Abstract
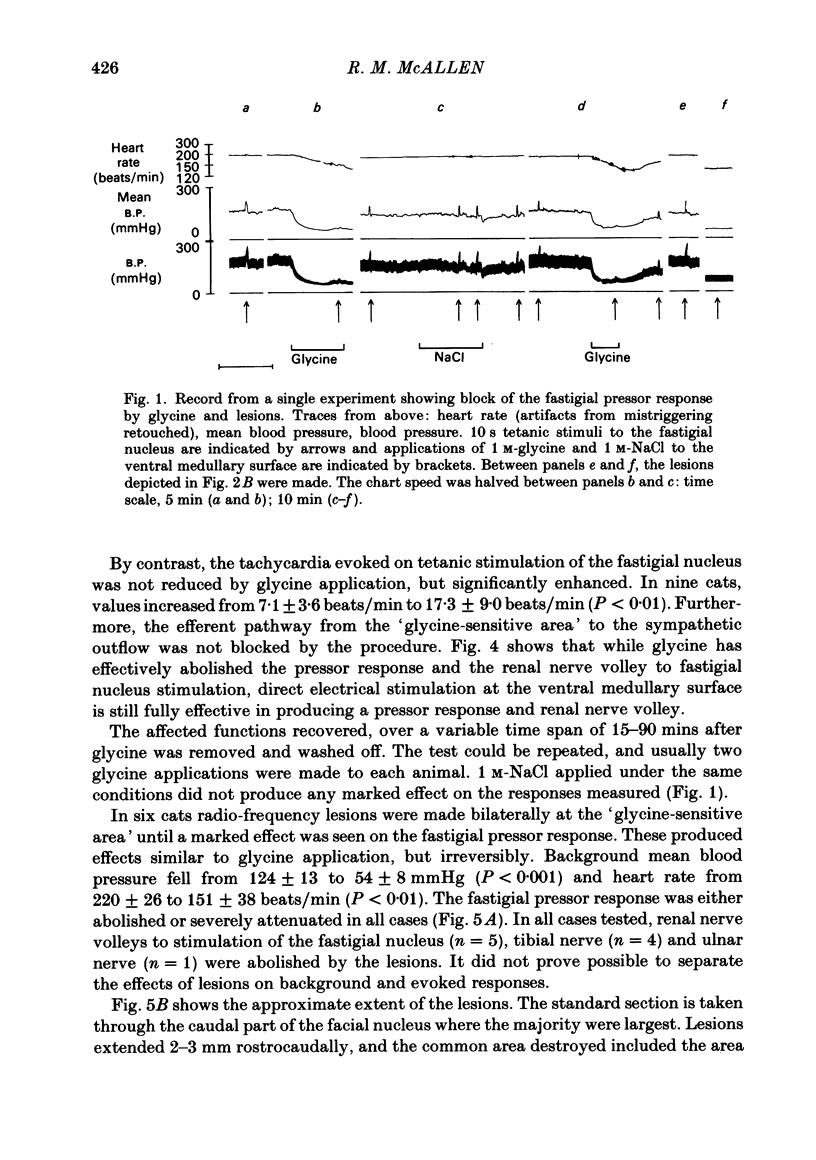
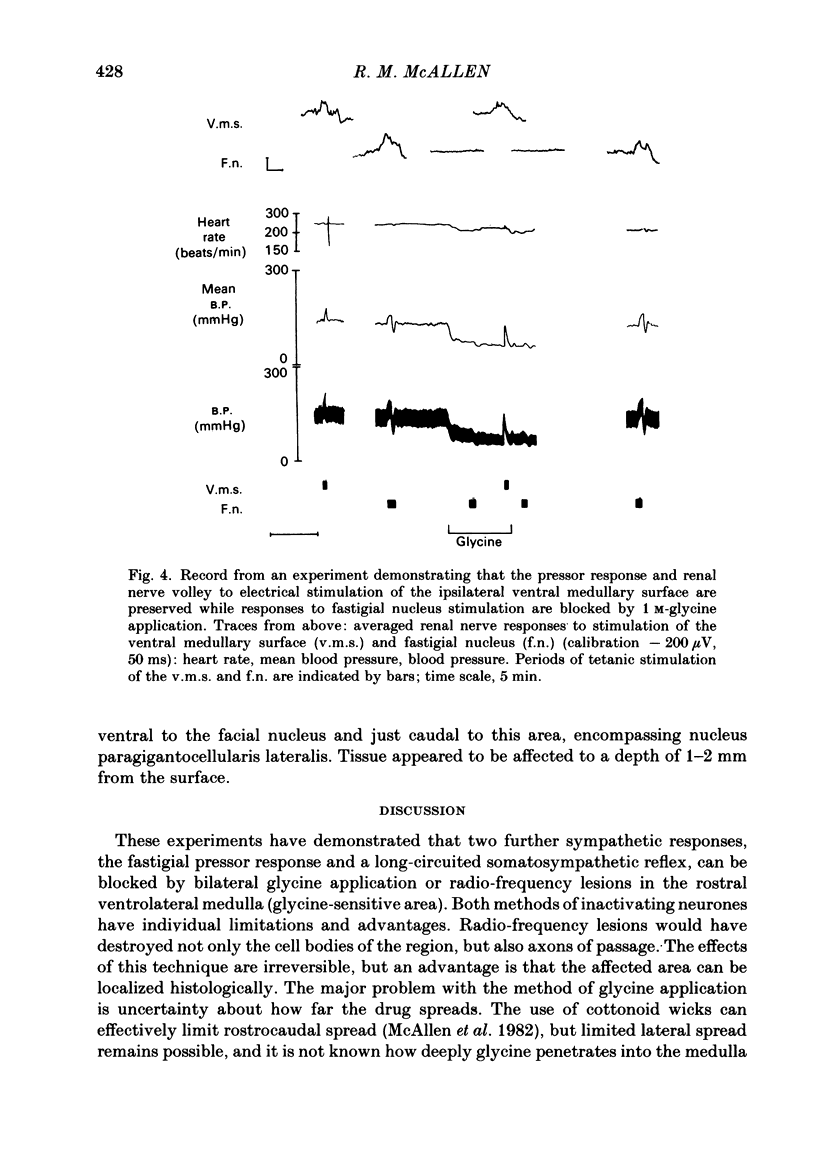
In chloralose-anaesthetized, artificially ventilated cats, the effects have been studied of inactivating neurones of the 'glycine-sensitive area' of the rostral ventrolateral medulla on evoked renal sympathetic and vasomotor responses. Glycine applied topically and bilaterally to the 'glycine-sensitive area' besides markedly lowering blood pressure and heart rate, reversibly abolished or severely attenuated both the pressor response and the renal nerve volley produced by electrical stimulation of the fastigial nucleus as well as the tibial to renal nerve somatosympathetic reflex. Bilateral radio-frequency lesions of the 'glycine-sensitive area' similarly lowered blood pressure and heart rate, blocked the fastigial pressor response and abolished renal nerve responses to fastigial nucleus or tibial nerve stimulation. Effective lesions extended greater than or equal to 1 mm deep from the medullary surface. These results are discussed with reference to the view that the 'glycine-sensitive area' contains neurones constituting a final descending bulbo-spinal pathway to preganglionic vasomotor neurones.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achari N. K., Downman C. B. Autonomic effector responses to stimulation of nucleus fastigius. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):637–650. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amendt K., Czachurski J., Dembowsky K., Seller H. Bulbospinal projections to the intermediolateral cell column: a neuroanatomical study. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1979 Oct;1(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(79)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrezik J. A., Dormer K. J., Foreman R. D., Person R. J. Fastigial nucleus projections to the brain stem in beagles: pathways for autonomic regulation. Neuroscience. 1984 Feb;11(2):497–507. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessing W. W., Goodchild A. K., Dampney R. A., Chalmers J. P. Cell groups in the lower brain stem of the rabbit projecting to the spinal cord, with special reference to catecholamine-containing neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Sep 21;221(1):35–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriello J., Calaresu F. R. Lateral reticular nucleus: a site of somatic and cardiovascular integration in the cat. Am J Physiol. 1977 Sep;233(3):R100–R109. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1977.233.3.R100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Downman C. B. Central pathways of some autonomic reflex discharges. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):714–729. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dampney R. A. Functional organization of central cardiovascular pathways. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1981 May-Jun;8(3):241–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1981.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dampney R. A., Goodchild A. K., Robertson L. G., Montgomery W. Role of ventrolateral medulla in vasomotor regulation: a correlative anatomical and physiological study. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):223–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dampney R. A., Moon E. A. Role of ventrolateral medulla in vasomotor response to cerebral ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):H349–H358. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.239.3.H349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembowsky K., Lackner K., Czachurski J., Seller H. Tonic catecholaminergic inhibition of the spinal somato-sympathetic reflexes originating in the ventrolateral medulla oblongata. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1981 Apr;3(2-4):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(81)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Guertzenstein P. G. Vasodepressor effects obtained by drugs acting on the ventral surface of the brain stem. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;258(2):337–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guertzenstein P. G., Silver A. Fall in blood pressure produced from discrete regions of the ventral surface of the medulla by glycine and lesions. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(2):489–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton S. M., Marshall J. M., Timms R. J. Ventral medullary relay neurones in the pathway from the defence areas of the cat and their effect on blood pressure. J Physiol. 1983 Dec;345:149–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi K., Brooks C. M. The integration of autonomic system reactions: a discussion of autonomic reflexes, their control and their association with somatic reactions. Ergeb Physiol. 1972;67:1–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisander B., Martner J. Interaction between the fastigial pressor response and the baroreceptor reflex. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Dec;83(4):505–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovick T. A., Hunt S. P. Substance P-immunoreactive and serotonin-containing neurones in the ventral brainstem of the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Apr 29;36(3):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllen R. M., Neil J. J., Loewy A. D. Effects of kainic acid applied to the ventral surface of the medulla oblongata on vasomotor tone, the baroreceptor reflex and hypothalamic autonomic responses. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 22;238(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90771-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllen R. M., Spyer K. M. The baroreceptor input to cardiac vagal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:365–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Reis D. J. A blood pressure response from fastigial nucleus and its relay pathway in brainstem. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1330–1336. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar G. M., Rucker H. K. Autoradiographic study of brain stem projections from fastigal pressor areas. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):492–496. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohlicek C. V., Polosa C. Mediation of pressor responses to cerebral ischemia by superficial ventral medullary areas. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):H962–H968. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.6.H962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Ruggiero D. A., Joh T. H., Park D. H., Reis D. J. Adrenaline synthesizing neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla: a possible role in tonic vasomotor control. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 29;273(2):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90862-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABER E. The cytoarchitecture of the brain stem of the cat. I. Brain stem nuclei of cat. J Comp Neurol. 1961 Feb;116:27–69. doi: 10.1002/cne.901160104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werman R., Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H. Inhibitory of glycine on spinal neurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1968 Jan;31(1):81–95. doi: 10.1152/jn.1968.31.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. A., McAllen R. M., Loewy A. D. GABA antagonists applied to the ventral surface of the medulla oblongata block the baroreceptor reflex. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 9;297(1):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90556-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


