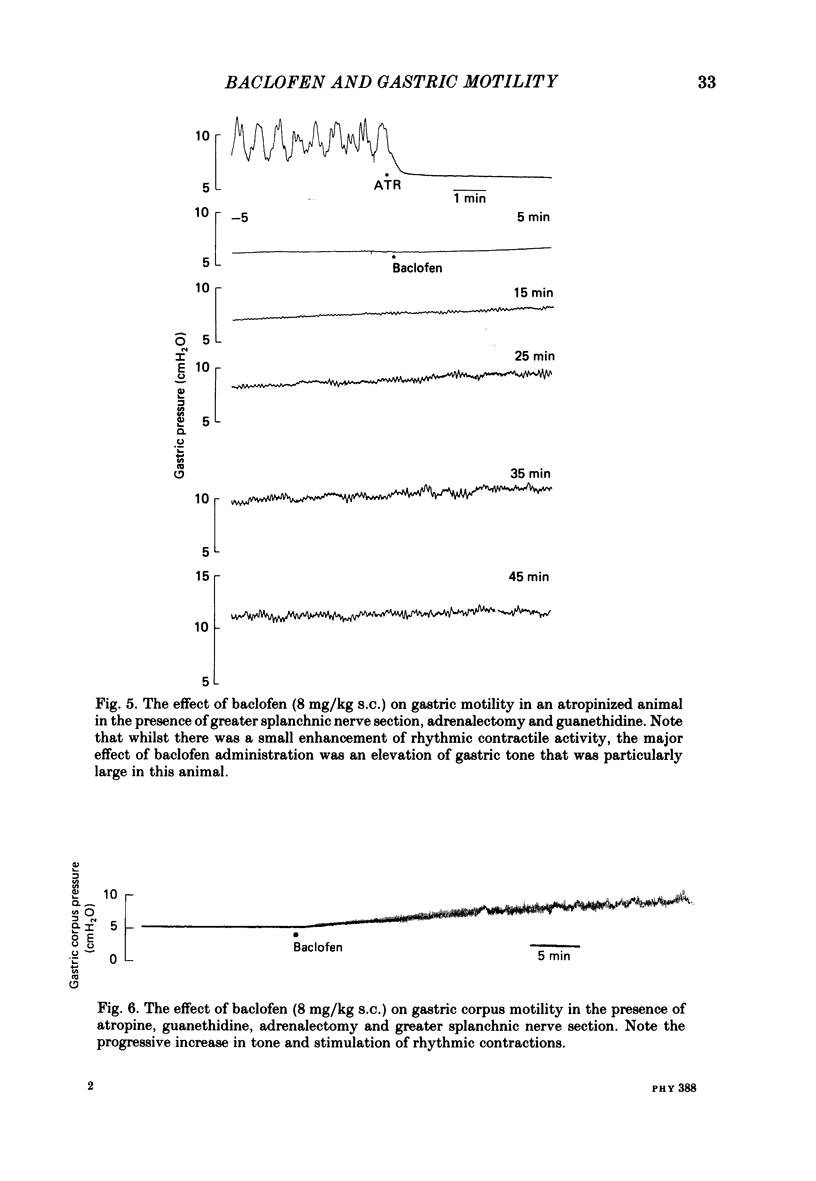
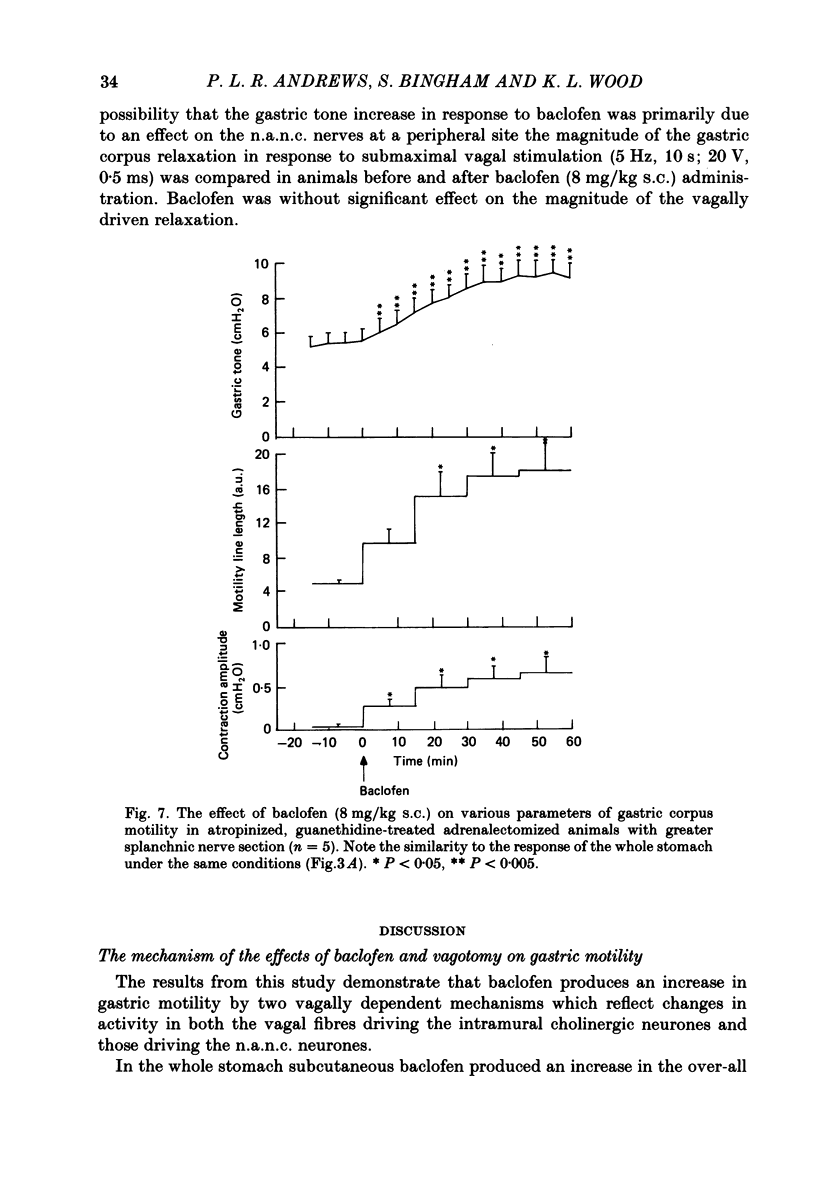
1. In the urethane-anaesthetized ferret vagotomy (cervical and abdominal) and hexamethonium both produced an increase in gastric corpus pressure after treatment with atropine and guanethidine, section of the greater splanchnic nerves and adrenalectomy. 2. The pressure increase was due to an interruption of a tonic vagal drive to the intramural non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory neurones. 3. The GABAB receptor agonist baclofen (8 mg/kg s.c.) produced an increase in gastric pressure and enhanced the amplitude of the rhythmic contractions. Baclofen was without effect in vagotomized animals. 4. In the presence of atropine, guanethidine, adrenalectomy and section of the greater splanchnic nerves, baclofen produced only a slight enhancement of rhythmic contractions but the large increase in gastric pressure was still present. Under the above conditions the effects of baclofen on the whole stomach were virtually identical to those observed in the corpus region alone. 5. Baclofen was without effect on the magnitude of the corpus relaxation produced by the submaximal vagal efferent stimulation in the presence of atropine. 6. These results demonstrate that the GABAB agonist baclofen, probably acting at a central site, enhanced rhythmic gastric activity by increasing the vagal drive to the intramural cholinergic neurones. Simultaneously gastric pressure was increased primarily by a reduction in the tonic vagal drive to the intramural non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory neurones in the corpus region. The results of both the baclofen and vagotomy studies further demonstrate the importance of the vagal innervation of the non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory neurones in the regulation of gastric pressure.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamsson H., Jansson G. Elicitation of reflex vagal relaxation of the stomach from pharynx and esophagus in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Sep-Oct;77(1):172–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson H., Jansson G. Vago-vagal gastro-gastric relaxation in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1973 Jul;88(3):289–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1973.tb05457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. L., Lawes I. N. Characteristics of the vagally driven non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory innervation of ferret gastric corpus. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:1–20. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. L., Lawes I. N. Interactions between splanchnic and vagus nerves in the control of mean intragastric pressure in the ferret. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:473–490. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. L., Lawes I. N. The role of vagal and intramural inhibitory reflexes in the regulation of intragastric pressure in the ferret. J Physiol. 1982 May;326:435–451. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. L., Scratcherd T. The gastric motility patterns induced by direct and reflex excitation of the vagus nerves in the anaesthetized ferret. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:363–378. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. L. The non-adrenergic non-cholinergic innervation of the stomach. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1986 Apr;280(2 Suppl):84–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. L., Wood K. L. Systemic baclofen stimulates gastric motility and secretion via a central action in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;89(3):461–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11145.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aune S. Intragastric pressure after vagotomy in man. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1969;4(5):447–452. doi: 10.3109/00365526909180631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIASSON S. Cerebral influence on gastric motility in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1952;26(95):1–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S., Krnjević K., Morris M. E., Puil E., Werman R. Action of baclofen on mammalian synaptic transmission. Neuroscience. 1978;3(6):495–515. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giotti A., Luzzi S., Spagnesi S., Zilletti L. GABAA and GABAB receptor-mediated effects in guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):469–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08807.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giotti A., Luzzi S., Spagnesi S., Zilletti L. Homotaurine: a GABAB antagonist in guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;79(4):855–862. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto Y., Debas H. T. GABA-mimetic effect on gastric acid secretion. Possible significance in central mechanisms. Dig Dis Sci. 1983 Jan;28(1):56–59. doi: 10.1007/BF01393361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto Y., Hollinshead J. W., Debas H. T. A new intraoperative test for completeness of vagotomy: the PCP-GABA (beta-parachlorophenol-gamma-aminobutyric acid) test. Am J Surg. 1984 Jan;147(1):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto Y., Tache Y., Debas H., Novin D. Gastric acid and vagus nerve response to GABA agonist baclofen. Life Sci. 1985 Jul 1;36(26):2471–2475. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy D., Scratcherd T. Effect of stimulation of the vagus nerve in bursts on gastric acid secretion and motility in the anaesthetized ferret. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:451–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARPER A. A., KIDD C., SCRATCHERD T. Vago-vagal reflex effects on gastric and pancreatic secretion and gastrointestinal motility. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:417–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley-Gius K. M., Neafsey E. J. The medial frontal cortex and gastric motility: microstimulation results and their possible significance for the overall pattern of organization of rat frontal and parietal cortex. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 19;365(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91635-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnberg T., Martinson J., Hultén L., Fasth S. Dynamic gastric response to expansion before and after vagotomy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(6):593–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. M. Effects of baclofen and gamma-aminobutyric acid on different types of medullary respiratory neurons. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 25;376(2):392–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisander B., Martner J. Effects on gastric motility from the cerebellar fastigial nucleus. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Jul;94(3):368–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb05896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami H., McCallum R. W. The physiology and pathophysiology of gastric emptying in humans. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jun;86(6):1592–1610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito N., Tanaka C. Immunohistochemical demonstration of GABA containing neurons in the guinea pig ileum using purified GABA antiserum. Brain Res. 1986 Jun 18;376(1):78–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90901-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadaas J. O. Intragastric pressure/volume relationship before and after proximal gastric vagotomy. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(2):129–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka C. gamma-Aminobutyric acid in peripheral tissues. Life Sci. 1985 Dec 16;37(24):2221–2235. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williford D. J., Ormsbee H. S., 3rd, Norman W., Harmon J. W., Garvey T. Q., 3rd, DiMicco J. A., Gillis R. A. Hindbrain GABA receptors influence parasympathetic outflow to the stomach. Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):193–194. doi: 10.1126/science.6269182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


