Abstract
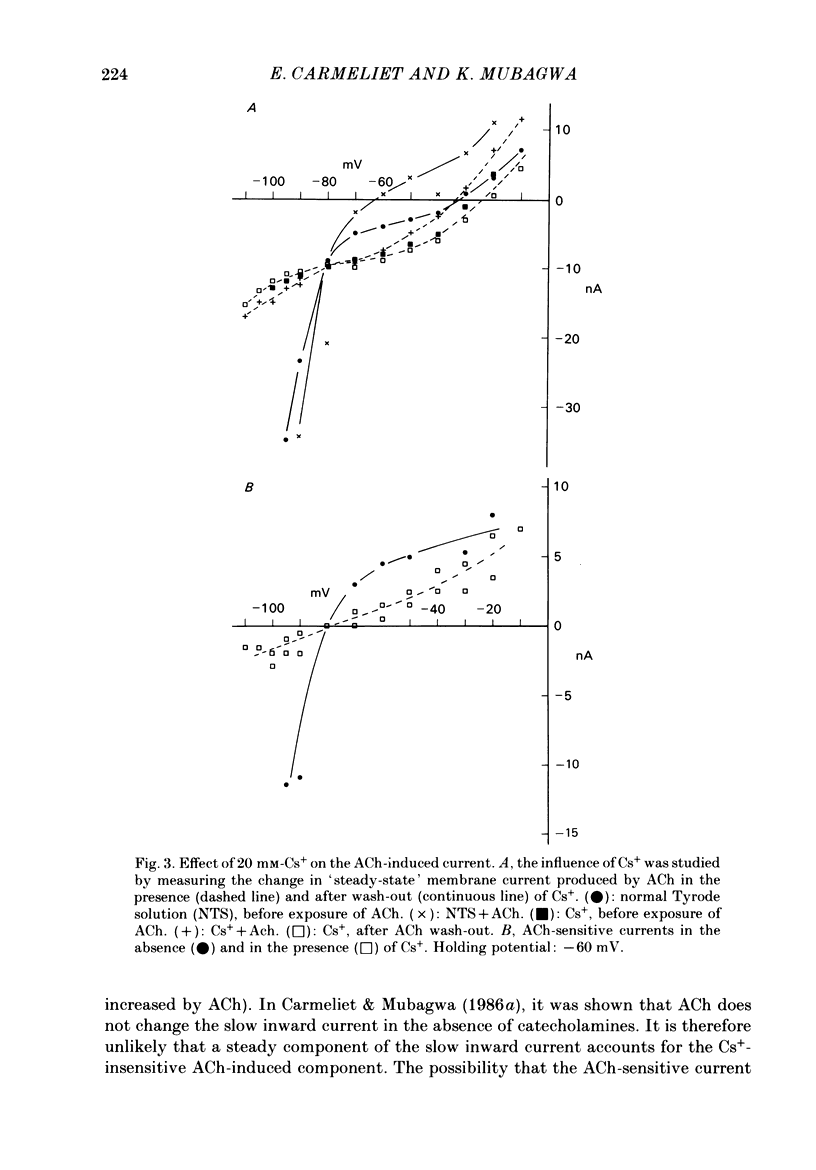
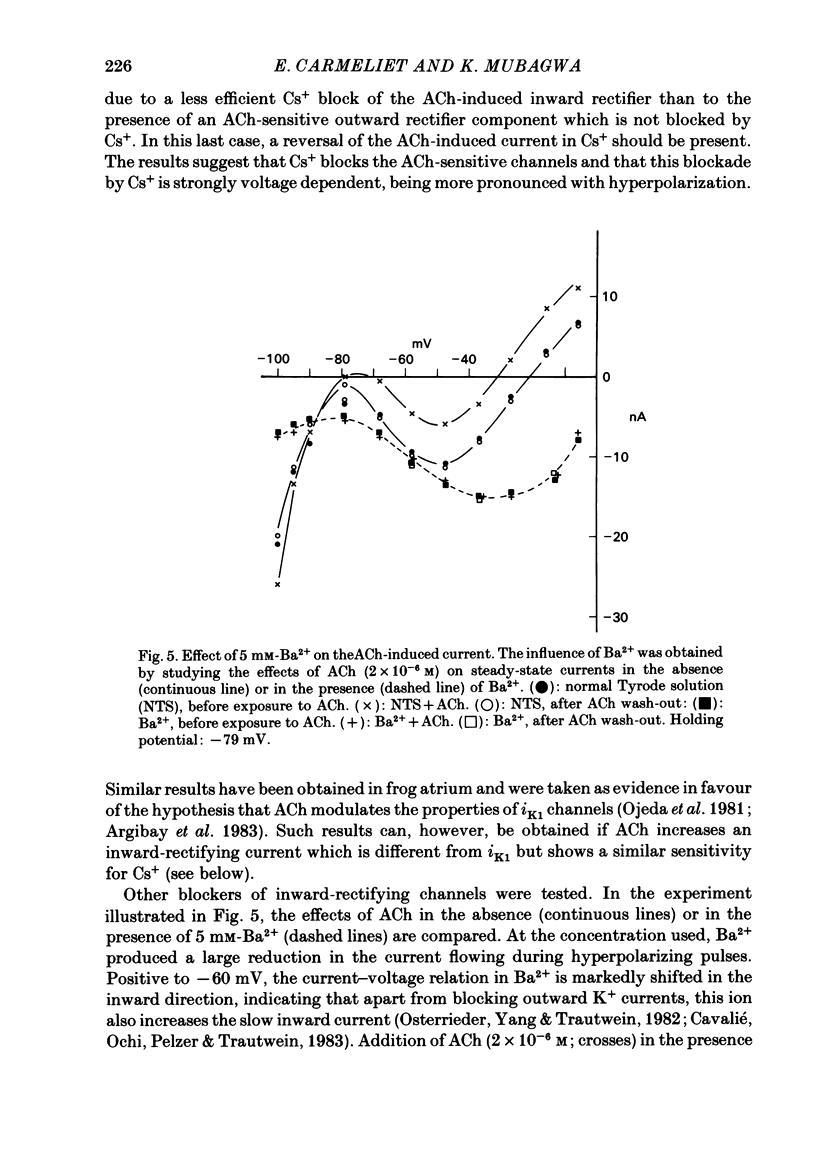
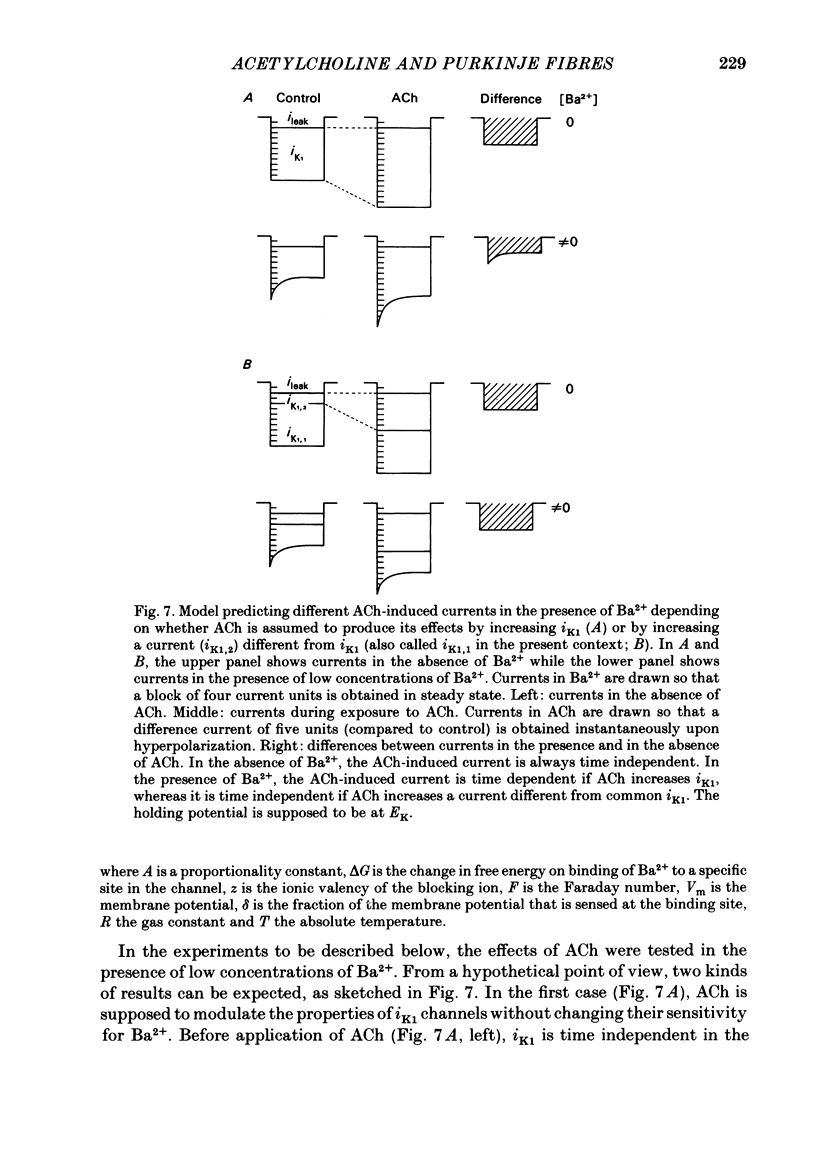
Acetylcholine (ACh) induces a K+ current in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. The question was studied whether ACh produces this effect by modifying the properties of K+ channels pre-existing in the absence of the neurotransmitter or whether it induces the formation of a different type of K+ channels. The relaxation properties of the ACh-induced current and its blockade by Cs+ and Ba2+ have been investigated using voltage clamp. During hyperpolarizing or depolarizing voltage pulses of moderate amplitude, the ACh-induced current is time independent. For large voltage pulses, time-dependent changes of the ACh-induced current are observed. These latter changes can be explained by intracellular K+ accumulation/depletion phenomena or by the effects of ACh on time-dependent currents (e.g. the late outward current, ix). Cs+ and Ba2+ block the ACh-induced current. The block produced by 20 mM-Cs+ is instantaneous and increases with hyperpolarization, i.e. it is voltage dependent. The block produced by Ba2+ at high concentrations (greater than 1 mM) is also instantaneous but complete at all potentials studied, and thus voltage independent. At these concentrations, either ion also blocks the background inward rectifier (iK1) current in a similar way. Low [Ba2+] (less than 0.1 mM) cause a block of the ACh-induced current which is instantaneous and little voltage dependent. The block of iK1 in contrast is time and voltage dependent for the same concentrations. These results indicate that the ACh-induced K+ current is different from the background iK1 current.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argibay J. A., Dutey P., Ildefonse M., Ojeda C., Rougier O., Tourneur Y. Block by Cs of K current iK1 and of carbachol induced K current iCch in frog atrium. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Jun 1;397(4):295–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00580264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechem M., Glitsch H. G., Pott L. Properties of an inward rectifying K channel in the membrane of guinea-pig atrial cardioballs. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Nov;399(3):186–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00656713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Mubagwa K. Changes by acetylcholine of membrane currents in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:201–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Mubagwa K. Desensitization of the acetylcholine-induced increase of potassium conductance in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:239–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Ramon J. Effect of acetylcholine on time-independent currents in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Sep;387(3):207–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00580972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E. Voltage dependent block of inward going rectification in cardiac Purkinje fibers by external Cs ions. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1979 Dec;242(2):294–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalié A., Ochi R., Pelzer D., Trautwein W. Elementary currents through Ca2+ channels in guinea pig myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Sep;398(4):284–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00657238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFrancesco D. A new interpretation of the pace-maker current in calf Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:359–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier D., Nargeot J., Ojeda C., Rougier O. The action of acetylcholine on background conductance in frog atrial trabeculae. J Physiol. 1978 Jan;274:381–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay L. A., Stanfield P. R. Cs(+) causes a voltage-dependent block of inward K currents in resting skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1977 May 12;267(5607):169–170. doi: 10.1038/267169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Rosenthal N. P. Potassium current and the effect of cesium on this current during anomalous rectification of the egg cell membrane of a starfish. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Jun;67(6):621–638. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G. Cardiac Purkinje fibers: cesium as a tool to block inward rectifying potassium currents. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Sep 30;365(2-3):99–106. doi: 10.1007/BF01067006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mubagwa K., Carmeliet E. Effects of acetylcholine on electrophysiological properties of rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibers. Circ Res. 1983 Dec;53(6):740–751. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.6.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Peper K., Trautwein W. Acetylcholine-induced potassium current fluctuations in the rabbit sino-atrial node. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Sep;381(3):255–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00583257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Trautwein W. Relaxation of the ACh-induced potassium current in the rabbit sinoatrial node cell. Pflugers Arch. 1978 Nov 30;377(3):193–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00584272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori H. Inactivation kinetics and steady-state current noise in the anomalous rectifier of tunicate egg cell membranes. J Physiol. 1978 Aug;281:77–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda C., Rougier O., Tourneur Y. Effects of Cs on acetylcholine induced current. Is ik1 increased by acetylcholine in frog atrium? Pflugers Arch. 1981 Jul;391(1):57–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00580695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterrieder W., Yang Q. F., Trautwein W. Effects of barium on the membrane currents in the rabbit S-A node. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jul;394(1):78–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01108311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Noma A., Trautwein W. Acetylcholine activation of single muscarinic K+ channels in isolated pacemaker cells of the mammalian heart. Nature. 1983 May 19;303(5914):250–253. doi: 10.1038/303250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmann B., Trube G. Voltage-dependent inactivation of inward-rectifying single-channel currents in the guinea-pig heart cell membrane. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:659–683. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. A potential- and time-dependent blockade of inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres by barium and strontium ions. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:169–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. Rubidium block and rubidium permeability of the inward rectifier of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Jul;304:415–435. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


