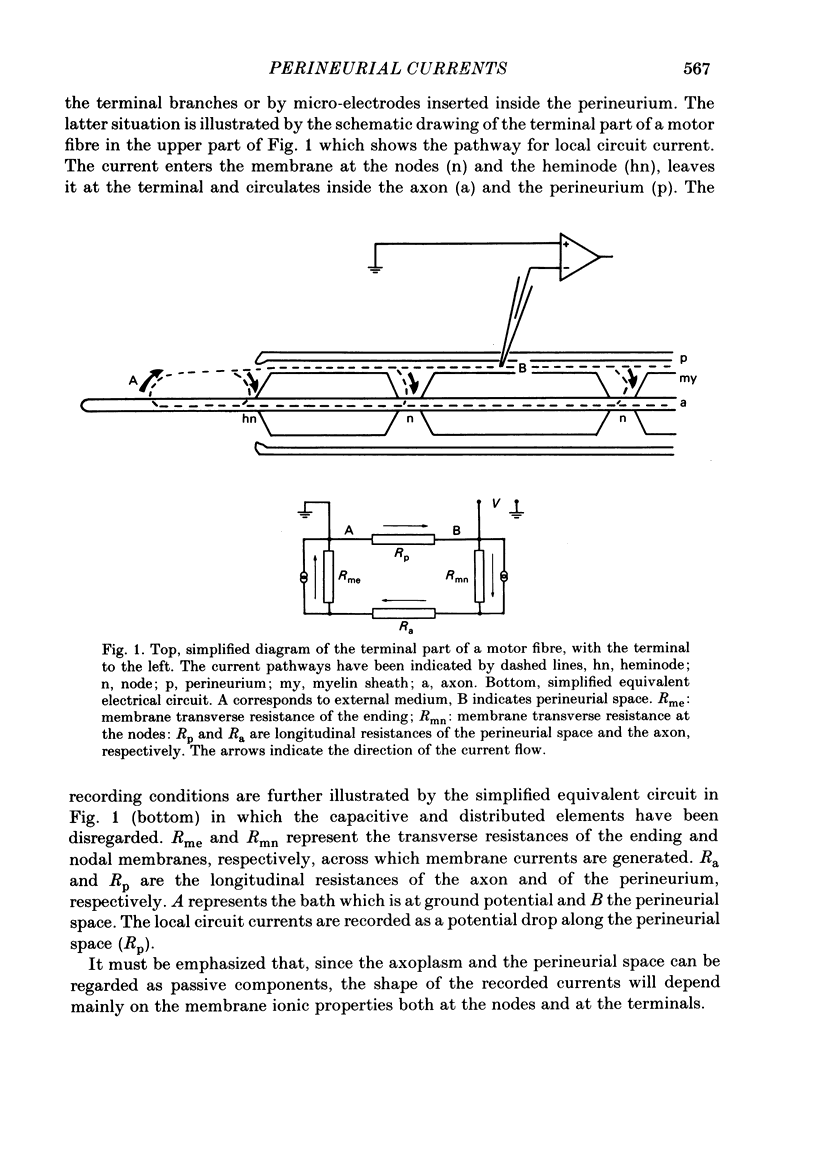
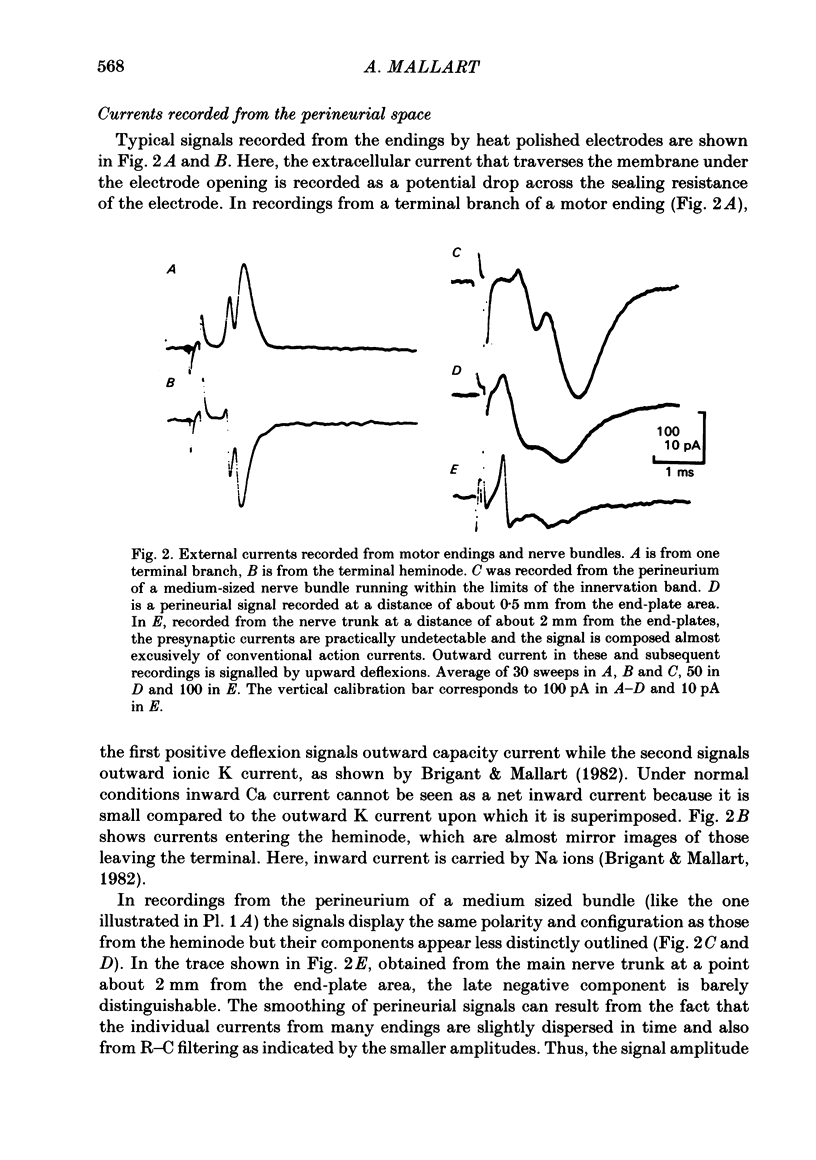
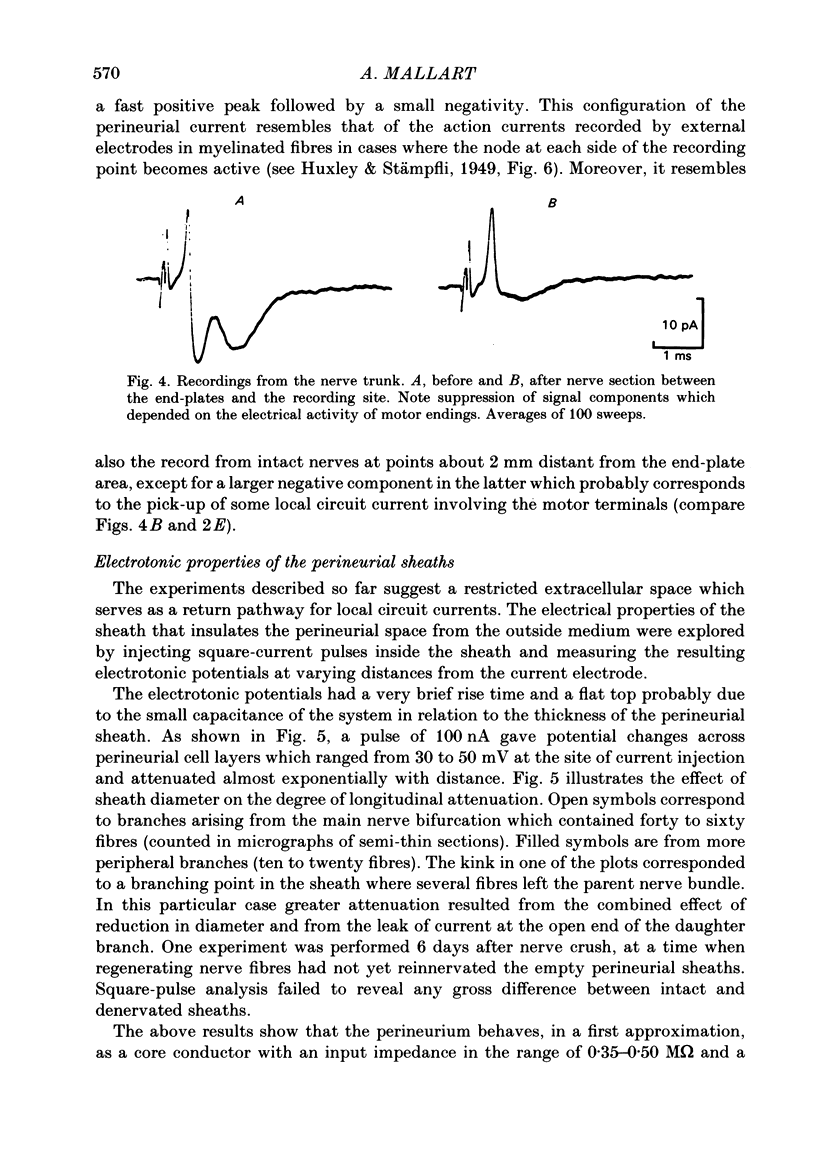
Abstract
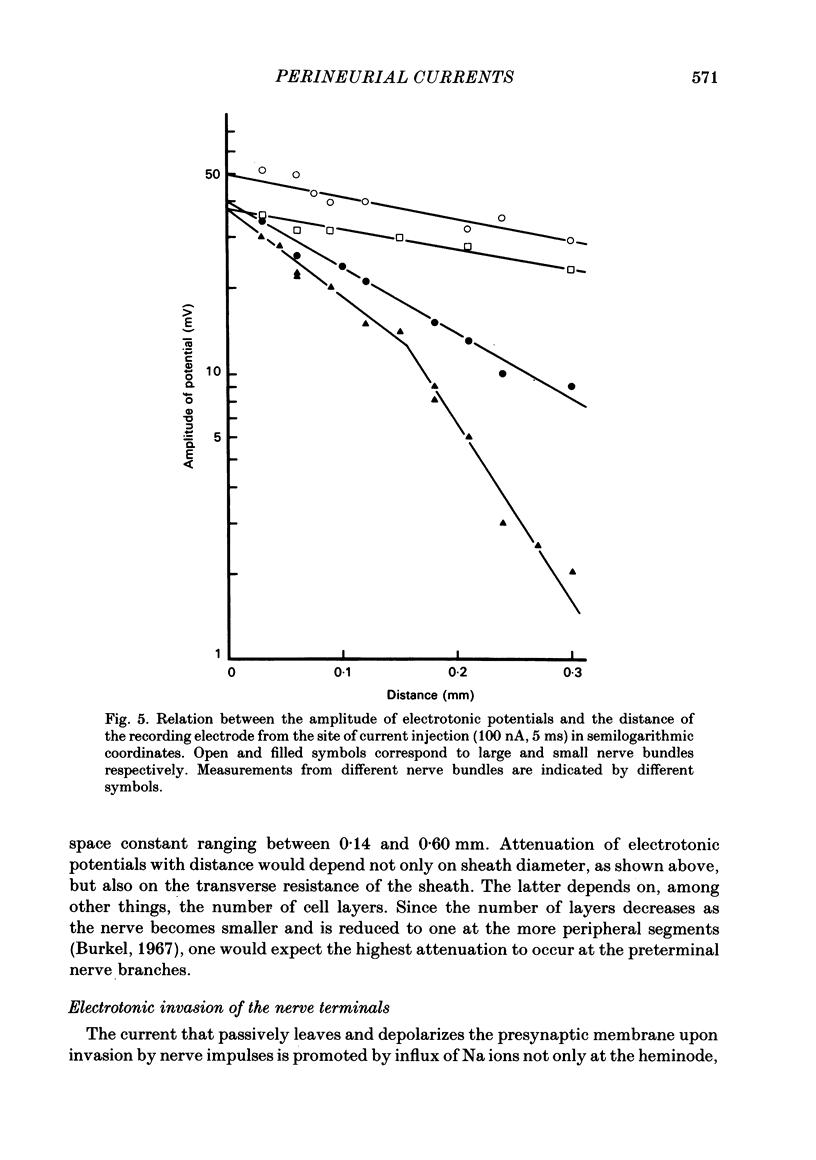
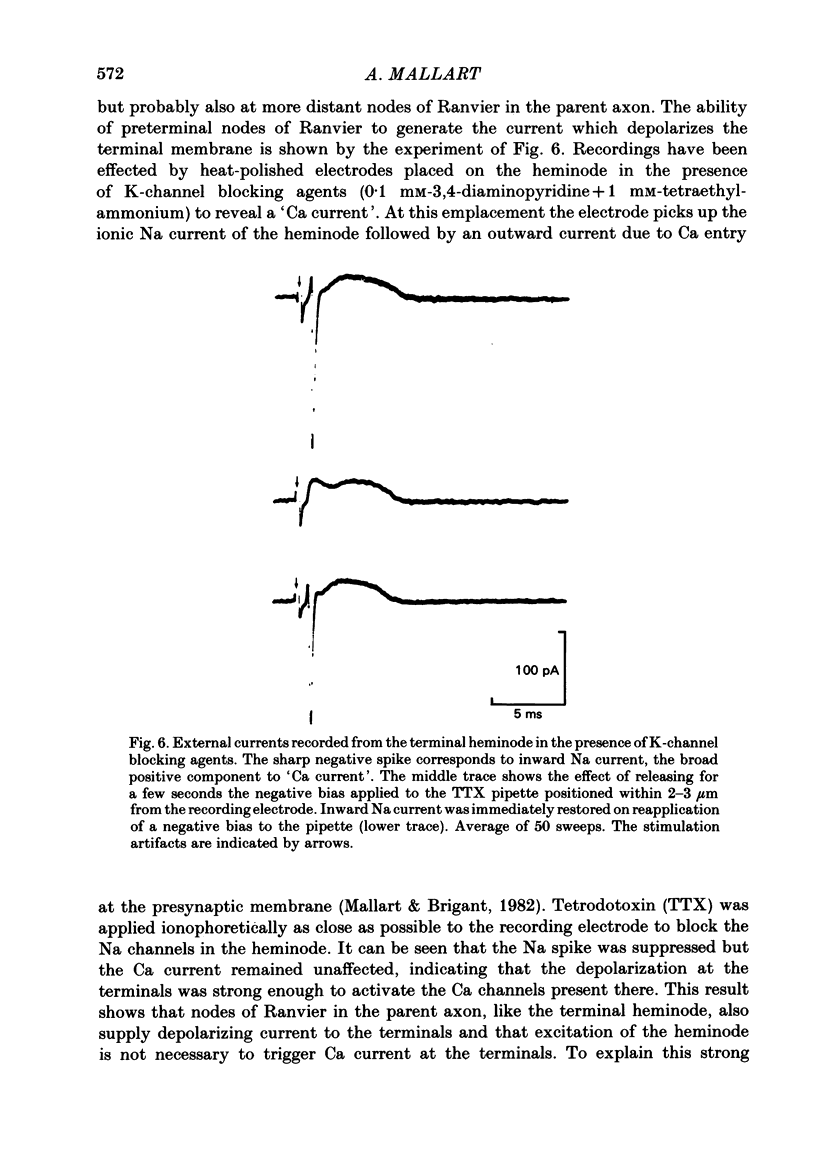
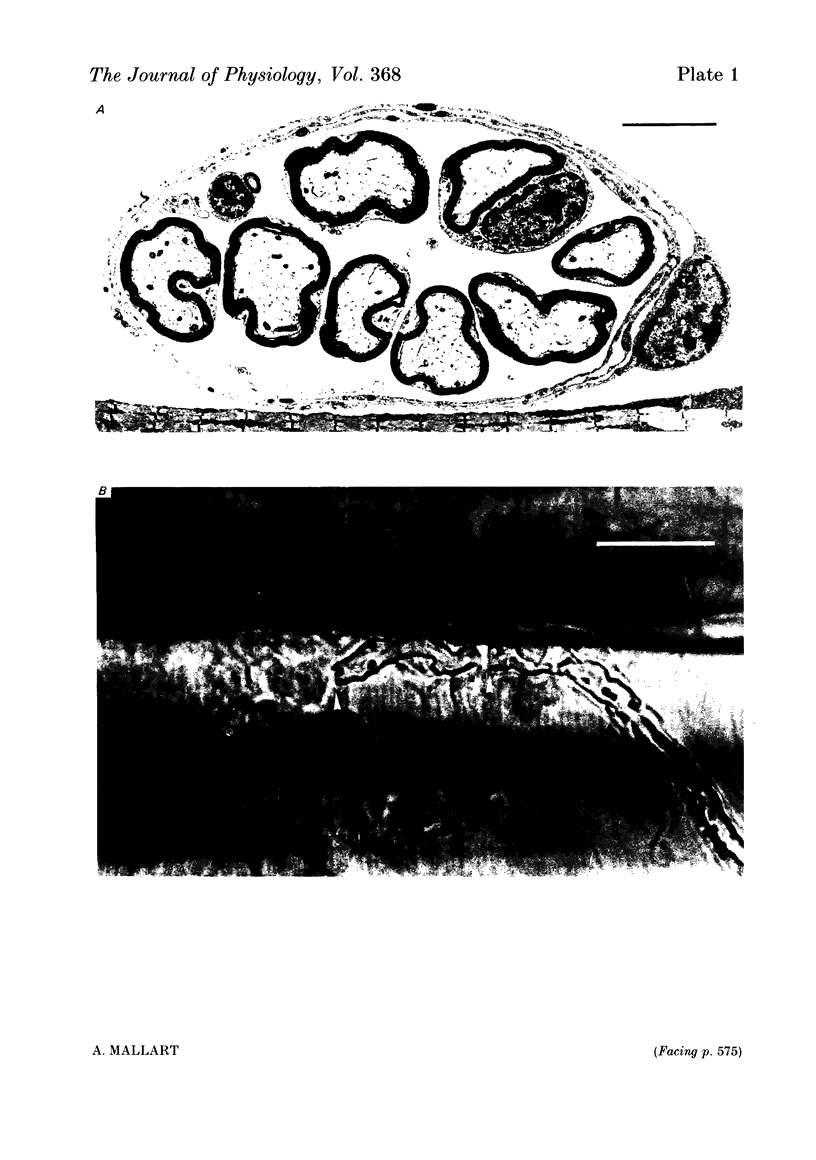
Micro-electrodes were inserted inside the perineurial space to record external currents along the superficial nerve bundles of the triangularis sterni muscle of the mouse upon motor nerve stimulation. Two kinds of external currents were distinguished, the first circulating between neighbouring nodes of Ranvier in each fibre and the second circulating between the nodes and the motor endings. Ending-node current was caused by differences in the time course and the amplitude of the potential change at the endings and at the nodes, which depended in turn, on differences between their respective membrane conductances. The stretch of nerve over which ending-node current extended served to estimate that about eight to ten nodes of Ranvier supply the motor endings with depolarizing current.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angaut-Petit D., McArdle J. J., Mallart A., Bournaud R., Pinçon-Raymond M., Rieger F. Electrophysiological and morphological studies of a motor nerve in 'motor endplate disease' of the mouse. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Apr 22;215(1198):117–125. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock H., Sears T. A. The internodal axon membrane: electrical excitability and continuous conduction in segmental demyelination. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:273–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigant J. L., Mallart A. Presynaptic currents in mouse motor endings. J Physiol. 1982 Dec;333:619–636. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T. Potential clamp analysis of membrane currents in rat myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:171–184. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkel W. E. The histological fine structure of perineurium. Anat Rec. 1967 Jun;158(2):177–189. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091580207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Ritchie J. M., Rogart R. B., Stagg D. A quantitative description of membrane currents in rabbit myelinated nerve. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:149–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen C. B., Katz B., Miledi R. The antagonism between botulinum toxin and calcium in motor nerve terminals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Oct 22;216(1204):369–376. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Stämpfli R. Evidence for saltatory conduction in peripheral myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1949 May 15;108(3):315–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K. Some observations on perfused frog sciatic nerves. J Physiol. 1954 Feb 26;123(2):338–356. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Suppression of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr;196(1125):465–469. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Schmitt O. H. Electric interaction between two adjacent nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1940 Feb 14;97(4):471–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1940.sp003823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi T., Sears T. A. Electrical activity of mouse motor nerve terminals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Jul 23;222(1226):115–120. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A. A calcium-activated potassium current in motor nerve terminals of the mouse. J Physiol. 1985 Nov;368:577–591. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArdle J. J., Angaut-Petit D., Mallart A., Bournaud R., Faille L., Brigant J. L. Advantages of the triangularis sterni muscle of the mouse for investigations of synaptic phenomena. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Aug;4(2):109–115. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quick D. C., Kennedy W. R., Donaldson L. Dimensions of myelinated nerve fibers near the motor and sensory terminals in cat tenuissimus muscles. Neuroscience. 1979;4(8):1089–1096. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I. Properties of myelinated fibers in frog sciatic nerve and in spinal cord as examined with micro-electrodes. Jpn J Physiol. 1952 Nov;3(1):73–94. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.3.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]