Abstract
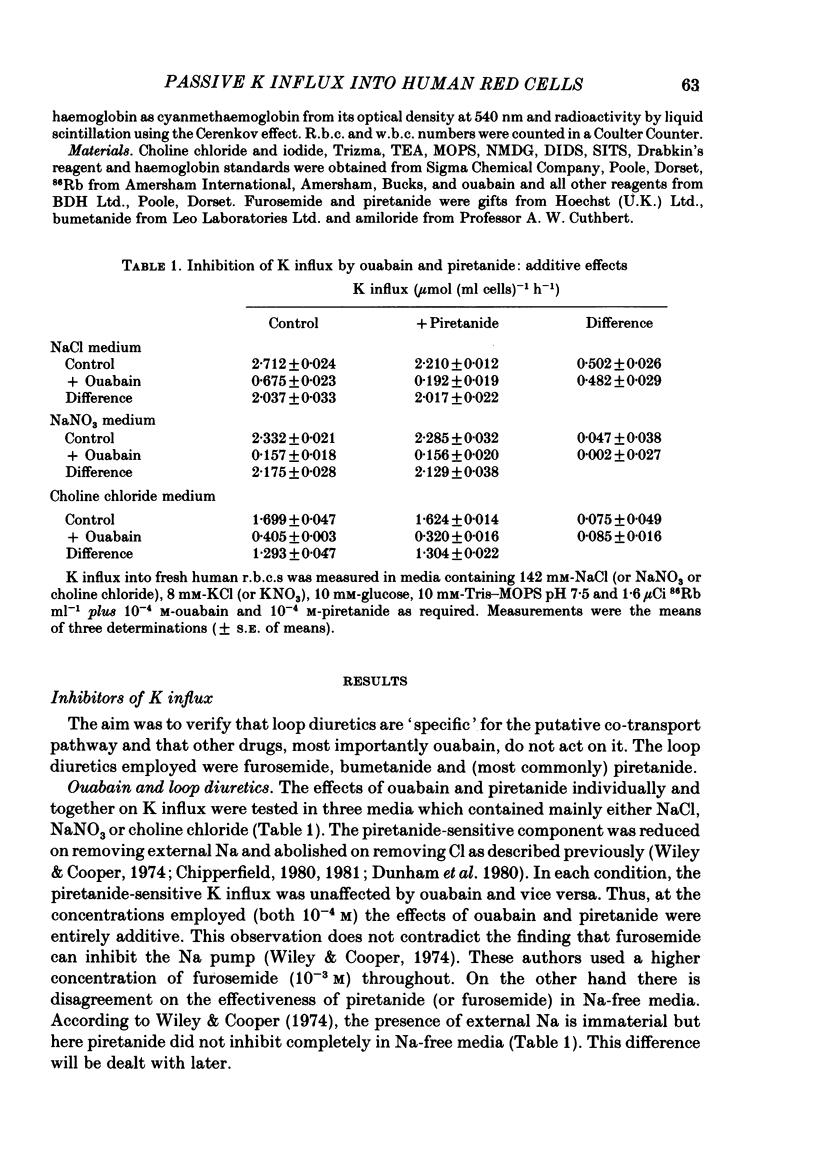
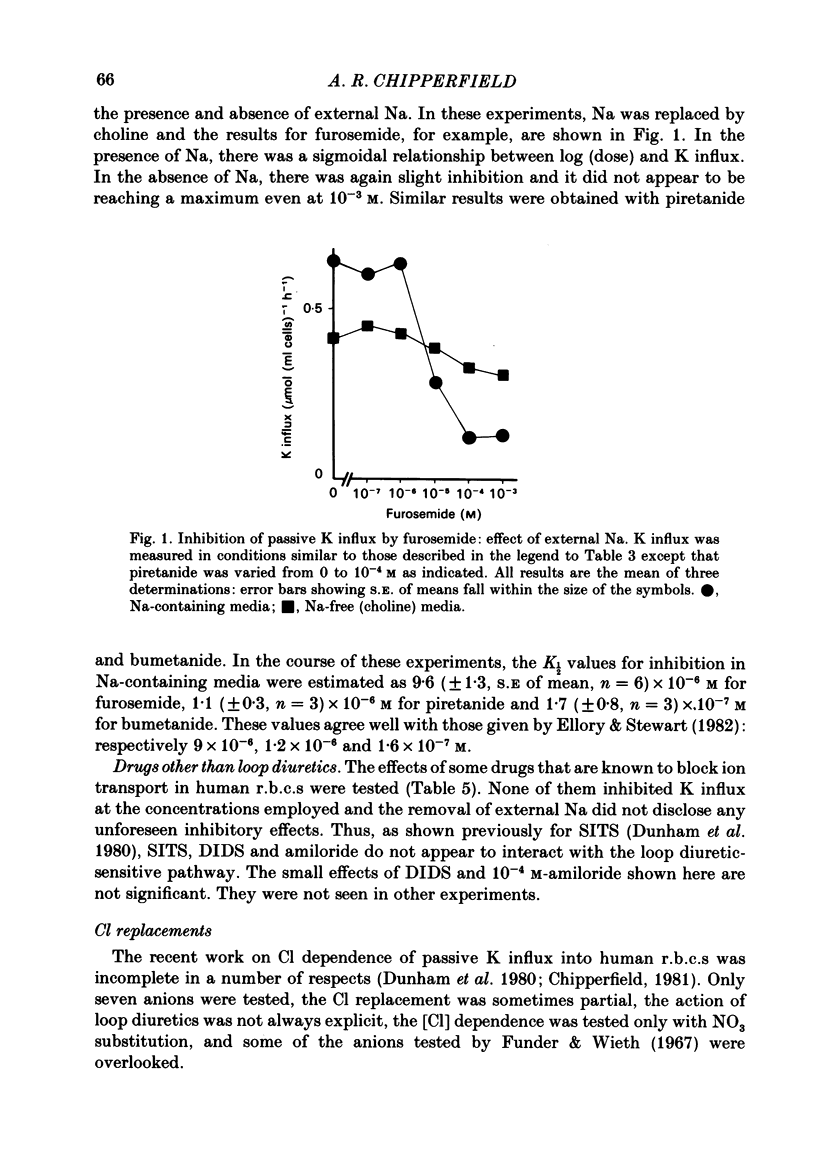
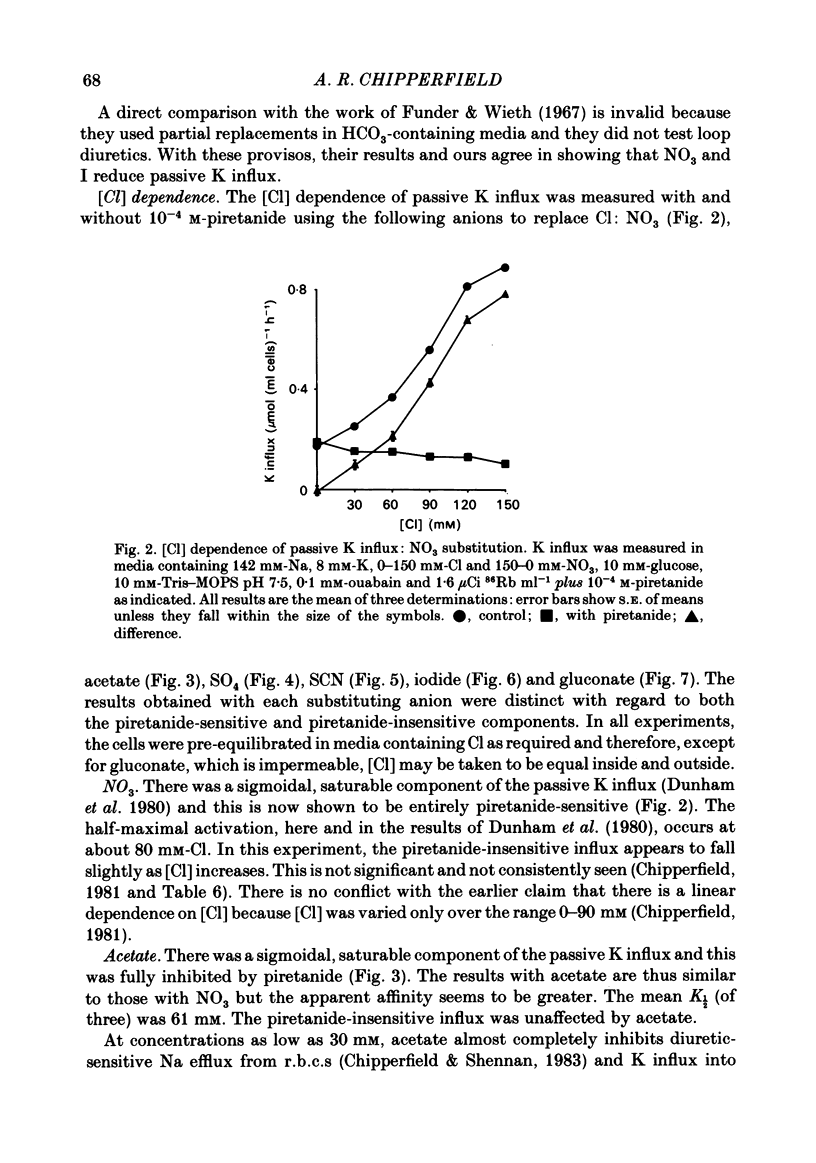
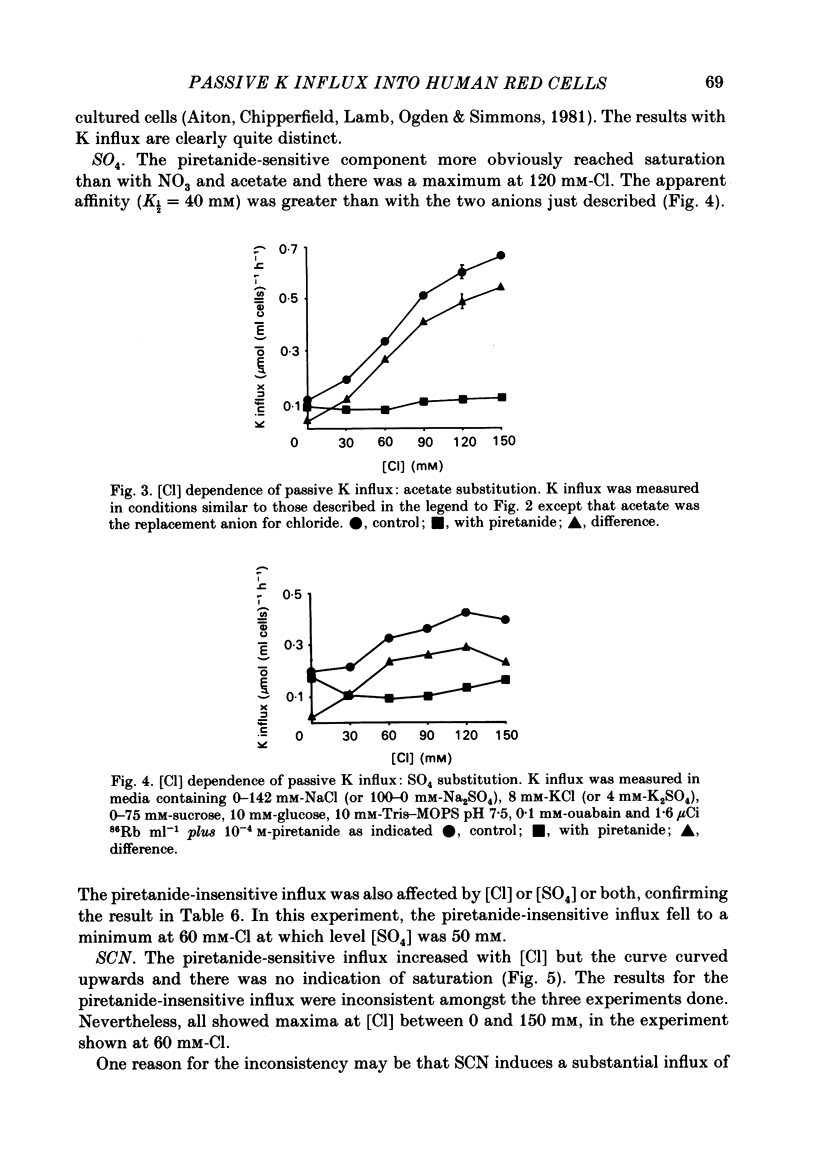
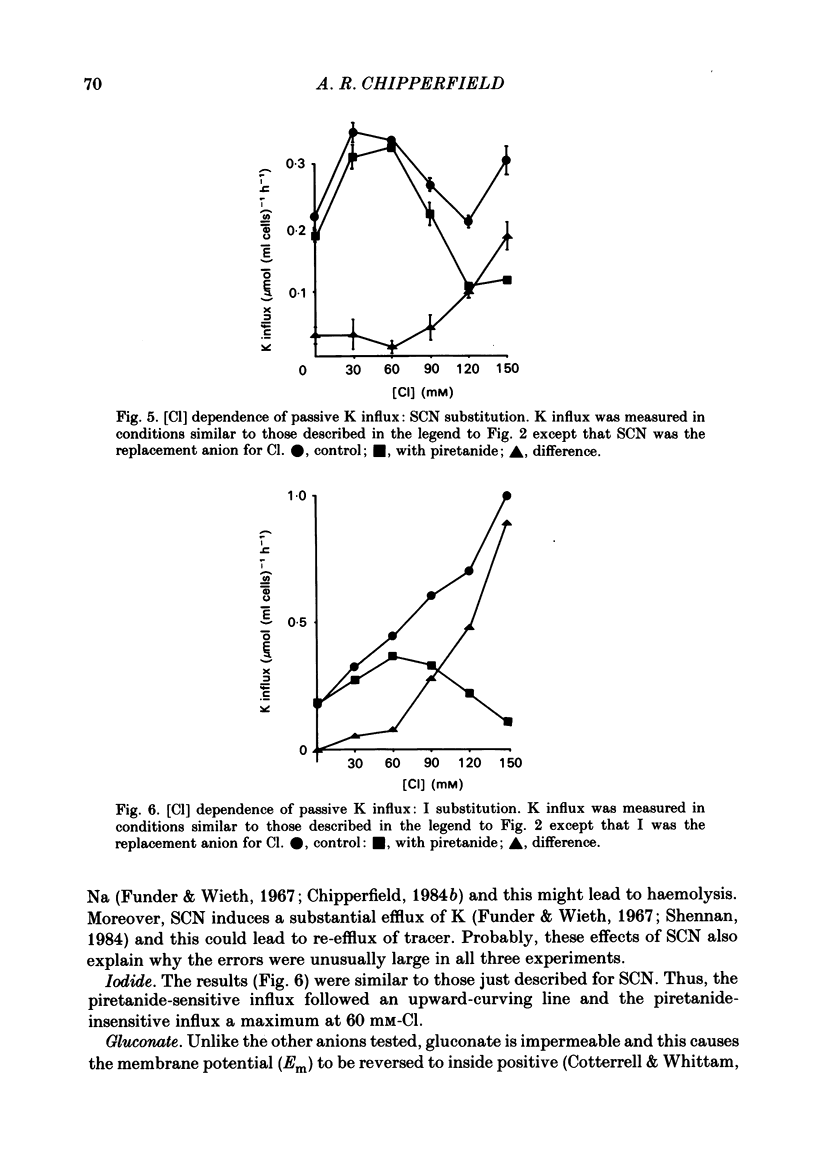
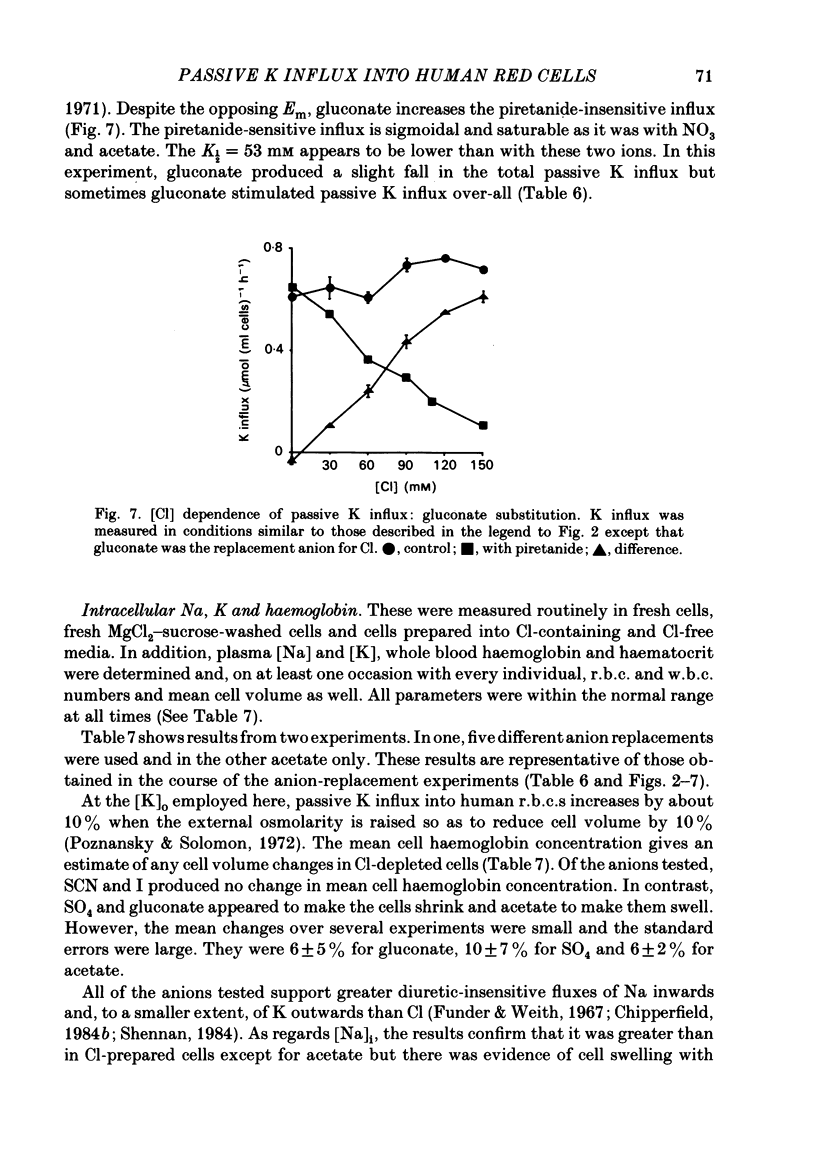
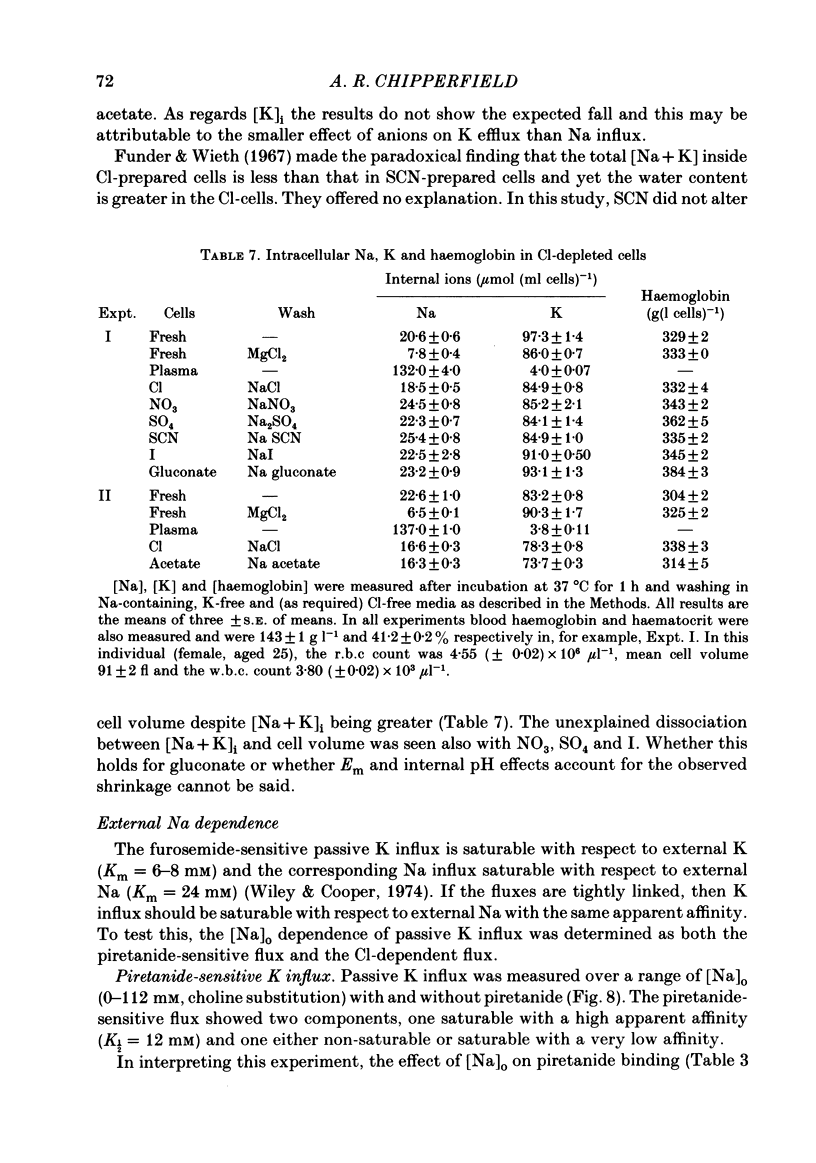
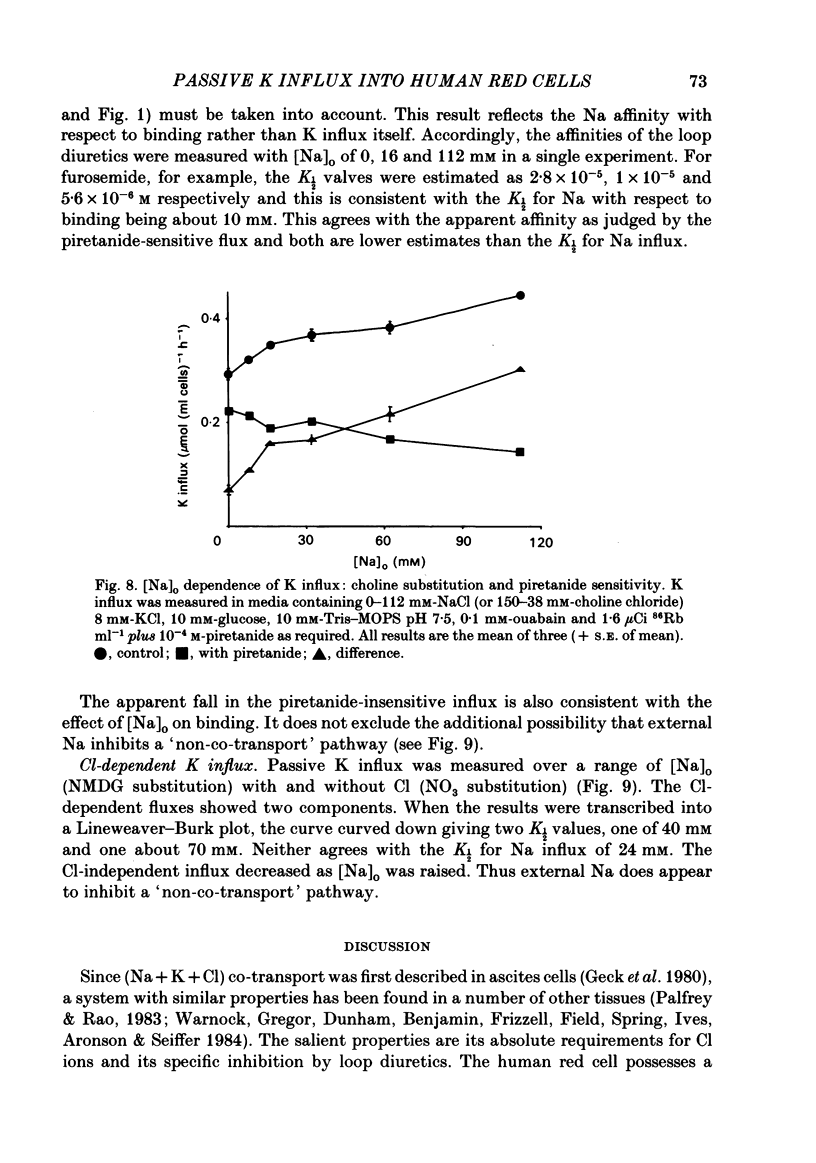
Passive K influx into human red cells was measured with and without Cl ions, Na ions and loop diuretics. Ouabain and loop diuretics appear to inhibit specifically and respectively the Na pump and (Na+K) 'co-transport'. Inhibitors of other pathways, e.g. 4,4'-diisothiocyantostilbene-2,2'-disulphonic acid or amiloride did not inhibit passive K influx. Loop diuretics inhibited with high apparent affinity in Na-containing media and with low apparent affinity in Na-free media where there was a substantial Cl-dependent component. The Cl concentration dependence was measured using six anion substitutions for Cl. With NO3, acetate and gluconate, the curves were sigmoidal and not fully saturable at 150 mM-Cl; with iodide and thiocyanate, the curves were convex; with sulphate, there was saturation at 120 mM-Cl. The half-maximal K influx as a function of [Na]0 was 40 mM for the Cl-dependent flux component and 12 mM for the diuretic-sensitive flux.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adragna N. C., Tosteson D. C. Effect of volume changes on ouabain-insensitive net outward cation movements in human red cells. J Membr Biol. 1984;78(1):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01872531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiton J. F., Chipperfield A. R., Lamb J. F., Ogden P., Simmons N. L. Occurrence of passive furosemide-sensitive transmembrane potassium transport in cultured cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 7;646(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield A. R. An effect of chloride on (Na+K) co-transport in human red blood cells. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):281–282. doi: 10.1038/286281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield A. R. Chloride dependence of frusemide- and phloretin-sensitive passive sodium and potassium fluxes in human red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:435–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield A. R. Loop diuretics may fail to inhibit (Na+, K+, Cl-) 'cotransport' in human red cells. Biosci Rep. 1985 Apr;5(4):299–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01116900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotterrell D., Whittam R. The influence of the chloride gradient across red cell membranes on sodium and potassium movements. J Physiol. 1971 May;214(3):509–536. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhm J., Göbel B. O. Role of the furosemide-sensitive Na+/K+ transport system in determining the steady-state Na+ and K+ content and volume of human erythrocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Membr Biol. 1984;77(3):243–254. doi: 10.1007/BF01870572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Stewart G. W., Ellory J. C. Chloride-activated passive potassium transport in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1711–1715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellory J. C., Dunham P. B., Logue P. J., Stewart G. W. Anion-dependent cation transport in erythrocytes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):483–495. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellory J. C., Stewart G. W. The human erythrocyte Cl-dependent Na-K cotransport system as a possible model for studying the action of loop diuretics. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman P. W. Sodium and potassium transport in ferret red cells. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:545–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbush B., 3rd, Palfrey H. C. [3H]bumetanide binding to membranes isolated from dog kidney outer medulla. Relationship to the Na,K,Cl co-transport system. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11787–11792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J., Wieth J. O. Effects of some monovalent anions on fluxes of Na and K, and on glucose metabolism of ouabain treated human red cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Oct-Nov;71(2):168–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Garrahan P. J. The interaction of sodium and potassium with the sodium pump in red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):297–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The sensitivity of the sodium pump to external sodium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):175–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geck P., Pietrzyk C., Burckhardt B. C., Pfeiffer B., Heinz E. Electrically silent cotransport on Na+, K+ and Cl- in Ehrlich cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 4;600(2):432–447. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90446-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. C., Ellory J. C., Klein R. A. Pressure and temperature effects on human red cell cation transport. J Membr Biol. 1982;68(1):47–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01872253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Ellory J. C., Lew V. L. Evidence against Na+-pump mediation of Ca2+-activated K+ transport and diuretic-sensitive (Na+/K+)-cotransport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 20;646(2):353–355. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRoberts J. A., Erlinger S., Rindler M. J., Saier M. H., Jr Furosemide-sensitive salt transport in the Madin-Darby canine kidney cell line. Evidence for the cotransport of Na+, K+, and Cl-. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2260–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey H. C., Rao M. C. Na/K/Cl co-transport and its regulation. J Exp Biol. 1983 Sep;106:43–54. doi: 10.1242/jeb.106.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poznansky M., Solomon A. K. Effect of cell volume on potassium transport in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestland R. N., Whittam R. The influence of external sodium ions on the sodium pump in erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):369–374. doi: 10.1042/bj1090369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Ouabain-insensitive sodium movements in the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Mar;57(3):259–282. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. G., Greger R., Dunham P. B., Benjamin M. A., Frizzell R. A., Field M., Spring K. R., Ives H. E., Aronson P. S., Seifter J. Ion transport processes in apical membranes of epithelia. Fed Proc. 1984 Jul;43(10):2473–2487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiater L. A., Dunham P. B. Passive transport of K+ and Na+ in human red blood cells: sulfhydryl binding agents and furosemide. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):C348–C356. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.5.C348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieth J. O. Paradoxical temperature dependence of sodium and potassium fluxes in human red cells. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):563–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley J. S., Cooper R. A. A furosemide-sensitive cotransport of sodium plus potassium in the human red cell. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):745–755. doi: 10.1172/JCI107613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


