Abstract
Airway smooth muscle cells from canine trachealis muscle were dispersed by treatment with collagenase and elastase. Cells were identified as smooth muscle by their binding of anti-smooth muscle gamma-isoactin monoclonal antibodies and by their contraction in response to acetylcholine. The patch-clamp technique was used to study single channel currents in cell-attached and isolated patches of membrane. The most common single channel currents had a conductance of 266 +/- 12 pS (mean +/- S.D., n = 7) in symmetrical 135 mM-K solutions. The reversal potential of the channel was unaltered by large chemical gradients for Cl, Na and Ca and was determined exclusively by the chemical K gradient. Thus, the channel is highly selective for K. In both cell-attached and isolated patches of membrane, depolarization increased the frequency of channel opening and the duration of the open state. In isolated patches of membrane, increasing [Ca] on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane from 10(-8) to 10(-6) M increased both the frequency of channel opening and the duration of the open state. Tetraethylammonium, tetramethylammonium, or Cs (10 mM) on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane caused a voltage-dependent decrease in conductance of the open channel while having no obvious effect on channel kinetics. These blocks were completely reversible. Ba (10 mM) on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane slightly decreased inward currents and completely blocked outward currents through the channel. External Ba (10 mM) caused a voltage-dependent decrease in inward current. External tetraethylammonium (10 mM) completely blocked single channel currents.
Full text
PDF



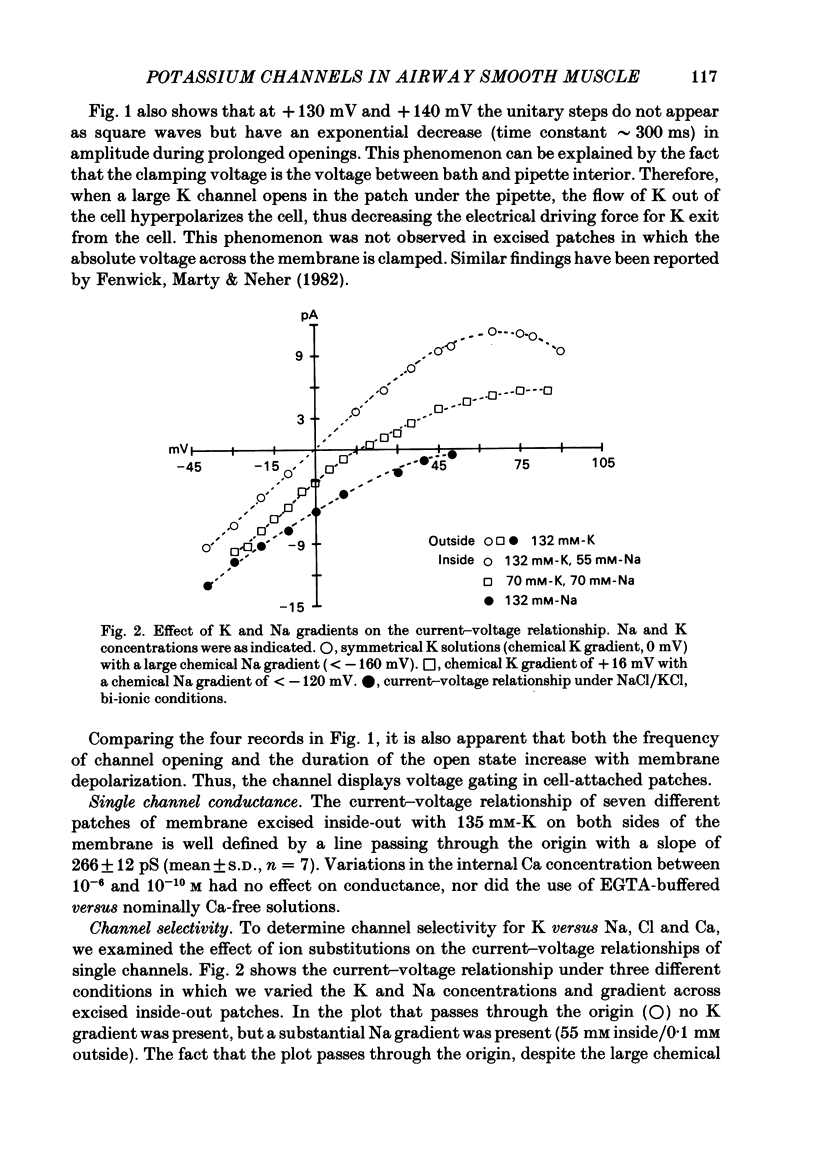
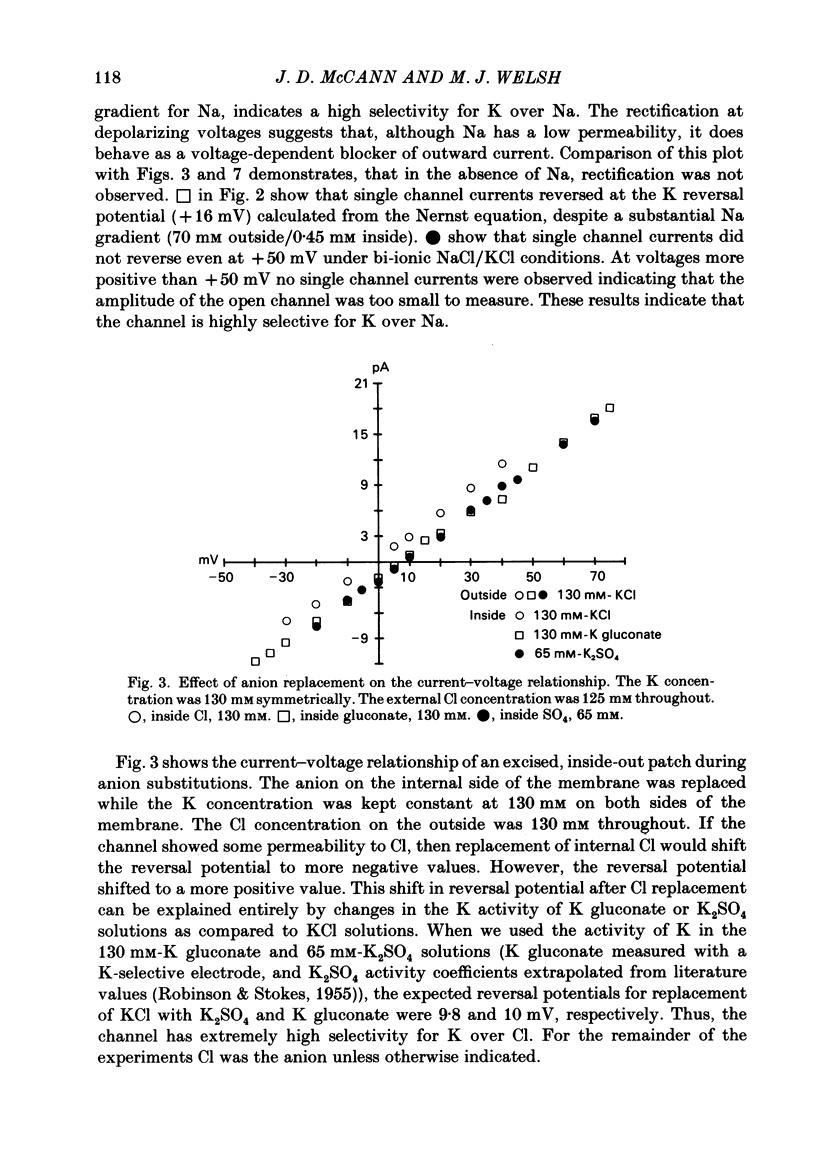
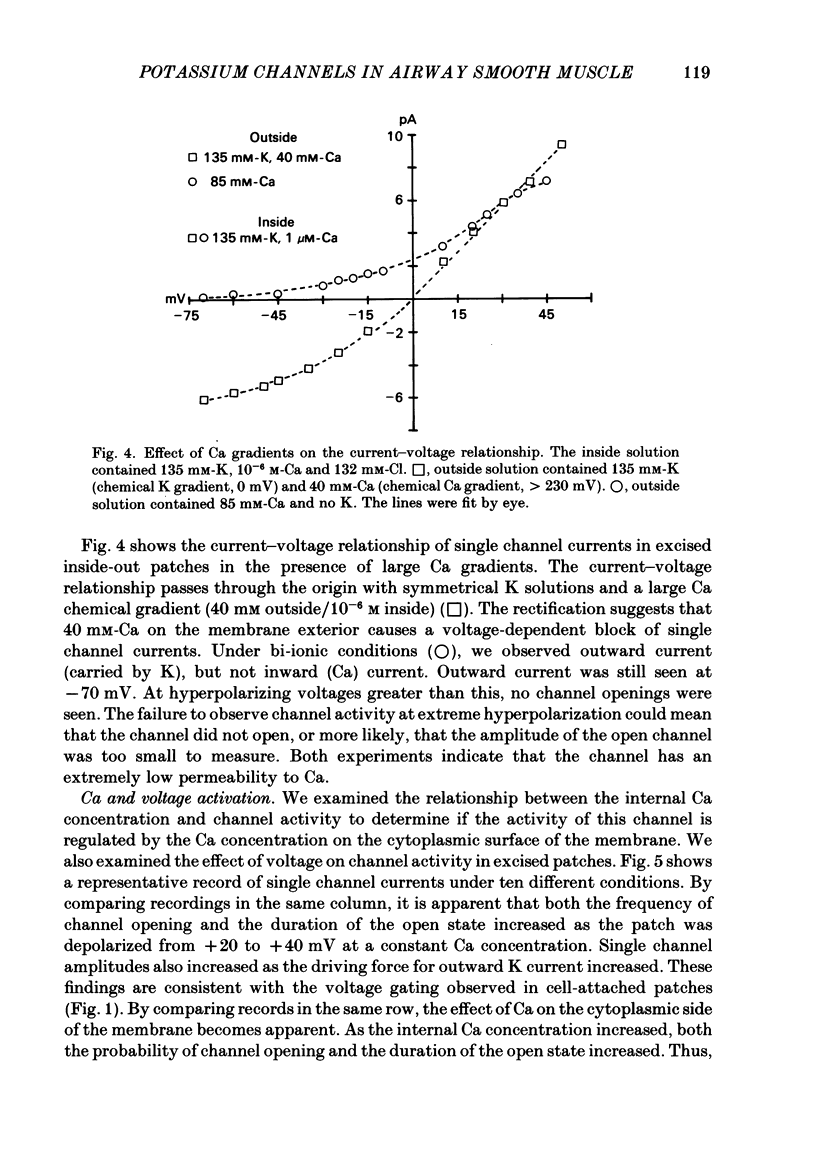

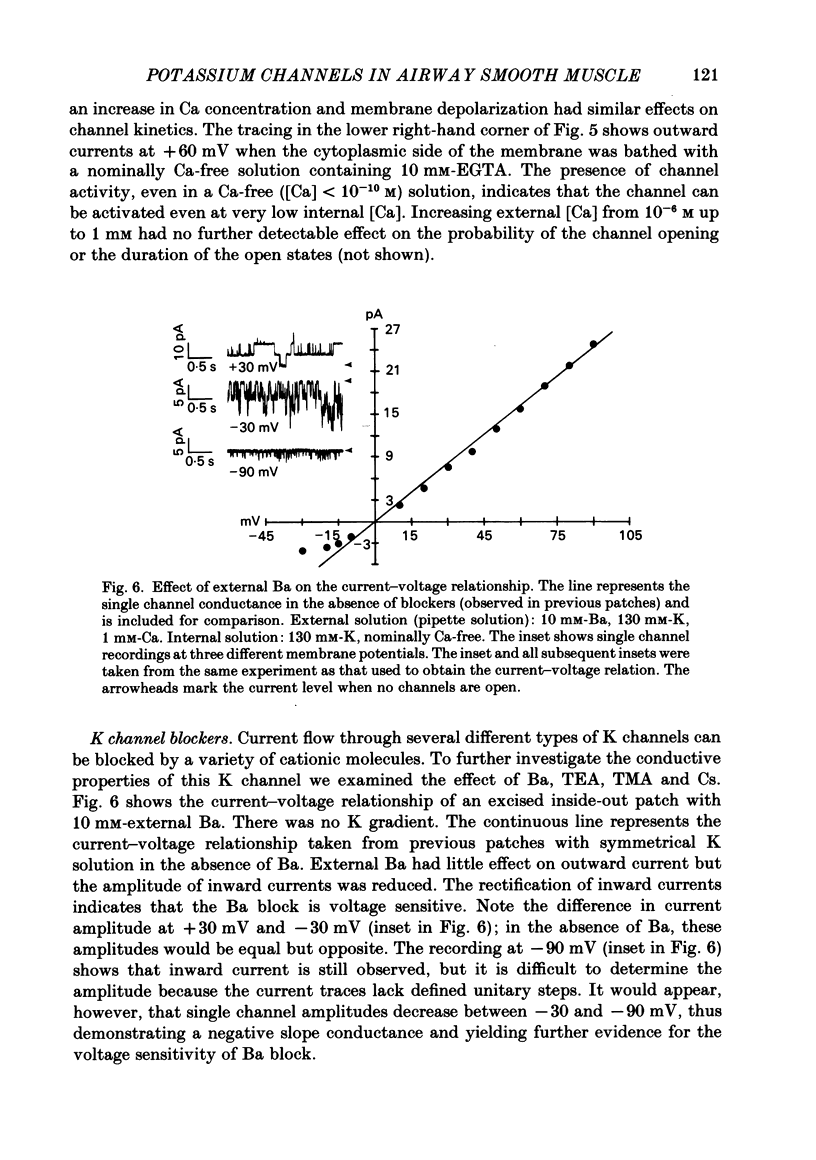
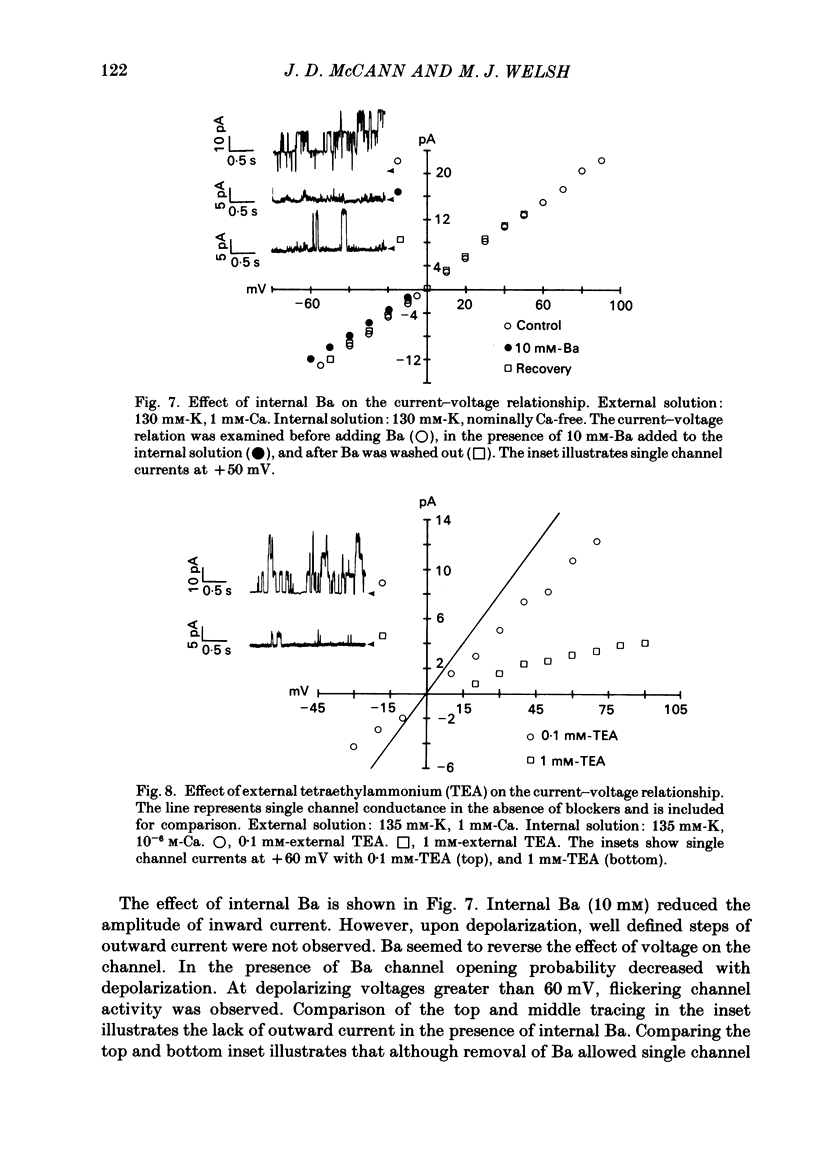
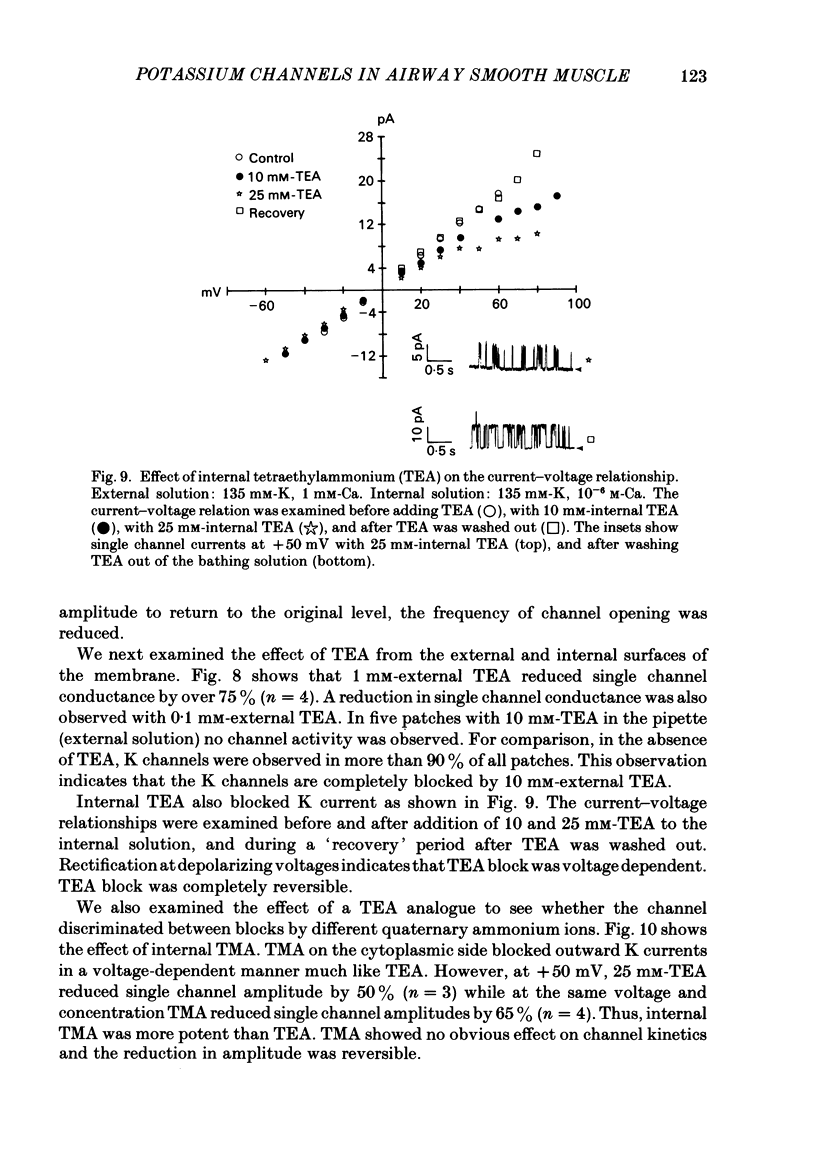
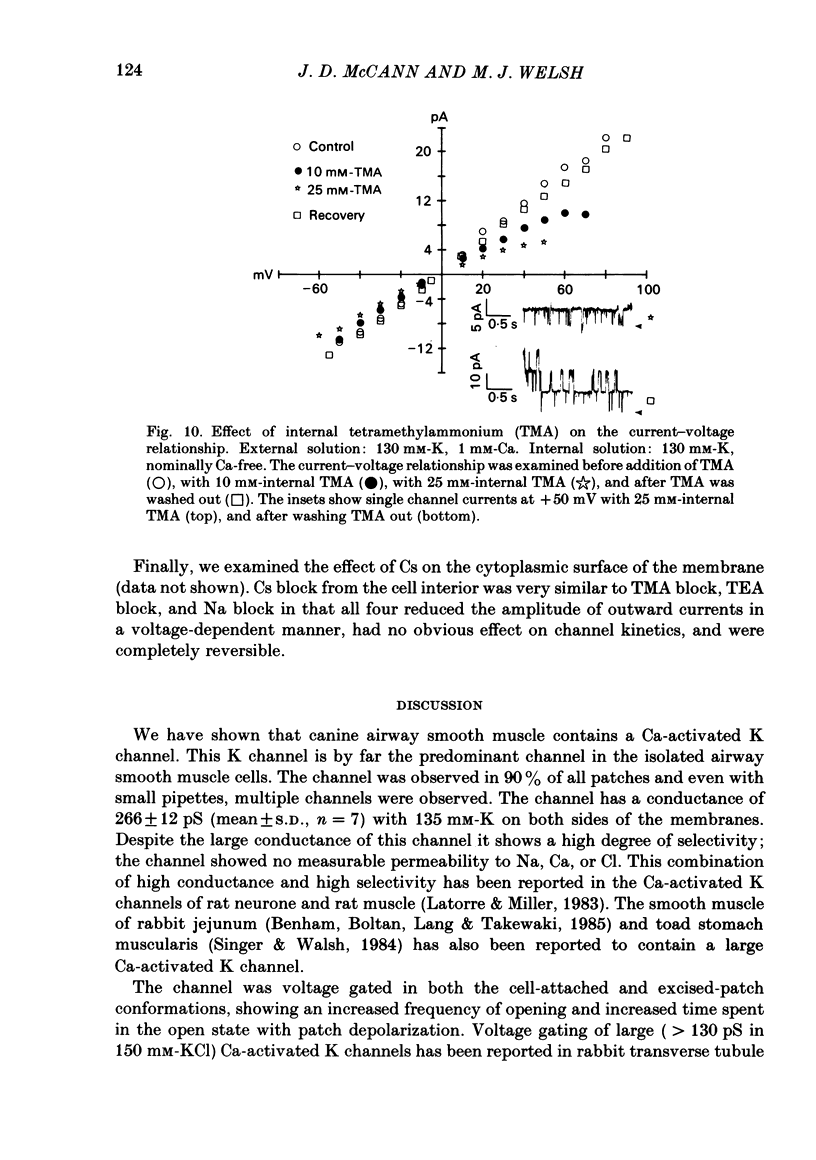



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., Takewaki T. The mechanism of action of Ba2+ and TEA on single Ca2+-activated K+ -channels in arterial and intestinal smooth muscle cell membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Feb;403(2):120–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00584088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Miller C. Conduction and block by organic cations in a K+-selective channel from sarcoplasmic reticulum incorporated into planar phospholipid bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Apr;79(4):529–547. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Watanabe M. The effect of tetraethylammonium chloride on potassium permeability in the smooth muscle cell membrane of canine trachea. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. T. Excitation and contraction in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):263–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger E. A., Stephens N. L. Effect of tetraethylammonium on tonic airway smooth muscle: initiation of phasic electrical activity. Am J Physiol. 1975 Feb;228(2):633–636. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.2.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Vergara C., Hidalgo C. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama Y., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channel in baso-lateral acinar cell membranes of mammalian salivary glands. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):827–829. doi: 10.1038/302827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Boheim G. The gating of single calcium-dependent potassium channels is described by an activation/blockade mechanism. Biophys Struct Mech. 1982;9(1):35–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00536014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Magleby K. L., Barrett J. N. Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):471–474. doi: 10.1038/293471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. J., Walsh J. V. Large conductance ca-activated k channels in smooth muscle cell membrane: reduction in unitary currents due to internal na ions. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):68–70. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(84)84112-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Latorre R. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar bilayers. Evidence for a Ca2+ and Ba2+ blockade. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):543–568. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Conduction, Blockade and Gating in a Ca -activated K Channel Incorporated into Planar Lipid Bilayers. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84114-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Lecar H., Adler M. Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84522-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Ionic permeation and blockade in Ca2+-activated K+ channels of bovine chromaffin cells. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Aug;84(2):157–186. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


