Abstract
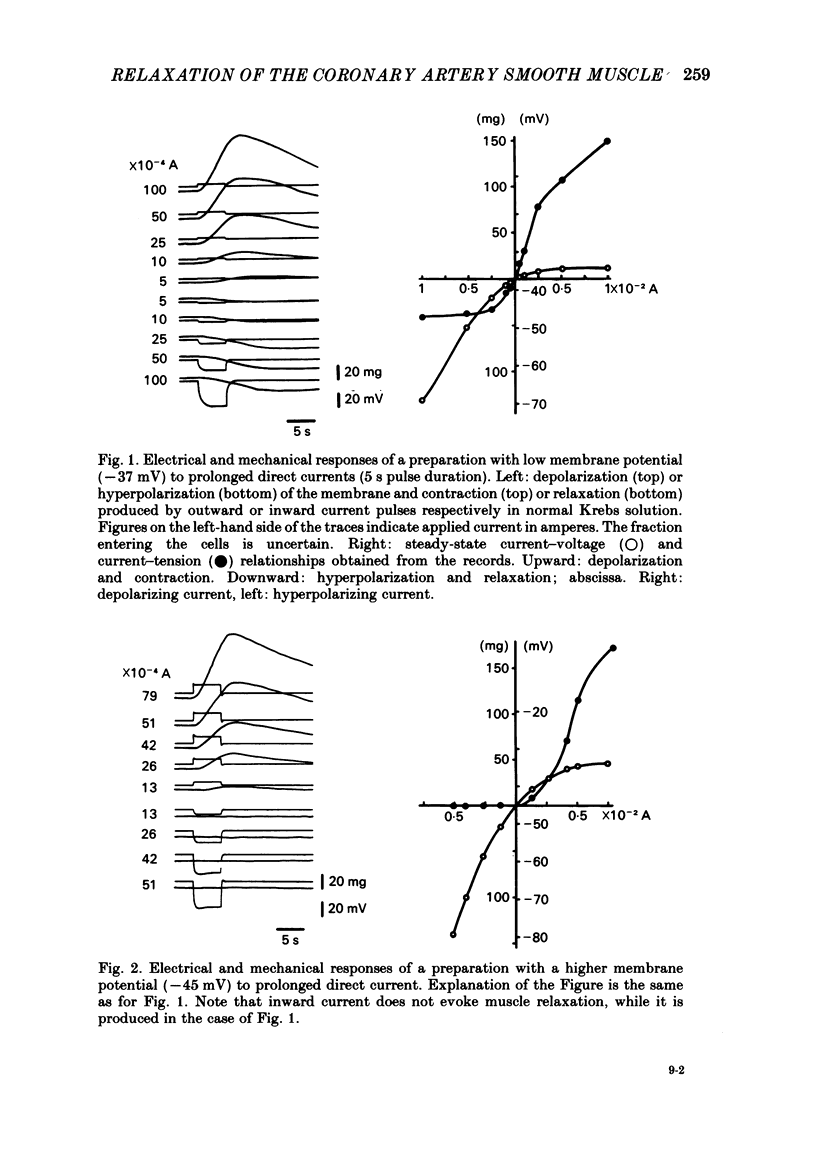
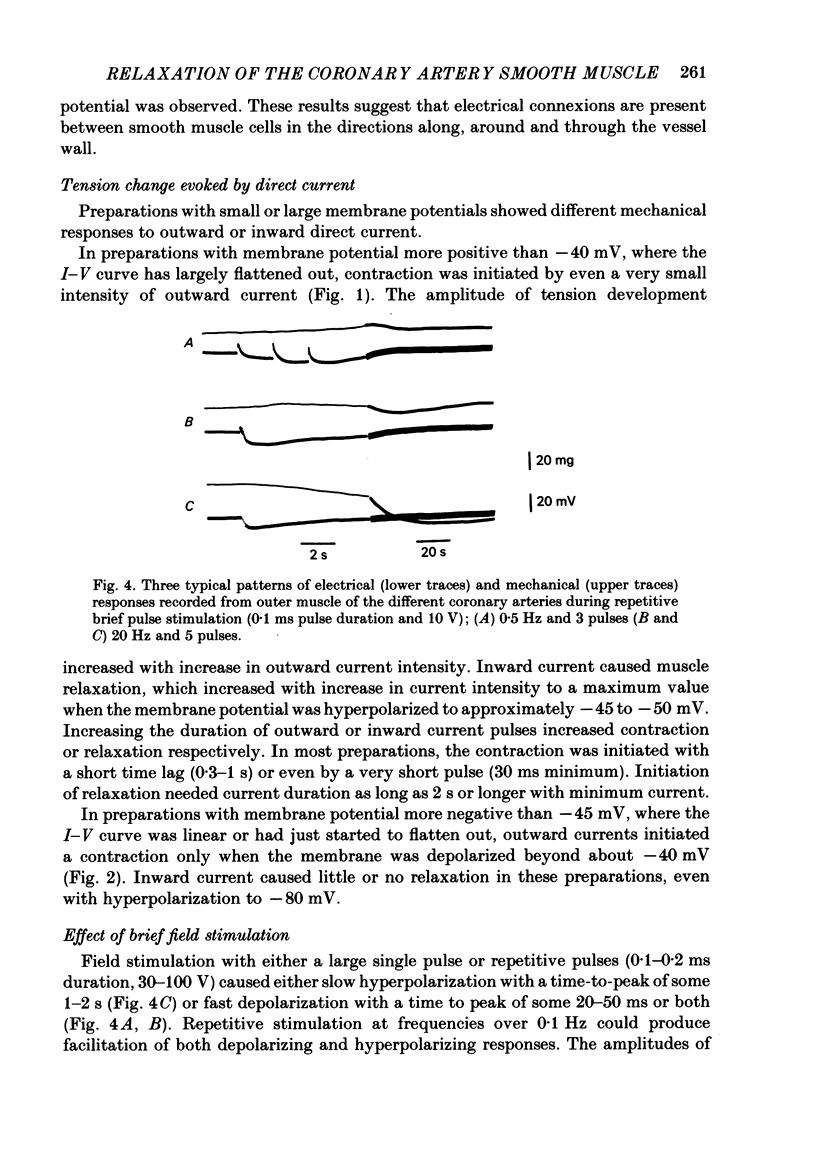
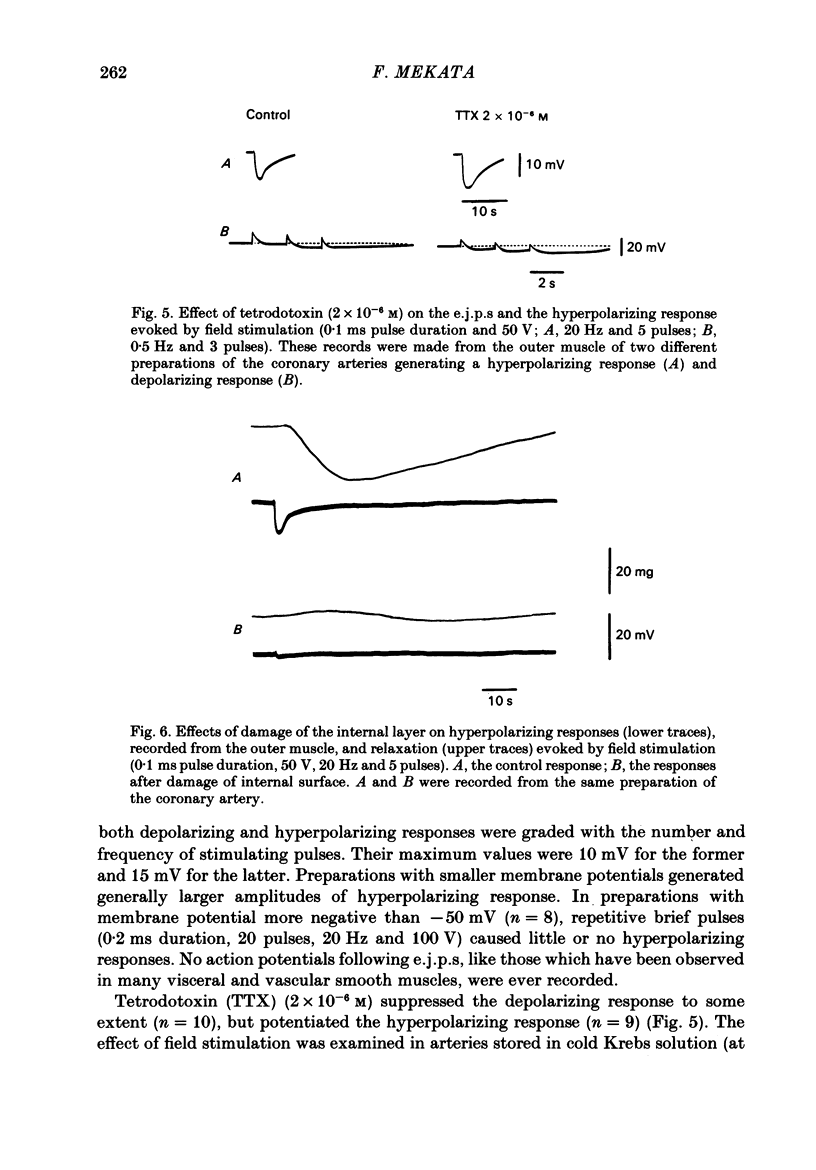
In monkey coronary arteries, outer and inner muscle had a similar resting potential (-39.5 and -40.0 mV). Both showed strong outward-going rectification, with no regenerative depolarization, on injection of depolarizing current. The depolarization spread electrotonically in all directions, particularly around the vessel wall. Hyperpolarization up to -45 mV by injection of constant current caused relaxation. Depolarization caused contraction. Pulses of field stimulation caused a brief depolarization which was reduced by tetrodotoxin or by stripping of the adventitia. They also caused a prolonged hyperpolarization which was not prevented by either, but was prevented by rubbing of the endothelium. The hyperpolarization in response to field stimulation therefore appears to result from electrically stimulated release of a substance from endothelial cells. Relaxation accompanied this hyperpolarization. It was twice the size of the relaxation produced by a similar hyperpolarization due to constant injection. Isoprenaline also produced hyperpolarization, and relaxation five times that seen with a similar hyperpolarization induced by direct current. Hyperpolarization appears to be an important, but not the only, mediator of relaxation induced in this artery both by endothelial cells and by beta-adrenergic stimulation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Properties of the inhibitory potential of smooth muscle as observed in the response to field stimulation of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):299–315. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung D. W. Spontaneous and evoked excitatory junction potentials in rat tail arteries. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:449–459. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks T. M., Angus J. A. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of coronary arteries by noradrenaline and serotonin. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):627–630. doi: 10.1038/305627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Heterogeneous behavior of the canine arterial and venous wall. Importance of the endothelium. Circ Res. 1982 Oct;51(4):439–447. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Surprenant A. M. Some properties of the excitatory junction potentials recorded from saphenous arteries of rabbits. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:337–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Effects of acetylcholine and catecholamines on the smooth muscle cell of the porcine coronary artery. J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:595–611. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Nitroglycerine and catecholamine actions on smooth muscle cells of the canine coronary artery. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:171–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keatinge W. R. Electrical and mechanical responses of vascular smooth muscle to vasodilator agents and vasoactive polypeptides. Circ Res. 1966 Jun;18(6):641–649. doi: 10.1161/01.res.18.6.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Effects of acetylcholine on the smooth muscle cell of isolated main coronary artery of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:119–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Current spread in the smooth muscle of the rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(1):143–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Different electrical responses of outer and inner muscle of rabbit carotid artery to noradrenaline and nerves. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:589–598. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Electrical current-induced contraction in the smooth muscle of the rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:149–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. Electrophysiological studies of the smooth muscle cell membrane of the rabbit common carotid artery. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Jun;57(6):738–751. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.6.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


