Abstract
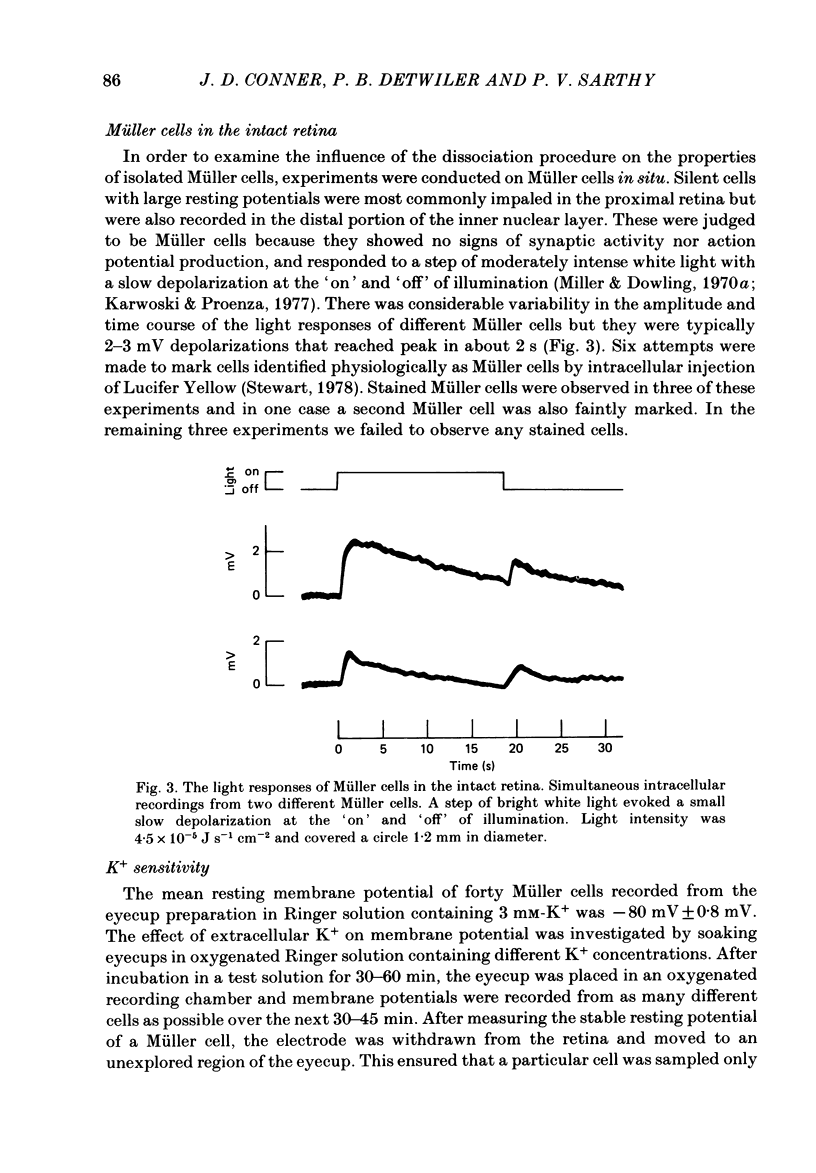
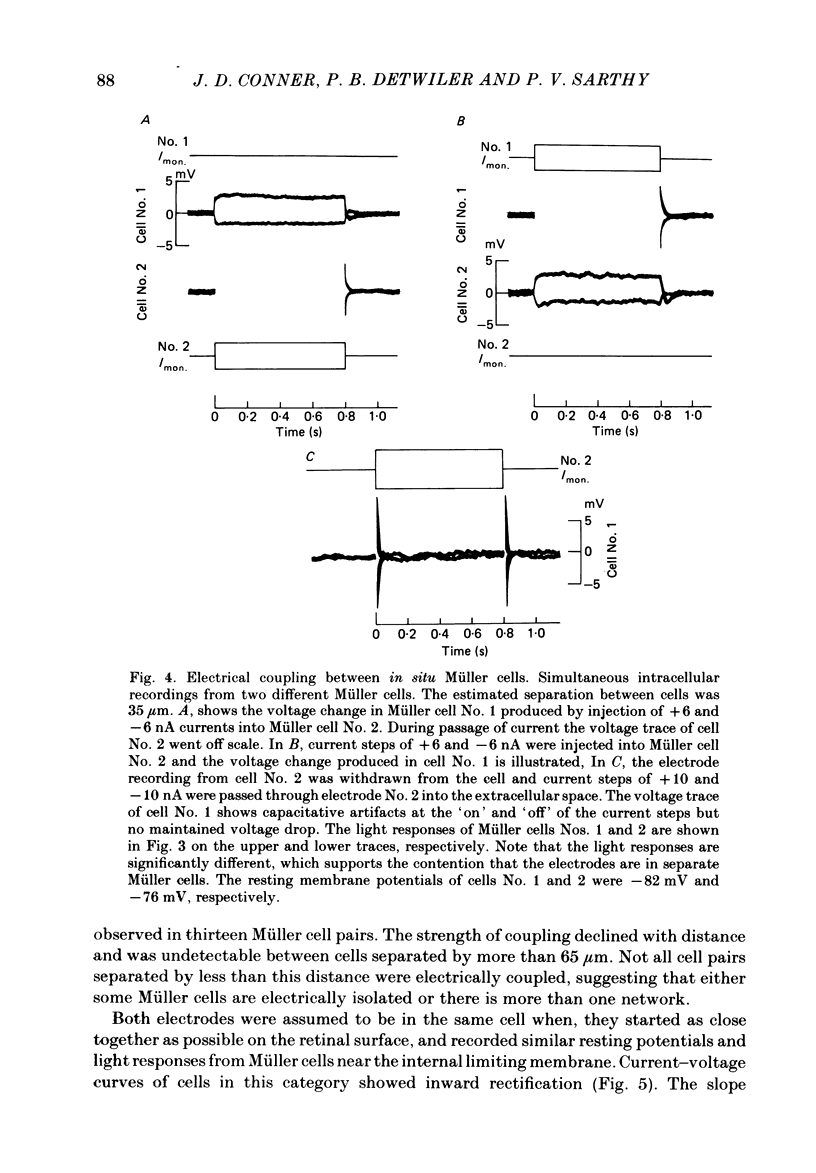
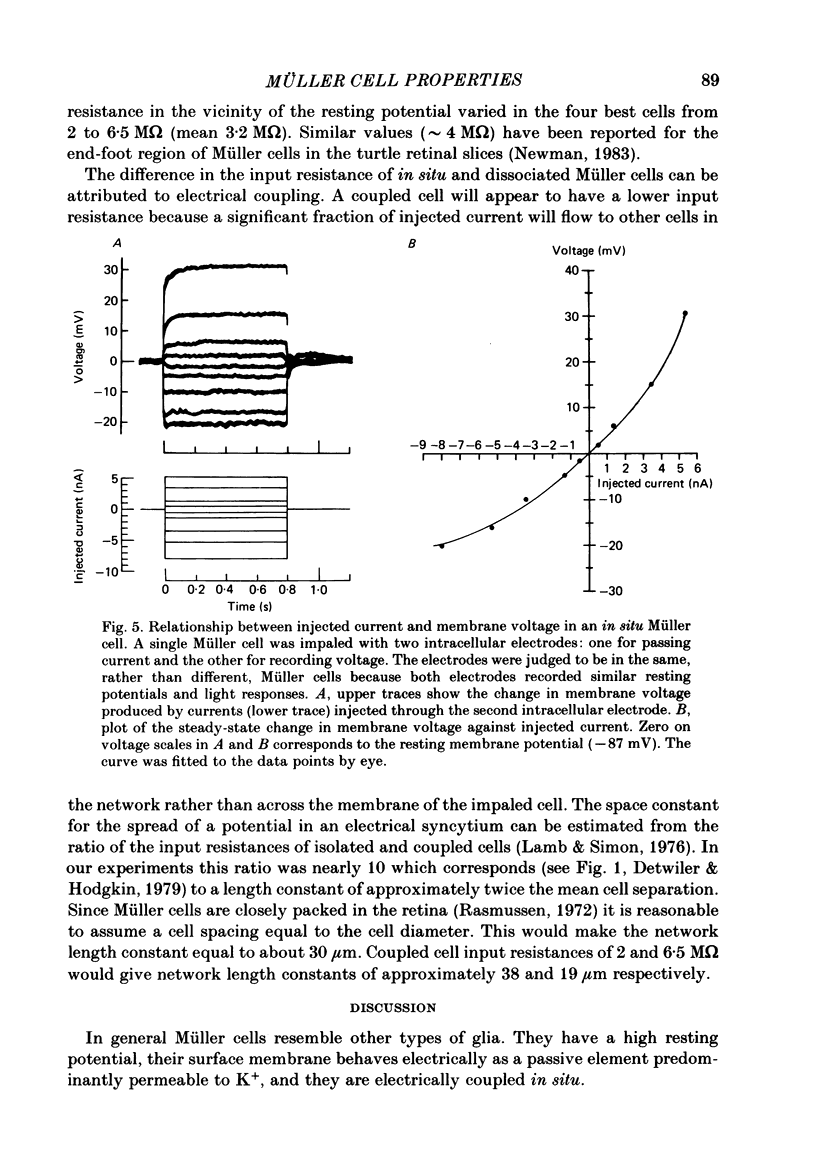
The ionic and electrophysiological properties of Müller cells, the principal glial element of the vertebrate retina, were investigated. The membrane potential of enzymatically dissociated and in situ Müller cells was about -80 mV and depended on external K+ concentration in a manner that was described by the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation with a Na+-K+ permeability ratio of 0.037. The current-voltage relation showed marked inward rectification, with the input resistance at the resting potential being about 30 M omega for dissociated cells and about 3 M omega for in situ cells. In situ Müller cells were found to be electrically coupled to each other which could explain their lower resistance. We conclude that Müller cells are similar to other types of glia. In spite of a finite Na+ permeability their membrane potential is determined mainly by K+, they are electrically inexcitable and form an electrically coupled network in the retina.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylor D. A., Hodgkin A. L. Detection and resolution of visual stimuli by turtle photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(1):163–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. J., Gerschenfeld H. M. Some physiological properties of identified mammalian neuroglial cells. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):211–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detwiler P. B., Hodgkin A. L. Electrical coupling between cones in turtle retina. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:75–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick E., Miller R. F. Light-evoked potassium activity in mudpuppy retina: its relationship to the b-wave of the electroretinogram. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 13;154(2):388–394. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90711-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
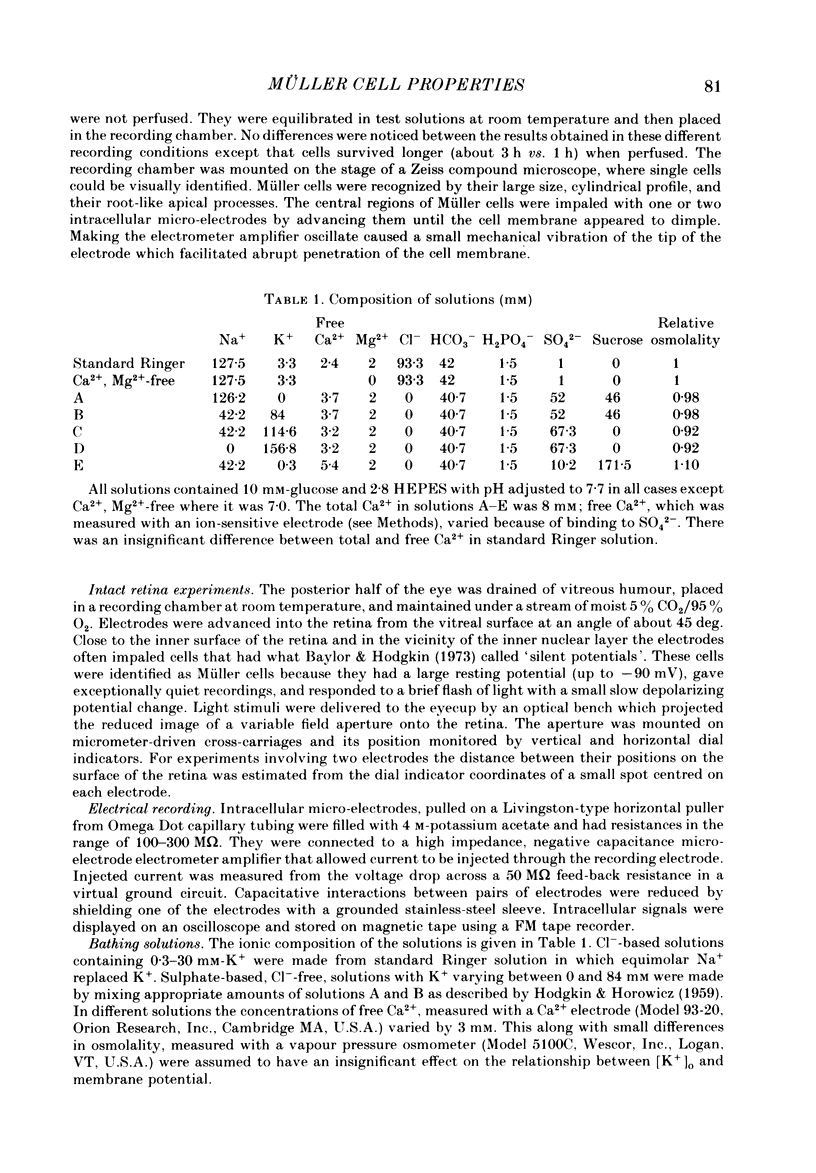
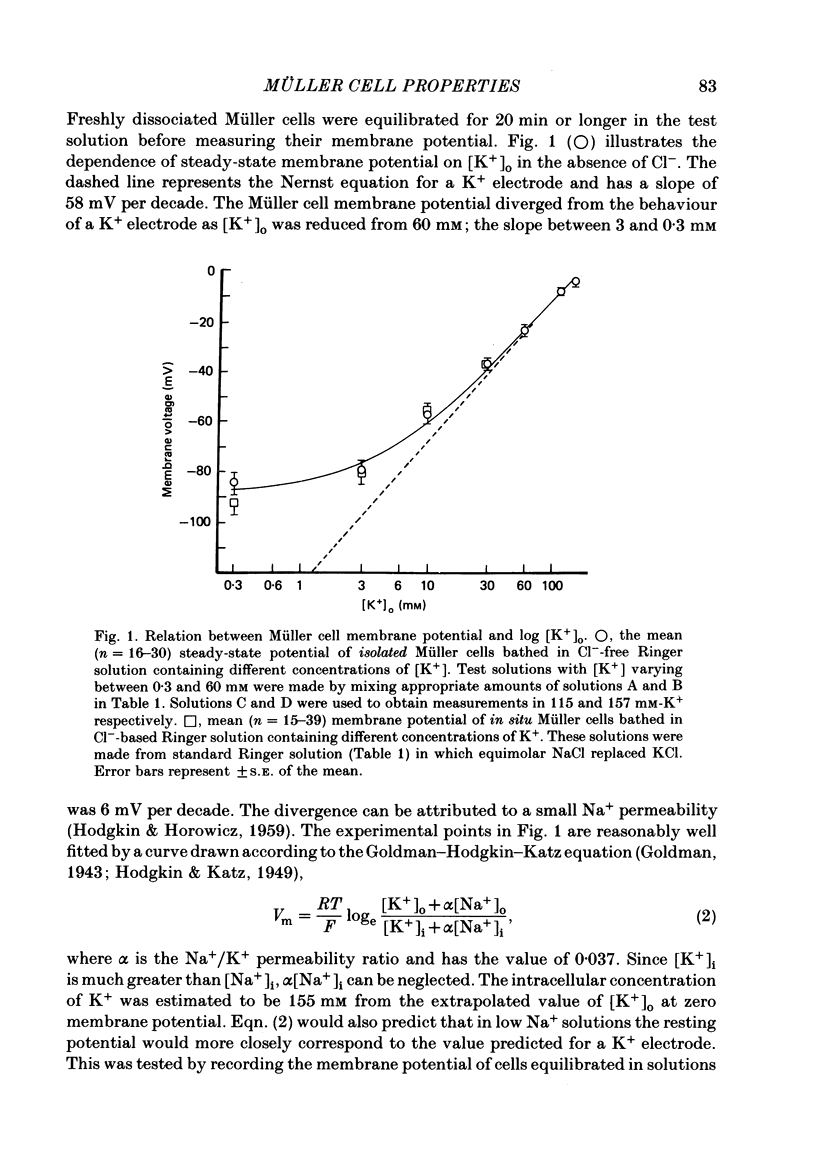
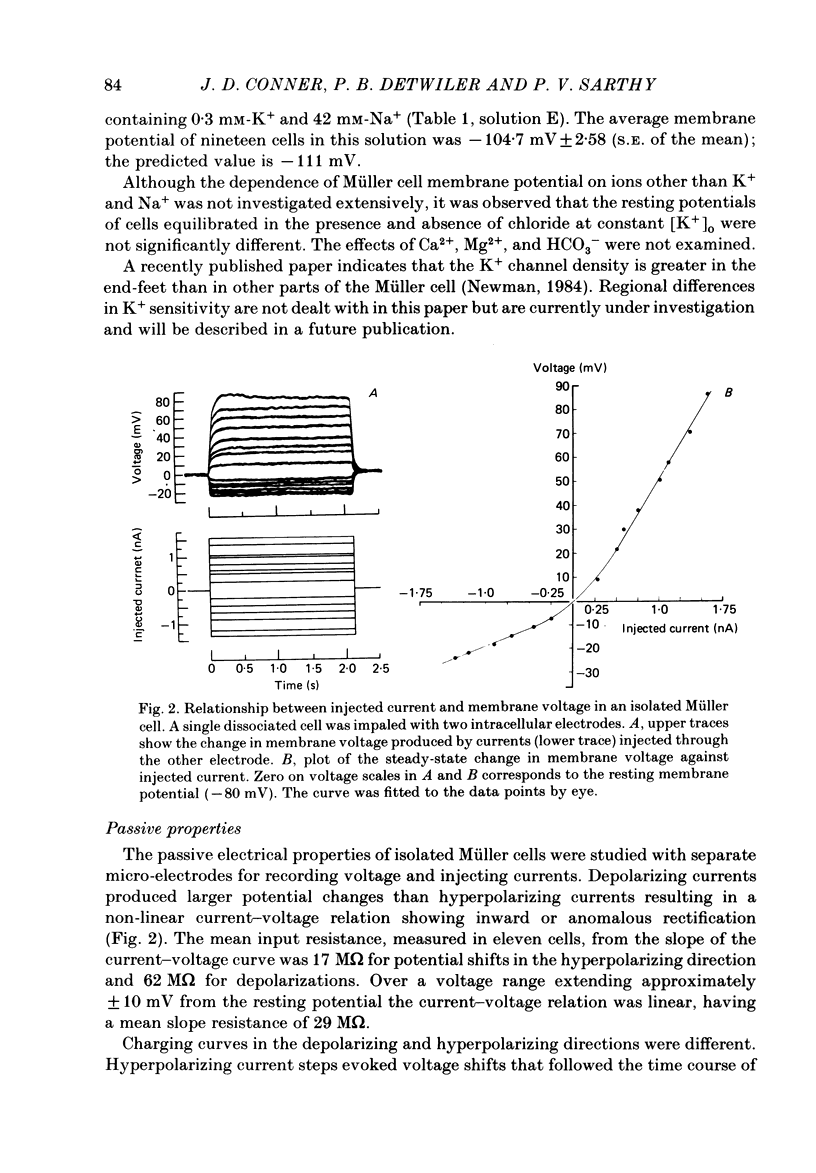
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:127–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., NICHOLIS J. G. GLIAL CELLS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF THE LEECH; THEIR MEMBRANE POTENTIAL AND POTASSIUM CONTENT. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1964 May 25;248:216–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00348592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karowski C. J., Proenza L. M. Relationship between Müller cell responses, a local transretinal potential, and potassium flux. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Mar;40(2):244–259. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karwoski C. J., Proenza L. M. Light-evoked changes in extracellular potassium concentration in munpuppy retina. Brain Res. 1978 Mar 10;142(3):515–530. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90913-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karwoski C. J., Proenza L. M. Neurons, potassium, and glia in proximal retina of Necturus. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Feb;75(2):141–162. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline R. P., Ripps H., Dowling J. E. Generation of b-wave currents in the skate retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5727–5731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Nicholls J. G., Orkand R. K. Physiological properties of glial cells in the central nervous system of amphibia. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Jul;29(4):768–787. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.4.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Nicholls J. G. The physiology of neuroglial cells. Ergeb Physiol. 1966;57:1–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. D., Simon E. J. The relation between intercellular coupling and electrical noise in turtle photoreceptors. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(2):257–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. F., Dowling J. E. Intracellular responses of the Müller (glial) cells of mudpuppy retina: their relation to b-wave of the electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol. 1970 May;33(3):323–341. doi: 10.1152/jn.1970.33.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A. Regional specialization of retinal glial cell membrane. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):155–157. doi: 10.1038/309155a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B., 2nd, Green D. G. Correlation of light-induced changes in retinal extracellular potassium concentration with c-wave of the electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Sep;39(5):1117–1133. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.5.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. G., Katzman R. Response of glia in cat sensorimotor cortex to increased extracellular potassium. Brain Res. 1972 Mar 10;38(1):71–92. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90590-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Goldring S. Ionic determinants of membrane potential of cells presumed to be glia in cerebral cortex of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1973 Sep;36(5):855–868. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.5.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen K. E. A morphometric study of the Müller cell cytoplasm in the rat retina. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Jun;39(5):413–429. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90095-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthy P. V., Bunt A. H. The ultrastructure of isolated glial (Müller) cells from the turtle retina. Anat Rec. 1982 Feb;202(2):275–283. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092020212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthy P. V., Lam D. M. Biochemical studies of isolated glial (Müller) cells from the turtle retina. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):675–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthy P. V. Release of [3H]gamma-aminobutyric acid from glial (Müller) cells of the rat retina: effects of K+, veratridine, and ethylenediamine. J Neurosci. 1983 Dec;3(12):2494–2503. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-12-02494.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somjen G. G. Electrophysiology of neuroglia. Annu Rev Physiol. 1975;37:163–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.37.030175.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart R. M., Rosenberg R. N. Physiology of glia: glial-neuronal interactions. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1979;21:275–309. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. W. Functional connections between cells as revealed by dye-coupling with a highly fluorescent naphthalimide tracer. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):741–759. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90256-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg M. C., Kornblith P. L., Häuptli J. Biophysical properties of cultured human glial cells. Brain Res. 1972 Mar 24;38(2):279–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90713-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uga S., Smelser Comparative study of the fine structure of retinal Müller cells in various vertebrates. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973 Jun;12(6):434–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. The electrical constants of Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1952 Nov;118(3):348–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]