Abstract
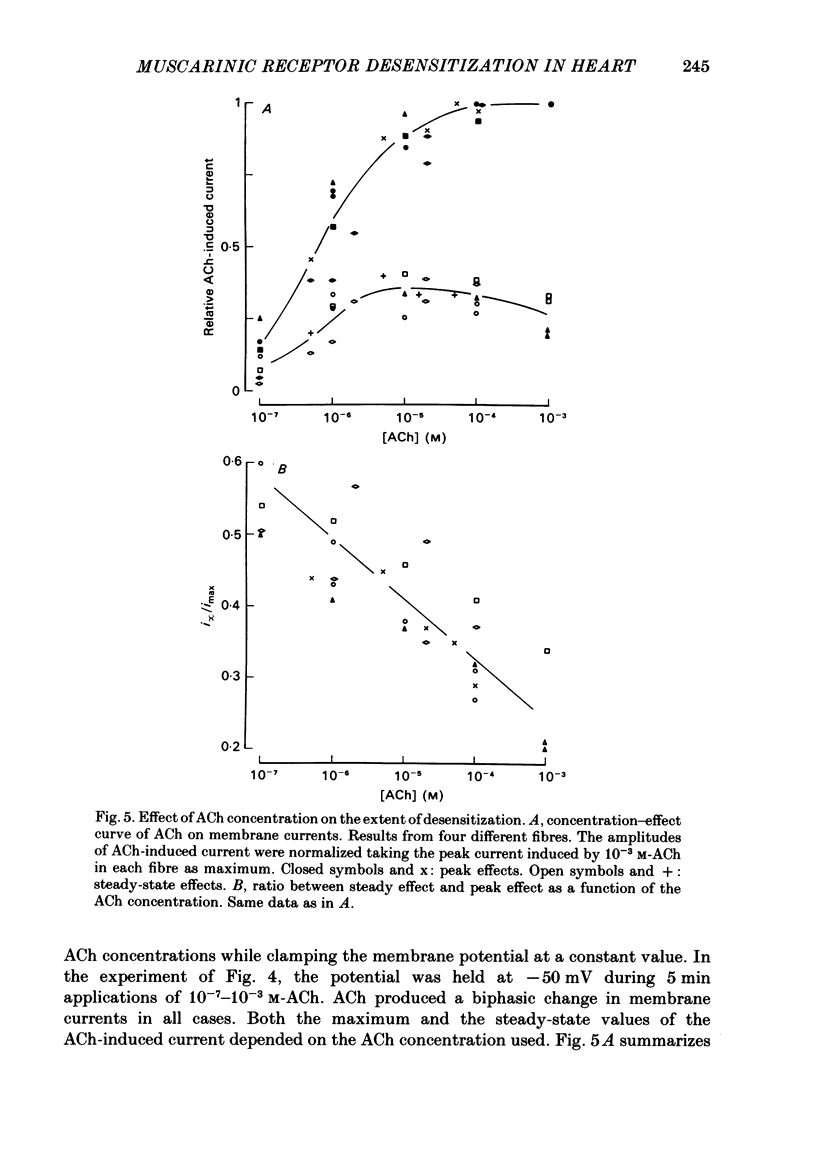
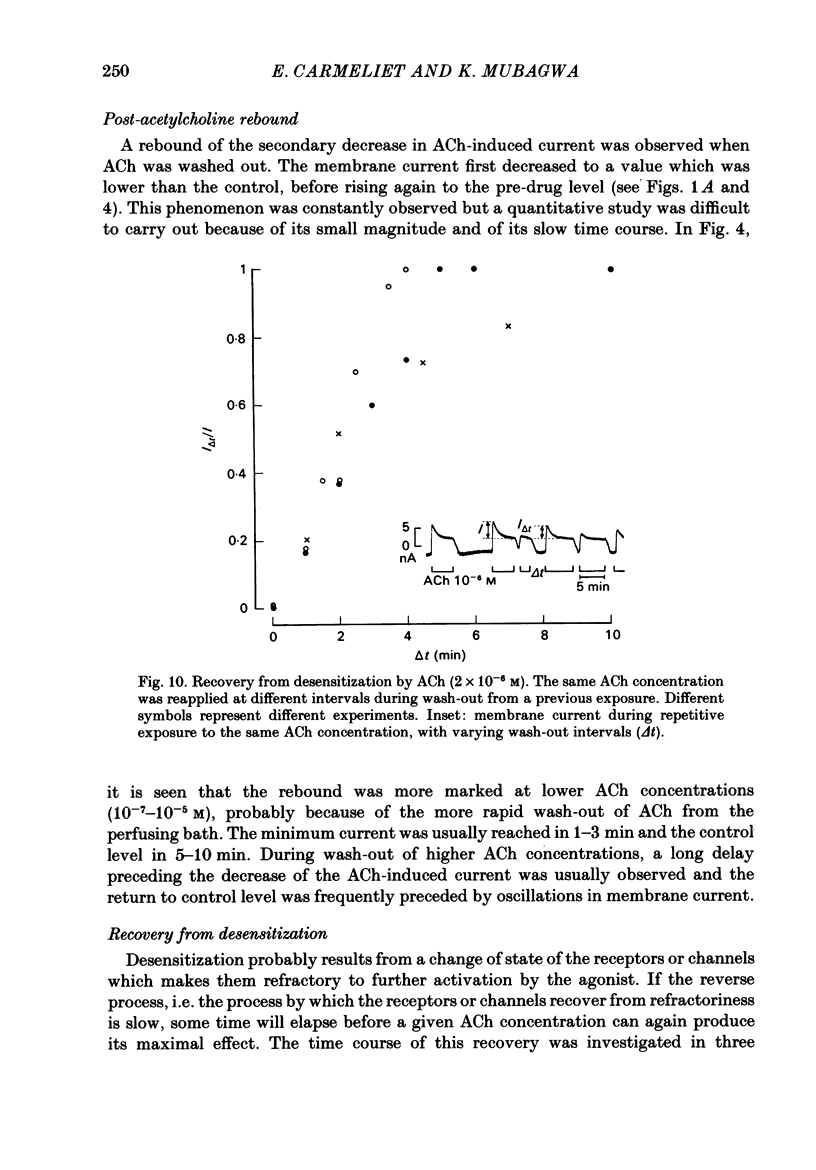
In rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres, acetylcholine (ACh) changes membrane electrophysiological properties in a biphasic time course. On wash-out of ACh a rebound phenomenon is observed (Mubagwa & Carmeliet, 1983). The underlying mechanisms have been studied by the voltage-clamp technique. The ACh-induced increase in K+ current follows a biphasic time course during exposure to ACh. This time course is not due to intercellular accumulation or depletion of K+, but results from a desensitization process. On wash-out a rebound is obtained, i.e. the membrane K+ conductance transiently decreases below the control value. In contrast, the inhibition of ACh of the catecholamine-induced increase of slow inward current follows a monophasic time course. The desensitization process or secondary decrease of ACh-induced change in K+ current follows a mono- or a biexponential time course. The extent and rate of desensitization depend on ACh concentration. The rate of desensitization is not influenced by membrane potential but its extent seems to be increased by depolarization. Recovery from desensitization is relatively rapid and has a half-time of about 2 min. Different existing models for desensitization are discussed, no one of which accounts for all results in rabbit Purkinje fibres. Therefore, a three-state receptor model is proposed to explain the results. The model assumes that the K+ channel is directly associated with the muscarinic receptor and that the channel-receptor complex may be in closed, open or desensitized state, in the presence as well as in the absence of agonist.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. A study of desensitization using voltage clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00580536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegon R. L., Pappano A. J. Dual mechanism for inhibition of calcium-dependent action potentials by acetylcholine in avian ventricular muscle. Relationship to cyclic AMP. Circ Res. 1980 Mar;46(3):353–362. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.3.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke G. H., Calaresu F. R. An experimental analysis of the tachycardia that follows vagal stimulation. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):491–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Mubagwa K. Changes by acetylcholine of membrane currents in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:201–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Mubagwa K. Characterization of the acetylcholine-induced potassium current in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:219–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Ramon J. Electrophysiological effects of acetylcholine in sheep cardiac Purkinje fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Sep;387(3):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00580971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colatsky T. J., Tsien R. W. Electrical properties associated with wide intercellular clefts in rabbit Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1979 May;290(2):227–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galper J. B., Dziekan L. C., Miura D. S., Smith T. W. Agonist-induced changes in the modulation of K+ permeability and beating rate by muscarinic agonists in cultured heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Aug;80(2):231–256. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gero A. Desensitization, two-state receptors and pharmacological parameters. J Theor Biol. 1983 Jul 7;103(1):137–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(83)90204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glitsch H. G., Pott L. Effects of acetylcholine and parasympathetic nerve stimulation on membrane potential in quiescent guinea-pig atria. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:655–668. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLENBERG M., CARRIERE S., BARGER A. C. BIPHASIC ACTION OF ACETYLCHOLINE ON VENTRICULAR MYOCARDIUM. Circ Res. 1965 Jun;16:527–536. doi: 10.1161/01.res.16.6.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Stickgold R., Yoshikami D. Synaptic excitation and inhibition resulting from direct action of acetylcholine on two types of chemoreceptors on individual amphibian parasympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):817–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalife J., Hamilton A. J., Moe G. K. Desensitization of the cholinergic receptor at the sinoatrial cell of the kitten. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):H439–H448. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.238.4.H439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. M., Dalton D. P., Moran J. M. Sensitivity differences of SA and AV node to vagal stimulation: attenuation of vagal effects at SA node. Am J Physiol. 1981 Nov;241(5):H684–H690. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.5.H684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Vyskocil F. Dependence of acetylcholine desensitization on the membrane potential of frog muscle fibre and on the ionic changes in the medium. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):507–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Levy M. N., Matsuda Y. Fade of cardiac responses during tonic vagal stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):H219–H225. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1982.243.2.H219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mubagwa K., Carmeliet E. Effects of acetylcholine on electrophysiological properties of rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibers. Circ Res. 1983 Dec;53(6):740–751. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.6.740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N. M., Klein W. L., Nirenberg M. Regulation of adenylate cyclase activity mediated by muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1788–1791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B. Desensitization of the muscarinic receptor in the mammalian atrial myocardium. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1983;42(5):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Peper K., Trautwein W. Acetylcholine-induced potassium current fluctuations in the rabbit sino-atrial node. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Sep;381(3):255–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00583257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. On the mechanism of desensitization at cholinergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;6(4):357–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siman R. G., Klein W. L. Cholinergic activity regulates muscarinic receptors in central nervous system cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4141–4145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J. R., Johnson E. A. Cardiac muscle. A comparative study of Purkinje fibers and ventricular fibers. J Cell Biol. 1968 Mar;36(3):497–526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptors: biochemical mechanisms of physiological regulation. Physiol Rev. 1984 Apr;64(2):661–743. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.2.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokimasa T., Hasuo H., Koketsu K. Desensitization of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor of atrium in bullfrogs. Jpn J Physiol. 1981;31(1):83–97. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.31.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe A. M., Besch H. R., Jr Interaction between cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic gunaosine monophosphate in guinea pig ventricular myocardium. Circ Res. 1975 Sep;37(3):309–317. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.3.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


