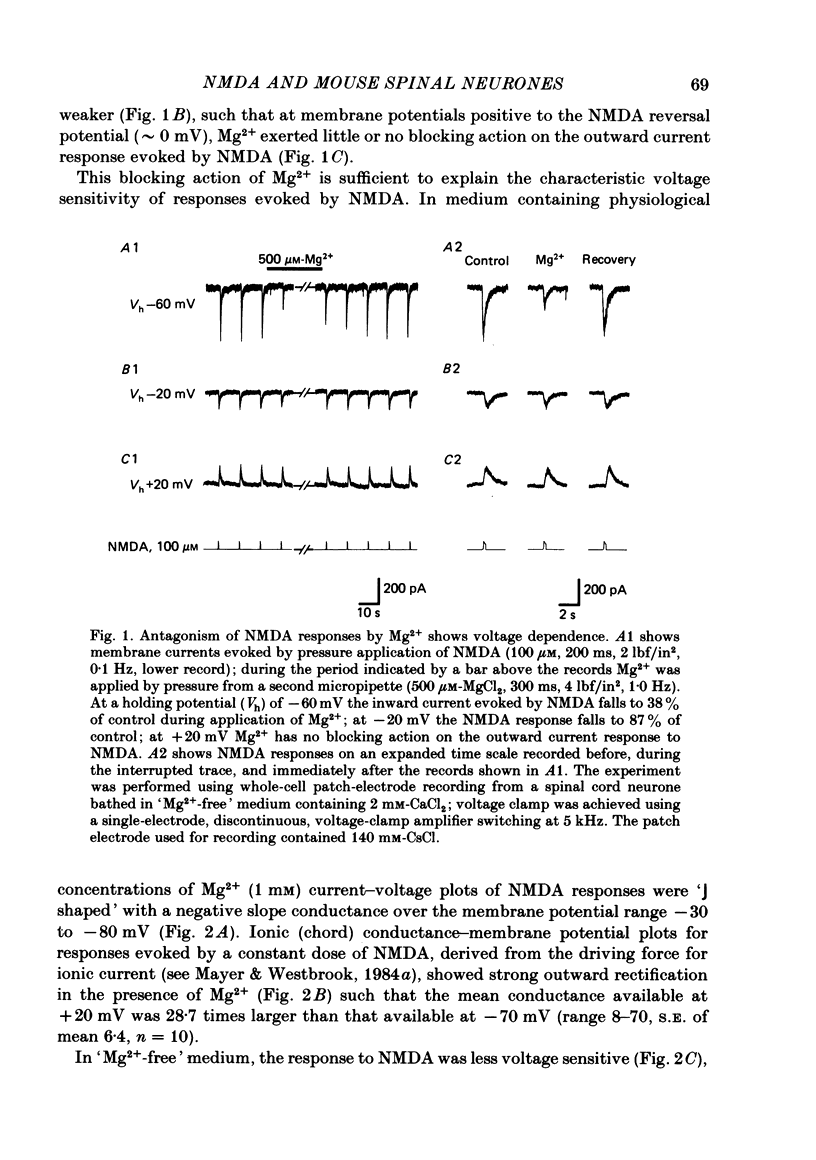
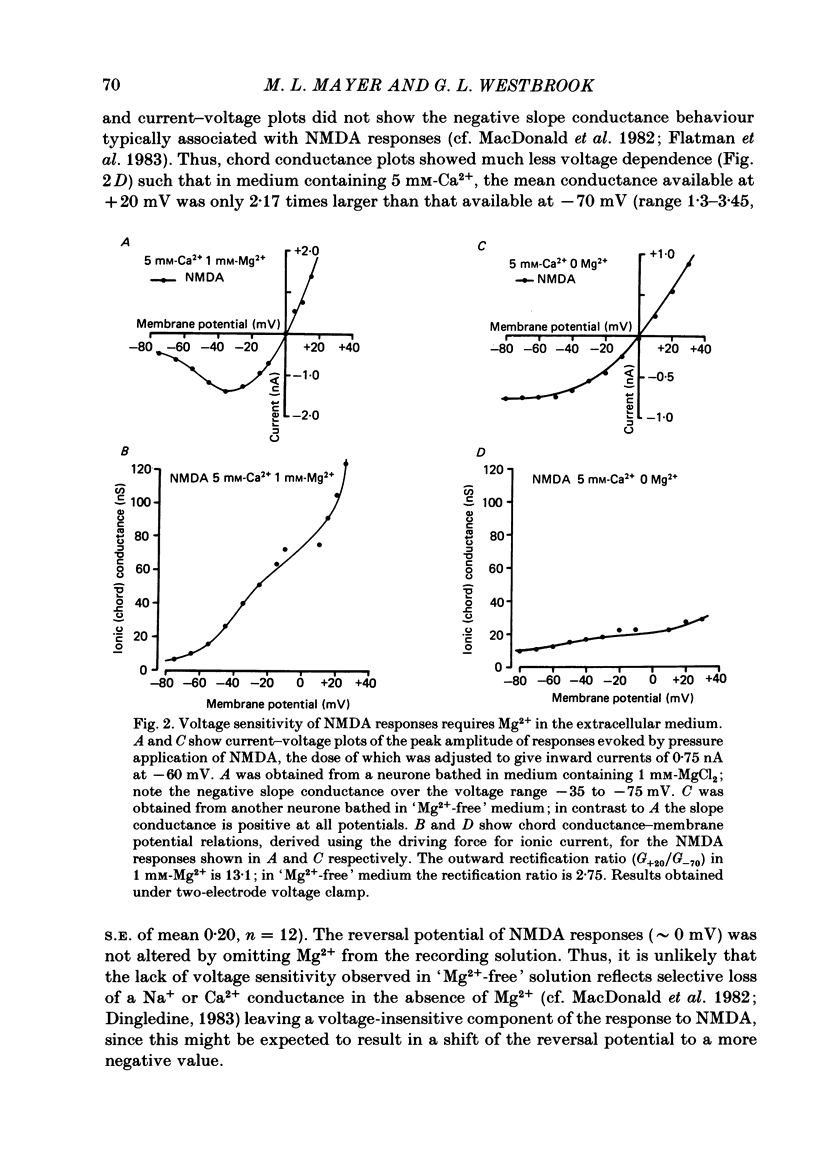
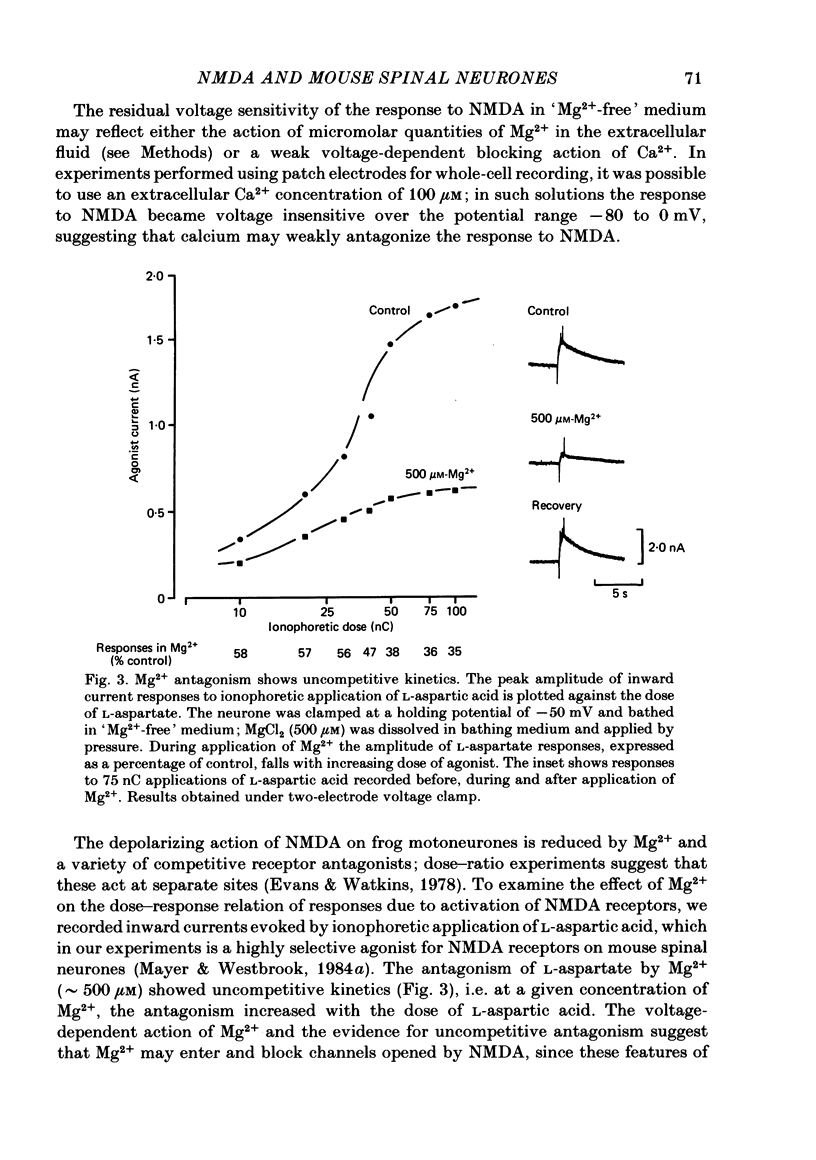
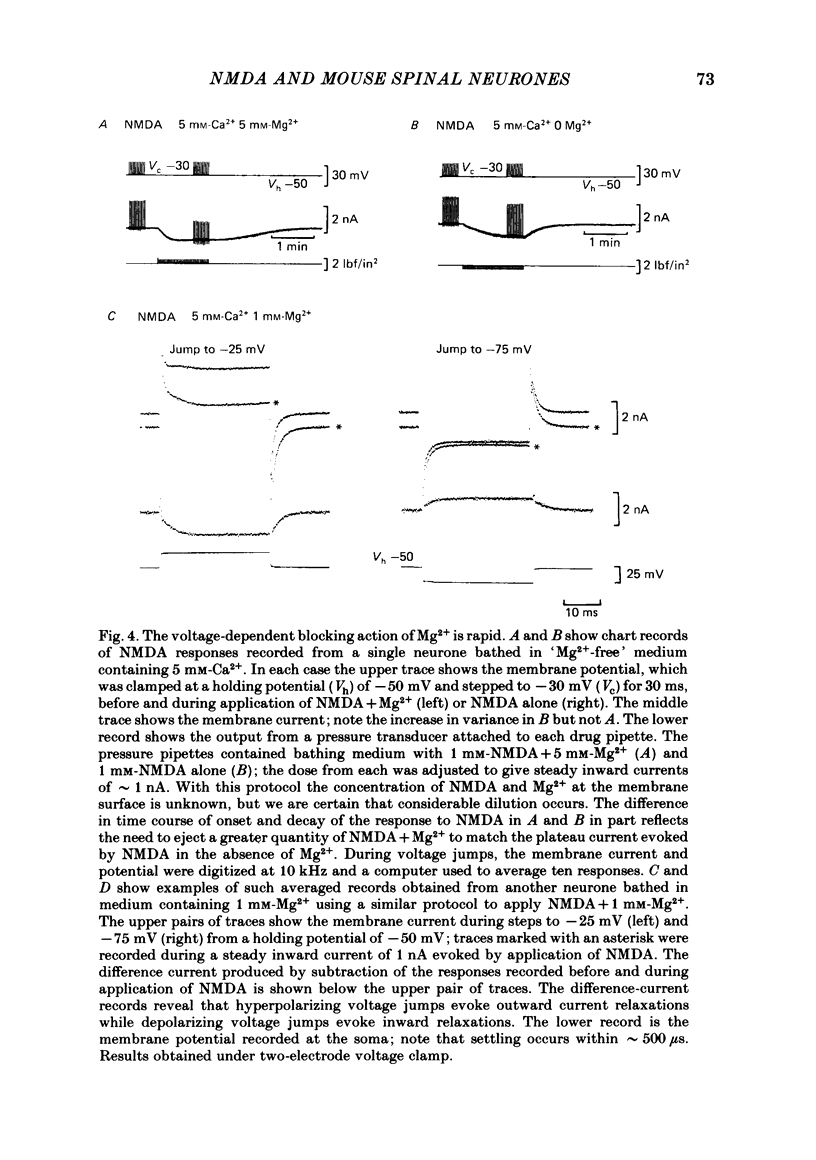
Abstract
Neurones from the ventral half of mouse embryo spinal cord were grown in dissociated culture and voltage clamped. The current-voltage relation of responses evoked by N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA), L-glutamic acid and kainic acid was recorded in media of different ionic composition. On removal of Mg2+ from the extracellular solution, responses to NMDA and L-glutamate became less voltage sensitive, such that NMDA responses were no longer associated with a region of negative slope conductance. The antagonism of NMDA responses produced by application of Mg2+ to neurones bathed in nominally Mg2+-free solutions shows voltage dependence and uncompetitive kinetics. Voltage-jump experiments showed that the voltage-dependent action of Mg2+ occurred rapidly, and with complex kinetics. Ni2+ and Cd2+, two potent blockers of calcium currents in spinal cord neurones, had significantly different potencies as NMDA antagonists, Ni2+ being of greater potency than Mg2+, and Cd2+ considerably weaker. The voltage-dependent block of NMDA responses produced by physiological concentrations of Mg2+ is sufficient to explain the apparent increase in membrane resistance produced by NMDA in current-clamp experiments, and the ability of NMDA to support repetitive firing. Substitution of choline for Na+ produced a hyperpolarizing shift in the reversal potential for responses evoked by kainic acid consistent with an increase in permeability to Na+ and K+. In choline-substituted solutions, the reversal potential of NMDA responses was more positive than that recorded for kainic acid, and in addition NMDA responses showed enhanced desensitization.
Full text
PDF







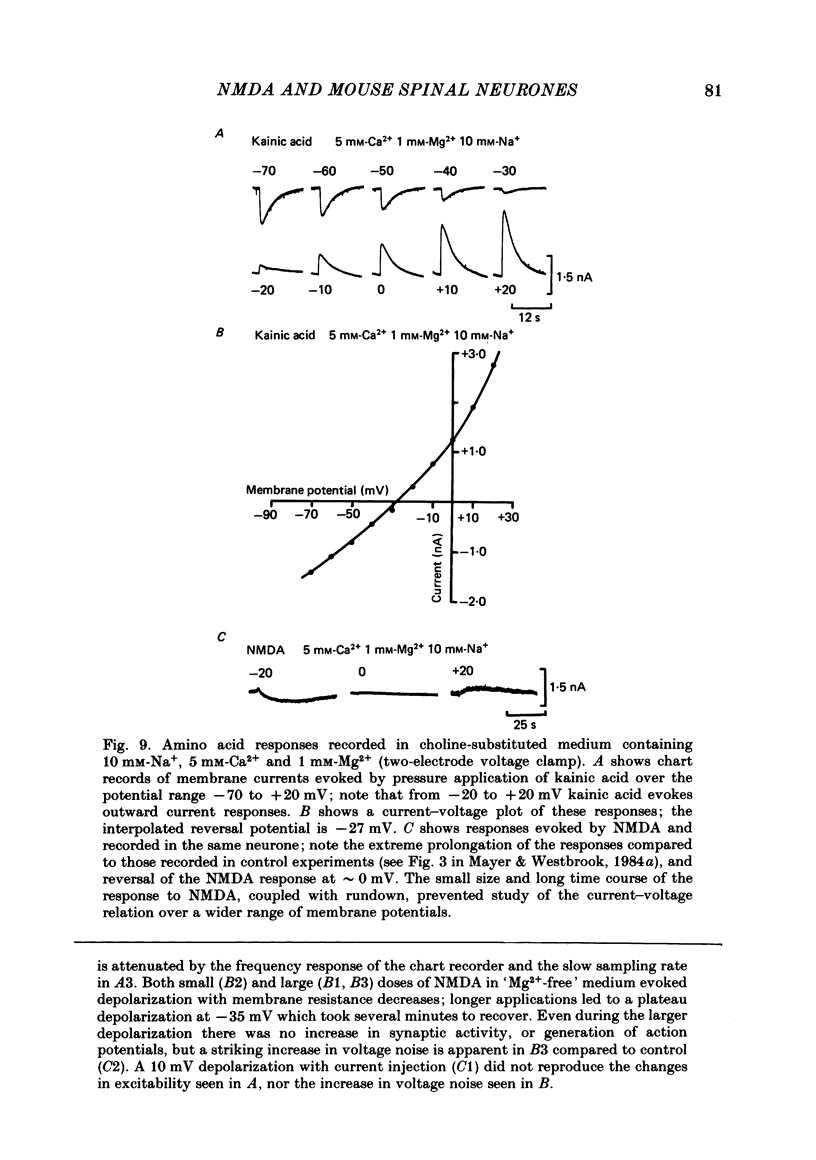
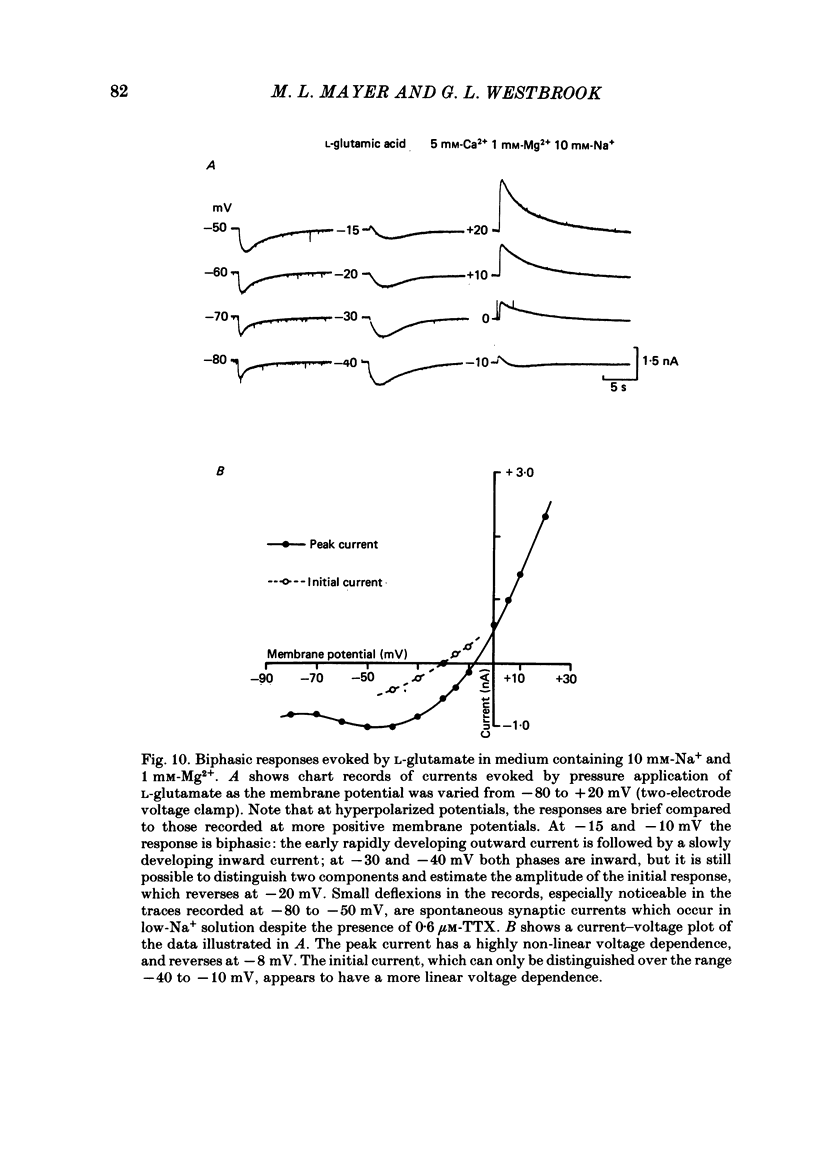
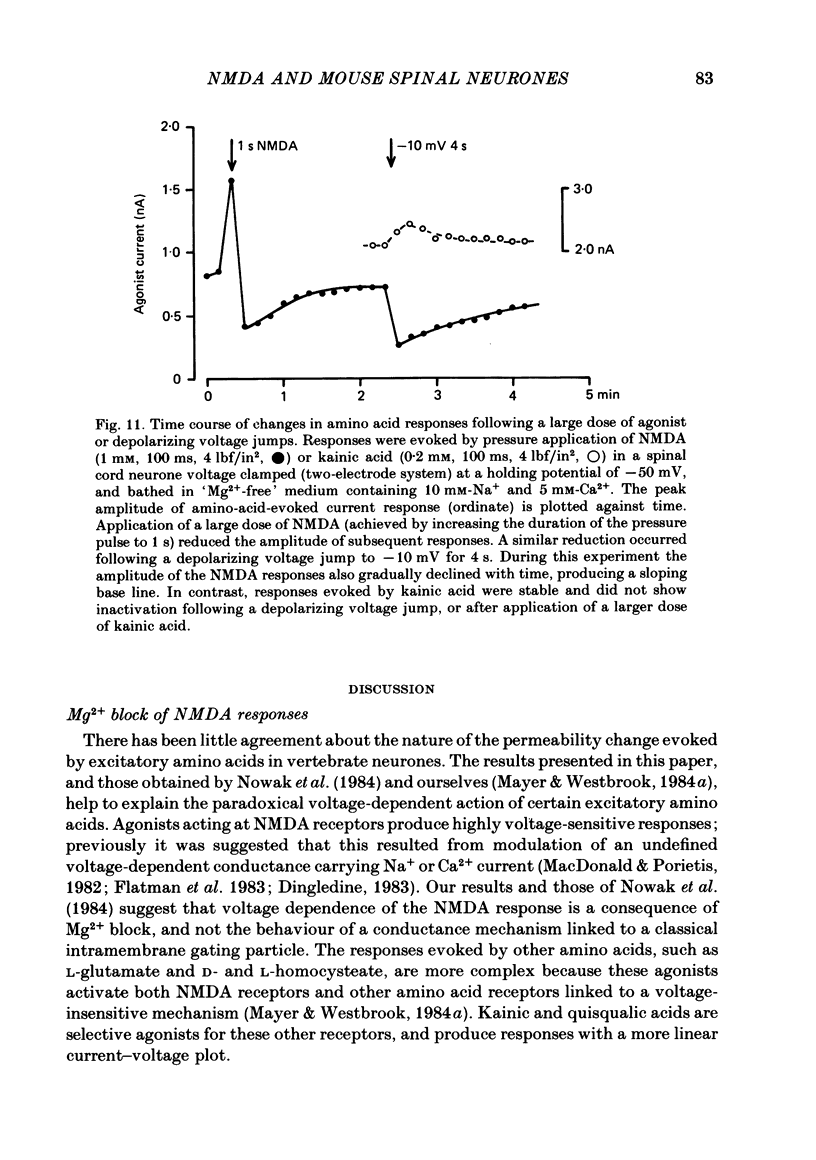
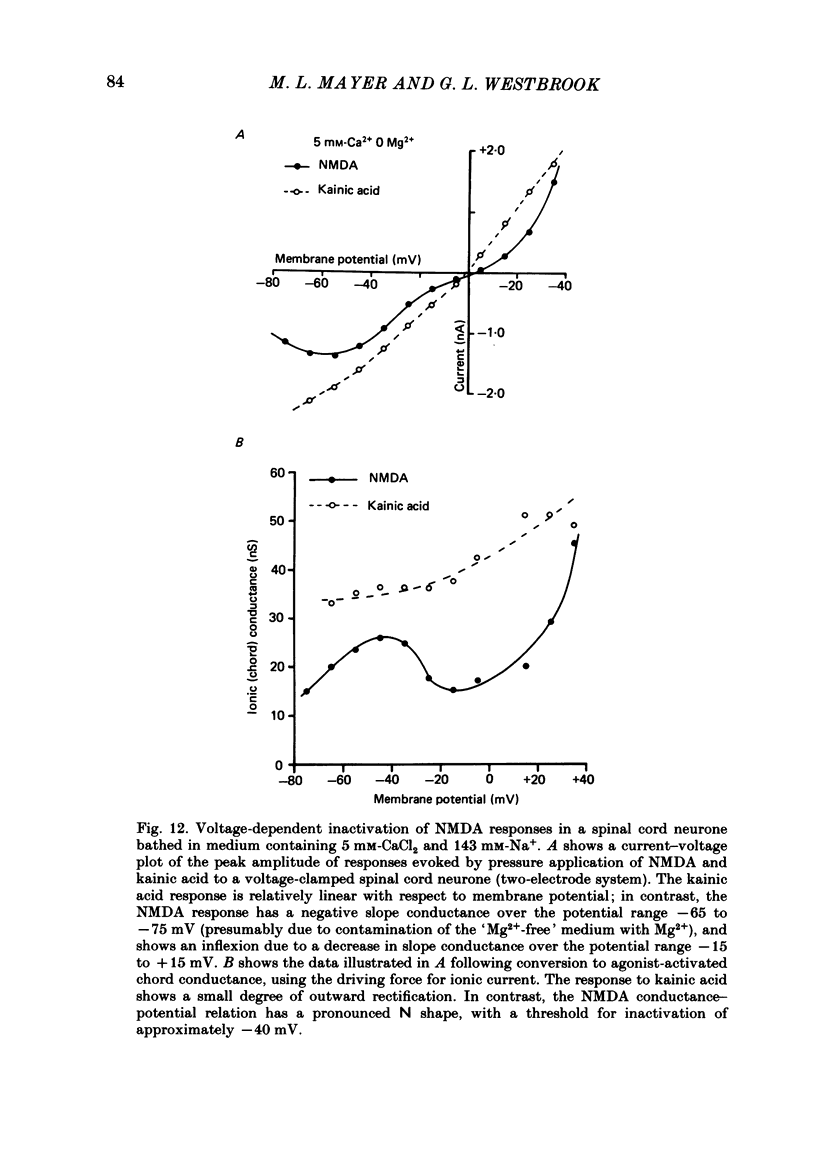






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. The permeability of endplate channels to monovalent and divalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):493–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R. Voltage jump analysis of procaine action at frog end-plate. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):291–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Brown A. M., Nishi K., Tsuda Y. Actions of verapamil, diltiazem and other divalent cations on the calcium-current of Helix neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;74(1):87–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwyl R. The effect of foreign cations, pH and pharmacological agents on the ionic permeability of an excitatory glutamate synapse. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(2):389–404. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Large W. A., Rang H. P. Studies on the mechanism of action of acetylcholine antagonists on rat parasympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:139–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Marty A., Neild T. O. The mode of action of antagonists of the excitatory response to acetylcholine in Aplysia neurones. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:207–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault B., Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Oakes D. J., Watkins J. C. Selective depression of excitatory amino acid induced depolarizations by magnesium ions in isolated spinal cord preparations. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:413–428. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Griffith W. H. Persistent slow inward calcium current in voltage-clamped hippocampal neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:303–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bührle C. P., Sonnhof U. The ionic mechanism of the excitatory action of glutamate upon the membranes of motoneurones of the frog. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Feb;396(2):154–162. doi: 10.1007/BF00615520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Neher E., Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Inward current channels activated by intracellular Ca in cultured cardiac cells. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):752–754. doi: 10.1038/294752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronado R., Miller C. Decamethonium and hexamethonium block K+ channels of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):495–497. doi: 10.1038/288495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingledine R. N-methyl aspartate activates voltage-dependent calcium conductance in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1983 Oct;343:385–405. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg I., Flatman J. A., Lambert J. D. The action of N-methyl-D-aspartic and kainic acids on motoneurones with emphasis on conductance changes [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;64(3):384P–385P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engberg I., Flatman J. A., Lambert J. D. The actions of excitatory amino acids on motoneurones in the feline spinal cord. J Physiol. 1979 Mar;288:227–261. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Watkins J. C. Selective antagonism by Mg2+ of amino acid-induced depolarization of spinal neurones. Experientia. 1977 Apr 15;33(4):489–491. doi: 10.1007/BF01922227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Watkins J. C. Dual sites for antagonism of excitatory amino acid actions on central neurones [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:57P–57P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagni L., Baudry M., Lynch G. Classification and properties of acidic amino acid receptors in hippocampus. I. Electrophysiological studies of an apparent desensitization and interactions with drugs which block transmission. J Neurosci. 1983 Aug;3(8):1538–1546. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-08-01538.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatman J. A., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E., Stafstrom C. E. Multiple actions of N-methyl-D-aspartate on cat neocortical neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 25;266(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Hermann A., Thomas M. V. Intracellular calcium and the control of neuronal pacemaker activity. Fed Proc. 1981 Jun;40(8):2233–2239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz J. J., Langmoen I. A. Excitation of hippocampal pyramidal cells by glutamate in the guinea-pig and rat. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:317–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Catterall W. A., Ehrenstein G. Selectivity of cations and nonelectrolytes for acetylcholine-activated channels in cultured muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Apr;71(4):397–410. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.4.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. L-glutamate as an excitatory transmitter at the Drosophila larval neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;262(1):215–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingle C. Blockade of cholinergic channels by chlorisondamine on a crustacean muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:395–417. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Porietis A. V. DL-quisqualic and L-aspartic acids activate separate excitatory conductances in cultured spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Aug 5;245(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90356-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Porietis A. V., Wojtowicz J. M. L-Aspartic acid induces a region of negative slope conductance in the current-voltage relationship of cultured spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 8;237(1):248–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Schneiderman J. H. L-aspartic acid potentiates 'slow' inward current in cultured spinal cord neurons. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 2;296(2):350–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F. Substitution of extracellular sodium ions blocks the voltage-dependent decrease of input conductance evoked by L-aspartate. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;62(1):109–115. doi: 10.1139/y84-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Wojtowicz J. M. The effects of L-glutamate and its analogues upon the membrane conductance of central murine neurones in culture. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;60(3):282–296. doi: 10.1139/y82-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthey A. A. The effect of calcium on the desensitization of membrane receptors at the neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):963–976. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. A voltage-clamp analysis of inward (anomalous) rectification in mouse spinal sensory ganglion neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:19–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Mixed-agonist action of excitatory amino acids on mouse spinal cord neurones under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:29–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk W. L., Parsons R. L. Factors in the inactivation of postjunctional membrane receptors of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Aug;56(2):218–249. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. G., Segal M., Barker J. L. A Ca-dependent Cl- conductance in cultured mouse spinal neurones. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):567–570. doi: 10.1038/311567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Time constants and electrotonic length of membrane cylinders and neurons. Biophys J. 1969 Dec;9(12):1483–1508. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86467-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scubon-Mulieri B., Parsons R. L. Desensitization and recovery at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):431–447. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C. Pharmacology of excitatory amino acid transmitters. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1981;29:205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook G. L., Mayer M. L. Glutamate currents in mammalian spinal neurons: resolution of a paradox. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 3;301(2):375–379. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. Single Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channels in neuroblastoma. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):357–359. doi: 10.1038/296357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


