Abstract
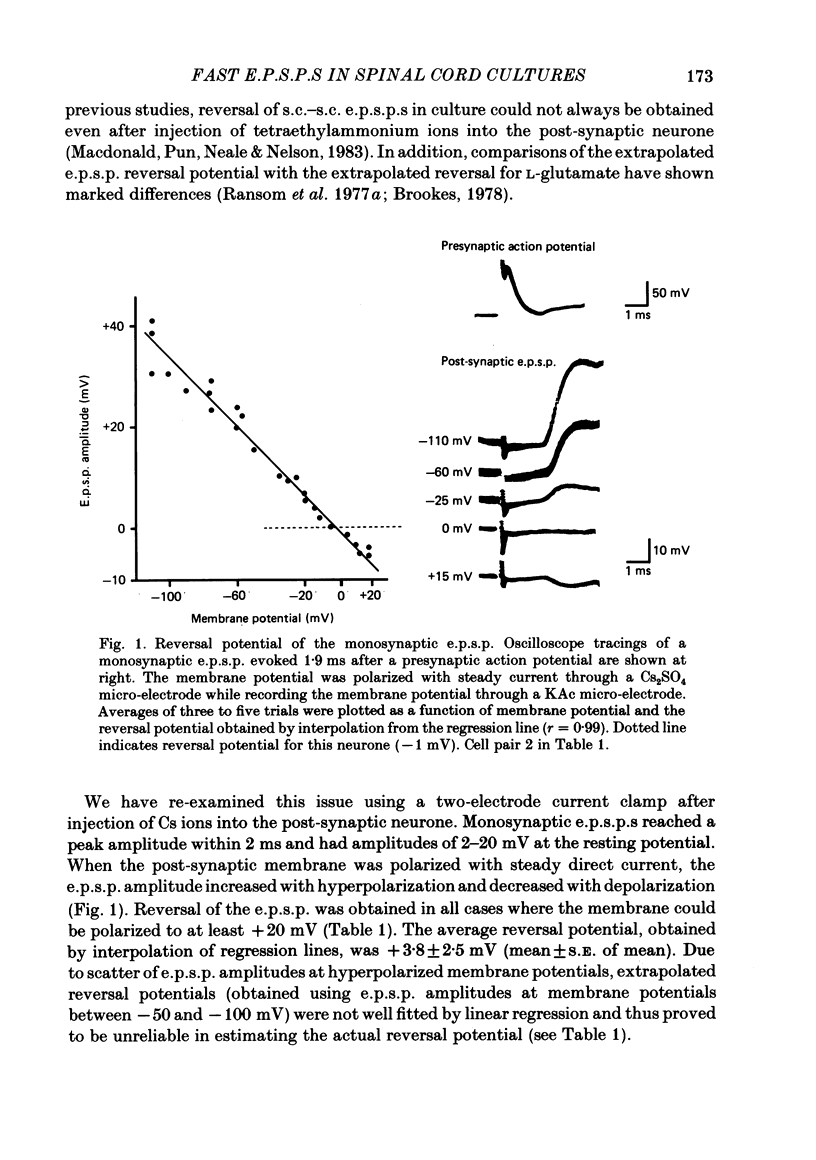
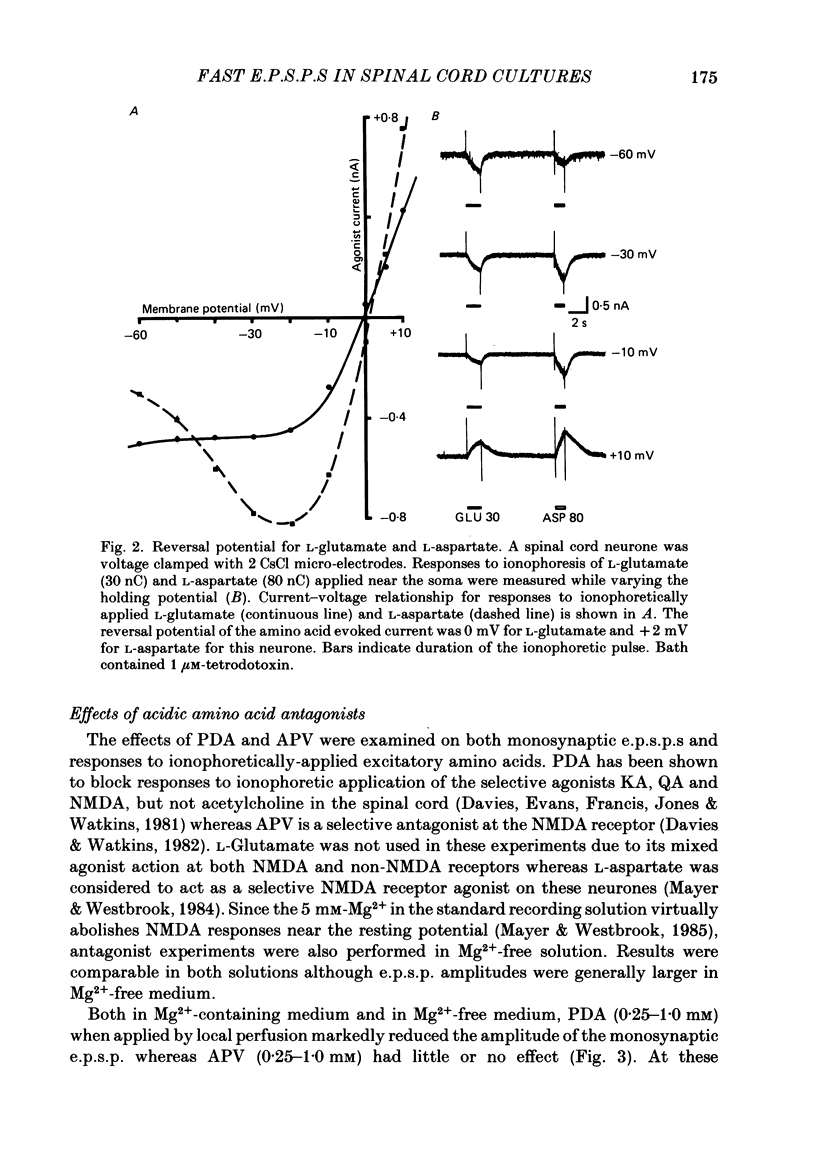
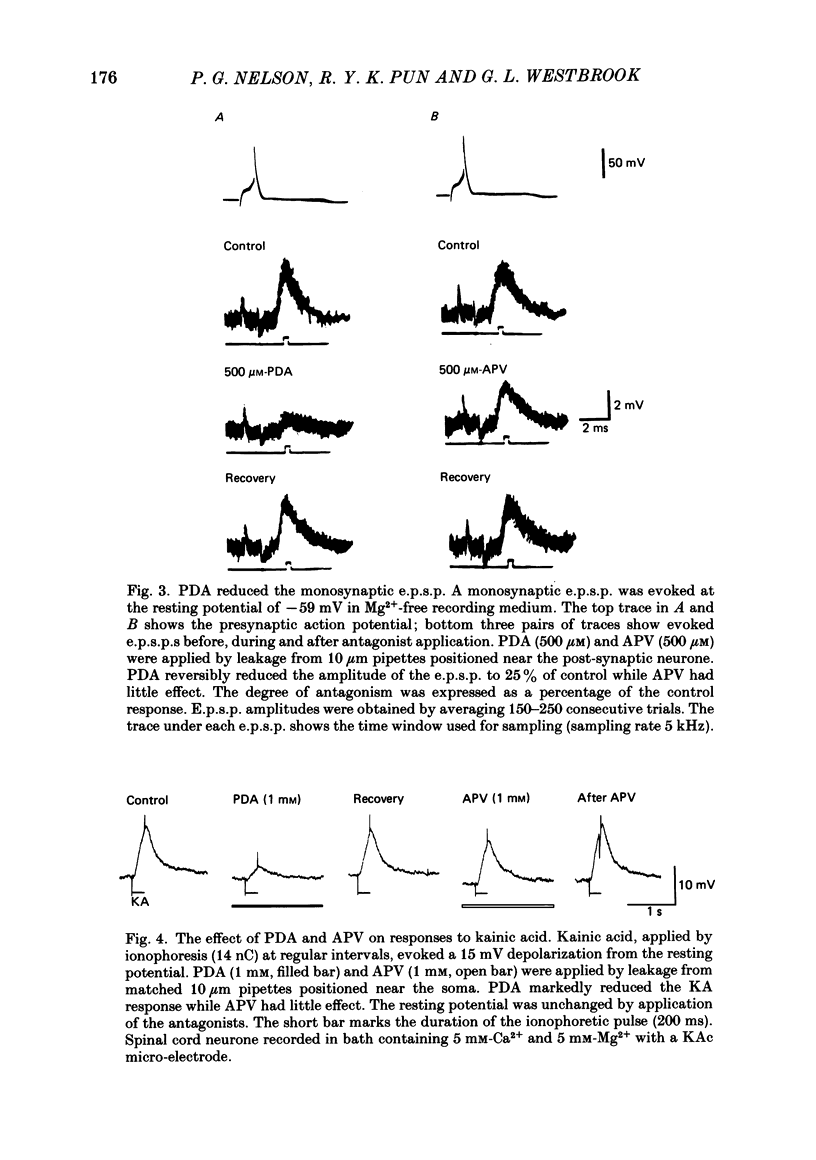
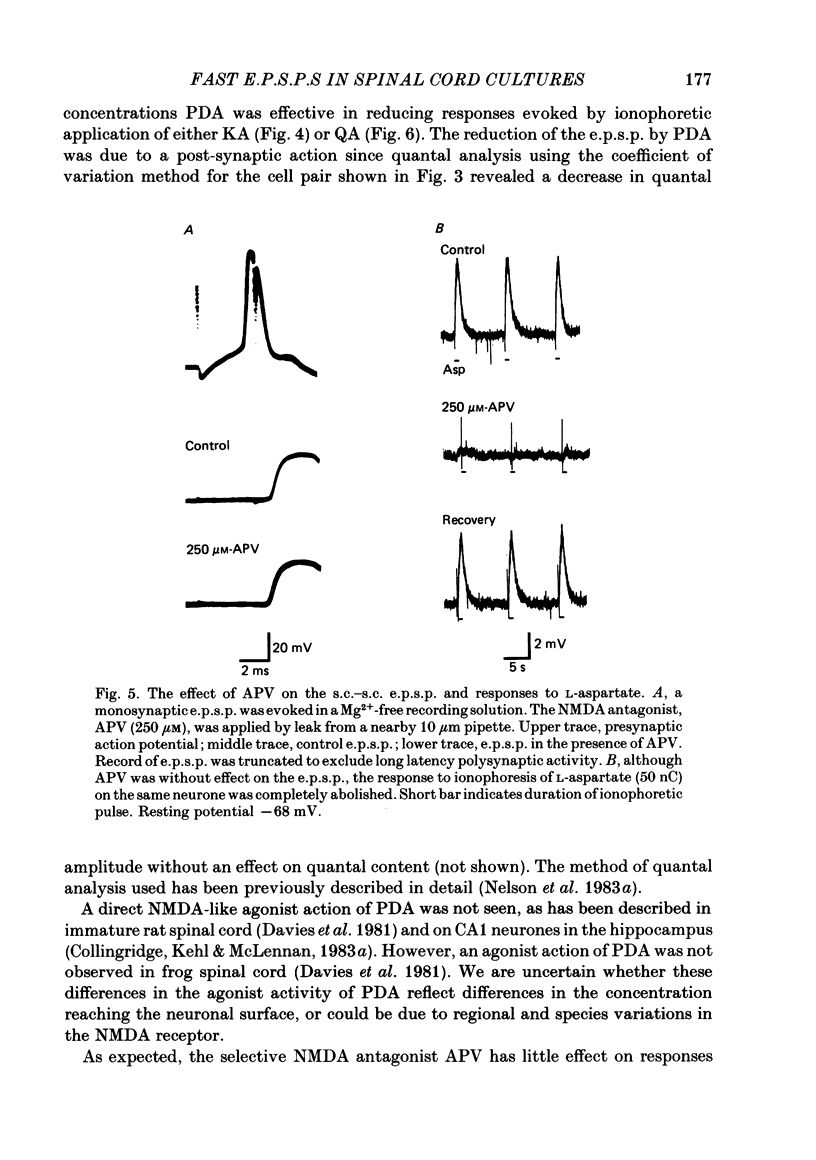
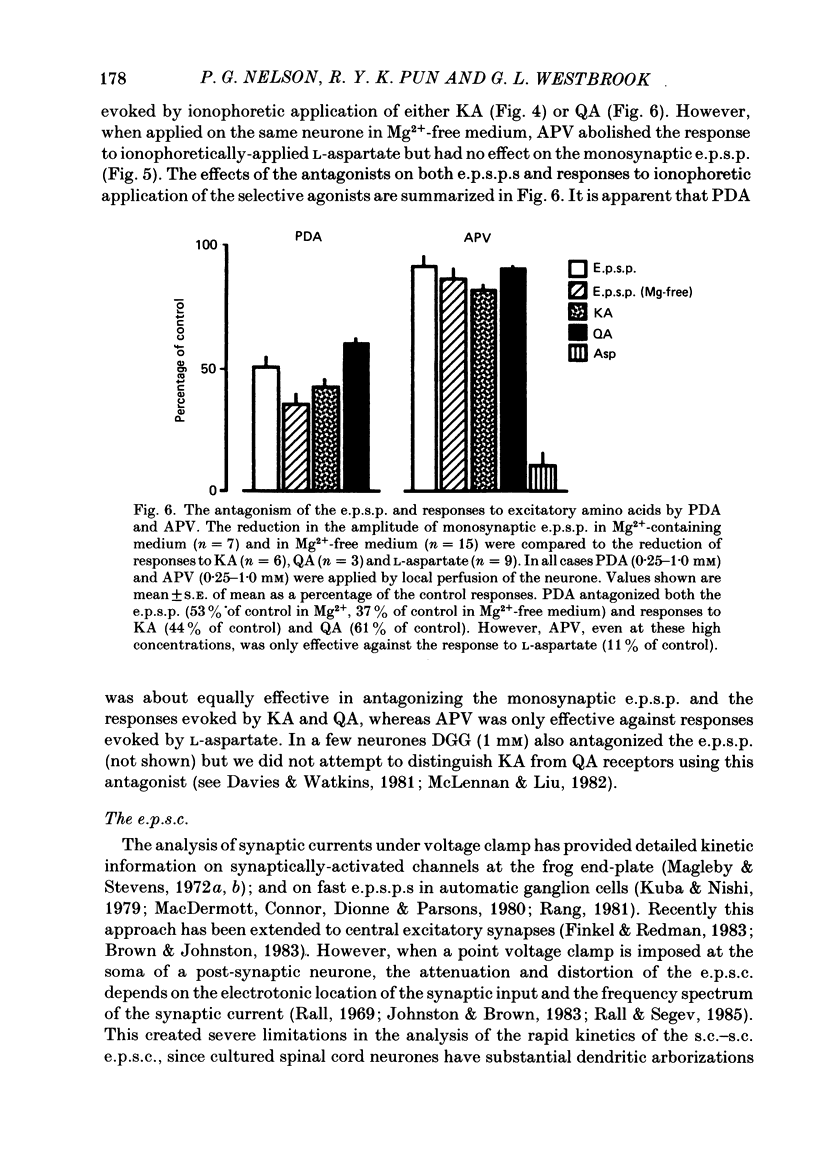
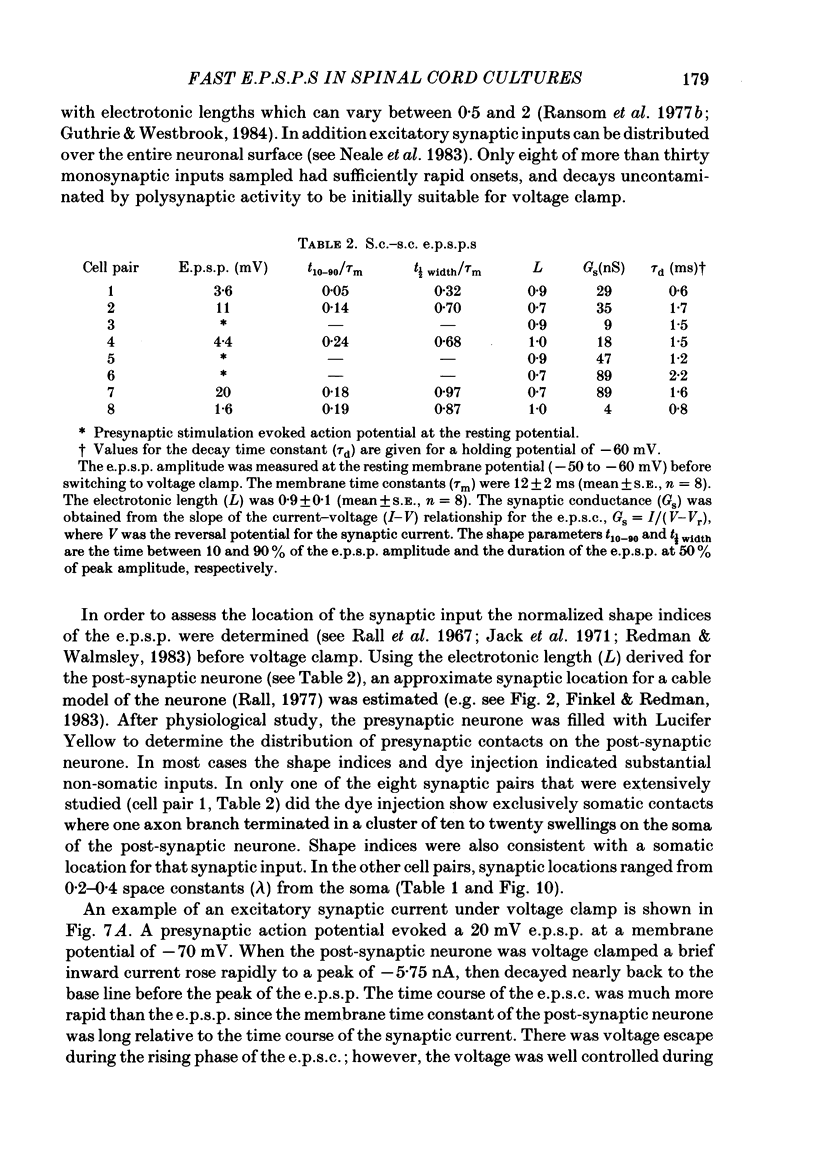
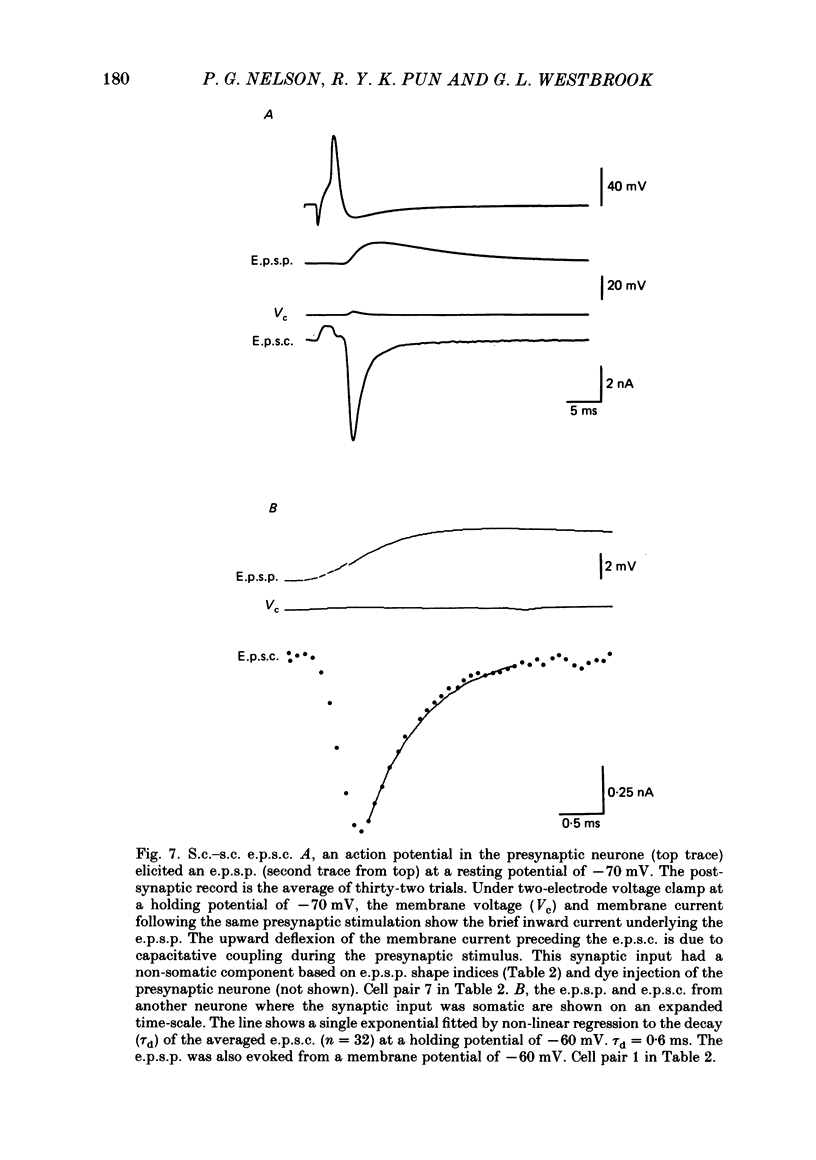
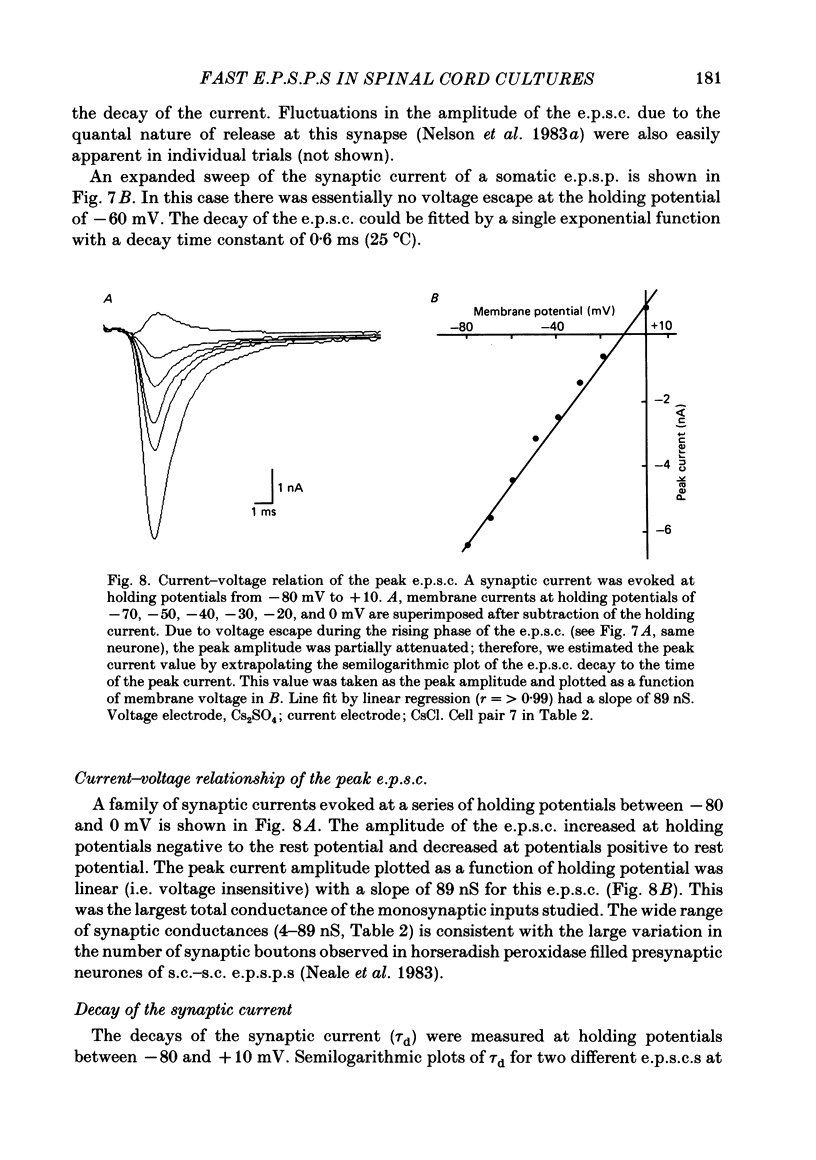
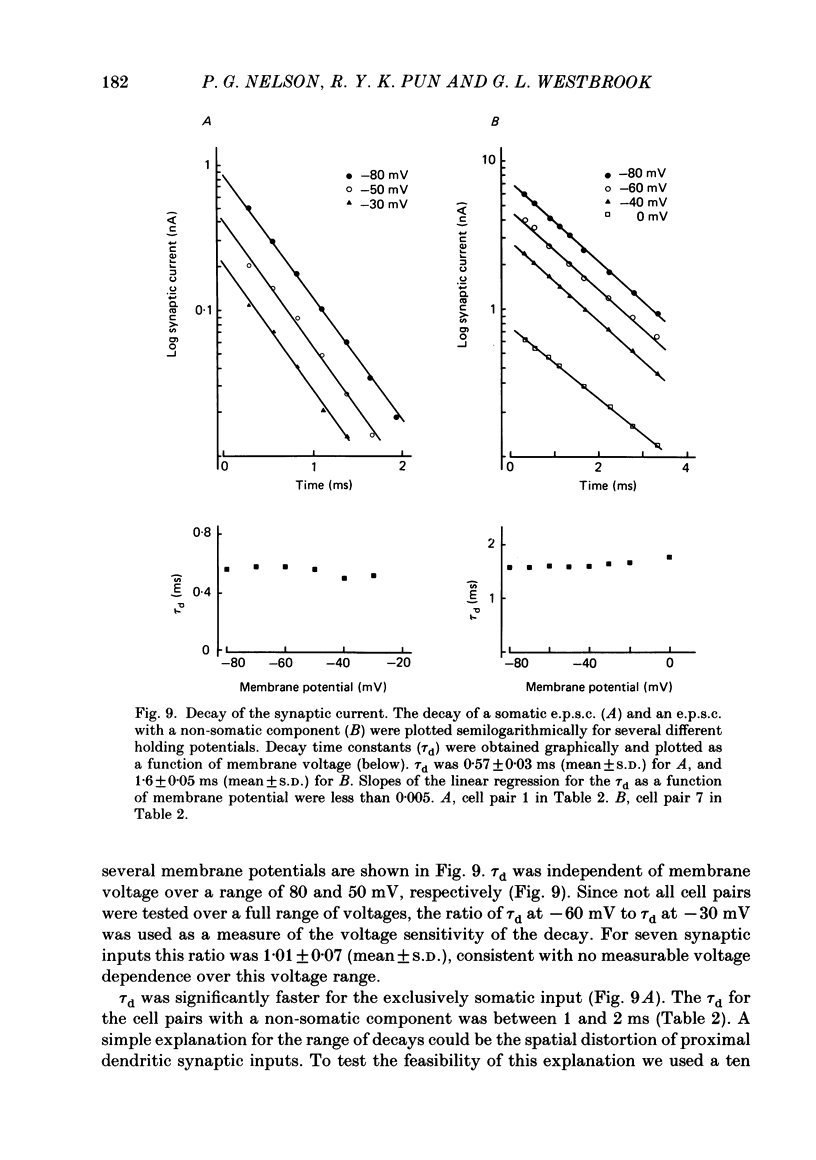
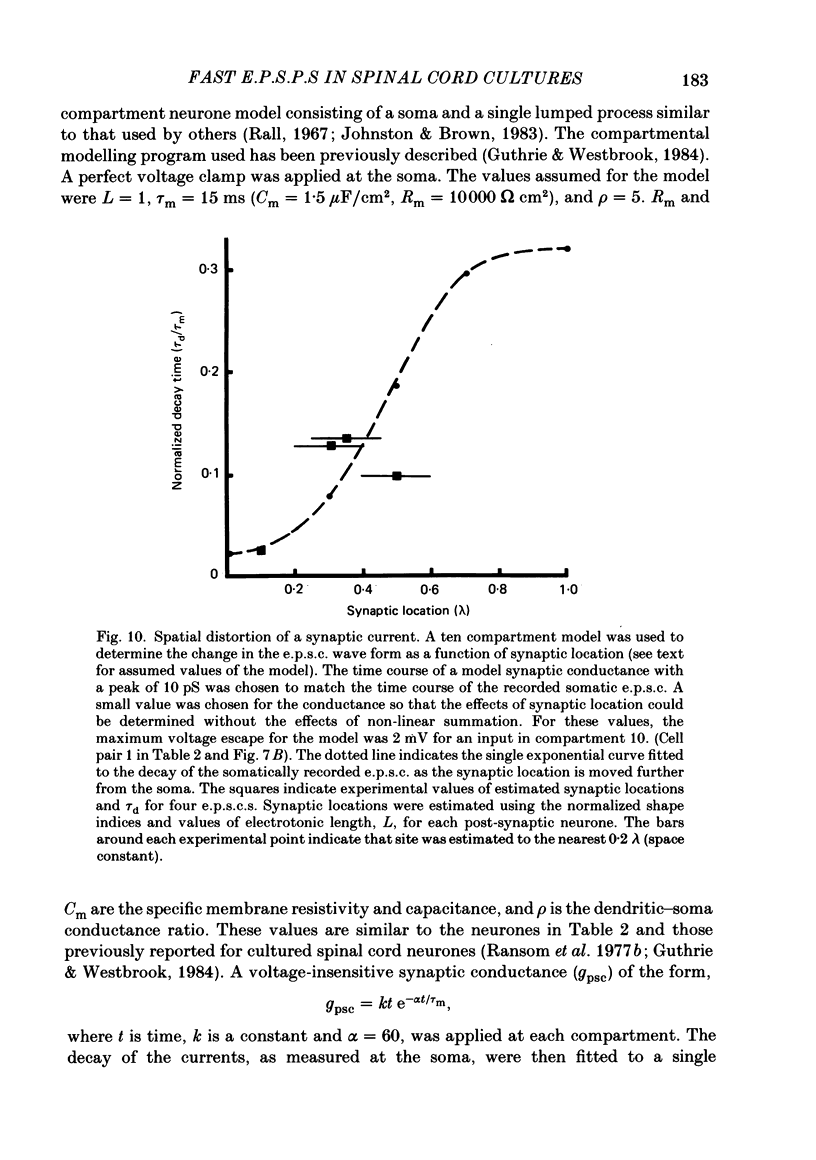
Fast monosynaptic excitatory post-synaptic potentials between spinal cord neurones in cell culture (s.c.-s.c. e.p.s.p.s) were studied with current-clamp and two-electrode voltage-clamp methods. The reversal potential, response to acidic amino acid antagonists, and behaviour of the synaptic current were examined. The amplitude of the e.p.s.p. increased with membrane potential hyperpolarization and decreased with depolarization. The reversal potential of the e.p.s.p. was +3.8 +/- 2.5 mV (mean +/- S.E. of mean). The reversal potential for responses to ionophoretically applied L-glutamate and L-aspartate was also near 0 mV. The acidic amino acid antagonist, cis-2,3-piperidine dicarboxylic acid (PDA, 0.25-1.0 mM) reversibly antagonized the monosynaptic e.p.s.p.s as well as responses to kainate (KA) or quisqualate (QA). The selective N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist, (+/-) 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV), had little effect on either the monosynaptic e.p.s.p.s or responses to QA or KA at concentrations that abolished responses to L-aspartate. Under voltage clamp, the peak synaptic current (e.p.s.c.) was linearly related to the membrane potential, increasing in amplitude with hyperpolarization and decreasing with depolarization from the resting potential. The decay of a somatic e.p.s.c. was well fitted by a single exponential function with a time constant of 0.6 ms at 25 degrees C. E.p.s.c.s which had proximal dendritic locations had decay time constants of 1-2 ms. The decay time constant was voltage-insensitive between -80 and +10 mV. We suggest that an acidic amino acid receptor other than that for NMDA mediates excitatory transmission at the s.c.-s.c. synapse; and that the underlying conductance mechanism is voltage insensitive with an estimated mean channel lifetime of less than 1 ms.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. The permeability of endplate channels to monovalent and divalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):493–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R. Drug blockade of open end-plate channels. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(3):531–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R. Voltage jump analysis of procaine action at frog end-plate. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):291–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwyl R. The effect of foreign cations, pH and pharmacological agents on the ionic permeability of an excitatory glutamate synapse. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):389–404. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcar V. J., Johnston G. A. The structural specificity of the high affinity uptake of L-glutamate and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2657–2666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. H., Johnston D. Voltage-clamp analysis of mossy fiber synaptic input to hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):487–507. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. The antagonism of amino acid-induced excitations of rat hippocampal CA1 neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:19–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Forda S., Kelly J. S. Blockade of amino acid-induced depolarizations and inhibition of excitatory post-synaptic potentials in rat dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:627–640. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Forda S., Kelly J. S. The reversal potential of excitatory amino acid action on granule cells of the rat dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:327–342. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Ogden D. C. Ion channels activated by L-glutamate and GABA in cultured cerebellar neurons of the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 May 22;224(1236):367–373. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale N., Roberts A. Dual-component amino-acid-mediated synaptic potentials: excitatory drive for swimming in Xenopus embryos. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:35–59. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. Antagonism of excitatory amino acid-induced and synaptic excitation of spinal neurones by cis-2,3-piperidine dicarboxylate. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):1305–1307. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Actions of D and L forms of 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate and 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 11;235(2):378–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Differentiation of kainate and quisqualate receptors in the cat spinal cord by selective antagonism with gamma-D(and L)-glutamylglycine. Brain Res. 1981 Feb 9;206(1):172–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber D. S., Funch P. G., Korn H. Evidence that receptors mediating central synaptic potentials extend beyond the postsynaptic density. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Matus A. Selective association of N-methyl aspartate and quisqualate types of L-glutamate receptor with brain postsynaptic densities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6876–6880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertuck H. C., Salpeter M. M. Quantitation of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by electron microscope autoradiography after 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding at mouse neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):144–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S., Redman S. J. The synaptic current evoked in cat spinal motoneurones by impulses in single group 1a axons. J Physiol. 1983 Sep;342:615–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney A. M., Rang H. P. The channel-blocking action of methonium compounds on rat submandibular ganglion cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):623–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz J. J., Langmoen I. A. Excitation of hippocampal pyramidal cells by glutamate in the guinea-pig and rat. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:317–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henn F. A., Goldstein M. N., Hamberger A. Uptake of the neurotransmitter candidate glutamate by glia. Nature. 1974 Jun 14;249(458):663–664. doi: 10.1038/249663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Miller S., Porter R., Redman S. J. The time course of minimal excitory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurones by group Ia afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Jessell T. M. Synaptic transmission between dorsal root ganglion and dorsal horn neurons in culture: antagonism of monosynaptic excitatory postsynaptic potentials and glutamate excitation by kynurenate. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2281–2289. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02281.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Brown T. H. Interpretation of voltage-clamp measurements in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Aug;50(2):464–486. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.2.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Nishi S. Characteristics of fast excitatory postsynaptic current in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Effects of membrane potential, temperature and Ca ions. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Jan 31;378(3):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00592737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Connor E. A., Dionne V. E., Parsons R. L. Voltage clamp study of fast excitatory synaptic currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jan;75(1):39–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Porietis A. V. DL-quisqualic and L-aspartic acids activate separate excitatory conductances in cultured spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Aug 5;245(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Porietis A. V., Wojtowicz J. M. L-Aspartic acid induces a region of negative slope conductance in the current-voltage relationship of cultured spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 8;237(1):248–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. L., Pun R. Y., Neale E. A., Nelson P. G. Synaptic interactions between mammalian central neurons in cell culture. I. Reversal potential for excitatory postsynaptic potentials. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Jun;49(6):1428–1441. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.6.1428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. A quantitative description of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):173–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magleby K. L., Stevens C. F. The effect of voltage on the time course of end-plate currents. J Physiol. 1972 May;223(1):151–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. A voltage-clamp analysis of inward (anomalous) rectification in mouse spinal sensory ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:19–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Mixed-agonist action of excitatory amino acids on mouse spinal cord neurones under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:29–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The action of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid on mouse spinal neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:65–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan H., Liu J. The action of six antagonists of the excitatory amino acids on neurones of the rat spinal cord. Exp Brain Res. 1982;45(1-2):151–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00235774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale E. A., Macdonald R. L., Nelson P. G. Intracellular horseradish peroxidase injection for correlation of light and electron microscopic anatomy with synaptic physiology of cultured mouse spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1978 Aug 25;152(2):265–282. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90255-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale E. A., Nelson P. G., Macdonald R. L., Christian C. N., Bowers L. M. Synaptic interactions between mammalian central neurons in cell culture. III. Morphophysiological correlates of quantal synaptic transmission. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Jun;49(6):1459–1468. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.6.1459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Marshall K. C., Pun R. Y., Christian C. N., Sheriff W. H., Jr, Macdonald R. L., Neale E. A. Synaptic interactions between mammalian central neurons in cell culture. II. Quantal Analysis of EPSPs. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Jun;49(6):1442–1458. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.6.1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peet M. J., Leah J. D., Curtis D. R. Antagonists of synaptic and amino acid excitation of neurones in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 25;266(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puil E. S-Glutamate: its interactions with spinal neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Dec;228(3):229–322. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(81)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Smith T. G., Nelson P. G., Frank K. Dendritic location of synapses and possible mechanisms for the monosynaptic EPSP in motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1169–1193. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Distinguishing theoretical synaptic potentials computed for different soma-dendritic distributions of synaptic input. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1138–1168. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Time constants and electrotonic length of membrane cylinders and neurons. Biophys J. 1969 Dec;9(12):1483–1508. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86467-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Colquhoun D., Rang H. P. The action of ganglionic blocking drugs on the synaptic responses of rat submandibular ganglion cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):151–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08768.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The characteristics of synaptic currents and responses to acetylcholine of rat submandibular ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:23–55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. III. Neuronal chemosensitivity and its relationship to synaptic activity. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1163–1177. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Neale E., Henkart M., Bullock P. N., Nelson P. G. Mouse spinal cord in cell culture. I. Morphology and intrinsic neuronal electrophysiologic properties. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1132–1150. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S. Junctional mechanisms at group Ia synapses. Prog Neurobiol. 1979;12(1):33–83. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(79)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman S., Walmsley B. The time course of synaptic potentials evoked in cat spinal motoneurones at identified group Ia synapses. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:117–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., West D. C., Lodge D. An N-methylaspartate receptor-mediated synapse in rat cerebral cortex: a site of action of ketamine? Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):479–481. doi: 10.1038/313479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C. Pharmacology of excitatory amino acid transmitters. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;29:205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigström H., Gustafsson B. A possible correlate of the postsynaptic condition for long-lasting potentiation in the guinea pig hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Feb 24;44(3):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


