Abstract
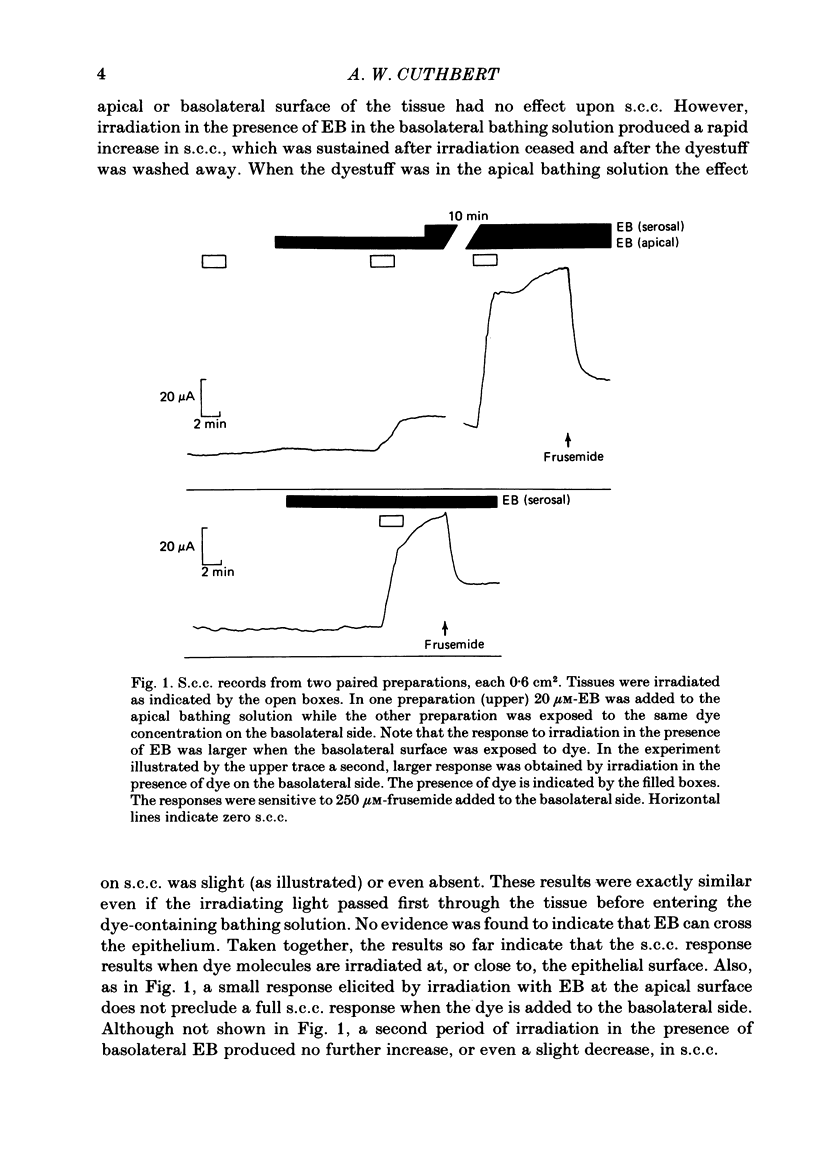
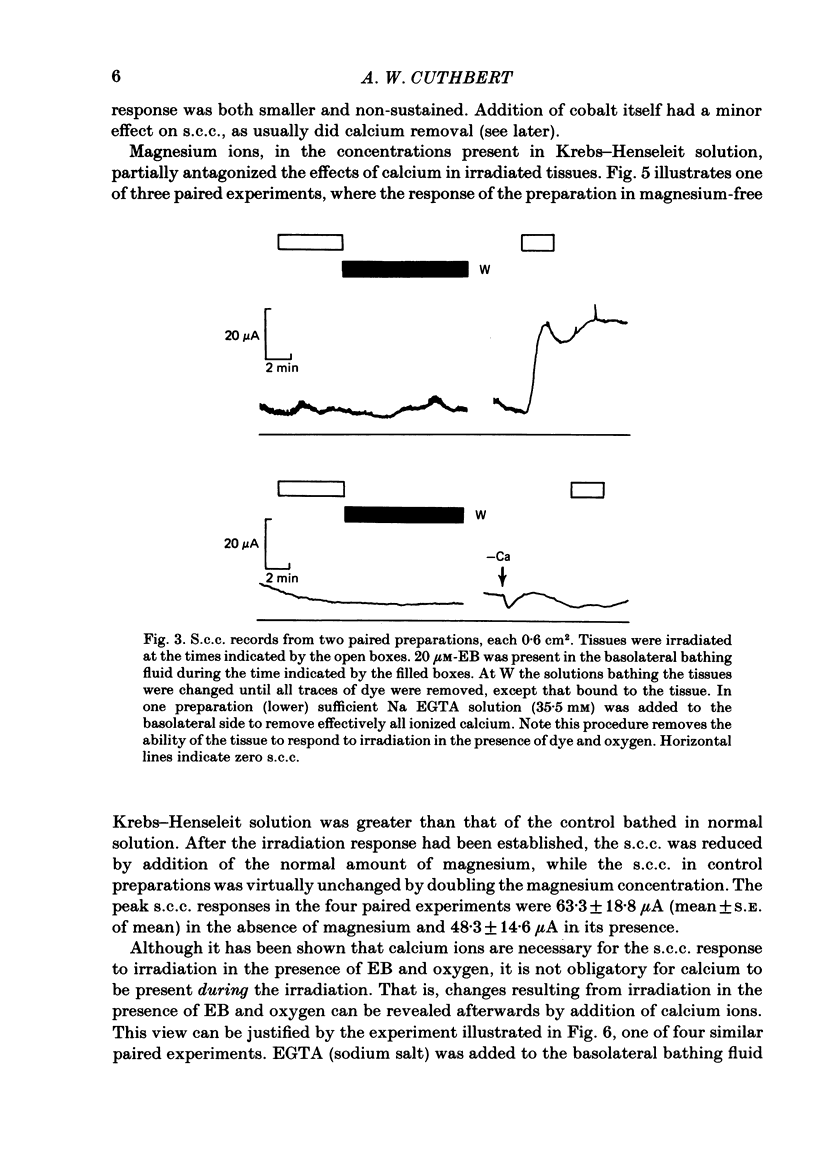
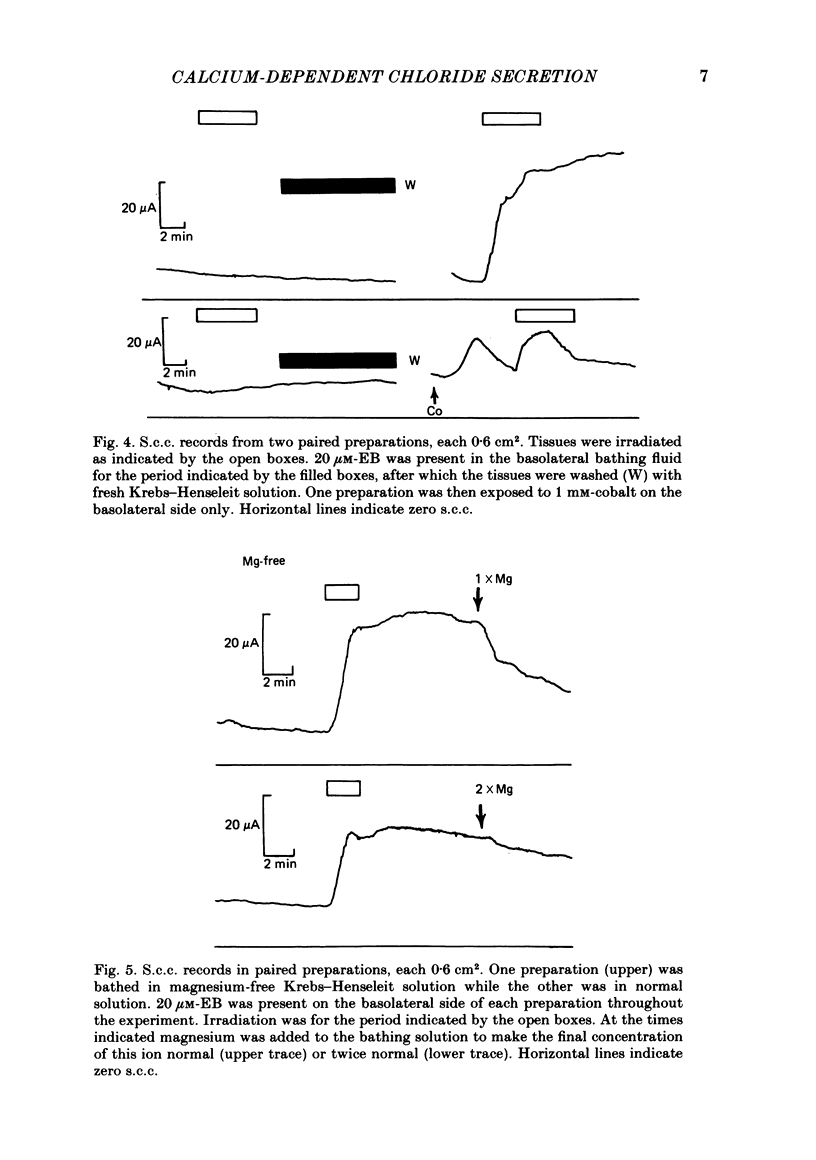
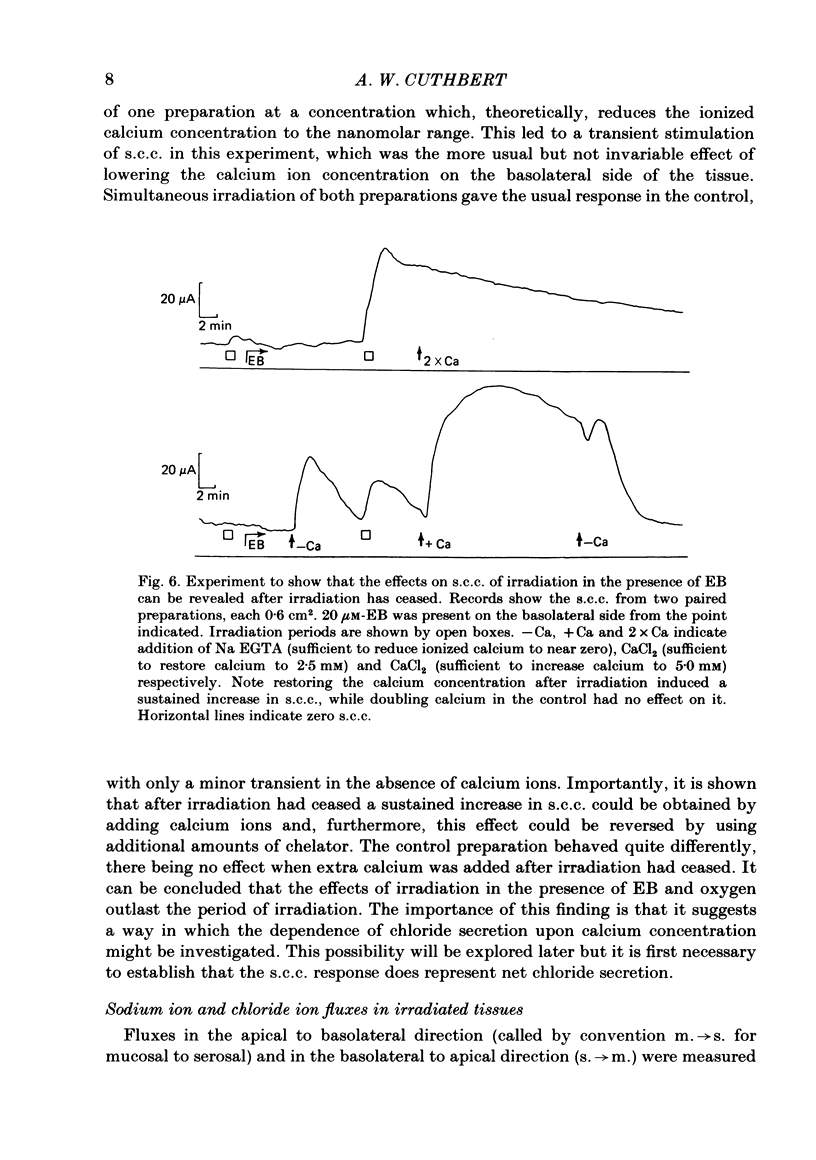
Epithelia, dissected from the descending rat colon, were studied under short-circuit conditions in Ussing chambers. The latter were modified to accept flexible light guides, so that the tissue could be irradiated, with white light, normal to its surface. Irradiation alone had no effect on short-circuit current (s.c.c.). In the presence of erythrosine B (which by itself had no effect on the s.c.c.) on the basolateral side of the tissue, irradiation produced a substantial increase in s.c.c.; this increase was sustained after irradiation had ceased and the dye had been washed away. The photodynamic effect of erythrosine B required the presence of oxygen in the bathing solution. Also calcium was essential for the s.c.c. response to occur. Thus, irradiation in the presence of the dye in the absence of calcium had no effect on s.c.c., but a s.c.c. increase could be revealed by subsequent addition of calcium after irradiation had ceased. Cobalt and magnesium ions antagonized the effect of calcium in the conditions described above. Ion flux measurements with 36Cl and 22Na showed that the photodynamic effect of erythrosine B abolished net sodium absorption and reversed net chloride absorption to secretion. The data are consistent with abolition of electroneutral sodium chloride absorption and the stimulation of electrogenic chloride secretion to an extent equivalent to the s.c.c. responses. Using calcium-containing buffers it was possible to compare the s.c.c. responses at low, known ionized calcium concentrations with the maximal chloride secretory effect following photodynamic activation. Chloride secretion was half-maximally activated when the basolateral bathing fluid contained 1 microM-ionized calcium and after the basolateral face of the tissue had been permeabilized by the photodynamic action of erythrosine B. The relation between ionized calcium concentration in the basolateral fluid and the chloride secretory response was steep.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augustine G. J., Levitan H. Presynaptic effect of Erythrosin B at the frog neuromuscular junction: ion and photon sensitivity. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:65–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Knight D. E. Calcium-dependent exocytosis in 'leaky' bovine adrenal medullary cells has a specific requirement for magnesium adenosine triphosphate [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:89P–89P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Knight D. E. Calcium-dependent exocytosis in bovine adrenal medullary cells with leaky plasma membranes. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):620–622. doi: 10.1038/276620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton J. E., Field M. Ca ionophore-stimulated ion secretion in rabbit ileal mucosa: relation to actions of cyclic 3',5'-AMP and carbamylcholine. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 30;35(2):159–173. doi: 10.1007/BF01869947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges R. J., Nell G., Rummel W. Influence of vasopressin and calcium on electrolyte transport across isolated colonic mucosa of the rat. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:463–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase H. S., Jr, Al-Awqati Q. Regulation of the sodium permeability of the luminal border of toad bladder by intracellular sodium and calcium: role of sodium-calcium exchange in the basolateral membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jun;77(6):693–712. doi: 10.1085/jgp.77.6.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Halushka P. V., Margolius H. S., Spayne J. A. Mediators of the secretory response to kinins. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):597–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10798.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Halushka P. V., Margolius H. S., Spayne J. A. Role of calcium ions in kinin-induced chloride secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):587–595. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Margolius H. S. Kinins stimulate net chloride secretion by the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;75(4):587–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W., Spayne J. A. Conversion of sodium channels to a form sensitive to cyclic AMP by component(s) from red cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;79(3):783–797. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A. Active chloride secretion by rabbit colon: calcium-dependent stimulation by ionophore A23187. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jun 30;35(2):175–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01869948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilundain A., Naftalin R. J. Role of Ca(2+)-dependent regulator protein in intestinal secretion. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):446–448. doi: 10.1038/279446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepka A. G., Grossweiner L. I. Photodynamic inactivation of lysozyme by eosin. Photochem Photobiol. 1973 Jul;18(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1973.tb06392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne-Saffran E., Kinne R. Localization of a calcium-stimulated ATPase in the basal-lateral plasma membranes of the proximal tubule of rat kidney cortex. J Membr Biol. 1974 Jul 12;17(3):263–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01870187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Mesler D. E. Photodynamic effects of erythrosine on the smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):555–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E., Mandel L. J. Cytosolic free calcium levels in rabbit proximal kidney tubules. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):C124–C128. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.1.C124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. New calcium indicators and buffers with high selectivity against magnesium and protons: design, synthesis, and properties of prototype structures. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2396–2404. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


