Abstract
The blood-perfused choroid plexuses from the lateral ventricles of the sheep were used to determine the nature of sugar exchanges between blood and cerebrospinal fluid (c.s.f.). There was a net entry of sugars from blood to c.s.f. at all concentrations of sugars which were used and this net entry was seen when the sugars were measured either directly by enzymic analysis or by the use of isotopically labelled sugars. From competition experiments the order of affinity of the transporting system from both blood to c.s.f. and c.s.f. to blood was the same, i.e. 2-deoxy-D-glucose much greater than D-glucose greater than 3-O-methyl-D-glucose much greater than D-galactose. The transport of sugars from c.s.f. to blood and blood to c.s.f. consists in both cases of a non-saturable and a saturable component. However, the affinity of the two systems is markedly different, the blood to c.s.f. being a system of low affinity and high capacity while that of the c.s.f. to blood has a high affinity and a low capacity. The concentration of glucose in the newly formed c.s.f. was estimated from the rate of c.s.f. secretion and the net flux of glucose across the choroid plexus. The concentration of glucose in this fluid was some 45-60% of that in plasma and so the low glucose concentration observed in bulk c.s.f. would appear to be a result of the entry process and not that of cerebral metabolism.
Full text
PDF






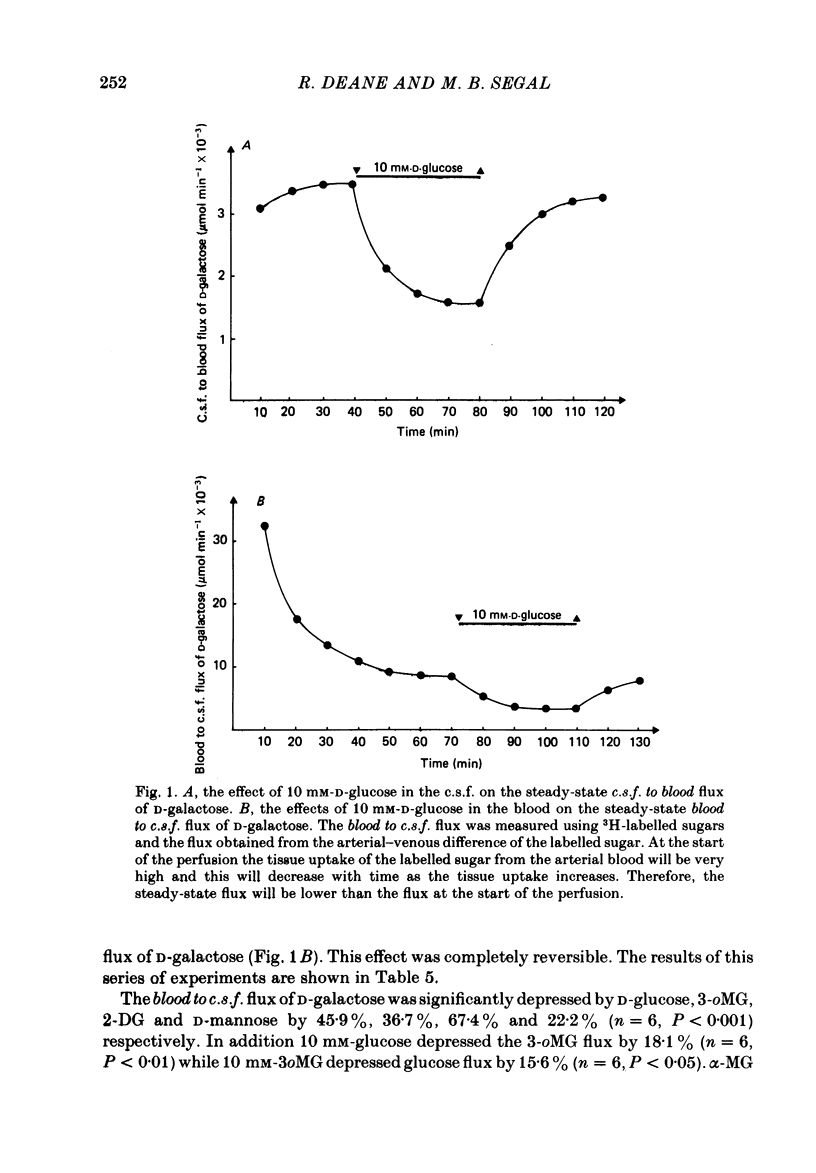
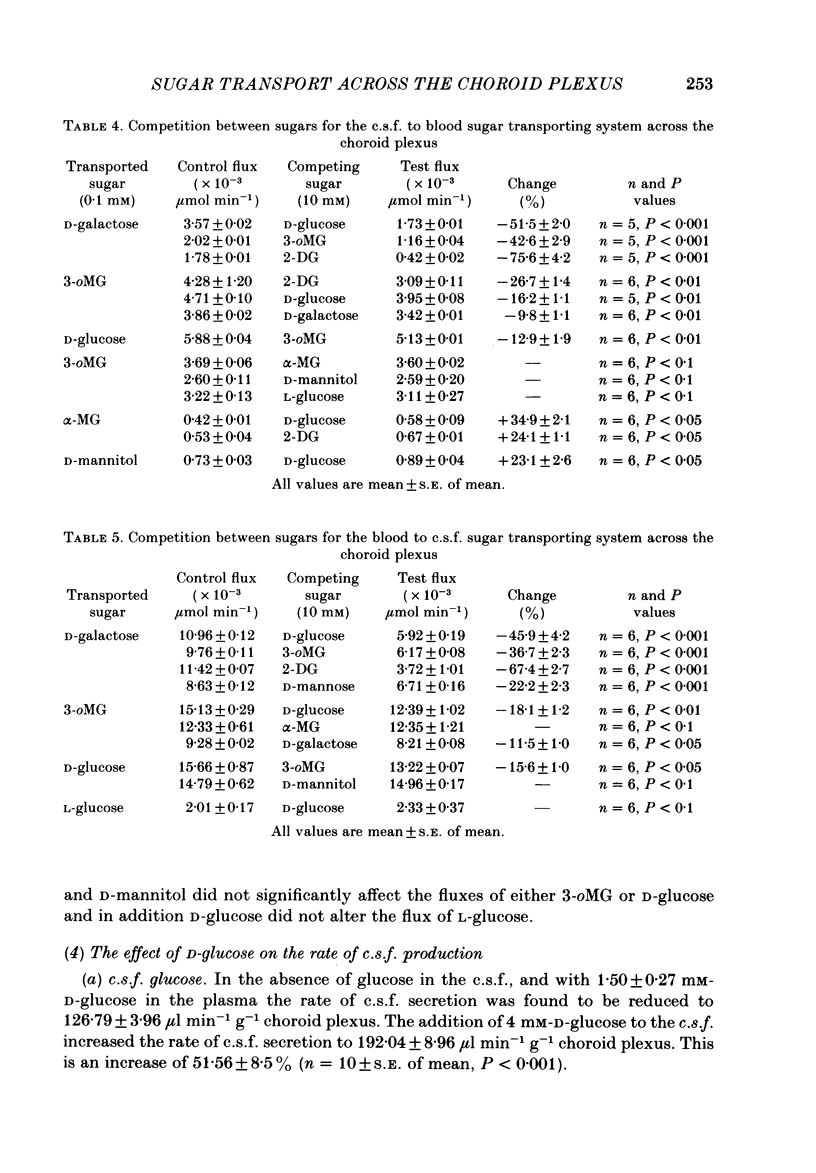







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bito L. Z., Davson H. Local variations in cerebrospinal fluid composition and its relationship to the composition of the extracellular fluid of the cortex. Exp Neurol. 1966 Mar;14(3):264–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(66)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Brondsted H. E. Sodium-dependent transport of sugars and iodide from the cerebral venticles of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(1):127–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKY T. Z., RIGOR B. M., Sr A CONCENTRATIVE MECHANISM FOR SUGARS IN THE CHOROID PLEXUS. Life Sci. 1964 Sep;3:931–936. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer J. E., Ray D. E., Sarna G. S., Cunningham V. J. A study of the kinetic behaviour of glucose based on simultaneous estimates of influx and phosphorylation in brain regions of rats in different physiological states. Brain Res. 1981 Sep 28;221(2):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90782-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserr H. F. Physiology of the choroid plexus. Physiol Rev. 1971 Apr;51(2):273–311. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csáky T. Z., Rigor B. M. The choroid plexus as a glucose barrier. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:147–158. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H. Dynamic aspects of cerebrospinal fluid. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 1972;27:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb09767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H. Review lecture. The blood-brain barrier. J Physiol. 1976 Feb;255(1):1–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H., Segal M. B. The effects of some inhibitors and accelerators of sodium transport on the turnover of 22Na in the cerebrospinal fluid and the brain. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):131–153. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. A., Reynolds J. M., Reynolds M. L., Saunders N. R., Segal M. B. The development of a blood-brain barrier mechanism in foetal sheep. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(2):371–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER R. G., COPENHAVER J. H. The metabolic activity in the choroid plexus. J Neurosurg. 1959 Mar;16(2):167–176. doi: 10.3171/jns.1959.16.2.0167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjedde A., Diemer N. H. Autoradiographic determination of regional brain glucose content. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1983 Sep;3(3):303–310. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1983.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEFEVRE P. G. Sugar transport in the red blood cell: structure-activity relationships in substrates and antagonists. Pharmacol Rev. 1961 Mar;13:39–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V., Cutler R. W. Amino acid transport by choroid plexus in vitro. J Neurochem. 1969 Apr;16(4):577–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb06857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V. The uptake and metabolism of D-(U-14C)glucose by the choroid plexus. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):435–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90301-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R., Setchell B. P. Cerebral glucose transport and oxygen consumption in sheep and rabbits. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):529–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollay M., Stevens A., Estrada E., Kaplan R. Extracorporeal perfusion of choroid plexus. J Appl Physiol. 1972 May;32(5):612–617. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. B., Pollay M. The secretion of cerebrospinal fluid. Exp Eye Res. 1977;25 (Suppl):127–148. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(77)80012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch K., Araki H., Arkins T. Electrical potentials of the lamina epithelialis choroidea of the fourth ventricle of the cat in vitro: relationship to the CSF blood potential. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 1972;27:146–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb09788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch K., Sadler K., Gold G. Volume flow across choroidal ependyma of the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1966 Feb;210(2):232–236. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch K., Sadler K. Permeability of the choroid plexus of the rabbit to several solutes. Am J Physiol. 1966 Mar;210(3):652–660. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.3.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M. Accumulation and transport of amino acids by the frog choroid plexus. Brain Res. 1972 Sep 15;44(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90376-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M. Mechanisms of ion transport across the choroid plexus. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):545–571. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


